Spillover of West Caucasian Bat Lyssavirus (WCBV) in a Domestic Cat and Westward Expansion in the Palearctic Region
Abstract
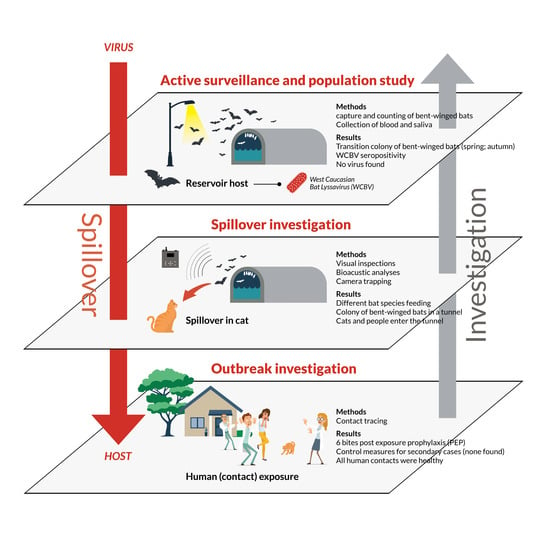
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Outbreak Investigation and Control Measures
2.2. Spillover Investigation
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Case Description and Viral Characterization
3.2. Tracing of Contacts and Secondary Cases
3.3. Spillover Investigation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Expert Consultation on Rabies. Third Report. World Health Organization-Technical Report Series. 2018, p. 1012. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/272364 (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Walker, P.J.; Blasdell, K.R.; Calisher, C.H.; Dietzgen, R.G.; Kondo, H.; Kurath, G.; Longdon, B.; Stone, D.M.; Tesh, R.B.; Tordo, N.; et al. ICTV Virus taxonomy profile: Rhabdoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coertse, J.; Grobler, C.S.; Sabeta, C.T.; Seamark, E.C.J.; Kearney, T.; Paweska, J.T.; Markotter, W. Lyssaviruses in Insectivorous Bats, South Africa, 2003–2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 3056–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupprecht, C.E.; Turmelle, A.; Kuzmin, I.V. A perspective on lyssavirus emergence and perpetuation. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shipley, R.; Wright, E.; Selden, D.; Wu, G.; Aegerter, J.; Fooks, A.R.; Banyard, A.C. Bats and Viruses: Emergence of Novel Lyssaviruses and Association of Bats with Viral Zoonoses in the EU. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, C.R.; Streicker, D.G.; Schnell, M.J. The spread and evolution of rabies virus: Conquering new frontiers. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streicker, D.G.; Turmelle, A.S.; Vonhof, M.J.; Kuzmin, I.V.; McCracken, G.F.; Rupprecht, C.E. Host phylogeny constrains cross-species emergence and establishment of rabies virus in bats. Science 2010, 329, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velasco-Villa, A.; Mauldin, M.R.; Shi, M.; Escobar, L.E.; Gallardo-Romero, N.F.; Damon, I.; Olson, V.A.; Streicker, D.G.; Emerson, G. The history of rabies in the Western Hemisphere. Antivir. Res. 2017, 146, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Sato, G.; Mochizuki, N.; Hirano, S.; Itou, T.; Carvalho, A.A.B.; Albas, A.; Santos, H.P.; Ito, F.H.; Sakai, T. Molecular and geographic analyses of vampire bat-transmitted cattle rabies in central Brazil. BMC Vet. Res. 2008, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leslie, M.J.; Messenger, S.; Rohde, R.E.; Smith, J.; Cheshier, R.; Hanlon, C.; Rupprecht, C.E. Bat-associated rabies virus in skunks. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1274–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, I.V.; Shi, M.; Orciari, L.A.; Yager, P.A.; Velasco-Villa, A.; Kuzmina, N.A.; Streicker, D.G.; Bergman, D.L.; Rupprecht, C.E. Molecular inferences suggest multiple host shifts of rabies viruses from bats to mesocarnivores in Arizona during 2001–2009. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rosa, E.S.T.; Kotait, I.; Barbosa, T.F.S.; Carrieri, M.L.; Brandão, P.E.; Pinheiro, A.S.; Begot, A.L.; Wada, M.Y.; De Oliveira, R.C.; Grisard, E.C.; et al. Bat-transmitted human rabies outbreaks, Brazilian amazon. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, J.A.; Velasco-Villa, A.; Godino, L.C.; Satheshkumar, P.S.; Ruby, N.; Rojas-Paniagua, E.; Shiva, C.; Falcon, N.; Streicker, D.G. Abortive vampire bat rabies infections in peruvian peridomestic livestock. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streicker, D.G.; Winternitz, J.C.; Satterfield, D.A.; Condori-Condori, R.E.; Broos, A.; Tello, C.; Recuenco, S.; Velasco-Villa, A.; Altizer, S.; Valderrama, W. Host-pathogen evolutionary signatures reveal dynamics and future invasions of vampire bat rabies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10926–10931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollentze, N.; Streicker, D.G.; Murcia, P.R.; Hampson, K.; Biek, R. Virulence mismatches in index hosts shape the outcomes of cross-species transmission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28859–28866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacheux, L.; Larrous, F.; Mailles, A.; Boisseleau, D.; Delmas, O.; Biron, C.; Bouchier, C.; Capek, I.; Muller, M.; Ilari, F.; et al. European bat lyssavirus transmission among cats, Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, D.A.; Banyard, A.C.; McElhinney, L.M.; Freuling, C.M.; Finke, S.; de Lamballerie, X.; Müller, T.; Fooks, A.R. The lyssavirus host-specificity conundrum—Rabies virus—the exception not the rule. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 28, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, N.A.; Morón, S.V.; Berciano, J.M.; Nicolás, O.; López, C.A.; Juste, J.; Nevado, C.R.; Setién, Á.A.; Echevarría, J.E. Novel lyssavirus in bat, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botvinkin, A.D.; Poleschuk, E.M.; Kuzmin, I.V.; Borisova, T.I.; Gazaryan, S.V.; Yager, P.; Rupprecht, C.E. Novel Lyssaviruses Isolated from Bats in Russia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 1623–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, C.A.; Kuzmin, I.V.; Blanton, J.D.; Weldon, W.C.; Manangan, J.S.; Rupprecht, C.E. Efficacy of rabies biologics against new lyssaviruses from Eurasia. Virus Res. 2005, 111, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echevarría, J.E.; Banyard, A.C.; Mcelhinney, L.M.; Fooks, A.R. Current Rabies Vaccines Do Not Confer Protective Immunity against Divergent Lyssaviruses Circulating in Europe. Viruses 2019, 11, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, J.S.; Horton, D.L.; Easton, A.J.; Fooks, A.R.; Banyard, A.C. Rabies virus vaccines: Is there a need for a pan-lyssavirus vaccine? Vaccine 2012, 30, 7447–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robardet, E.; Bosnjak, D.; Englund, L.; Demetriou, P.; Martín, P.R.; Cliquet, F. Zero endemic cases of wildlife rabies (Classical rabies virus, RABV) in the European Union by 2020: An achievable goal. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gossner, C.M.; Mailles, A.; Aznar, I.; Dimina, E.; Echevarria, J.E.; Feruglio, S.L.; Lange, H.; Maraglino, F.P.; Parodi, P.; Perevoscikovs, J.; et al. Prevention of human rabies: A challenge for the European Union and the European Economic Area. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. EUVET Mission to Poland on Rabies. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/system/files/2021-06/reg-com_ahw_20210617_rabies-euvet_pol.pdf (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Nokireki, T.; Tammiranta, N.; Kokkonen, U.-M.; Kantala, T.; Gadd, T. Tentative novel lyssavirus in a bat in Finland. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leopardi, S.; Priori, P.; Zecchin, B.; Poglayen, G.; Trevisiol, K.; Lelli, D.; Zoppi, S.; Scicluna, M.T.; D’Avino, N.; Schiavon, E.; et al. Active and passive surveillance for bat lyssaviruses in Italy revealed serological evidence for their circulation in three bat species. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D.P.R. 8 Febbraio 1954, N. 320, Regolamento di Polizia Veterinaria. 2006. Available online: https://www.normattiva.it/atto/caricaDettaglioAtto?atto.dataPubblicazioneGazzetta=1954-06-24&atto.codiceRedazionale=054U0320&atto.articolo.numero=0&atto.articolo.sottoArticolo=1&atto.articolo.sottoArticolo1=10&qId=983c498b-ca6e-43f2-b57a-f384a5979fae&tabID=0.170451470510395&title=lbl.dettaglioAtto (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Comune di Arezzo Regolamento Comunale per la Tutela Degli Animali. 2014, pp. 1–26. Available online: https://www.comune.arezzo.it/statutieregolamenti/regolamento-tutela-degli-animali (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- OIE. Infection with rabies virus. In Terrestrial Animal Health Code; Office International des Epizooties: Paris, France, 2019; p. 35. Available online: https://www.oie.int/en/what-we-do/standards/codes-and-manuals/terrestrial-code-online-access/?id=169&L=1&htmfile=chapitre_rabies.htm (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Marabelli, R. Self-declaration from Italy on the recovery of its rabies-free status. OIE 2013, 2, 62–63. [Google Scholar]
- The European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/620. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2021/620/oj (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Kitts-Morgan, S.E.; Caires, K.C.; Bohannon, L.A.; Parsons, E.I.; Hilburn, K.A. Free-ranging farm cats: Home range size and predation on a livestock unit in Northwest Georgia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopardi, S.; Priori, P.; Zecchin, B.; Zamperin, G.; Milani, A.; Tonon, F.; Giorgiutti, M.; Beato, M.S.; Benedictis, P. De Interface between Bats and Pigs in Heavy Pig Production. Viruses 2021, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, D.; Jones, G. Identification of twenty-two bat species (Mammalia: Chiroptera) from Italy by analysis of time-expanded recordings of echolocation calls. J. Zool. 2002, 258, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fenton, M.B.; Grinnel, A.D.; Popper, A.N.; Fay, R.R. Bat Bioacoustics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781493935253. [Google Scholar]
- Von Helversen, S.D. Illustrated Identification key to Illustrated identification key to the bats of Europe. Europe 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OIE. Rabies (infection with rabies virus and other lyssaviruses). In Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals; Office International des Epizooties: Paris, France, 2018; Available online: https://www.oie.int/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/3.01.17_RABIES.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Wakeley, P.R.; Johnson, N.; McElhinney, L.M.; Marston, D.; Sawyer, J.; Fooks, A.R. Development of a Real-Time, TaqMan Reverse Transcription-PCR Assay for Detection and Differentiation of Lyssavirus Genotypes 1, 5, and 6. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2786–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Benedictis, P.; De Battisti, C.; Dacheux, L.; Marciano, S.; Ormelli, S.; Salomoni, A.; Caenazzo, S.T.; Lepelletier, A.; Bourhy, H.; Capua, I.; et al. Lyssavirus detection and typing using pyrosequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1932–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dell’Armelina Rocha, P.R.; Velasco-Villa, A.; de Lima, E.M.; Salomoni, A.; Fusaro, A.; da Conceição Souza, E.; Negreiros, R.L.; Zafino, V.L.; Zamperin, G.; Leopardi, S.; et al. Unexpected rabies variant identified in kinkajou (Potos flavus), Mato Grosso, Brazil. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marston, D.A.; McElhinney, L.M.; Johnson, N.; Müller, T.; Conzelmann, K.K.; Tordo, N.; Fooks, A.R. Comparative analysis of the full genome sequence of European bat lyssavirus type 1 and type 2 with other lyssaviruses and evidence for a conserved transcription termination and polyadenylation motif in the G-L 3′ non-translated region. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1302–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dereeper, A.; Guignon, V.; Blanc, G.; Audic, S.; Buffet, S.; Chevenet, F.; Dufayard, J.F.; Guindon, S.; Lefort, V.; Lescot, M.; et al. Phylogeny.fr: Robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, D.A.; Jennings, D.L.; Maclaren, N.C.; Dorey-Robinson, D.; Fooks, A.R.; Banyard, A.C.; McElhinney, L.M. Pan-lyssavirus real time rt-pcr for rabies diagnosis. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Handy, S.M.; Deeds, J.R.; Ivanova, N.V.; Hebert, P.D.N.; Hanner, R.H.; Ormos, A.; Weigt, L.A.; Moore, M.M.; Yancy, H.F. A single-laboratory validated method for the generation of DNA barcodes for the identification of fish for regulatory compliance. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. Barcoding, Bold: The Barcode of Life Data System (www.barcodinglife.org). NPR Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gigante, C.M.; Dettinger, L.; Powell, J.W.; Seiders, M.; Condori, R.E.C.; Griesser, R.; Okogi, K.; Carlos, M.; Pesko, K.; Breckenridge, M.; et al. Multi-site evaluation of the LN34 pan-lyssavirus real-time RT-PCR assay for postmortem rabies diagnostics. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Laboratory Techniques in Rabies, 5th ed.; Rupprecht, C.E., Fooks, A.R., Abela-Ridder, B., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 1, Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/310837/9789241515306-eng.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puechmaille, S.J.; Allegrini, B.; Benda, P. A new species of the Miniopterus schreibersii species complex. Zootaxa 2014, 3794, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.; Pereira, M.J.R.; Rainho, A.; Palmeirim, J.M. Behavioural determinants of gene flow in the bat Miniopterus schreibersii. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2010, 64, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.G.R.; Newton, J.; Agnelli, P.; Budinski, I.; Di Salvo, I.; Flaquer, C.; Fulco, A.; Georgiakakis, P.; Martinoli, A.; Mas, M.; et al. Hydrogen isotopes reveal evidence of migration of Miniopterus schreibersii in Europe. BMC Ecol. 2020, 20, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürün, K.; Furman, A.; Juste, J.; Pereira, M.J.R.; Palmeirim, J.M.; Puechmaille, S.J.; Hulva, P.; Presetnik, P.; Hamidovic, D.; Ibáñez, C.; et al. A continent-scale study of the social structure and phylogeography of the bent-wing bat, Miniopterus schreibersii (Mammalia: Chiroptera), using new microsatellite data. J. Mammal. 2019, 100, 1865–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.; Palmeirim, J.M. Migratory behaviour of the Schreiber’s bat: When, where and why do cave bats migrate in a Mediterranean region? J. Zool. 2008, 274, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, D.; Jones, G. Use of foraging habitats by bats in a Mediterranean area determined by acoustic surveys: Conservation implications. Ecography 2003, 26, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, A.J.; McKinley, T.J.; Baker, K.S.; Barr, J.A.; Crameri, G.; Hayman, D.T.S.; Feng, Y.R.; Broder, C.C.; Wang, L.F.; Cunningham, A.A.; et al. Use of cross-reactive serological assays for detecting novel pathogens in wildlife: Assessing an appropriate cutoff for henipavirus assays in African bats. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 193, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brook, C.E.; Ranaivoson, H.C.; Broder, C.C.; Cunningham, A.A.; Héraud, J.-M.; Peel, A.J.; Gibson, L.; Wood, J.L.N.; Metcalf, C.J.; Dobson, A.P. Disentangling serology to elucidate henipa- and filovirus transmission in Madagascar fruit bats. J. Anim. Ecol. 2019, 88, 1001–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, A.T.; Fooks, A.R.; Hayman, D.T.S.; Horton, D.L.; Müller, T.; Plowright, R.; Peel, A.J.; Bowen, R.; Wood, J.L.N.; Mills, J.; et al. Deciphering serology to understand the ecology of infectious diseases in wildlife. Ecohealth 2013, 10, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warrilow, D.; Smith, I.L.; Harrower, B.; Smith, G.A. Sequence analysis of an isolate from a fatal human infection of Australian bat lyssavirus. Virology 2002, 297, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garin, I.; Aihartza, J.; Agirre-Mendi, P.T.; Alcalde, J.T.; De Lucas, J.; De Paz, O.; Goiti, U.; Artazcoz, A. Seasonal movements of the Schreibers’ bat, Miniopterus schreibersii, in the northern Iberian Peninsula. Ital. J. Zool. 2008, 75, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Cobo, J.; Sanz-Trullén, V.; Martínez-Rica, J.P. Migratory movements of Miniopterus schreibersii in the north-east of Spain. Acta Theriol. 1998, 43, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cliquet, F.; Freuling, C.; Smreczak, M.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Horton, D.; Fooks, A.R.; Robardet, E.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Müller, T. Development of harmonised schemes for monitoring and reporting of rabies in animals in the European Union. Scientific report submitted to EFSA. EFSA Support. Publ. 2010, 7, 67E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, N.; Vos, A.; Neubert, L.; Freuling, C.; Mansfield, K.L.; Kaipf, I.; Denzinger, A.; Hicks, D.; Núñez, A.; Franka, R.; et al. Experimental study of European bat lyssavirus type-2 infection in Daubenton’s bats (Myotis daubentonii). J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2662–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard-Meyer, E.; Beven, V.; Hirchaud, E.; Guillaume, C.; Larcher, G.; Robardet, E.; Servat, A.; Blanchard, Y.; Cliquet, F. Lleida Bat Lyssavirus isolation in Miniopterus schreibersii in France. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 66, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negredo, A.; Palacios, G.; Vázquez-Morón, S.; González, F.; Dopazo, H.; Molero, F.; Juste, J.; Quetglas, J.; Savji, N.; de la Cruz Martínez, M.; et al. Discovery of an ebolavirus-like filovirus in Europe. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kemenesi, G.; Kurucz, K.; Dallos, B.; Zana, B.; Földes, F.; Boldogh, S.; Görföl, T.; Carroll, M.W.; Jakab, F. Re-emergence of Lloviu virus in Miniopterus schreibersii bats, Hungary, 2016 correspondence. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Arellano, E.R.; Sanchez-Lockhart, M.; Perteguer, M.J.; Bartlett, M.; Ortiz, M.; Campioli, P.; Hernández, A.; Gonzalez, J.; Garcia, K.; Ramos, M.; et al. First evidence of antibodies against Lloviu virus in Schreiber’s bent-winged insectivorous bats demonstrate a wide circulation of the virus in Spain. Viruses 2019, 11, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manhart, W.A.; Pacheco, J.R.; Hume, A.J.; Cressey, T.N.; Deflubé, L.R.; Mühlberger, E. A Chimeric Lloviu Virus Minigenome System Reveals that the Bat-Derived Filovirus Replicates More Similarly to Ebolaviruses than Marburgviruses. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 2573–2580.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ancillotto, L.; Serangeli, M.T.; Russo, D. Curiosity killed the bat: Domestic cats as bat predators. Mamm. Biol. 2013, 78, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Council of the European Communities Council Directive 92/43/EEC on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1992, L 269, 1–52.
- Tjørnehøj, K.; Fooks, A.R.; Agerholm, J.S.; Rønsholt, L. Natural and Experimental Infection of Sheep with European Bat Lyssavirus Type-1 of Danish Bat Origin. J. Comp. Pathol. 2006, 134, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Cox, J.; Peter, W.; Schäfer, R.; Johnson, N.; McElhinney, L.M.; Geue, J.L.; Tjørnehøj, K.; Fooks, A.R. Spill-over of European bat lyssavirus type 1 into a stone marten (Martes foina) in Germany. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2004, 51, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On, I.; Centre, N.R.; Centre, N.R.; Origin, I.; Youpee, B. Identification of a rabid dog in France illegally introduced from Morocco. Euro Surveill. 2008, 13, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Dogs | Cats | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Notifications of suspect cases | 32 | 14 | |
| Notifications of biting animals | 23 | 11 | |
| Notifications of free roaming animals | 9 | 3 | |
| Active inspection of strayed populations within 1 km from the index case | 35 | ||
| Active inspection of strayed populations 1–3 km from the index case | 78 | ||
| Interview with volunteers working with stray animals | within 1 km | 43 | |
| 1–3 km away | 39 | ||
| Virological analyses on suspect cases | 1 | 2 | |
| Passive surveillance on biting animals (tested for lyssavirus infection) | 4 | ||
| Date | Salivary Swabs (n) | Positive | Prevalence Excluded (%) | Sera (n) | Positive | % Positivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| September 2020 | 75 | 0 | 3 | 56 | 24 | 42.8 |
| October 2020 | 82 | 0 | 2 | 52 | 16 | 30.8 |
| April 2021 | 64 | 0 | 2.5 | 46 | 5 | 10.9 |
| May 2021 | 47 | 0 | 7 | 36 | 11 | 30.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leopardi, S.; Barneschi, E.; Manna, G.; Zecchin, B.; Priori, P.; Drzewnioková, P.; Festa, F.; Lombardo, A.; Parca, F.; Scaravelli, D.; et al. Spillover of West Caucasian Bat Lyssavirus (WCBV) in a Domestic Cat and Westward Expansion in the Palearctic Region. Viruses 2021, 13, 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102064
Leopardi S, Barneschi E, Manna G, Zecchin B, Priori P, Drzewnioková P, Festa F, Lombardo A, Parca F, Scaravelli D, et al. Spillover of West Caucasian Bat Lyssavirus (WCBV) in a Domestic Cat and Westward Expansion in the Palearctic Region. Viruses. 2021; 13(10):2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102064
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeopardi, Stefania, Ettore Barneschi, Giuseppe Manna, Barbara Zecchin, Pamela Priori, Petra Drzewnioková, Francesca Festa, Andrea Lombardo, Fabio Parca, Dino Scaravelli, and et al. 2021. "Spillover of West Caucasian Bat Lyssavirus (WCBV) in a Domestic Cat and Westward Expansion in the Palearctic Region" Viruses 13, no. 10: 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102064
APA StyleLeopardi, S., Barneschi, E., Manna, G., Zecchin, B., Priori, P., Drzewnioková, P., Festa, F., Lombardo, A., Parca, F., Scaravelli, D., Maroni Ponti, A., & De Benedictis, P. (2021). Spillover of West Caucasian Bat Lyssavirus (WCBV) in a Domestic Cat and Westward Expansion in the Palearctic Region. Viruses, 13(10), 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102064