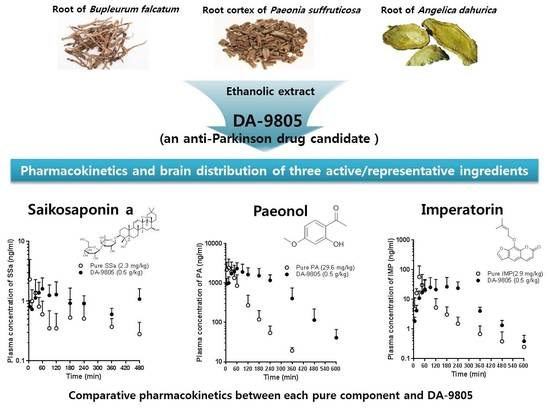
Pharmacokinetics and Brain Distribution of the Active Components of DA-9805, Saikosaponin A, Paeonol and Imperatorin in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Intravenous Drug Administration
2.4. Oral Drug Administration
2.5. Brain Distribution of Saikosaponin A(SSa), Paeonol (PA), and Imperatorin (IMP) Following Multiple Oral Doses of DA-9805
2.6. Measurement of the Protein Binding of SSa, PA, and IMP in Rat Plasma and Brain Homogenates
2.7. LC-MS/MS Analyses of SSa, PA, and IMP
2.8. Pharmacokinetic Analyses
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. PKs of SSa, PA, and IMP after Intravenous Administration of Each Pure Compound
3.2. PKs of SSa after the Oral Administration of Pure SSa and DA-9805
3.3. PKs of PA after the Oral Administration of Pure PA and DA-9805
3.4. PKs of IMP after the Oral Administration of Pure IMP and DA-9805
3.5. Protein Binding of SSa, PA, and IMP in Rat Plasma and Brain-Tissue Homogenates
3.6. Brain and CSF Distribution of SSa, PA, and IMP after the Oral Administration of DA-9805
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ae0–24h | the percentage of the dose excreted in the urine during 24 h |
| AUC | area under the plasma concentration–time curve |
| CL | time-averaged total body clearance |
| CLNR | time-averaged nonrenal clearance |
| CLR | time-averaged renal clearance |
| Cmax | maximum plasma concentration |
| F | the extent of absolute oral bioavailability |
| fu | unbound fraction |
| GI24 h | the percentage of the dose recovered from the gastrointestinal tract at 24 h (including their contents and feces during 24 h) |
| IMP | imperatorin |
| IS | internal standard |
| LC-MS/MS | liquid chromatographic–tandem mass spectrometry |
| LLOQ | lower limit of quantification |
| MRT | mean residence time |
| PA | paeonol |
| PKs | pharmacokinetics |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SSa | saikosaponin a |
| Tmax | time to reach Cmax |
| Vss | apparent volume of distribution at steady state |
References
- Amro, M.S.; Teoh, S.L.; Norzana, A.G.; Srijit, D. The potential role of herbal products in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Ter. 2018, 169, e23–e33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Francardo, V.; Schmitz, Y.; Sulzer, D.; Cenci, M.A. Neuroprotection and neurorestoration as experimental therapeutics for Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 298, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.H.; Kang, S.; Piao, Y.; Pak, C.J.; Oh, M.S.; Kim, J.; Kang, M.S.; Pak, Y.K. Ethanol extract of Bupleurum falcatum and saikosaponins inhibit neuroinflammation via inhibition of NF-κB. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 174, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Oh, T.H.; Yune, T.Y. Ethanol extract of Bupleurum falcatum improves functional recovery by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 activation and inflammation after spinal cord injury. Exp. Neurobiol. 2010, 19, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Shim, I.; Lee, H.; Hahm, D.H. Effect of Bupleurum falcatum on the stress-induced impairment of spatial working memory in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.G.; Park, G.; Piao, Y.; Kang, M.S.; Pak, Y.K.; Hong, S.P.; Oh, M.S. Effects of the root bark of Paeonia suffruticosa on mitochondria-mediated neuroprotection in an MPTP-induced model of Parkinson’s disease. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, M.S.; Pak, Y.K.; Park, K.S.; Oh, T.H.; Yune, T.Y. Inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress by Angelica dahuricae radix extract decreases apoptotic cell death and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 90, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhu, H.Y.; Huang, C.G. A high-performance liquid chromatographic method for saikosaponin a quantification in rat plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.F.; Huang, C.C.; Liu, P.S.; Chen, C.H.; Shiu, L.Y. Saikosaponin a and saikosaponin d inhibit proliferation and migratory activity of rat HSC-T6 cells. J. Med. Food 2013, 16, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Bi, Y.F.; Ding, L.; Zhu, W.W.; Gao, W. Saikosaponin a functions as anti-epileptic effect in pentylenetetrazol induced rats through inhibiting mTOR signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 81, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Miao, G.; Tao, X.; Hao, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Hou, Z.; Tian, R.; Lu, T.; Ma, J.; et al. Saikosaponin a protects TBI rats after controlled cortical impact and the underlying mechanism. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Pan, R. Review on the toxic effects of Radix Bupleuri. Curr. Opin. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014, 1, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Song, R.; Tian, J.X.; Tian, Y.; Liu, G.Q.; Zhang, Z.J. Analysis of saikosaponins in rat plasma by anionic adducts-based liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2012, 26, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, M. LC tissue distribution study of paeonol in rats after oral administration. Chromatographia 2011, 73, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Bao, J.X.; Xu, J.W.; Murad, F.; Bian, K. Vascular dilation by paeonol—A mechanism study. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2010, 53, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Shin, Y.W.; Bae, E.A.; Han, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, D.H. Antiallergic effect of the root of Paeonia lactiflora and its constituents paeoniflorin and paeonol. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2008, 31, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Fong, Y.C.; Wu, J.B.; Chen, Y.F.; Tsuzuki, M.; Tang, C.H. Paeonol inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting ERK, p38 and NF-kappaB pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 588, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.L.; Cheng, C.Y.; Tsai, T.H.; Lin, I.H.; Liu, C.H.; Chiang, S.Y.; Lin, J.G.; Lao, C.J.; Tang, N.Y. Paeonol reduced cerebral infarction involving the superoxide anion and microglia activation in ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 106, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.B.; Song, N.N.; Wei, X.B.; Guan, H.S.; Zhang, X.M. Protective effects of paeonol on cultured rat hippocampal neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 264, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.Z.; Ge, Q.H.; Qu, R.; Li, Q.; Ma, S.P. Paeonol attenuates neurotoxicity and ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by D-galactose in ICR mice. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 277, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.H.; Chou, C.J.; Chen, C.F. Pharmacokinetics of paeonol after intravenous administration in rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 1994, 83, 1307–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wong, Y.F.; Xu, H.X.; Jiang, Z.H.; Liu, L. Study on the pharmacokinetics and metabolism of paeonol in rats treated with pure paeonol and an herbal preparation containing paeonol by using HPLC-DAD-MS method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 46, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Jiang, Z.H.; Zhou, H.; Ma, W.Z.; Wong, Y.F.; Liu, Z.Q.; Liu, L. The pharmacokinetic study of sinomenine, paeoniflorin and paeonol in rats after oral administration of a herbal product Qingfu Guanjiesu capsule by HPLC. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 28, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Sheng, Y.X.; Zhang, J.L. LC-MS determination and pharmacokinetic studies of paeonol in rat plasma after administration of different compatibility of Su-Xiao-Xin-Tong prescriptions. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2008, 22, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, M.J.; de las Heras, B.; Silvan, A.M.; Pascual, R.; Bermejo, P.; Rodriquez, B.; Villar, A.M. Effects of furocoumarins from Cachrys trifida on some macrophage functions. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, H.S.; Lim, S.S.; Suzuki, K.; Jung, S.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.S.; Shin, K.H.; Ohuchi, K. Inhibitory effects of furanocoumarins isolated from the roots of Angelica dahurica on prostaglandin E2 production. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wu, L.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. The protective activity of imperatorin in cultured neural cells exposed to hypoxia re-oxygenation injury via anti-apoptosis. Fitoterapia 2013, 90, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budzynska, B.; Boguszewska-Czubara, A.; Kruk-Slomka, M.; Skalicka-Wozniak, K.; Michalak, A.; Musik, I.; Biala, G.; Glowniak, K. Effects of imperatorin on nicotine-induced anxiety- and memory-related responses and oxidative stress in mice. Physiol. Behav. 2013, 122, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luszczki, J.J.; Glowniak, K.; Czuczwar, S.J. Time-course and dose-response relationships of imperatorin in the mouse maximal electroshock seizure threshold model. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 59, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Peng, C.; Du, W.; Wang, S. Simultaneous determination of imperatorin and its metabolites in vitro and in vivo by a GC-MS method: Application to a bioavailability and protein binding ability study in rat plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 28, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Fu, S.; Li, T.; Wang, S.; Zhao, M.; Ding, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q. Simultaneous determination of imperatorin and its metabolite xanthotoxol in rat plasma by using HPLC-ESI-MS coupled with hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 945–946, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Cao, W.; Yang, Q.; Miao, S.; Wang, S. Brain distribution study of imperatorin in rats after oral administration assessed by HPLC. Chromatographia 2011, 74, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lili, W.; Yehong, S.; Qi, Y.; Yan, H.; Jinhui, Z.; Yan, L.; Cheng, G. In vitro permeability analysis, pharmacokinetic and brain distribution study in mice of imperatorin, isoimperatorin and cnidilin in Radix Angelicae dahuricae. Fitoterapia 2013, 85, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tai, W.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, C. Challenges and solutions of pharmacokinetics for efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine. Curr. Drug Metab. 2015, 16, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; Yoon, J.N.; Jung, J.W.; Choi, H.D.; Shin, Y.J.; Han, C.K.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, H.E. Pharmacokinetics of hederacoside C, an active ingredient in AG NPP709, in rats. Xenobiotica 2013, 43, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.H.; Jeong, J.S.; Ryu, J.; Cho, Y.W.; Kang, H.E. Simultaneous determination of saikosaponin a, paeonol, and imperatorin, components of DA-9805, in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS and application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1068–1069, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, W.L. Critical Evaluation of the potential error in pharmacokinetic studies of using the linear trapezoidal rule method for the calculation of the area under the plasma level–time curve. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1978, 6, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibaldi, M.; Perrier, D. Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed.; Marcel-Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1982; ISBN 9780824710422. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, B.; Morris, T. Physiological parameters in laboratory animals and humans. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Amagaya, S.; Ogihara, Y. Structural transformation of saikosaponins by gastric juice and intestinal flora. J. Pharmacobiodyn. 1985, 8, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kida, H.; Akao, T.; Meselhy, M.R.; Hattori, M. Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of orally administered saikosaponin b1 in conventional, germ-free and Eubacterium Sp. A-44-infected gnotobiote rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 21, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Zhong, Y.H.; Yuan, M.; Li, H.; Zhao, C.J. Inhibitory Effect of imperatorin and isoimperatorin on activity of cytochrome p450 enzyme in human and rat liver microsomes. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2013, 38, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.X.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.Q.; Li, W.; Yang, L. CYP1A2 is the major isoform responsible for paeonol O-demethylation in human liver microsomes. Xenobiotica 2009, 39, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Tian, Y.; Li, G.; Xu, L.; Song, R.; Zhang, Z. Metabolism of saikosaponin a in rats: Diverse oxidations on the aglycone moiety in liver and intestine in addition to hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2013, 41, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Chou, M.H.; Lin, M.F.; Yang, L.L. Effects of Paeoniae Radix, a traditional Chinese medicine, on the pharmacokinetics of phenytoin. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2001, 26, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Ueda, C.; Aoki, S.; Tajima, K.; Tanaka, N.; Yamahara, J. Anticholinergic action of paeony root and its active constituents. Yakugaku Zasshi 1990, 110, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, B.S.; Shin, M.K. Korean Domestic Pharmaceutical Pharmacopoeia (Herbal Medicine); Yeongnimsa: Seoul, Korea, 2003; pp. 412–414. ISBN 9788985897044. [Google Scholar]







| Parameters | SSa | PA | IMP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.3 mg/kg (n = 5) | 4.6 mg/kg (n = 4) | 14.8 mg/kg (n = 5) | 29.6 mg/kg (n = 5) | 59.2 mg/kg (n = 6) | 2.9 mg/kg (n = 5) | 5.8 mg/kg (n = 6) | 11.5 mg/kg (n = 5) | |
| Body weight (g) | 290 ± 7.91 | 288 ± 8.66 | 262 ± 7.58 | 263 ± 12.5 | 258 ± 7.58 | 274 ± 10.7 | 280 ± 10.5 | 289 ± 11.9 |
| AUC0–inf (μg∙min/mL) a | 517 ± 64.3 | 1840 ± 349 b | 511 ± 65.3 | 1250 ± 250 | 2820 ± 400 f | 55.9 ± 12.4 | 126 ± 23.9 | 496 ± 66.5 h |
| CL (mL/min/kg) | 4.51 ± 0.583 | 2.56 ± 0.418 c | 29.3 ± 3.60 | 24.4 ± 4.03 | 21.4 ± 3.29 g | 53.9 ± 11.9 | 47.5 ± 9.85 | 23.5 ± 3.07 i |
| CLR (μL/min/kg) | 321 ± 177 | 60.2 ± 34.2 d | 587 ± 535 | 232 ± 110 | 556 ± 382 | 39.4 ± 9.33 | 42.5 ± 27.7 | 13.8 ± 4.35 |
| CLNR (mL/min/kg) | 4.19 ± 0.492 | 2.50 ± 0.387 c | 28.7 ± 3.75 | 24.2 ± 3.98 | 20.8 ± 3.16 g | 53.9 ± 11.9 | 47.5 ± 9.87 | 23.5 ± 3.07 i |
| Vss (mL/kg) | 126 ± 11.1 | 102 ± 8.16 e | 1130 ± 290 | 1290 ± 327 | 1100 ± 429 | 1760 ± 595 | 1600 ± 333 | 1470 ± 254 |
| MRT (min) | 28.2 ± 4.33 | 40.3 ± 4.73 e | 38.5 ± 8.43 | 53.5 ± 14.0 | 51.4 ± 18.9 | 32.1 ± 5.46 | 39.4 ± 15.2 | 63.1 ± 12.1 i |
| Terminal half-life (min) | 93.9 ± 18.7 | 91.5 ± 16.0 | 81.5 ± 17.4 | 157 ± 53.7 | 214 ± 111 | 77.8 ± 5.58 | 75.1 ± 18.2 | 77.7 ± 36.0 |
| Ae0–24h (% of dose) | 6.94 ± 3.67 | 2.22 ± 1.16 d | 2.06 ± 1.87 | 0.941 ± 0.362 | 2.55 ± 1.78 | 0.0750 ± 0.0191 | 0.0986 ± 0.0785 | 0.0605 ± 0.0223 |
| GI24h (% of dose) | 0.701 ± 1.17 | 0.481 ± 0.219 | 0.182 ± 0.124 | 0.186 ± 0.223 | 0.153 ± 0.165 | 0.0105 ± 0.00709 | 0.0103 ±0.00265 | 0.0153 ± 0.0106 |
| Parameters | Oral Doses | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 mg/kg as SSa | 2.3 mg/kg as SSa | 4.6 mg/kg as SSa | |||
| DA-9805 0.25 g/kg (n = 5) | Pure SSa 2.3 mg/kg (n = 4) | DA-9805 0.5 g/kg (n = 5) | Pure SSa 4.6 mg/kg (n = 5) | DA-9805 1 g/kg (n = 5) | |
| Body weight (g) | 257 ± 5.70 | 249 ± 6.29 | 252 ± 6.71 | 204 ± 9.62 | 212 ± 5.70 |
| AUC0–8h (μg∙min/mL) a | 0.285 ± 0.0948 | 0.206 ± 0.129 | 0.404 ± 0.0839 * | 0.460 ± 0.0451 | 1.21 ± 0.586 * |
| AUC0–10h (μg∙min/mL) a | 0.490 ± 0.0521 | 1.49 ± 0.769 * | |||
| Cmax (μg/mL) a | 1.61 ± 0.248 | 3.00 ± 2.22 | 1.91 ± 0.808 | 4.67 ± 0.883 | 6.70 ± 3.46 |
| Tmax (min) b | 45 (15–60) | 17.5 (5–30) | 60 (60–120) | 30 (15–45) | 45 (15–480) |
| GI24h (% of dose) | 2.19 ± 5.47 | 1.99 ± 1.49 | 26.5 ± 6.99 *** | 14.2 ± 12.4 | 44.4 ± 7.17 *** |
| F (%) | 0.0399 | 0.0783 | 0.0251 | 0.0659 | |
| Parameters | Oral Doses | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14.8 mg/kg as PA | 29.6 mg/kg as PA | 59.2 mg/kg as PA | ||||
| Pure PA 14.8 mg/kg (n = 4) | DA-9805 0.25 g/kg (n = 5) | Pure PA 29.6 mg/kg (n = 5) | DA-9805 0.5 g/kg (n = 5) | Pure PA 59.2 mg/kg (n = 4) | DA-9805 1 g/kg (n = 5) | |
| Body weight (g) | 251 ± 12.5 | 257 ± 5.70 | 247 ± 6.71 | 252 ± 6.71 | 204 ± 7.50 | 212 ± 5.70 |
| AUC0–inf (μg∙min/mL) a | 82.4 ± 11.5 | 147 ± 129 | 153 ± 101 | 404 ± 83.9 * | 462 ± 142 | 1180 ± 341 ** |
| Terminal half-life (min) | 79.1 ± 51.7 | 98.8 ± 56.1 | 70.5 ± 29.7 | 66.8 ± 15.6 | 50.5 ± 13.4 | 84.2 ± 55.4 |
| Cmax (μg/mL) a | 2.05 ± 0.956 | 1.05 ± 0.855 | 2.78 ± 1.46 | 2.48 ± 0.853 | 8.20 ± 2.63 | 4.17 ± 1.53 * |
| Tmax (min) b | 15 (15) | 30 (15–120) | 15 (5–30) | 60 (60–180) | 5 (5–15) | 120 (30–120) |
| GI24h (% of dose) | 0.406 ± 0.212 | 0.511 ± 1.01 | 0.0572 ± 0.0426 | 1.24 ± 1.39 | 0.119 ± 0.143 | 0.167 ± 0.128 |
| F (%) | 16.1 | 28.7 | 12.2 | 40.5 | 16.4 | 41.7 |
| Parameters | Oral Doses | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.4 mg/kg as IMP | 2.9 mg/kg as IMP | 5.8 mg/kg as IMP | ||||
| Pure IMP 1.4 mg/kg (n = 6) | DA-9805 0.25 g/kg (n = 5) | Pure IMP 2.9 mg/kg (n = 6) | DA-9805 0.5 g/kg (n = 5) | Pure IMP 5.8 mg/kg (n = 5) | DA-9805 1 g/kg (n = 5) | |
| Body weight (g) | 258 ± 10.8 | 257 ± 5.70 | 253 ± 6.12 | 252 ± 6.71 | 204 ± 11.9 | 212 ± 5.70 |
| AUC0–inf (μg∙min/mL) a | 1.53 ± 0.851 | 3.02 ± 2.38 | 2.95 ± 3.13 | 6.74 ± 5.29 | 36.2 ± 18.1 # | 22.5 ± 12.6 |
| Terminal half-life (min) | 121 ± 38.3 | 120 ± 51.1 | 99.9 ± 31.5 | 73.8 ± 24.7 | 101 ± 29.2 | 56.5 ± 7.26 * |
| Cmax (μg/mL) a | 17.7 ± 6.79 | 28.4 ± 20.8 | 58.6 ± 76.4 | 33.5 ± 25.7 | 568 ± 312 # | 88.2 ± 46.2 ** |
| Tmax (min) b | 22.5 (5–45) | 60 (30–120) | 30 (15–30) | 240 (90–240) | 30 (15–60) | 240 (30–360) |
| GI24h (% of dose) | 0.0285 ± 0.0152 | 2.19 ± 5.47 | 0.153 ± 0.228 | 0.846 ± 0.854 | 1.37 ± 1.09 | 6.30 ± 2.89 |
| F (%) | 5.27 | 12.1 | 28.7 | 17.8 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, M.H.; Jeong, J.S.; Ryu, J.; Cho, Y.W.; Kang, H.E. Pharmacokinetics and Brain Distribution of the Active Components of DA-9805, Saikosaponin A, Paeonol and Imperatorin in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030133
Kwon MH, Jeong JS, Ryu J, Cho YW, Kang HE. Pharmacokinetics and Brain Distribution of the Active Components of DA-9805, Saikosaponin A, Paeonol and Imperatorin in Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(3):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030133
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Mi Hye, Jin Seok Jeong, Jayoung Ryu, Young Woong Cho, and Hee Eun Kang. 2018. "Pharmacokinetics and Brain Distribution of the Active Components of DA-9805, Saikosaponin A, Paeonol and Imperatorin in Rats" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 3: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030133
APA StyleKwon, M. H., Jeong, J. S., Ryu, J., Cho, Y. W., & Kang, H. E. (2018). Pharmacokinetics and Brain Distribution of the Active Components of DA-9805, Saikosaponin A, Paeonol and Imperatorin in Rats. Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030133