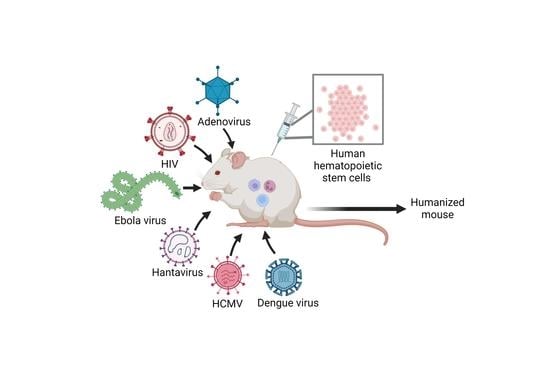
Recent Developments in NSG and NRG Humanized Mouse Models for Their Use in Viral and Immune Research
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Humanization Protocols
2.1. Generation of Humanized Mice by Transplantation in Young NSG Mice
2.2. Generation of Humanized Mice by Transplantation of Newborn NSG Mice
2.3. Generation of Humanized NRG Mice
3. Viral Infections in NSG and NRG Humanized Mouse Models
3.1. Human Adenovirus Infection
3.2. Ebola Virus Infection
3.3. Dengue Virus (DENV) Infection
3.4. Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Infection
3.5. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection
3.6. Hantaan Orthohantavirus (HNTV) Infection
4. Closing Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masopust, D.; Sivula, C.P.; Jameson, S.C. Of Mice, Dirty Mice, and Men: Using Mice to Understand Human Immunology. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.M.; Brehm, M.A.; Bridges, S.; Ferguson, S.; Kumar, P.; Mirochnitchenko, O.; Palucka, K.; Pelanda, R.; Sanders-Beer, B.; Shultz, L.D.; et al. Humanized Immune System Mouse Models: Progress, Challenges and Opportunities. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosma, G.C.; Custer, R.P.; Bosma, M.J. A Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Mutation in the Mouse. Nature 1983, 301, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, D.E.; Gulizia, R.J.; Baird, S.M.; Wilson, D.B. Transfer of a Functional Human Immune System to Mice with Severe Combined Immunodeficiency. Nature 1988, 335, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapidot, T.; Pflumio, F.; Doedens, M.; Murdoch, B.; Williams, D.E.; Dick, J.E. Cytokine Stimulation of Multilineage Hematopoiesis from Immature Human Cells Engrafted in SCID Mice. Science 1992, 255, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, D.L.; Hesselton, R.A.; Shultz, L.D. SCID Mouse Models of Human Stem Cell Engraftment. Stem Cells 1998, 16, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, L.D.; Schweitzer, P.A.; Christianson, S.W.; Gott, B.; Schweitzer, I.B.; Tennent, B.; McKenna, S.; Mobraaten, L.; Rajan, T.V.; Greiner, D.L. Multiple Defects in Innate and Adaptive Immunologic Function in NOD/LtSz-Scid Mice. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselton, R.M.; Greiner, D.L.; Mordes, J.P.; Rajan, T.V.; Sullivan, J.L.; Shultz, L.D. High Levels of Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Engraftment and Enhanced Susceptibility to Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection in NOD/LtSz-Scid/Scid Mice. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, S.W.; Greiner, D.L.; Schweitzer, I.B.; Gott, B.; Beamer, G.L.; Schweitzer, P.A.; Hesselton, R.M.; Shultz, L.D. Role of Natural Killer Cells on Engraftment of Human Lymphoid Cells and on Metastasis of Human T-Lymphoblastoid Leukemia Cells in C57BL/6J-ScidMice and in C57BL/6J-Scid BgMice. Cell. Immunol. 1996, 171, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, T.; Markees, T.G.; Serreze, D.V.; Pierce, M.A.; Marron, M.P.; Wicker, L.S.; Peterson, L.B.; Shultz, L.D.; Mordes, J.P.; Rossini, A.A.; et al. Genetic Disassociation of Autoimmunity and Resistance to Costimulation Blockade-Induced Transplantation Tolerance in Nonobese Diabetic Mice. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walsh, N.C.; Kenney, L.L.; Jangalwe, S.; Aryee, K.-E.; Greiner, D.L.; Brehm, M.A.; Shultz, L.D. Humanized Mouse Models of Clinical Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2017, 12, 187–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, L.D.; Brehm, M.A.; Bavari, S.; Greiner, D.L. Humanized Mice as a Preclinical Tool for Infectious Disease and Biomedical Research. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1245, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, F.; Yasukawa, M.; Lyons, B.; Yoshida, S.; Miyamoto, T.; Yoshimoto, G.; Watanabe, T.; Akashi, K.; Shultz, L.D.; Harada, M. Development of Functional Human Blood and Immune Systems in NOD/SCID/IL2 Receptor γ Chainnull Mice. Blood 2005, 106, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, L.D.; Lyons, B.L.; Burzenski, L.M.; Gott, B.; Chen, X.; Chaleff, S.; Kotb, M.; Gillies, S.D.; King, M.; Mangada, J.; et al. Human Lymphoid and Myeloid Cell Development in NOD/LtSz- Scid IL2R γ null Mice Engrafted with Mobilized Human Hemopoietic Stem Cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 6477–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, T.; Shultz, L.D.; Miller, D.; King, M.; Laning, J.; Fodor, W.; Cuthbert, A.; Burzenski, L.; Gott, B.; Lyons, B.; et al. Non-Obese Diabetic–Recombination Activating Gene-1 (NOD– Rag 1 Null) Interleukin (IL)-2 Receptor Common Gamma Chain (IL 2 Rγ Null) Null Mice: A Radioresistant Model for Human Lymphohaematopoietic Engraftment. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 154, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, L.D.; Brehm, M.A.; Garcia-Martinez, J.V.; Greiner, D.L. Humanized Mice for Immune System Investigation: Progress, Promise and Challenges. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, M.A.; Bortell, R.; Verma, M.; Shultz, L.D.; Greiner, D.L. Humanized Mice in Translational Immunology. In Translational Immunology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 285–326. [Google Scholar]
- Shultz, L.D.; Saito, Y.; Najima, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Ochi, T.; Tomizawa, M.; Doi, T.; Sone, A.; Suzuki, N.; Fujiwara, H.; et al. Generation of Functional Human T-Cell Subsets with HLA-Restricted Immune Responses in HLA Class I Expressing NOD/SCID/IL2rγ null Humanized Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13022–13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, J.; Vuyyuru, R.; Siglin, A.; Root, M.; Manser, T. Evaluation of the Efficiency of Human Immune System Reconstitution in NSG Mice and NSG Mice Containing a Human HLA.A2 Transgene Using Hematopoietic Stem Cells Purified from Different Sources. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 422, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danner, R.; Chaudhari, S.N.; Rosenberger, J.; Surls, J.; Richie, T.L.; Brumeanu, T.-D.; Casares, S. Expression of HLA Class II Molecules in Humanized NOD.Rag1KO.IL2RgcKO Mice Is Critical for Development and Function of Human T and B Cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Chen, Q. Humanized Mouse Models for the Study of Infection and Pathogenesis of Human Viruses. Viruses 2018, 10, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connell, A.K.; Douam, F. Humanized Mice for Live-Attenuated Vaccine Research: From Unmet Potential to New Promises. Vaccines 2020, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.C.; Choi, B.-S.; Kim, K.-C.; Park, K.H.; Lee, H.J.; Cho, Y.K.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, S.S.; Oh, Y.-K.; Kim, Y.B. A Simple Mouse Model for the Study of Human Immunodeficiency Virus. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2016, 32, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.A.; Covassin, L.; Brehm, M.A.; Racki, W.; Pearson, T.; Leif, J.; Laning, J.; Fodor, W.; Foreman, O.; Burzenski, L.; et al. Human Peripheral Blood Leucocyte Non-Obese Diabetic-Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Interleukin-2 Receptor Gamma Chain Gene Mouse Model of Xenogeneic Graft- versus -Host-like Disease and the Role of Host Major Histocompatibility Complex. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 157, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, M.B.; Vbranac, V.; Tivey, T.; Tsang, K.; Tager, A.M.; Aliprantis, A.O. Graft versus Host Disease in the Bone Marrow, Liver and Thymus Humanized Mouse Model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkias, J.; Yen, B.; Taylor, K.T.; Reinhartz, O.; Winoto, A.; Robey, E.A.; Melichar, H.J. Conserved and Divergent Aspects of Human T-cell Development and Migration in Humanized Mice. Immunol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 93, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmig, S.; Kronstein-Wiedemann, R.; Fohgrub, J.; Kronstein, N.; Nevmerzhitskaya, A.; Bornhäuser, M.; Gassmann, M.; Platz, A.; Ordemann, R.; Tonn, T.; et al. Improved Human Erythropoiesis and Platelet Formation in Humanized NSGW41 Mice. Stem Cell Rep. 2016, 7, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stripecke, R.; Münz, C.; Schuringa, J.J.; Bissig, K.; Soper, B.; Meeham, T.; Yao, L.; di Santo, J.P.; Brehm, M.; Rodriguez, E.; et al. Innovations, Challenges, and Minimal Information for Standardization of Humanized Mice. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e8662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guil-Luna, S.; Sedlik, C.; Piaggio, E. Humanized Mouse Models to Evaluate Cancer Immunotherapeutics. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2021, 5, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, M.; Mairesse, M.; Matas-Céspedes, A.; Bareham, B.; Pellegrini, G.; Liaunardy, A.; Powell, E.; Sargeant, R.; Cuomo, E.; Stebbings, R.; et al. Recent Advancements and Applications of Human Immune System Mice in Preclinical Immuno-Oncology. Toxicol. Pathol. 2020, 48, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, N.; PLoSs, A.; Balling, R.; Becker, P.D.; Borsotti, C.; Brezillon, N.; Debarry, J.; de Jong, Y.; Deng, H.; di Santo, J.P.; et al. Humanized Mice for Modeling Human Infectious Disease: Challenges, Progress, and Outlook. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 6, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.; Ban, H.-S.; Kim, S.-S.; Wu, H.; Pearson, T.; Greiner, D.L.; Laouar, A.; Yao, J.; Haridas, V.; Habiro, K.; et al. T Cell-Specific SiRNA Delivery Suppresses HIV-1 Infection in Humanized Mice. Cell 2008, 134, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Li, G.; Jeffrey, J.; Kovalev, G.I.; Su, L. Efficient Infection, Activation, and Impairment of PDCs in the BM and Peripheral Lymphoid Organs during Early HIV-1 Infection in Humanized Rag2−/−γ C−/− Mice in Vivo. Blood 2011, 117, 6184–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakki, M.; Goldman, D.C.; Streblow, D.N.; Hamlin, K.L.; Krekylwich, C.N.; Fleming, W.H.; Nelson, J.A. HCMV Infection of Humanized Mice after Transplantation of G-CSF–Mobilized Peripheral Blood Stem Cells from HCMV-Seropositive Donors. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdtke, A.; Oestereich, L.; Ruibal, P.; Wurr, S.; Pallasch, E.; Bockholt, S.; Ip, W.H.; Rieger, T.; Gómez-Medina, S.; Stocking, C.; et al. Ebola Virus Disease in Mice with Transplanted Human Hematopoietic Stem Cells. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4700–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobak, L.; Raftery, M.J.; Voigt, S.; Kühl, A.A.; Kilic, E.; Kurth, A.; Witkowski, P.; Hofmann, J.; Nitsche, A.; Schaade, L.; et al. Hantavirus-Induced Pathogenesis in Mice with a Humanized Immune System. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, E.; Ip, W.H.; Kolbe, V.; Hartmann, K.; Pilnitz-Stolze, G.; Tekin, N.; Gómez-Medina, S.; Muñoz-Fontela, C.; Krasemann, S.; Dobner, T. Humanized Mice Reproduce Acute and Persistent Human Adenovirus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero-Pérez, B.; Ruibal, P.; Rottstegge, M.; Lüdtke, A.; Port, J.R.; Hartmann, K.; Gómez-Medina, S.; Müller-Guhl, J.; Nelson, E.V.; Krasemann, S.; et al. Comparative Pathogenesis of Ebola Virus and Reston Virus Infection in Humanized Mice. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e126070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodmer, B.S.; Breithaupt, A.; Heung, M.; Brunetti, J.E.; Henkel, C.; Müller-Guhl, J.; Rodríguez, E.; Wendt, L.; Winter, S.L.; Vallbracht, M.; et al. In Vivo Characterization of the Novel Ebolavirus Bombali Virus Suggests a Low Pathogenic Potential for Humans. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2164216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharides, A.P.A.; Rongvaux, A.; Fritsch, K.; Flavell, R.A.; Manz, M.G. Humanized Hemato-Lymphoid System Mice. Haematologica 2016, 101, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huey, D.D.; Niewiesk, S. Production of Humanized Mice through Stem Cell Transfer. Curr. Protoc. Mouse Biol. 2018, 8, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftery, M.J.; Lalwani, P.; Lütteke, N.; Kobak, L.; Giese, T.; Ulrich, R.G.; Radosa, L.; Krüger, D.H.; Schönrich, G. Replication in the Mononuclear Phagocyte System (MPS) as a Determinant of Hantavirus Pathogenicity. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, J.; Rico-Hesse, R. Dengue Virus Tropism in Humanized Mice Recapitulates Human Dengue Fever. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.W.K.; Watanabe, S.; Kavishna, R.; Alonso, S.; Vasudevan, S.G. Animal Models for Studying Dengue Pathogenesis and Therapy. Antivir. Res. 2015, 123, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronel-Ruiz, C.; Gutiérrez-Barbosa, H.; Medina-Moreno, S.; Velandia-Romero, M.L.; Chua, J.V.; Castellanos, J.E.; Zapata, J.C. Humanized Mice in Dengue Research: A Comparison with Other Mouse Models. Vaccines 2020, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, J.; Rico-Hesse, R. Humanized Mice Show Clinical Signs of Dengue Fever According to Infecting Virus Genotype. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 8638–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traggiai, E.; Chicha, L.; Mazzucchelli, L.; Bronz, L.; Piffaretti, J.-C.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Manz, M.G. Development of a Human Adaptive Immune System in Cord Blood Cell-Transplanted Mice. Science 2004, 304, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theobald, S.J.; Khailaie, S.; Meyer-Hermann, M.; Volk, V.; Olbrich, H.; Danisch, S.; Gerasch, L.; Schneider, A.; Sinzger, C.; Schaudien, D.; et al. Signatures of T and B Cell Development, Functional Responses and PD-1 Upregulation After HCMV Latent Infections and Reactivations in Nod.Rag.Gamma Mice Humanized With Cord Blood CD34+ Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salguero, G.; Daenthanasanmak, A.; Münz, C.; Raykova, A.; Guzmán, C.A.; Riese, P.; Figueiredo, C.; Länger, F.; Schneider, A.; Macke, L.; et al. Dendritic Cell–Mediated Immune Humanization of Mice: Implications for Allogeneic and Xenogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 4636–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialek-Waldmann, J.K.; Domning, S.; Esser, R.; Glienke, W.; Mertens, M.; Aleksandrova, K.; Arseniev, L.; Kumar, S.; Schneider, A.; Koenig, J.; et al. Induced Dendritic Cells Co-Expressing GM-CSF/IFN-α/TWT1 Priming T and B Cells and Automated Manufacturing to Boost GvL. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 21, 621–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theobald, S.J.; Kreer, C.; Khailaie, S.; Bonifacius, A.; Eiz-Vesper, B.; Figueiredo, C.; Mach, M.; Backovic, M.; Ballmaier, M.; Koenig, J.; et al. Repertoire Characterization and Validation of GB-Specific Human IgGs Directly Cloned from Humanized Mice Vaccinated with Dendritic Cells and Protected against HCMV. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Koenig, J.; Schneider, A.; Wermeling, F.; Boddul, S.; Theobald, S.J.; Vollmer, M.; Kloos, D.; Lachmann, N.; Klawonn, F.; et al. In Vivo Lentiviral Gene Delivery of Hla-Dr and Vaccination of Humanized Mice for Improving the Human t and b Cell Immune Reconstitution. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.; Kajon, A. Adenovirus: Epidemiology, Global Spread of Novel Serotypes, and Advances in Treatment and Prevention. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 37, 586–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greber, U.F.; Flatt, J.W. Adenovirus Entry: From Infection to Immunity. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lion, T. Adenovirus Infections in Immunocompetent and Immunocompromised Patients. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 441–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, J.R.; Cook, J.L. Human Adenovirus Infections. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Chard, L.S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Syrian Hamster as an Animal Model for the Study on Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, W.; Fan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Li, K.; Zheng, Z.; Tian, X.; Zhou, R. Chinese Tree Shrew: A Permissive Model for in Vitro and in Vivo Replication of Human Adenovirus Species B. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertzbach, L.D.; Ip, W.H.; Dobner, T. Animal Models in Human Adenovirus Research. Biology 2021, 10, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronan, B.A.; Agrwal, N.; Carey, E.J.; de Petris, G.; Kusne, S.; Seville, M.T.; Blair, J.E.; Vikram, H.R. Fulminant Hepatitis due to Human Adenovirus. Infection 2014, 42, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, H.; Machemer, T.; Philopena, J.; Wen, S.-F.; Quijano, E.; Ramachandra, M.; Tsai, V.; Ralston, R. Acute Hepatotoxicity of Oncolytic Adenoviruses in Mouse Models Is Associated with Expression of Wild-Type E1a and Induction of TNF-α. Virology 2004, 328, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krzywkowski, T.; Ciftci, S.; Assadian, F.; Nilsson, M.; Punga, T. Simultaneous Single-Cell In Situ Analysis of Human Adenovirus Type 5 DNA and MRNA Expression Patterns in Lytic and Persistent Infection. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00166-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.T.; Crozier, I.; Fischer, W.A.; Hewlett, A.; Kraft, C.S.; Vega, M.-A.; de la Soka, M.J.; Wahl, V.; Griffiths, A.; Bollinger, L.; et al. Ebola Virus Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/about.html (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Haddock, E.; Saturday, G.; Feldmann, F.; Hanley, P.W.; Okumura, A.; Lovaglio, J.; Long, D.; Thomas, T.; Scott, D.P.; Pulliam, M.; et al. Reston Virus Causes Severe Respiratory Disease in Young Domestic Pigs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 118, e2015657118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoni, D.; Hamlet, A.; Michaelis, M.; Wass, M.N.; Rossman, J.S. Risks Posed by Reston, the Forgotten Ebolavirus. mSphere 2016, 1, e00322-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Strong, J.E.; Feldmann, H. Considerations in the Use of Nonhuman Primate Models of Ebola Virus and Marburg Virus Infection: Table 1. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, S91–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetria, C.; Smith, I.; Tan, T.; Villarico, D.; Simon, E.M.; Centeno, R.; Tachedjian, M.; Taniguchi, S.; Shimojima, M.; Miranda, N.L.J.; et al. Reemergence of Reston Ebolavirus in Cynomolgus Monkeys, the Philippines, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, J.R.; Prescott, J.; Feldmann, H.; Spiropoulou, C.F. Human Immune System Mouse Models of Ebola Virus Infection. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 25, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screaton, G.; Mongkolsapaya, J.; Yacoub, S.; Roberts, C. New Insights into the Immunopathology and Control of Dengue Virus Infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsheten, T.; Clements, A.C.A.; Gray, D.J.; Adhikary, R.K.; Furuya-Kanamori, L.; Wangdi, K. Clinical Predictors of Severe Dengue: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2021, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Quispe, C.; Herrera-Bravo, J.; Sarkar, C.; Sharma, R.; Garg, N.; Fredes, L.I.; Martorell, M.; Alshehri, M.M.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; et al. Production, Transmission, Pathogenesis, and Control of Dengue Virus: A Literature-Based Undivided Perspective. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 4224816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.V.; Ye, W.; Chen, Q.; Teixeira, M.M.; Preiser, P.; Ooi, E.E.; Chen, J. Dengue Virus-Infected Dendritic Cells, but Not Monocytes, Activate Natural Killer Cells through a Contact-Dependent Mechanism Involving Adhesion Molecules. mBio 2017, 8, e00741-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbein, G. High-Risk Oncogenic Human Cytomegalovirus. Viruses 2022, 14, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Fang, F. Congenital Human Cytomegalovirus Infection and Neurologic Diseases in Newborns. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Gao, W.; Lv, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z. Congenital Human Cytomegalovirus Infection Inducing Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 649690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, P.; Reeves, M. Pathogenesis of Human Cytomegalovirus in the Immunocompromised Host. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mana, H.; Yassine, H.M.; Younes, N.N.; Al-Mohannadi, A.; Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Alhababi, D.; Nasser, E.A.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Al Mana, H.; Al-Mohannadi, A.; et al. The Current Status of Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Prevalence in the MENA Region: A Systematic Review. Pathogens 2019, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, M.R.; Wills, M.R.; Sinclair, J.H. HCMV Antivirals and Strategies to Target the Latent Reservoir. Viruses 2021, 13, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.L.W.; Deere, J.D.; Kieu, H.T.; Castillo, L.D.; Machmach, K.; Shen, X.; Tomaras, G.D.; Shacklett, B.L.; Barry, P.A.; Hartigan-O’Connor, D.J.; et al. RhCMV Serostatus and Vaccine Adjuvant Impact Immunogenicity of RhCMV/SIV Vaccines. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burwitz, B.J.; Malouli, D.; Bimber, B.N.; Reed, J.S.; Ventura, A.B.; Hancock, M.H.; Uebelhoer, L.S.; Bhusari, A.; Hammond, K.B.; Espinosa Trethewy, R.G.; et al. Cross-Species Rhesus Cytomegalovirus Infection of Cynomolgus Macaques. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1006014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.; Theobald, S.J.; Stripecke, R. Modeling Human Cytomegalovirus in Humanized Mice for Vaccine Testing. Vaccines 2020, 8, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomić, A.; Varanasi, P.R.; Golemac, M.; Malić, S.; Riese, P.; Borst, E.M.; Mischak-Weissinger, E.; Guzmán, C.A.; Krmpotić, A.; Jonjić, S.; et al. Activation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity by a Recombinant Human Cytomegalovirus Strain Expressing an NKG2D Ligand. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1006015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Piot, P.; Abdool Karim, S.S.; Hecht, R.; Legido-Quigley, H.; Buse, K.; Stover, J.; Resch, S.; Ryckman, T.; Møgedal, S.; Dybul, M.; et al. Defeating AIDS—Advancing Global Health. Lancet 2015, 386, 171–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, N.W. Metabolic Complications of Chronic HIV Infection: A Narrative Review. Pathogens 2022, 11, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Prete, G.Q.; Lifson, J.D.; Keele, B.F. Nonhuman Primate Models for the Evaluation of HIV-1 Preventive Vaccine Strategies. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2016, 11, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesan, S.; Li, H.; Burnett, J.C.; Takahashi, M.; Li, S.; Wu, S.X.; Synold, T.W.; Rossi, J.J.; Zhou, J. HIV Replication and Latency in a Humanized NSG Mouse Model during Suppressive Oral Combinational Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02118-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochat, M.-A.; Schlaepfer, E.; Kuster, S.P.; Li, D.; Audige, A.; Ivic, S.; Fahrny, A.; Speck, R.F. Monitoring HIV DNA and Cellular Activation Markers in HIV-Infected Humanized Mice under CART. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majji, S.; Wijayalath, W.; Shashikumar, S.; Pow-Sang, L.; Villasante, E.; Brumeanu, T.D.; Casares, S. Differential Effect of HLA Class-I versus Class-II Transgenes on Human T and B Cell Reconstitution and Function in NRG Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, J.K.; Ortega-Prieto, A.M.; Dorner, M. A Hitchhiker’s Guide to Humanized Mice: New Pathways to Studying Viral Infections. Immunology 2018, 154, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillgrass, A.; Wessels, J.M.; Yang, J.X.; Kaushic, C. Advances in Humanized Mouse Models to Improve Understanding of HIV-1 Pathogenesis and Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 617516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Ma, J.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Li, G.; Li, F.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Yasui, F.; Ye, C.; et al. Blocking Type I Interferon Signaling Enhances T Cell Recovery and Reduces HIV-1 Reservoirs. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 127, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.-L.; Murakowski, D.K.; Bournazos, S.; Schoofs, T.; Sarkar, D.; Halper-Stromberg, A.; Horwitz, J.A.; Nogueira, L.; Golijanin, J.; Gazumyan, A.; et al. Enhanced Clearance of HIV-1–Infected Cells by Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies against HIV-1 In Vivo. Science 2016, 352, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahodantin, J.; Nio, K.; Funaki, M.; Zhai, X.; Wilson, E.; Kottilil, S.; Cheng, L.; Li, G.; Su, L. Type I Interferons and TGF-β Cooperate to Induce Liver Fibrosis during HIV-1 Infection under Antiretroviral Therapy. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e152738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöhr, W.; Fidler, S.; McClure, M.; Weber, J.; Cooper, D.; Ramjee, G.; Kaleebu, P.; Tambussi, G.; Schechter, M.; Babiker, A.; et al. Duration of HIV-1 Viral Suppression on Cessation of Antiretroviral Therapy in Primary Infection Correlates with Time on Therapy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, P.K.; Kaminski, R.; Bella, R.; Su, H.; Mathews, S.; Ahooyi, T.M.; Chen, C.; Mancuso, P.; Sariyer, R.; Ferrante, P.; et al. Sequential LASER ART and CRISPR Treatments Eliminate HIV-1 in a Subset of Infected Humanized Mice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, P.K.; Gorantla, S.; Poluektova, L.; Hasan, M.; Waight, E.; Zhang, C.; Markovic, M.; Edagwa, B.; Machhi, J.; Olson, K.E.; et al. Humanized Mice for Infectious and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Retrovirology 2021, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepard, M.; Yang, J.X.; Afkhami, S.; Nazli, A.; Zganiacz, A.; Tang, S.; Choi, M.W.Y.; Vahedi, F.; Deshiere, A.; Tremblay, M.J.; et al. Comparing Current and Next-Generation Humanized Mouse Models for Advancing HIV and HIV/Mtb Co-Infection Studies. Viruses 2022, 14, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avšič-Županc, T.; Saksida, A.; Korva, M. Hantavirus Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 21, e6–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocato, R.L.; Hooper, J.W. Progress on the Prevention and Treatment of Hantavirus Disease. Viruses 2019, 11, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, J.W.; Hammerbeck, C.D.; Mucker, E.M.; Brocato, R.L. Animal Models for the Study of Rodent-Borne Hemorrhagic Fever Viruses: Arenaviruses and Hantaviruses. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 793257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönrich, G.; Raftery, M.J. Exploring the Immunopathogenesis of Viral Hemorrhagic Fever in Mice with a Humanized Immune System. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López, R.; Vial, C.; Graf, J.; Calvo, M.; Ferrés, M.; Mertz, G.; Cuiza, A.; Agüero, B.; Aguilera, D.; Araya, D.; et al. Platelet Count in Patients with Mild Disease at Admission Is Associated with Progression to Severe Hantavirus Cardiopulmonary Syndrome. Viruses 2019, 11, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-M.; Yang, W.-L.; Yang, F.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, W.-J.; Hou, W.; Fan, C.-F.; Jin, R.-H.; Feng, Y.-M.; Wang, Y.-C.; et al. Cathepsin L Plays a Key Role in SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Humans and Humanized Mice and Is a Promising Target for New Drug Development. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2021, 6, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.N.; Zhao, Y. Cancer Immunotherapies and Humanized Mouse Drug Testing Platforms. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steichen, J.M.; Lin, Y.-C.; Havenar-Daughton, C.; Pecetta, S.; Ozorowski, G.; Willis, J.R.; Toy, L.; Sok, D.; Liguori, A.; Kratochvil, S.; et al. A Generalized HIV Vaccine Design Strategy for Priming of Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Responses. Science 2019, 366, eaax4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Lyu, Y.; Yang, Y.-G.; Hu, Z. Humanized Rodent Models for Cancer Research. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, A.; Lang, J.; Pitts, T.M.; Jordan, K.R.; Lieu, C.H.; Davis, S.L.; Diamond, J.R.; Kopetz, S.; Barbee, J.; Peterson, J.; et al. Characterization of Immune Responses to Anti-PD-1 Mono and Combination Immunotherapy in Hematopoietic Humanized Mice Implanted with Tumor Xenografts. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Katano, I.; Ito, R.; Goto, M.; Abe, H.; Mizuno, S.; Kawai, K.; Sugiyama, F.; Ito, M. Enhanced Antibody Responses in a Novel NOG Transgenic Mouse with Restored Lymph Node Organogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 8, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, D.J.; O’Connell, A.K.; Turcinovic, J.; Montanaro, P.; Hekman, R.M.; Tamura, T.; Berneshawi, A.R.; Cafiero, T.R.; Al Abdullatif, S.; Blum, B.; et al. Humanized Mice Reveal a Macrophage-Enriched Gene Signature Defining Human Lung Tissue Protection during SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Wee, C.Y.Y.; Chen, Q. Establishment of Humanized Mice for the Study of HBV. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 638447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Alam, M.M. Rise of the Human-Mouse Chimeric Brain Models. Cell Regen. 2022, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Henderson, M.; Muth, S.; Murphy, A.; Zheng, L. Preclinical Mouse Models for Immunotherapeutic and Non-Immunotherapeutic Drug Development for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Pancreat. Cancer 2020, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Year of Generation | Virus | Mouse Strain | Humanization | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 2011 | HIV | NSG NRG | CD34+, newborn | [32,33] |
| 2014 | HCMV | NSG NSG-A2 | CD34+, newborn | [34] |
| 2015 | EBOV | NSG-A2 | CD34+ HSC, young mice | [35] |
| 2015 | Hantaviruses | NSG | CD34+ HSC, young mice | [36] |
| 2017 | HAdV | NSG-A2 | CD34+ HSC, young mice | [37] |
| 2019 | EBOV, SUDV, RESTV, etc. | NSG-A2 | CD34+ HSC, young mice | [38,39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kitsera, M.; Brunetti, J.E.; Rodríguez, E. Recent Developments in NSG and NRG Humanized Mouse Models for Their Use in Viral and Immune Research. Viruses 2023, 15, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020478
Kitsera M, Brunetti JE, Rodríguez E. Recent Developments in NSG and NRG Humanized Mouse Models for Their Use in Viral and Immune Research. Viruses. 2023; 15(2):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020478
Chicago/Turabian StyleKitsera, Maksym, Jesús Emanuel Brunetti, and Estefanía Rodríguez. 2023. "Recent Developments in NSG and NRG Humanized Mouse Models for Their Use in Viral and Immune Research" Viruses 15, no. 2: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020478
APA StyleKitsera, M., Brunetti, J. E., & Rodríguez, E. (2023). Recent Developments in NSG and NRG Humanized Mouse Models for Their Use in Viral and Immune Research. Viruses, 15(2), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020478