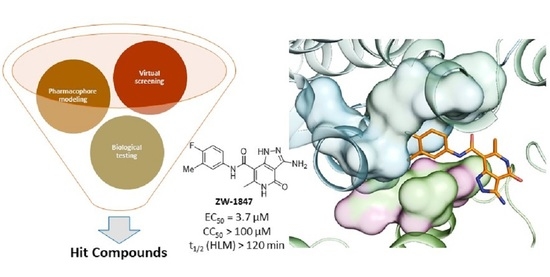
Discovery of New Small Molecule Hits as Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly Modulators: Structure and Pharmacophore-Based Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virtual Screening Workflow
2.1.1. Protein Preparation
2.1.2. Receptor Grid Generation
2.1.3. Ligand Preparation
2.1.4. Virtual Screening
2.1.5. Pharmacophore Modelling
2.2. Chemistry
2.3. Biology
2.3.1. Reagents
2.3.2. Cp Purification
2.3.3. Thermal Shift Assay
2.3.4. Antiviral Assays
2.3.5. Cytotoxicity Assays
2.3.6. ADME Assays
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuen, M.-F.; Chen, D.-S.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Lau, D.T.Y.; Locarnini, S.A.; Peters, M.G.; Lai, C.-L. Hepatitis B virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, G.C.; Zoulim, F.; Hou, J.; Bertoletti, A. Therapeutic strategies for hepatitis B virus infection: Towards a cure. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassal, M. HBV cccDNA: Viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015, 64, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deres, K.; Schröder, C.H.; Paessens, A.; Goldmann, S.; Hacker, H.J.; Weber, O.; Krämer, T.; Niewöhner, U.; Pleiss, U.; Stoltefuss, J.; et al. Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Drug-Induced Depletion of Nucleocapsids. Science 2003, 299, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, W.-K.; Lo, Y.-R.; Pawlotsky, J.-M.; Yuen, M.-F. Chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2018, 392, 2313–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinazi, R.F.; Ehteshami, M.; Bassit, L.; Asselah, T. Towards HBV curative therapies. Liver Int. 2018, 38 (Suppl. 1), 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wynne, S.A.; Crowther, R.A.; Leslie, A.G.W. The Crystal Structure of the Human Hepatitis B Virus Capsid. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatakrishnan, B.; Zlotnick, A. The Structural Biology of Hepatitis B Virus: Form and Function. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 429–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wei, Y.; Liu, T. A dimorphism shift of hepatitis B virus capsids in response to ionic conditions. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 16984–16989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asor, R.; Schlicksup, C.J.; Zhao, Z.; Zlotnick, A.; Raviv, U. Rapidly forming early intermediate structures dictate the pathway of capsid assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 7868–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, Z.; Pionek, K.; Unchwaniwala, N.; Maguire, M.L.; Loeb, D.D.; Zlotnick, A. The interface between Hepatitis B virus capsid proteins affects self-assembly, pregenomic RNA packaging, and reverse transcription. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3275–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.-H.; Li, Y.-N.; Zhao, J.-R.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Z. HBc binds to the CpG islands of HBV cccDNA and promotes an epigenetic permissive state. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zlotnick, A.; Venkatakrishnan, B.; Tan, Z.; Lewellyn, E.; Turner, W.; Francis, S. Core protein: A pleiotropic keystone in the HBV lifecycle. Antivir. Res. 2015, 121, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, S.; Gao, L.; Han, X.; Hu, T.; Hu, Y.; Liu, H.; Thomas, A.W.; Yan, Z.; Yang, S.; Young, J.A.T.; et al. Discovery of Small Molecule Therapeutics for Treatment of Chronic HBV Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanathan, U.; Mani, N.; Hu, Z.; Ban, H.; Du, Y.; Hu, J.; Chang, J.; Guo, J.-T. Targeting the multifunctional HBV core protein as a potential cure for chronic hepatitis B. Antivir. Res. 2020, 182, 104917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijampatnam, B.; Liotta, D.C. Recent advances in the development of HBV capsid assembly modulators. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 50, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Pei, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Jiang, C.; Tan, X.; Dong, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, G. Discovery of (1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridin-5-yl)sulfonamide Analogues as Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly Modulators by Conformation Constraint. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 6066–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Hu, T.; Zhou, X.; Wildum, S.; Garcia-Alcalde, F.; Xu, Z.; Wu, D.; Mao, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Heteroaryldihydropyrimidine (HAP) and Sulfamoylbenzamide (SBA) Inhibit Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Different Molecular Mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stray, S.J.; Bourne, C.R.; Punna, S.; Lewis, W.G.; Finn, M.G.; Zlotnick, A. A heteroaryldihydropyrimidine activates and can misdirect hepatitis B virus capsid assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8138–8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourne, C.R.; Finn, M.G.; Zlotnick, A. Global Structural Changes in Hepatitis B Virus Capsids Induced by the Assembly Effector HAP1. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11055–11061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, G. Virtual screening: An endless staircase? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Byrne, R.; Schneider, G.; Yang, S. Concepts of Artificial Intelligence for Computer-Assisted Drug Discovery. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 10520–10594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, G. Automating drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. ZINC—A free database of commercially available compounds for virtual screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ripphausen, P.; Nisius, B.; Bajorath, J. State-of-the-art in ligand-based virtual screening. Drug Discov. Today 2011, 16, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Huber, A.D.; Pineda, D.L.; Boschert, K.N.; Wolf, J.J.; Kankanala, J.; Xie, J.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Wang, Z. 5-Aminothiophene-2,4-dicarboxamide analogues as hepatitis B virus capsid assembly effectors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 164, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandyck, K.; Last, S.J.; Rombouts, G.; Verschueren, W.G.; Raboisson, P.J.B. Sulfamoyl-Arylamides and the Use Thereof as Medicaments for the Treatment of Hepatitis B. U.S. Patent 20150266890, 24 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vandyck, K.; Kesteleyn, B.R.R.; Pieters, S.M.A.; Rombouts, G.; Verschueren, W.G.; Raboisson, P.J.B. Glyoxamide Substituted Pyrrolamide Derivatives and the Use Thereof as Medicaments for the Treatment of Hepatitis B. WO Patent 2015011281, 29 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Amblard, F.; Boucle, S.; Bassit, L.; Cox, B.; Sari, O.; Tao, S.; Chen, Z.; Ozturk, T.; Verma, K.; Russell, O.; et al. Novel Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly Modulator Induces Potent Antiviral Responses In Vitro and in Humanized Mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.L.; Smondyrev, A.M.; Knoll, E.H.; Rao, S.N.; Shaw, D.E.; Friesner, R.A. PHASE: A new engine for pharmacophore perception, 3D QSAR model development, and 3D database screening: 1. Methodology and preliminary results. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2006, 20, 647–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.L.; Smondyrev, A.M.; Rao, S.N. PHASE: A novel approach to pharmacophore modeling and 3D database searching. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2006, 67, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, M.L.; Ferro, S.; Rao, A.; De Luca, L.; Zappalà, M.; Monforte, A.-M.; Debyser, Z.; Witvrouw, M.; Chimirri, A. Pharmacophore-Based Design of HIV-1 Integrase Strand-Transfer Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 7084–7088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peukert, S.; Brendel, J.; Pirard, B.; Strübing, C.; Kleemann, H.-W.; Böhme, T.; Hemmerle, H. Pharmacophore-based search, synthesis, and biological evaluation of anthranilic amides as novel blockers of the Kv1.5 channel. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 2823–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, R.; Perumal, R.V.; Pandi, P.V. Pharmacophore Based Synthesis of 3-Chloroquinoxaline-2-carboxamides as Serotonin3 (5-HT3) Receptor Antagonist. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qingzhi, G.; Lulu, Y.; Yongqiang, Z. Pharmacophore Based Drug Design Approach as a Practical Process in Drug Discovery. Curr. Comput. Aided Drug Des. 2010, 6, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Song, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhan, P.; Rai, D.; Liang, X.; Ma, C.; Liu, X. Design, synthesis and primary biological evaluation of the novel 2-pyridone derivatives as potent non-nucleoside HBV inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 136, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Bai, F.; Liu, N.; Liang, X.; Zhan, P.; Ma, C.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X. Design, synthesis and evaluation of pyrazole derivatives as non-nucleoside hepatitis B virus inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Yu, J.; Du, X.; Cherukupalli, S.; Zhan, P.; Liu, X. Design, diversity-oriented synthesis and biological evaluation of novel heterocycle derivatives as non-nucleoside HBV capsid protein inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 202, 112495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, A.D.; Pineda, D.L.; Liu, D.; Boschert, K.N.; Gres, A.T.; Wolf, J.J.; Coonrod, E.M.; Tang, J.; Laughlin, T.G.; Yang, Q.; et al. Novel Hepatitis B Virus Capsid-Targeting Antiviral That Aggregates Core Particles and Inhibits Nuclear Entry of Viral Cores. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavi Sastry, G.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and ligand preparation: Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra Precision Glide: Docking and Scoring Incorporating a Model of Hydrophobic Enclosure for Protein−Ligand Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 2. Enrichment Factors in Database Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 1. Method and Assessment of Docking Accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, F.H.S.; de Souza, R.O.M.A.; Garden, S.J. An efficient green protocol for the preparation of acetoacetamides and application of the methodology to a one-pot synthesis of Biginelli dihydropyrimidines. Expansion of dihydropyrimidine topological chemical space. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 70915–70928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrazek, F.M.; Sharaf, M.F.; Metz, P.; Jaeger, A. The reaction of 2-dimethylaminomethylene-3-oxo-N-phenylbutyramide with active methylene nitriles. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2010, 47, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrazek, F.M.; Sobhy, N.A.; Metz, P.; Bazbouz, A.A. Synthetic studies with 3-Oxo-N-[4-(3-oxo- 3-phenylpropionylamino)-phenyl]-3-phenylpropionamide. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2012, 49, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savant, M.M.; Ladva, K.D.; Pandit, A.B. Facile synthesis of highly functionalized novel pyrazolopyridones using oxoketene dithioacetal and their anti-HIV activity. Synth. Commun. 2018, 48, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stray, S.J.; Johnson, J.M.; Kopek, B.G.; Zlotnick, A. An in vitro fluorescence screen to identify antivirals that disrupt hepatitis B virus capsid assembly. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotnick, A.; Lee, A.; Bourne, C.R.; Johnson, J.M.; Domanico, P.L.; Stray, S.J. In Vitro screening for molecules that affect virus capsid assembly (and other protein association reactions). Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zlotnick, A.; Cheng, N.; Conway, J.F.; Booy, F.P.; Steven, A.C.; Stahl, S.J.; Wingfield, P.T. Dimorphism of hepatitis B virus capsids is strongly influenced by the C-terminus of the capsid protein. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 7412–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, R.A.; Kiselev, N.A.; Böttcher, B.; Berriman, J.A.; Borisova, G.P.; Ose, V.; Pumpens, P. Three-dimensional structure of hepatitis B virus core particles determined by electron cryomicroscopy. Cell 1994, 77, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-A.; Kim, S.; Park, M.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, S.; Hwang, J.-R.; Kim, Y.-C.; Jun Kim, Y.; Cho, Y.; et al. Ciclopirox inhibits Hepatitis B Virus secretion by blocking capsid assembly. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Compound | Structure | EC50 (µM) a | CC50 (µM) b |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZW-1840 |  | 21.1 ± 4.8 | >100 |
| ZW-1841 |  | 6.6 ± 0.4 | >100 |
| ZW-1842 |  | >30 | >100 |
| ZW-1843 |  | >30 | >100 |
| ZW-1845 |  | 22.4 ± 3.8 | >100 |
| ZW-1847 |  | 3.7 ± 1.0 | >100 |
| ZW-1888 |  | 17.2 ± 3.1 | 46.6 ± 2.4 |
| ZW-1889 |  | >30 | 58.2 ± 5.6 |
| ZW-1918 |  | >30 | 47.6 ± 0.2 |
| ZW-1929 |  | 21.7 ± 3.1 | 41.3 ± 1.7 |
| ZW-1946 |  | >30 | 44.1 ± 0.6 |
| Compound | Aqueous Solubility (µM) a, n = 3 | Plasma Stability t1/2 (h), n = 3 | Microsomal Stability b t1/2 (min), n = 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | Mouse | Human | Mouse | ||
| ZW-1841 | 0.31 ± 0.03 | >6 | >6 | >120 | 32.6 ± 1.6 |
| ZW-1847 | 2.14 ± 0.03 | >6 | >6 | >120 | >120 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senaweera, S.; Du, H.; Zhang, H.; Kirby, K.A.; Tedbury, P.R.; Xie, J.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Wang, Z. Discovery of New Small Molecule Hits as Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly Modulators: Structure and Pharmacophore-Based Approaches. Viruses 2021, 13, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050770
Senaweera S, Du H, Zhang H, Kirby KA, Tedbury PR, Xie J, Sarafianos SG, Wang Z. Discovery of New Small Molecule Hits as Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly Modulators: Structure and Pharmacophore-Based Approaches. Viruses. 2021; 13(5):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050770
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenaweera, Sameera, Haijuan Du, Huanchun Zhang, Karen A. Kirby, Philip R. Tedbury, Jiashu Xie, Stefan G. Sarafianos, and Zhengqiang Wang. 2021. "Discovery of New Small Molecule Hits as Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly Modulators: Structure and Pharmacophore-Based Approaches" Viruses 13, no. 5: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050770
APA StyleSenaweera, S., Du, H., Zhang, H., Kirby, K. A., Tedbury, P. R., Xie, J., Sarafianos, S. G., & Wang, Z. (2021). Discovery of New Small Molecule Hits as Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly Modulators: Structure and Pharmacophore-Based Approaches. Viruses, 13(5), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050770