Protein Folding Activity of the Ribosome (PFAR) –– A Target for Antiprion Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Antiprion compound screening assays
2.1. Proteinase K assay

2.2. Fluorescence-Based Assay
2.3. Yeast-Prion Based Assay
3. Identification of New Antiprion Compounds in Yeast-Prion Based Assays

4. Cellular Targets of the Antiprion Compounds 6AP and GA
6AP and GA Target the Ribosome by Binding to the Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
5. 6AP, GA and IQ Inhibit Protein Folding Activity of the Ribosome (PFAR)
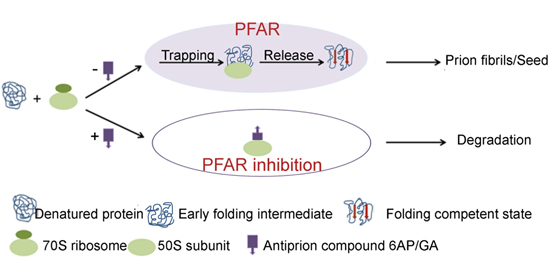
5.1. PFAR
5.2. The PFAR Assay

5.3. Inhibition of PFAR by 6AP, GA and IQ and Their Derivatives
6. Mode of Inhibition of PFAR by 6AP and Its Derivatives
6.1. 6AP Inhibits PFAR by Binding to Specific Sites on the Domain V rRNA

6.2. 6AP Binding Sites Overlap with Protein Binding Sites
6.3. Both PFAR and 6AP/Protein Substrate-Binding are Sensitive to Mutations on Domain V rRNA
6.4. Competitive Inhibition of PFAR by 6AP and GA
6.5. Comparison of 6AP Derivatives for Their Affinity to Domain V rRNA

6.6. Density Functional Theory (DFT) Calculations Explain why 6APi Cannot Bind to Domain V rRNA
7. PFAR and Prion Correlation: Conclusions and Future Perspectives

Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Prusiner, S.B. Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science 1991, 252, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissmann, C.; Aguzzi, A. Approaches to therapy of prion diseases. Annu. Rev. Med. 2005, 56, 321–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riek, R.; Hornemann, S.; Wider, G.; Glockshuber, R.; Wüthrich, K. NMR characterization of the full-length recombinant murine prion protein, mPrP(23–231). FEBS Lett. 1997, 413, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tycko, R.; Savtchenko, R.; Ostapchenko, V.G.; Makarava, N.; Baskakov, I.V. The α-helical C-terminal domain of full-length recombinant PrP converts to an in-register parallel β-sheet structure in PrP fibrils: Evidence from solid state nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 9488–9497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrett, J.T.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. Seeding “one-dimensional crystallization” of amyloid: A pathogenic mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease and scrapie? Cell 1993, 73, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinge, J.; Clarke, A.R. A general model of prion strains and their pathogenicity. Science 2007, 318, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deleault, N.R.; Lucassen, R.W.; Supattapone, S. RNA molecules stimulate prion protein conversion. Nature 2003, 425, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, Y.; Machado, F.; Juliano, L.; Juliano, M.A.; Brentani, R.R.; Foguel, D.; Silva, J.L. DNA converts cellular prion protein into the β-sheet conformation and inhibits prion peptide aggregation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 49400–49409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.P.B.; Cordeiro, Y.; Silva, J.L. The peculiar interaction between mammalian prion protein and RNA. Prion 2008, 2, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedo, B.; Millen, T.A.; Braga, C.A.C.A.; Gomes, M.P.B.; Ferreira, P.S.; Kraineva, J.; Winter, R.; Silva, J.L.; Cordeiro, Y. Nonspecific prion protein–nucleic acid interactions lead to different aggregates and cytotoxic species. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 5402–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.L.; Lima, L.M.; Foguel, D.; Cordeiro, Y. Intriguing nucleic-acid-binding features of mammalian prion protein. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, Y.; Lima, L.M.; Gomes, M.P.; Foguel, D.; Silva, J.L. Modulation of prion protein oligomerization, aggregation, and beta-sheet conversion by 4,4'-dianilino-1,1'-binaphthyl-5,5'-sulfonate (bis-ANS). J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 5346–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.P.; Vieira, T.C.; Cordeiro, Y.; Silva, J.L. The role of RNA in mammalian prion protein conversion. Wiley Interdiscipl. Rev. RNA 2012, 3, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinley, M.P.; Bolton, D.C.; Prusiner, S.B. A protease-resistant protein is a structural component of the Scrapie prion. Cell 1983, 35, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, R.K.; McKinley, M.P.; Bowman, K.A.; Braunfeld, M.B.; Barry, R.A.; Prusiner, S.B. Separation and properties of cellular and scrapie prion proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 2310–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korth, C.; May, B.C.H.; Cohen, F.E.; Prusiner, S.B. Acridine and phenothiazine derivatives as pharmacotherapeutics for prion disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9836–9841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocisko, D.A.; Baron, G.S.; Rubenstein, R.; Chen, J.; Kuizon, S.; Caughey, B. New Inhibitors of Scrapie-Associated Prion Protein Formation in a Library of 2000 Drugs and Natural Products. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 10288–10294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertsch, U.; Winklhofer, K.F.; Hirschberger, T.; Bieschke, J.; Weber, P.; Hartl, F.U.; Tavan, P.; Tatzelt, J.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Giese, A. systematic identification of antiprion drugs by high-throughput screening based on scanning for intensely fluorescent targets. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7785–7791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, S.; Talarek, N.; Andrieu, T.; Vierfond, J.-M.; Mettey, Y.; Galons, H.; Dormont, D.; Meijer, L.; Cullin, C.; Blondel, M. Isolation of drugs active against mammalian prions using a yeast-based screening assay. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, S.; Tribouillard, D.; Talarek, N.; Desban, N.; Gug, F.; Galons, H.; Blondel, M. A yeast-based assay to isolate drugs active against mammalian prions. Methods 2006, 39, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tribouillard-Tanvier, D.; Béringue, V.; Desban, N.; Gug, F.; Bach, S.; Voisset, C.; Galons, H.; Laude, H.; Vilette, D.; Blondel, M. Antihypertensive drug guanabenz is active in vivo against both yeast and mammalian prions. PLoS One 2008, 3, E1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oumata, N.; Nguyen, P.H.; Beringue, V.; Soubigou, F.; Pang, Y.; Desban, N.; Massacrier, C.; Morel, Y.; Paturel, C.; Contesse, M.A.; et al. The toll-like receptor agonist Imiquimod is active against prions. PLoS One 2013, 8, e72112. [Google Scholar]
- Tribouillard-Tanvier, D.; Dos Reis, S.; Gug, F.; Voisset, C.; Be´ringue, V.; Sabate, R.; Kikovska, E.; Talarek, N.; Bach, S.; Huang, C.; et al. Protein folding activity of ribosomal RNA Is a selective target of two unrelated antiprion drugs. PLoS One 2008, 3, e2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gug, F.; Oumata, N.; Tribouillard-Tanvier, D.; Voisset, C.; Desban, N.; Bach, S.; Blondel, M.; Galons, H. Synthesis of conjugates of 6-Aminophenanthridine and guanabenz, two structurally unrelated prion inhibitors, for the determination of their cellular targets by affinity chromatography. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Das, A.; Samanta, D.; Ghosh, J.; Dasgupta, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Basu, A.; Sanyal, S.; Dasgupta, C. Role of the ribosome in protein folding. Biotech. J. 2008, 3, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisset, C.; Saupe, S.J.; Blondel, M. The various facets of the protein-folding activity of the ribosome. Biotech J. 2011, 6, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudlicki, W.; Coffman, A.; Kramer, G.; Hardesty, B. Ribosomes and ribosomal RNA as chaperones for folding of proteins. Fold Des. 1997, 2, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.; Gupta, C.D. Reconstitution of denatured E. coli alkaline phosphatase with E. coli ribosome. Indian J. Biochem. Biol. 1992, 29, 512–515. [Google Scholar]
- Das, B.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Das Gupta, C. Reactivation of denatured fungal glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and E. coli alkaline phosphatase with E. coli ribosome. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 1992, 183, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argent, R.H.; Parrott, A.M.; Day, P.J.; Roberts, L.M.; Stockley, P.G.; Lord, J.M.; Radford, S.E. Ribosome-mediated folding of partially unfolded ricin A-chain. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9263–9269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Bera, A.K.; Dasgupta, C. In vitro protein folding by ribosomes from Escherichia coli, wheat germ and rat liver. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 235, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, S.C.; Pal, S.; Chaudhuri, S.; Dasgupta, C. 23S rRNA assisted folding of cytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase is distinctly different from its self-folding. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 2390–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, A.K.; Das, B.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Dasgupta, C. Refolding of denatured restriction endonucleases with ribosomal preparations from Methanosarcina barkeri. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1994, 32, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Das, B.; Bera, A.K.; Dasgupta, D.; Dasgupta, C. Refolding of denatured lactate dehydrogenase by Escherichia coli ribosomes. Biochem. J. 1994, 300, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Das, B.; Dasgupta, C. Reactivation of denatured proteins by 23S ribosomal RNA: Role of domain V. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8284–8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, D.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Chandra, S.; Sarkar, D.; Chakraborty, A.; Dasgupta, C. Reactivation of denatured proteins by domain V of bacterial 23S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 5047–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Chandra, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Sarkar, D.; Ghosh, A.N.; Gupta, C.D. Complementary role of two fragments of domain V of 23 s ribosomal RNA in protein folding. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 32771–32777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, D.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Chowdhury, S.; Ghosh, J.; Pal, S.; Basu, A.; Bhattacharya, A.; Das, A.; Das, D.; DasGupta, C. Protein folding by domain V of Escherichia coli 23S rRNA: Specificity of RNA-protein interactions. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 3344–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, N.; Nissen, P.; Hansen, J.; Moore, P.B.; Steitz, T.A. The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science 2000, 289, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Samanta, D.; Das, D.; Chowdhury, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Ghosh, J.; Das, A.; DasGupta, C. In vitro protein folding by E. coli ribosome: Unfolded protein splitting 70S to interact with 50S subunit. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2008, 366, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.; Pathak, B.K.; Ray, S.; Barat, C. Impact of P-site tRNA and antibiotics on ribosome mediated protein folding: studies using the Escherichia coli ribosome. PLoS One 2014, 9, e101293. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, J.; Basu, A.; Pal, S.; Chowdhuri, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Pal, D.; Chattoraj, D.K.; DasGupta, C. Ribosome–DnaK interactions in relation to protein folding. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 1679–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, S.D.; Pang, Y.; Vishnu, N.; Voisset, C.; Galons, H.; Blondel, M.; Sanyal, S. Mode of action of the antiprion drugs 6AP and GA on ribosome assisted protein folding. Biochimie 2011, 93, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, D.; Vovusha, H.; Pang, Y.; Oumata, N.; Sanyal, B.; Sanyal, S. Spectroscopic and DFT studies on 6-Aminophenanthridine and its derivatives provide insights in their activity towards ribosomal RNA. Biochimie 2014, 97, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Kurella, S.; Voisset, C.; Samanta, D.; Banerjee, D.; Schabe, A.; Dasgupta, C.; Galons, H.; Blondel, M.; Sanyal, S. The antiprion compound 6-Aminophenanthridine inhibits protein folding activity of the ribosome by direct competition. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 19081–19089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banerjee, D.; Sanyal, S. Protein Folding Activity of the Ribosome (PFAR) –– A Target for Antiprion Compounds. Viruses 2014, 6, 3907-3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6103907
Banerjee D, Sanyal S. Protein Folding Activity of the Ribosome (PFAR) –– A Target for Antiprion Compounds. Viruses. 2014; 6(10):3907-3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6103907
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanerjee, Debapriya, and Suparna Sanyal. 2014. "Protein Folding Activity of the Ribosome (PFAR) –– A Target for Antiprion Compounds" Viruses 6, no. 10: 3907-3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6103907
APA StyleBanerjee, D., & Sanyal, S. (2014). Protein Folding Activity of the Ribosome (PFAR) –– A Target for Antiprion Compounds. Viruses, 6(10), 3907-3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6103907