Superresolution Imaging of Human Cytomegalovirus vMIA Localization in Sub-Mitochondrial Compartments
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Conventional Confocal Imaging of vMIA Localization with Mitochondrial Markers



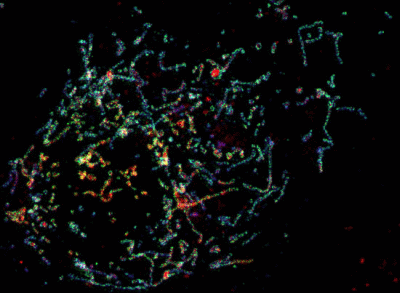
2.2. Single Color GSTED Imaging of vMIA Localization


2.3. MSIM Imaging of vMIA and Mitochondrial Marker
2.4. PALM Imaging of PA-mCherry-vMIA


3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture and Lipofection
3.2. Construction of pTRE-Tight Promoter-vMIA-EGFP
3.3. Confocal Microscopy
3.4. GSTED Microscopy
3.5. Deconvolution Analysis
3.6. MSIM
3.7. MSIM Data Collection and Analysis
3.8. PALM Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Hayashi, T.; Rizzuto, R.; Hajnoczky, G.; Su, T.P. MAM: More than just a housekeeper. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bononi, A.; Missiroli, S.; Poletti, F.; Suski, J.M.; Agnoletto, C.; Bonora, M.; de Marchi, E.; Giorgi, C.; Marchi, S.; Patergnani, S.; et al. Mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs) as hotspot Ca(2+) signaling units. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 740, 411–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, S.; Patergnani, S.; Pinton, P. The endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria connection: One touch, multiple functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1837, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabadkai, G.; Bianchi, K.; Varnai, P.; de Stefani, D.; Wieckowski, M.R.; Cavagna, D.; Nagy, A.I.; Balla, T.; Rizzuto, R. Chaperone-mediated coupling of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial Ca2+ channels. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 175, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, C.; Miller, R.A.; Smith, I.; Bui, T.; Molgo, J.; Muller, M.; Vais, H.; Cheung, K.H.; Yang, J.; Parker, I.; et al. Essential regulation of cell bioenergetics by constitutive InsP3 receptor Ca2+ transfer to mitochondria. Cell 2010, 142, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, R.; Vicencio, J.M.; Parra, V.; Troncoso, R.; Munoz, J.P.; Bui, M.; Quiroga, C.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Verdejo, H.E.; Ferreira, J.; et al. Increased ER-mitochondrial coupling promotes mitochondrial respiration and bioenergetics during early phases of ER stress. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanier, C.; Arnoult, D. Mitochondrial localization of viral proteins as a means to subvert host defense. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1813, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiban, J.; Caputo, L.; Colombini, M. Ceramide synthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum can permeabilize mitochondria to proapoptotic proteins. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, S.J.; Vance, J.E. Phosphatidylserine synthase-1 and -2 are localized to mitochondria-associated membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 34534–34540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Fujimoto, M. Detergent-resistant microdomains determine the localization of sigma-1 receptors to the endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria junction. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 77, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajate, C.; Gonzalez-Camacho, F.; Mollinedo, F. Lipid raft connection between extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 380, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanier, C.; Garcin, D.; Vazquez, A.; Arnoult, D. Mitochondrial dynamics regulate the RIG-I-like receptor antiviral pathway. EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, S.M.; Liu, H.M.; Park, H.S.; Briley, J.; Gale, M., Jr. Mitochondrial-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (MAM) form innate immune synapses and are targeted by hepatitis C virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14590–14595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboredo, M.; Greaves, R.F.; Hahn, G. Human cytomegalovirus proteins encoded by UL37 exon 1 protect infected fibroblasts against virus-induced apoptosis and are required for efficient virus replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 3555–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon-Friling, R.; Goodhouse, J.; Colberg-Poley, A.M.; Shenk, T. Human cytomegalovirus pUL37x1 induces the release of endoplasmic reticulum calcium stores. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19117–19122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldmacher, V.S.; Bartle, L.M.; Skaletskaya, A.; Dionne, C.A.; Kedersha, N.L.; Vater, C.A.; Han, J.W.; Lutz, R.J.; Watanabe, S.; Cahir McFarland, E.D.; et al. A cytomegalovirus-encoded mitochondria-localized inhibitor of apoptosis structurally unrelated to Bcl-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12536–12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoult, D.; Bartle, L.M.; Skaletskaya, A.; Poncet, D.; Zamzami, N.; Park, P.U.; Sharpe, J.; Youle, R.J.; Goldmacher, V.S. Cytomegalovirus cell death suppressor vMIA blocks Bax- but not Bak-mediated apoptosis by binding and sequestering Bax at mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7988–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poncet, D.; Larochette, N.; Pauleau, A.L.; Boya, P.; Jalil, A.A.; Cartron, P.F.; Vallette, F.; Schnebelen, C.; Bartle, L.M.; Skaletskaya, A.; et al. An anti-apoptotic viral protein that recruits Bax to mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 22605–22614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayajneh, W.A.; Colberg-Poley, A.M.; Skaletskaya, A.; Bartle, L.M.; Lesperance, M.M.; Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D.G.; Kedersha, N.L.; Goldmacher, V.S. The sequence and antiapoptotic functional domains of the human cytomegalovirus UL37 exon 1 immediate early protein are conserved in multiple primary strains. Virology 2001, 279, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavinakere, M.S.; Williamson, C.D.; Goldmacher, V.S.; Colberg-Poley, A.M. Processing of human cytomegalovirus UL37 mutant glycoproteins in the endoplasmic reticulum lumen prior to mitochondrial importation. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6771–6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozidis, P.; Williamson, C.D.; Colberg-Poley, A.M. Mitochondrial and secretory human cytomegalovirus UL37 proteins traffic into mitochondrion-associated membranes of human cells. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 2715–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozidis, P.; Williamson, C.D.; Wong, D.S.; Colberg-Poley, A.M. Trafficking of UL37 proteins into mitochondrion-associated membranes during permissive human cytomegalovirus infection. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7898–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, C.D.; Colberg-Poley, A.M. Intracellular Sorting Signals for Sequential Trafficking of Human Cytomegalovirus UL37 Proteins to the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondria. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 6400–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colberg-Poley, A.M.; Patel, M.B.; Erezo, D.P.; Slater, J.E. Human cytomegalovirus UL37 immediate-early regulatory proteins traffic through the secretory apparatus and to mitochondria. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 1779–1789. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, C.D.; Colberg-Poley, A.M. Access of viral proteins to mitochondria via mitochondria-associated membranes. Rev. Med. Virol. 2009, 19, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, C.D.; Zhang, A.; Colberg-Poley, A.M. The human cytomegalovirus protein UL37 exon 1 associates with internal lipid rafts. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2100–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Hildreth, R.L.; Colberg-Poley, A.M. Human cytomegalovirus inhibits apoptosis by proteasome-mediated degradation of Bax at endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrion contacts. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5657–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.Y.; Yaneva, R.; Hinson, E.R.; Cresswell, P. Human cytomegalovirus directly induces the antiviral protein viperin to enhance infectivity. Science 2011, 332, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.Y.; Cresswell, P. Viperin regulates cellular lipid metabolism during human cytomegalovirus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, K.L.; Youle, R.J. Cytomegalovirus proteins vMIA and m38.5 link mitochondrial morphogenesis to Bcl-2 family proteins. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6232–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Edlich, F.; Bermejo, G.A.; Norris, K.L.; Youle, R.J.; Tjandra, N. Structural mechanism of Bax inhibition by cytomegalovirus protein vMIA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20901–20906. [Google Scholar]
- Poncet, D.; Pauleau, A.L.; Szabadkai, G.; Vozza, A.; Scholz, S.R.; Le Bras, M.; Briere, J.J.; Jalil, A.; Le Moigne, R.; Brenner, C.; et al. Cytopathic effects of the cytomegalovirus-encoded apoptosis inhibitory protein vMIA. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 174, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, A.L.; Smith, V.L.; Chow, D.; Mocarski, E.S. Disruption of mitochondrial networks by the human cytomegalovirus UL37 gene product viral mitochondrion-localized inhibitor of apoptosis. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumier, T.; Szabadkai, G.; Simoni, A.M.; Perfettini, J.L.; Paulau, A.L.; Castedo, M.; Metivier, D.; Badley, A.; Rizzuto, R.; Kroemer, G. HIV-1 protease inhibitors and cytomegalovirus vMIA induce mitochondrial fragmentation without triggering apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, A.L.; Roback, L.; Mocarski, E.S. HtrA2/Omi terminates cytomegalovirus infection and is controlled by the viral mitochondrial inhibitor of apoptosis (vMIA). PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altan-Bonnet, N.; Sougrat, R.; Liu, W.; Snapp, E.L.; Ward, T.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Golgi inheritance in mammalian cells is mediated through endoplasmic reticulum export activities. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 990–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.R.; Lackner, L.L.; West, M.; DiBenedetto, J.R.; Nunnari, J.; Voeltz, G.K. ER tubules mark sites of mitochondrial division. Science 2011, 334, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.H.; Xia, C.; Zhong, G.; Babcock, H.P.; Vaughan, J.C.; Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Bi, G.Q.; Zhuang, X. Super-resolution fluorescence imaging of organelles in live cells with photoswitchable membrane probes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13978–13983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Kner, P.; Rego, E.H.; Gustafsson, M.G. Super-resolution 3D microscopy of live whole cells using structured illumination. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 1044–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoult, D.; Skaletskaya, A.; Estaquier, J.; Dufour, C.; Goldmacher, V.S. The murine cytomegalovirus cell death suppressor m38.5 binds Bax and blocks Bax-mediated mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. Apoptosis 2008, 13, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, D.S. 3D deconvolution microscopy. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, A.G.; Parekh, S.H.; Dalle Nogare, D.; Fischer, R.S.; Temprine, K.; Mione, M.; Chitnis, A.B.; Combs, C.A.; Shroff, H. Resolution doubling in live, multicellular organisms via multifocal structured illumination microscopy. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hell, S.W. Far-field optical nanoscopy. Science 2007, 316, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hell, S.W.; Wichmann, J. Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated emission: stimulated-emission-depletion fluorescence microscopy. Opt. Lett. 1994, 19, 780–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jans, D.C.; Wurm, C.A.; Riedel, D.; Wenzel, D.; Stagge, F.; Deckers, M.; Rehling, P.; Jakobs, S. STED super-resolution microscopy reveals an array of MINOS clusters along human mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8936–8941. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, D.; Buckers, J.; Kastrup, L.; Hell, S.W.; Jakobs, S. Two-color STED microscopy reveals different degrees of colocalization between hexokinase-I and the three human VDAC isoforms. PMC Biophys. 2010, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Lu, R.; Rodriguez, P.F.; Wu, Y.; Bopassa, J.C.; Stefani, E.; Toro, L. Visualization and quantification of cardiac mitochondrial protein clusters with STED microscopy. Mitochondrion 2012, 12, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Patterson, G.H. Photoactivatable fluorescent proteins for diffraction-limited and super-resolution imaging. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauleau, A.L.; Larochette, N.; Giordanetto, F.; Scholz, S.R.; Poncet, D.; Zamzami, N.; Goldmacher, V.S.; Kroemer, G. Structure-function analysis of the interaction between Bax and the cytomegalovirus-encoded protein vMIA. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7067–7080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildreth, R.L.; Bullough, M.D.; Zhang, A.; Chen, H.L.; Schwartz, P.H.; Panchision, D.M.; Colberg-Poley, A.M. Viral mitochondria-localized inhibitor of apoptosis (UL37 exon 1 protein) does not protect human neural precursor cells from human cytomegalovirus-induced cell death. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, C.M.; Hung, C.H.; Thomas, L.; Wan, L.; Thomas, G. Role of PACS-1 in trafficking of human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B and virus production. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 11105–11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colberg-Poley, A.M.; Williamson, C.D. Intracellular sorting and trafficking of cytomegalovirus proteins during permissive infection. In Cytomegaloviruses: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Intervention, 2nd ed.; Reddehase, M.J., Ed.; Caister Academic Press/Horizon: Norwich, UK, 2013; Volume I, pp. 196–229. [Google Scholar]
- Gossen, M.; Bujard, H. Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 5547–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Punge, A.; Hollopeter, G.; Willig, K.I.; Hobson, R.J.; Davis, M.W.; Hell, S.W.; Jorgensen, E.M. Protein localization in electron micrographs using fluorescence nanoscopy. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subach, F.V.; Patterson, G.H.; Manley, S.; Gillette, J.M.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Verkhusha, V.V. Photoactivatable mCherry for high-resolution two-color fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adair, R.; Liebisch, G.W.; Su, Y.; Colberg-Poley, A.M. Alteration of cellular RNA splicing and polyadenylation machineries during productive human cytomegalovirus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 3541–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicidomini, G.; Moneron, G.; Han, K.Y.; Westphal, V.; Ta, H.; Reuss, M.; Engelhardt, J.; Eggeling, C.; Hell, S.W. Sharper low-power STED nanoscopy by time gating. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingaramo, M.; York, A.G.; Wawrzusin, P.; Milberg, O.; Hong, A.; Weigert, R.; Shroff, H.; Patterson, G.H. Two-photon excitation improves multifocal structured illumination in thick scattering tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein, A.; Amodaj, N.; Hoover, K.; Vale, R.; Stuurman, N. Computer control of microscopes using microManager. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, A.G. MSIM Superresolution Fluorescence Microscopy of Multicellular Organisms. Available online: http://code.google.com/p/msim/ (accessed on 3 May 2012).
- Richardson, W.H. Bayesian-based iterative method of image restoration. JOSA 1972, 62, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucy, L. An iterative technique for the rectification of observed distributions. Astron. J. 1974, 79, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, A.G.; Chandris, P.; Nogare, D.D.; Head, J.; Wawrzusin, P.; Fischer, R.S.; Chitnis, A.; Shroff, H. Instant super-resolution imaging in live cells and embryos via analog image processing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzig, E.; Patterson, G.H.; Sougrat, R.; Lindwasser, O.W.; Olenych, S.; Bonifacino, J.S.; Davidson, M.W.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Hess, H.F. Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science 2006, 313, 1642–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willig, K.I.; Kellner, R.R.; Medda, R.; Hein, B.; Jakobs, S.; Hell, S.W. Nanoscale resolution in GFP-based microscopy. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 721–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudheti, M.V.; Curthoys, N.M.; Gould, T.J.; Kim, D.; Gunewardene, M.S.; Gabor, K.A.; Gosse, J.A.; Kim, C.H.; Zimmerberg, J.; Hess, S.T. Actin mediates the nanoscale membrane organization of the clustered membrane protein influenza hemagglutinin. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 2182–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.H.; Chan, J.; Lambele, M.; Thali, M. Clustering and mobility of HIV-1 Env at viral assembly sites predict its propensity to induce cell-cell fusion. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7516–7525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, J.R.; Llewellyn, G.N.; Soheilian, F.; Nagashima, K.; Veatch, S.L.; Ono, A. Roles played by capsid-dependent induction of membrane curvature and Gag-ESCRT interactions in tetherin recruitment to HIV-1 assembly sites. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4650–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felts, R.L.; Narayan, K.; Estes, J.D.; Shi, D.; Trubey, C.M.; Fu, J.; Hartnell, L.M.; Ruthel, G.T.; Schneider, D.K.; Nagashima, K.; et al. 3D visualization of HIV transfer at the virological synapse between dendritic cells and T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13336–13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.H.; Suomalainen, M.; Andriasyan, V.; Kilcher, S.; Mercer, J.; Neef, A.; Luedtke, N.W.; Greber, U.F. Tracking viral genomes in host cells at single-molecule resolution. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, C.A.; Neumann, D.; Lauterbach, M.A.; Harke, B.; Egner, A.; Hell, S.W.; Jakobs, S. Nanoscale distribution of mitochondrial import receptor Tom20 is adjusted to cellular conditions and exhibits an inner-cellular gradient. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13546–13551. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, C.D.; DeBiasi, R.L.; Colberg-Poley, A.M. Viral product trafficking to mitochondria, mechanisms and roles in pathogenesis. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2012, 12, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhuvanendran, S.; Salka, K.; Rainey, K.; Sreetama, S.C.; Williams, E.; Leeker, M.; Prasad, V.; Boyd, J.; Patterson, G.H.; Jaiswal, J.K.; et al. Superresolution Imaging of Human Cytomegalovirus vMIA Localization in Sub-Mitochondrial Compartments. Viruses 2014, 6, 1612-1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6041612
Bhuvanendran S, Salka K, Rainey K, Sreetama SC, Williams E, Leeker M, Prasad V, Boyd J, Patterson GH, Jaiswal JK, et al. Superresolution Imaging of Human Cytomegalovirus vMIA Localization in Sub-Mitochondrial Compartments. Viruses. 2014; 6(4):1612-1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6041612
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhuvanendran, Shivaprasad, Kyle Salka, Kristin Rainey, Sen Chandra Sreetama, Elizabeth Williams, Margretha Leeker, Vidhya Prasad, Jonathan Boyd, George H. Patterson, Jyoti K. Jaiswal, and et al. 2014. "Superresolution Imaging of Human Cytomegalovirus vMIA Localization in Sub-Mitochondrial Compartments" Viruses 6, no. 4: 1612-1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6041612
APA StyleBhuvanendran, S., Salka, K., Rainey, K., Sreetama, S. C., Williams, E., Leeker, M., Prasad, V., Boyd, J., Patterson, G. H., Jaiswal, J. K., & Colberg-Poley, A. M. (2014). Superresolution Imaging of Human Cytomegalovirus vMIA Localization in Sub-Mitochondrial Compartments. Viruses, 6(4), 1612-1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6041612