Sustained Release Drug Delivery Applications of Polyurethanes
Abstract
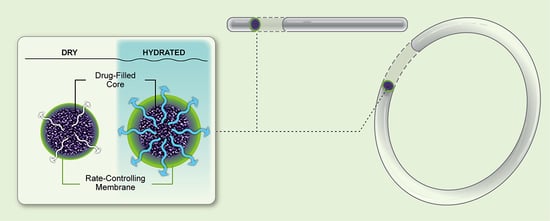
:1. Introduction
2. Chemistry of Polyurethanes
2.1. Isocyanates
2.2. Chain Extenders
2.3. Polyols
2.4. Synthesis
3. Drug Release Mechanisms
3.1. Solute Diffusion
3.2. Polymer Swelling
3.3. Polymer Erosion and Degradation
4. Approaches to Modulate Drug Release Kinetics
4.1. Intrinsic Drivers of Drug Release through a Polymer
4.1.1. Drug Solubility in Polymer
4.1.2. Drug Diffusivity through Polymer
4.2. The Use of Pore Formers
5. Mechanical Properties of Polyurethane-Based Dosage Forms
5.1. Patient Perceptions
5.2. Mechanical Testing of Finished Product
5.3. Gamma Irradiation
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Engels, H.-W.; Pirkl, H.-G.; Albers, R.; Albach, R.W.; Krause, J.; Hoffmann, A.; Casselmann, H.; Dormish, J. Polyurethanes: Versatile Materials and Sustainable Problem Solvers for Today’s Challenges. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9422–9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, O. Das Di-Isocyanat-Polyadditionsverfahren (Polyurethane). Angew. Chem. 1947, 59, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherng, J.Y.; Hou, T.Y.; Shih, M.F.; Talsma, H.; Hennink, W.E. Polyurethane-based drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 450, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, E.; Na, K. Polyurethane membrane with porous surface for controlled drug release in drug eluting stent. Biomater. Res. 2014, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Knight, P.T.; Mather, P.T. Tailored drug release from biodegradable stent coatings based on hybrid polyurethanes. J. Control. Release 2009, 137, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xu, H.; Yang, X. Preparation and characterization of PEG-modified polyurethane pressure-sensitive adhesives for transdermal drug delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2009, 35, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Brown, K.V.; Wenke, J.C.; Guelcher, S.A. Sustained release of vancomycin from polyurethane scaffolds inhibits infection of bone wounds in a rat femoral segmental defect model. J. Control. Release 2010, 145, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorna, K.; Gogolewski, S. Preparation, degradation, and calcification of biodegradable polyurethane foams for bone graft substitutes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2003, 67A, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yoshii, T.; Hafeman, A.E.; Nyman, J.S.; Wenke, J.C.; Guelcher, S.A. The effects of rhBMP-2 released from biodegradable polyurethane/microsphere composite scaffolds on new bone formation in rat femora. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6768–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, A.; D’Ilario, L.; Francolini, I.; Piozzi, A. Water state effect on drug release from an antibiotic loaded polyurethane matrix containing albumin nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 407, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Gao, H.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.-W.; Wu, G.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Ma, J. Temperature- and pH-responsive nanoparticles of biocompatible polyurethanes for doxorubicin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, P.; Adhikari, B.; Banerjee, I.; Maiti, T.K. Sustained release of antibiotic from polyurethane coated implant materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, S.A.L.; Lima, L.D.C.; Andrade, S.P.; Silva-Cunha Junior, A. Da; Órefice, R.L.; Ayres, E.; Da Silva, G.R. Local Drug Delivery System: Inhibition of Inflammatory Angiogenesis in a Murine Sponge Model by Dexamethasone-Loaded Polyurethane Implants. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 2886–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.J.; Gupta, K.M.; Fabian, J.; Albright, T.H.; Kiser, P.F. Segmented polyurethane intravaginal rings for the sustained combined delivery of antiretroviral agents dapivirine and tenofovir. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 39, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraete, G.; Vandenbussche, L.; Kasmi, S.; Nuhn, L.; Brouckaert, D.; Van Renterghem, J.; Grymonpré, W.; Vanhoorne, V.; Coenye, T.; De Geest, B.G.; et al. Thermoplastic polyurethane-based intravaginal rings for prophylaxis and treatment of (recurrent) bacterial vaginosis. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 529, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesquita, P.M.M.; Rastogi, R.; Segarra, T.J.; Teller, R.S.; Torres, N.M.; Huber, A.M.; Kiser, P.F.; Herold, B.C. Intravaginal ring delivery of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for prevention of HIV and herpes simplex virus infection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1730–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.M.; Pearce, S.M.; Poursaid, A.E.; Aliyar, H.A.; Tresco, P.A.; Mitchnik, M.A.; Kiser, P.F. Polyurethane Intravaginal Ring for Controlled Delivery of Dapivirine, a Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor of HIV-1. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4228–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traore, Y.L.; Chen, Y.; Bernier, A.-M.; Ho, E.A. Impact of Hydroxychloroquine-Loaded Polyurethane Intravaginal Rings on Lactobacilli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7680–7686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.M.; Rastogi, R.; Teller, R.S.; Srinivasan, P.; Mesquita, P.M.M.; Nagaraja, U.; McNicholl, J.M.; Hendry, R.M.; Dinh, C.T.; Martin, A.; et al. Intravaginal ring eluting tenofovir disoproxil fumarate completely protects macaques from multiple vaginal simian-HIV challenges. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16145–16150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.J.; Clark, M.R.; Albright, T.H.; Nebeker, J.S.; Tuitupou, A.L.; Clark, J.T.; Fabian, J.; McCabe, R.T.; Chandra, N.; Doncel, G.F.; et al. A 90-day tenofovir reservoir intravaginal ring for mucosal HIV prophylaxis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 6272–6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, M.J.; Mesquita, P.M.; Marzinke, M.A.; Teller, R.; Espinoza, L.; Atrio, J.M.; Lo, Y.; Frank, B.; Srinivasan, S.; Fredricks, D.N.; et al. A phase 1 randomized placebo-controlled safety and pharmacokinetic trial of a tenofovir disoproxil fumarate vaginal ring. AIDS 2016, 30, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teller, R.S.; Malaspina, D.C.; Rastogi, R.; Clark, J.T.; Szleifer, I.; Kiser, P.F. Controlling the hydration rate of a hydrophilic matrix in the core of an intravaginal ring determines antiretroviral release. J. Control. Release 2016, 224, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.M.; Srinivasan, P.; Teller, R.S.; Lo, Y.; Dinh, C.T.; Kiser, P.F.; Herold, B.C. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate intravaginal ring protects high-dose depot medroxyprogesterone acetate-treated macaques from multiple SHIV exposures. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2015, 68, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.R.; Johnson, T.J.; McCabe, R.T.; Clark, J.T.; Tuitupou, A.; Elgendy, H.; Friend, D.R.; Kiser, P.F. A hot-melt extruded intravaginal ring for the sustained delivery of the antiretroviral microbicide UC781. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friend, D.R.; Clark, J.T.; Kiser, P.F.; Clark, M.R. Multipurpose prevention technologies: Products in development. Antiviral Res. 2013, 100, S39–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claeys, B.; Bruyn, S. De; Hansen, L.; Beer, T. De; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. Release characteristics of polyurethane tablets containing dicarboxylic acids as release modifiers—A case study with diprophylline. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarus, J.; Pagliery, M.; Lachman, L. Factors Influencing the Release of a Drug from a Prolonged-Action Matrix. J. Pharm. Sci. 1964, 53, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.M.; Hiltner, A.; Wiggins, M.J.; Schubert, M.A.; Collier, T.O.; Kao, W.J.; Mathur, A.B. Recent advances in biomedical polyurethane biostability and biodegradation. Polym. Int. 1998, 46, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, S.L.; Guan, J. Advances in Polyurethane Biomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; ISBN 9780081006221. [Google Scholar]
- Boretos, J.W.; Pierce, W.S. Segmented polyurethane: A polyether polymer. An initial evalution for biomedical applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1968, 2, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogolewski, S. Selected topics in biomedical polyurethanes. A review. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1989, 267, 757–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunatillake, P.A.; Martin, D.J.; Meijs, G.F.; McCarthy, S.J.; Adhikari, R. Designing Biostable Polyurethane Elastomers for Biomedical Implants. Aust. J. Chem. 2003, 56, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, N.M.K.; Woodhouse, K.A.; Cooper, S.L. Polyurethanes in Biomedical Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Vermette, P.; Griesser, H.J.; Laroche, G.; Guidoin, R. (Eds.) Biomedical Applications of Polyurethanes; Landes Bioscience: Georgetown, TX, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Irusta, L.; Fernandez-Berridi, M.J. Aromatic poly(ester–urethanes): Effect of the polyol molecular weight on the photochemical behaviour. Polymer 2000, 41, 3297–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBattista, G.; Peerlings, H.W.I.; Kaufhold, W. Aliphatic TPUs for light-stable applications. Rubber World 2003, 227, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Szycher, M.; Siciliano, A.A. An Assessment of 2,4 TDA Formation from Surgitek Polyurethane Foam under Simulated Physiological Conditions. J. Biomater. Appl. 1991, 5, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kääriä, K.; Hirvonen, A.; Norppa, H.; Piirilä, P.; Vainio, H.; Rosenberg, C. Exposure to 4,4′-methylenediphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) during moulding of rigid polyurethane foam: Determination of airborne MDI and urinary 4,4′-methylenedianiline (MDA). Analyst 2001, 126, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbari, E.; Khakpour, M. Morphology of and release behavior from porous polyurethane microspheres. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2073–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.G.; Osborn, J.C.; Kober, E.M.; Schoonover, J.R. Effects of hydrolysis-induced molecular weight changes on the phase separation of a polyester polyurethane. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 3360–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, B.; Hirt, T.D.; Welti, M.; Uhlschmid, G.K.; Neuenschwander, P.; Suter, U.W. Development of degradable polyesterurethanes for medical applications: In vitro and in vivo evaluations. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 36, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Gupta, K.M.; Poursaid, A.E.; Karra, P.; Mahalingam, A.; Aliyar, H.A.; Kiser, P.F. Engineering a degradable polyurethane intravaginal ring for sustained delivery of dapivirine. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2011, 1, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Lin, F.; Lin, P.; Gao, Y.; Becker, M.L. Phenylalanine-Based Poly(ester urea): Synthesis, Characterization, and in vitro Degradation. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychlý, J.; Lattuati-Derieux, A.; Lavédrine, B.; Matisová-Rychlá, L.; Malíková, M.; Csomorová, K.; Janigová, I. Assessing the progress of degradation in polyurethanes by chemiluminescence and thermal analysis. II. Flexible polyether- and polyester-type polyurethane foams. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilgör, E.; Burgaz, E.; Yurtsever, E.; Yilgör, İ. Comparison of hydrogen bonding in polydimethylsiloxane and polyether based urethane and urea copolymers. Polymer 2000, 41, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggins, M.J.; Wilkoff, B.; Anderson, J.M.; Hiltner, A. Biodegradation of polyether polyurethane inner insulation in bipolar pacemaker leads. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 58, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenson, E.M.; Dadsetan, M.; Wiggins, M.; Anderson, J.M.; Hiltner, A. Poly(carbonate urethane) and poly(ether urethane) biodegradation: In vivo studies. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2004, 69, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Kohjiya, S.; Takesako, S.; Yamashita, S. Polyurethane elastomer with PEO-PTMO-PEO soft segment for sustained release of drugs. Biomaterials 1990, 11, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M.; Rodriguez, A.; Chang, D.T. Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kricheldorf, H.R.; Quirk, R.P.; Holden, G. Thermoplastic Elastomers; Hanser Gardner Publications: Munich, Germany, 2004; ISBN 9783446223752. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, T.O.; Choi, I.S.; Jeong, H.M.; Cho, K. Thermal and mechanical properties of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers from different polymerization methods. Polym. Int. 1993, 31, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, D.Y.; Lee, L.Y.; Wang, C.-H. Mathematical modeling and simulation of drug release from microspheres: Implications to drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1274–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F. Mathematical modeling of drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.T.; Johnson, T.J.; Clark, M.R.; Nebeker, J.S.; Fabian, J.; Tuitupou, A.L.; Ponnapalli, S.; Smith, E.M.; Friend, D.R.; Kiser, P.F. Quantitative evaluation of a hydrophilic matrix intravaginal ring for the sustained delivery of tenofovir. J. Control. Release 2012, 163, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugaonkar, S.R.; Clark, J.T.; English, L.B.; Johnson, T.J.; Buckheit, K.W.; Bahde, R.J.; Appella, D.H.; Buckheit, R.W.; Kiser, P.F. An Intravaginal Ring for the Simultaneous Delivery of an HIV-1 Maturation Inhibitor and Reverse-Transcriptase Inhibitor for Prophylaxis of HIV Transmission. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 3426–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Laarhoven, J.A.; Kruft, M.A.; Vromans, H. In vitro release properties of etonogestrel and ethinyl estradiol from a contraceptive vaginal ring. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 232, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2nd ed.; Oxford Science Publications; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1979; ISBN 978-0-19-853411-2. [Google Scholar]
- Vergnaud, J.-M. Controlled Drug Release of Oral Dosage Forms; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, T. Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J. Pharm. Sci. 1963, 52, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claeys, B.; Vervaeck, A.; Hillewaere, X.K.D.; Possemiers, S.; Hansen, L.; De Beer, T.; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. Thermoplastic polyurethanes for the manufacturing of highly dosed oral sustained release matrices via hot melt extrusion and injection molding. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 90, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yasuda, H.; Lamaze, C.E.; Ikenberry, L.D. Permeability of solutes through hydrated polymer membranes. Part I. Diffusion of sodium chloride. Die Makromol. Chem. 1968, 118, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go¨pferich, A.; Langer, R. Modeling monomer release from bioerodible polymers. J. Control. Release 1995, 33, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, R.; Peppas, N. Chemical and Physical Structure of Polymers as Carriers for Controlled Release of Bioactive Agents: A Review. J. Macromol. Sci. Part C 1983, 23, 61–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release II. Fickian and anomalous release from swellable devices. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeman, A.E.; Li, B.; Yoshii, T.; Zienkiewicz, K.; Davidson, J.M.; Guelcher, S.A. Injectable Biodegradable Polyurethane Scaffolds with Release of Platelet-derived Growth Factor for Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2387–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeman, A.E.; Zienkiewicz, K.J.; Carney, E.; Litzner, B.; Stratton, C.; Wenke, J.C.; Guelcher, S.A. Local Delivery of Tobramycin from Injectable Biodegradable Polyurethane Scaffolds. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2010, 21, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hombreiro-Pérez, M.; Siepmann, J.; Zinutti, C.; Lamprecht, A.; Ubrich, N.; Hoffman, M.; Bodmeier, R.; Maincent, P. Non-degradable microparticles containing a hydrophilic and/or a lipophilic drug: Preparation, characterization and drug release modeling. J. Control. Release 2003, 88, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Brabant, L.; Siepmann, F.; De Beer, T.; Bouquet, W.; Van Hoorebeke, L.; Siepmann, J.; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. Sustained release from hot-melt extruded matrices based on ethylene vinyl acetate and polyethylene oxide. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallury, P.; Alimohammadi, N.; Kalachandra, S. Poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) copolymer matrix for delivery of chlorhexidine and acyclovir drugs for use in the oral environment: Effect of drug combination, copolymer composition and coating on the drug release rate. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, T.T.; Hadano, M.; Takahara, A. Controlled Release of Model Drug from Biodegradable Segmented Polyurethane Ureas: Morphological and Structural Features. Macromol. Symp. 2006, 242, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.T.-P.; Langer, R. Polymers for the controlled release of macromolecules: Effect of molecular weight of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1985, 19, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Liang, D.; He, X.; Li, J.; Tan, H.; Li, J.; Fu, Q.; Gu, Q. The degradation and biocompatibility of pH-sensitive biodegradable polyurethanes for intracellular multifunctional antitumor drug delivery. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2734–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, M.; Bahadur, A.; Iqbal, S.; Rahman, M.S.U.; Ahmed, S.; Shabir, G.; Javaid, M.A. Relationship of hard segment concentration in polyurethane-urea elastomers with mechanical, thermal and drug release properties. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 37, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, G.; Van Renterghem, J.; Van Bockstal, P.J.; Kasmi, S.; De Geest, B.G.; De Beer, T.; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. Hydrophilic thermoplastic polyurethanes for the manufacturing of highly dosed oral sustained release matrices via hot melt extrusion and injection molding. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 506, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-E.; Kim, S.-R.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Kim, D.-D. The effect of pore formers on the controlled release of cefadroxil from a polyurethane matrix. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 201, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelli, G.; Francolini, I.; Ruggeri, V.; Guaglianone, E.; D’Ilario, L.; Piozzi, A. Pore formers promoted release of an antifungal drug from functionalized polyurethanes to inhibit Candida colonization. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreenivasan, K. Effect of blending methyl β-cyclodextrin on the release of hydrophobic hydrocortisone into water from polyurethane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 81, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, R.; Folkman, J. Polymers for the sustained release of proteins and other macromolecules. Nature 1976, 263, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindholm, T.; Lindholm, B.-Å.; Niskanen, M.; Koskiniemi, J. Polysorbate 20 as a drug release regulator in ethyl cellulose film coatings. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1986, 38, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodmeier, R.; Paeratakul, O. Theophylline Tablets Coated with Aqueous Latexes Containing Dispersed Pore Formers. J. Pharm. Sci. 1990, 79, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohoff-Hülsmann, M.A.; Schmitz, A.; Lippold, B.C. Aqueous ethyl cellulose dispersions containing plasticizers of different water solubility and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as coating material for diffusion pellets: I. Drug release rates from coated pellets. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 177, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, D.; Watts, A.B.; Coots, L.B.; Zheng, W.C.; McGinity, J.W. Influence of polymeric subcoats on the drug release properties of tablets powder-coated with pre-plasticized Eudragit® L 100-55. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 367, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, M.; Ahmed, A.R.; Kolter, K.; Bodmeier, R.; Dashevskiy, A. Curing mechanism of flexible aqueous polymeric coatings. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 115, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bounds, W.; Szarewski, A.; Lowe, D.; Guillebaud, J. Preliminary report of unexpected local reactions to a progestogen-releasing contraceptive vaginal ring. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 1993, 48, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetsawang, S.; Gao, J.; Krishna, U.; Cuadros, A.; Dhall, G.I.; Wyss, R.; la Puenta, J.R.; Andrade, A.T.L.; Khan, T.; Kononova, E.S.; et al. Microdose intravaginal levonorgestrel contraception: A multicentre clinical trial. Contraception 1990, 41, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow Guthrie, K.; Vargas, S.; Shaw, J.G.; Rosen, R.K.; van den Berg, J.J.; Kiser, P.F.; Buckheit, K.; Bregman, D.; Thompson, L.; Jensen, K.; et al. The Promise of Intravaginal Rings for Prevention: User Perceptions of Biomechanical Properties and Implications for Prevention Product Development. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0145642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, M.M.; Butkyavichene, I.; Gilman, J.; Kennedy, S.; Kopin, E.; Malone, A.M.; Nguyen, C.; Smith, T.J.; Friend, D.R.; Clark, M.R.; et al. An intravaginal ring for the simultaneous delivery of multiple drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 2833–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM International. ASTM D2240-15e1, Standard Test Method for Rubber Property—Durometer Hardness; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. ISO 8009 Mechanical Contraceptives—Reusable Natural and Silicone Rubber Contraceptive Diaphragms—Requirements and Tests; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, J.T.; Clark, M.R.; Shelke, N.B.; Johnson, T.J.; Smith, E.M.; Andreasen, A.K.; Nebeker, J.S.; Fabian, J.; Friend, D.R.; Kiser, P.F. Engineering a Segmented Dual-Reservoir Polyurethane Intravaginal Ring for Simultaneous Prevention of HIV Transmission and Unwanted Pregnancy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crnich, C.J.; Halfmann, J.A.; Crone, W.C.; Maki, D.G. The Effects of Prolonged Ethanol Exposure on the Mechanical Properties of Polyurethane and Silicone Catheters Used for Intravascular Access. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2005, 26, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, L.K. The Effects of Sterilization Methods on Plastics and Elastomers: The Definitive User’s Guide and Databook; William Andrew Pub: Norwich, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 0815515057. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, G.A.; Frontini, P.M.; Cuadrado, T.R. Physical and mechanical behavior of sterilized biomedical segmented polyurethanes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 65, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, A.; Hyvarinen, J.; Poole-Warren, L. The effect of sterilisation on a poly(dimethylsiloxane)/poly(hexamethylene oxide) mixed macrodiol-based polyurethane elastomer. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4484–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorna, K.; Gogolewski, S. The effect of gamma radiation on molecular stability and mechanical properties of biodegradable polyurethanes for medical applications. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 79, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Punshon, G.; Darbyshire, A.; Seifalian, A.M. Effects of sterilization treatments on bulk and surface properties of nanocomposite biomaterials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2013, 101, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Dosage Form Type | Drug Concentration in Polymer | Release Kinetics | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monolithic | Cdrug ≤ Csolubility | Geometry and drug load dependent | [57,58] |
| Cdrug > Csolubility | Geometry and drug load dependent | [59] | |
| Reservoir | Cdrug ≤ Csolubility | First order | [54,55] |
| Cdrug > Csolubility | Zero order | [56] |
| Driver | Approach | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Drug Solubility in Polymer | Polymer selection to increase or reduce drug solubility | [14,17,54,56] |
| Drug Diffusivity Through Polymer | Polymer selection to increase or reduce polymer crystallinity | [68,69,70] |
| Polymer selection to increase or reduce polymer molecular weight | [71,72] | |
| Polymer selection to increase or reduce soft segment to hard segment ratio | [73,74] | |
| Drug Diffusion Through Water-filled Channels | Polymer selection to increase or reduce soft segment to hard segment ratio | [73,74] |
| Incorporation of additional component as pore former | [75,76,77] |
| Formulation | Hardness a (shore A) | Max. Load a (N) | Max. Elongation b (%) | OD1′/OD1 c (%) | OD2′/OD2 c (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | |||||
| Nuvaring™ | 75 ± 4 | 102.4 ± 12.7 | 650.1 ± 11.8 | 92.1 | 107.5 |
| Treatment | |||||
| 25/75 metronidazole/SP-93-100 | 72 ± 3 | 82.8 ± 13.7 | 587.9 ± 117.4 | 94.6 | 104.6 |
| 50/50 metronidazole/SP-93-100 | 91 ± 2 | 68.1 ± 10.2 | 51.7 ± 21.4 | 88.3 | 110.2 |
| Prophylaxis | |||||
| 20/80 Lactic Acid/EG-80A | 51 ± 1 | 49.7 ± 12.4 | 517.0 ± 4.9 | 98.0 | 101.7 |
| 20/80 Lactic Acid/EG-85A | 62 ± 2 | 68.6 ± 22.7 | 389.4 ± 34.3 | 98.2 | 101.3 |
| 20/80 Lactic Acid/EG-93A | 71 ± 2 | 87.7 ± 8.15 | 336.7 ± 24.9 | 96.0 | 103.8 |
| 20/80 Lactic Acid/EG-100A | 80 ± 2 | 98.6 ± 11.6 | 244.6 ± 37.4 | 94.3 | 105.1 |
| 20/80 Lactic Acid/EG-60D | 80 ± 4 | 105.4 ± 13.8 | 173.8 ± 22.2 | 93.7 | 107.2 |
| 20/80 Lactic Acid/EG-72D | 86.3 ± 3 | 129.3 ± 14.1 | 125.7 ± 13.9 | 89.5 | 110.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lowinger, M.B.; Barrett, S.E.; Zhang, F.; Williams, R.O., III. Sustained Release Drug Delivery Applications of Polyurethanes. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020055
Lowinger MB, Barrett SE, Zhang F, Williams RO III. Sustained Release Drug Delivery Applications of Polyurethanes. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(2):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020055
Chicago/Turabian StyleLowinger, Michael B., Stephanie E. Barrett, Feng Zhang, and Robert O. Williams, III. 2018. "Sustained Release Drug Delivery Applications of Polyurethanes" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 2: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020055
APA StyleLowinger, M. B., Barrett, S. E., Zhang, F., & Williams, R. O., III. (2018). Sustained Release Drug Delivery Applications of Polyurethanes. Pharmaceutics, 10(2), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020055