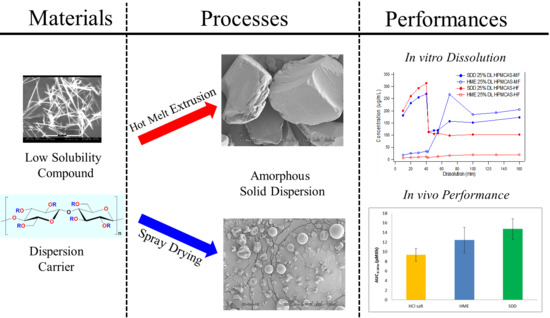
Processing Impact on Performance of Solid Dispersions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Spray Drying Dispersions Preparation
2.2.2. Hot Melt Extrusion Preparation
2.2.3. Formulation Preparation for PK Studies
2.2.4. In Vitro Dissolution
- FaSSIF (fasted state simulated intestinal fluid) was prepared from Phares SIF powder (Croyden, Surrey, UK), following their recommended composition, dissolved in a buffer of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium chloride, and sodium hydroxide, adjusted to pH 6.5.
- SGF (simulated gastric fluid) was prepared from a preparation of 0.034 M sodium chloride adjusted to pH 1.8 with concentrated hydrochloric acid [26].
- For two-stage dissolution, a 2× FaSSIF medium was prepared at twice the concentration of standard FaSSIF [27].
- 1 µm filtration and 80 K spin down were used for the sample preparation.
2.2.5. In Vivo Dog PK Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Need for an Enabled Formulation
3.2. Comparison of In Vitro Dissolution of Spray-Dried and HME Solid Dispersions
3.3. The Impact of Solid Dispersion Properties on In Vitro Dissolution
3.4. Stability of Solid Dispersions
3.4.1. Chemical Stability
3.4.2. Physical Stability
3.5. In Vivo Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basit, A.W.; Podczeck, F.; Newton, M.J.; Waddington, W.A.; Ell, P.J.; Lacey, L.F. The use of formulation technology to assess regional gastrointestinal drug absorption in humans. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 21, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, J.; Alexander, K.; Riga, A. Characterization of polymeric dispersions of dimenhydrinate in ethyl cellulose for controlled release. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 308, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.K.; Wagh, K.S.; Parik, V.B.; Akarte, A.M.; Baviskar, D.T. Strategies for solubility enhancement of poorly soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2011, 8, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Fahr, A.; Liu, X. Drug delivery strategies for poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2007, 4, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesisoglou, F.; Panmai, S.; Wu, Y. Nanosizing—Oral formulation development and biopharmaceutical evaluation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damayanthi, R.D.; Narayanan, N.; Elango, K.; Jayshree, N.; Reddy, P.N.; Sadhwani, N.C. Soft gelatin capsules—A review. Pharm. Rev. 2008, 6, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Benza, H.I.; Munyendo, W.L.L. A review of progress and challenges in soft gelatin capsules formulations for oral administration. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2011, 10, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Sarmento, B.; Costa, P. Solid dispersions as strategy to improve oral bioavailability of poor water soluble drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Baboota, S.; Ali, M.; Kumar, A.; Ali, J. Solid dispersion: An alternative technique for bioavailability enhancement of poorly soluble drugs. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2009, 30, 1458–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Zhu, W.; Kesisoglou, F. Physiologically based absorption modeling for amorphous solid dispersion formulations. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3206–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghel, S.; Cathcart, H.; O’Reilly, N.J. Polymeric amorphous solid dispersions: A review of amorphization, crystallization, stabilization, solid-state characterization, and aqueous solubilization of biopharmaceutical classification system class II drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Marques, S.; Neves, J.; Sarmento, B. Amorphous solid dispersions: Rational selection of a manufacturing process. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noyes, A.A.; Whitney, W.R. The rate of solution of solid substances in their own solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1897, 19, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohri, N.; Yamayoshi, Y.; Xin, H.; Iseki, K.; Sato, N.; Todo, S.; Miyazaki, K. Improving the oral bioavailability of albendazole in rabbits by the solid dispersion technique. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1999, 51, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Kesisoglou, F.; Beauchamp, M.; Zhu, W.; Chiti, F.; Wu, Y. Using absorption simulation and gastric pH modulated dog model for formulation development to overcome achlorhydria effect. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 2216–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Chatterji, A.; Sandhu, H.; Choi, D.S.; Chokshi, H.; Shah, N. Evaluation of solid state properties of solid dispersions prepared by hot-melt extrusion and solvent co-precipitation. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 355, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usui, F.; Maeda, K.; Kusai, A.; Nishimura, K.; Yamamoto, K. Inhibitory effects of water-soluble polymers on precipitation of RS-8359. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 154, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshman, J.; Cao, Y.; Kowalski, J.; Serajuddin, A.T. Application of melt extrusion in the development of a physically and chemically stable high-energy amorphous solid dispersion of a poorly water-soluble drug. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, J.; Broyles, J.; Liu, L. Enhancing bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs using spray dried solid dispersions Part I. Am. Pharm. Rev. 2008, 11, 70–71. [Google Scholar]
- Emas, M.; Nyqvist, H. Methods of studying aging and stabilization of spray-congealed solid dispersions with carnauba wax. 1. Microcalorimetric investigation. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 197, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wen, M.; Li, W. Preparation and characterization of baicalin-poly-vinylpyrrolidone coprecipitate. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 408, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesen, D.T.; Shanker, R.; Crew, M.; Smithey, D.T.; Curatolo, W.J.; Nightingale, J.A.S. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate-based spray-dried dispersions: An overview. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 1003–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masters, K. Spray Drying in Practice; SprayDryConsult: Charlottenlund, Denmark, 2002; ISBN 8798660683. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmah, O.; Tabbakh, R.; Kelly, A.; Paradkar, A. A comparative study of the effect of spray drying and hot-melt extrusion on the properties of amorphous solid dispersions containing felodipine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 66, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormes, J.D.; Zhang, D.; Chen, A.M.; Hou, S.; Krueger, D.; Nelson, T.; Templeton, A. Design of experiments utilization to map the processing capabilities of a micro-spray dryer: Particle design and throughput optimization in support of drug discovery. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagat, N.B.; Yadav, A.V.; Mali, S.S.; Khutale, R.A.; Hajare, A.A.; Salunkhe, S.S.; Nadaf, S.J. A review on development of biorelevant dissolution medium. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2014, 4, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertzoni, M.; Fotaki, N.; Kostewicz, E.; Stippler, E.; Leuner, C.; Nicolaides, E.; Dressman, J.; Reppas, C. Dissolution media simulating the intraluminal composition of the small intestine: Physiological issues and practical aspects. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawy, S.I.F.; Gray, D.B.; Zhao, F.; Sun, D.; Schuster, A.E.; Hussain, M.A. Formulation of solid dosage forms to overcome gastric pH interaction of the factor Xa inhibitor, BMS-561389. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, P.; Galipeau, K.; Xu, W.; Brown, C.; Wuelfing, P.W. Mechanism of dissolution-induced nanoparticle formation from a copovidone-based amorphous solid dispersion. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 1467–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Chemical Structure |  | |
| Drug Form | HCl Salt Anhydrous Crystalline Form | Free Base Hydrate Crystalline Form |
| Melting Point (°C) | 249 | 133 |
| pKa | 5.9 and 2.2 | |
| Log P (free base) | 4.5 | |
| BCS Classification | II | |
| Solubility (µg/mL) | H2O: 661 (pH = 3.5) Simulated Gastric Fluid (SGF): 525 Fasted Simulated Small Intestine Fluid (FaSSIF): 21 | H2O: 0.3 (pH = 7.3) Simulated Gastric Fluid (SGF): 907 Fasted Simulated Small Intestine Fluid (FaSSIF): 2 |
| Stability | Chemically stable in the solid-state; Physically stable at various temperatures and humidity conditions but sensitive to mechanical stress | Chemically and physically stable |
| Period | Group A (n = 3) | Group B (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | HME capsules | SDD capsules |
| 2 | Solution | HME capsules |
| 3 | SDD suspension | SDD suspension |
| Solid Dispersions | Morphology (SEM) | Particle Size (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| Spray dried |  | 7 |
| Fitz-milled HME |  | 213 |
| Ball-milled HME |  | 59 |
| Cryo-milled HME |  | 16 |
| Polymer | Condition | Initial (% Area) | 2 Weeks at 40 °C/75% RH Closed (% Area) | 2 Weeks at 40 °C/75% RH Closed Physical Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MK-A (FB) | - | 98.8 | 98.8 | - |
| SDD HPMCAS-HF | 25% DL | 96.7 | 90.3 | Amorphous |
| SDD HPMCAS-HF | 40% DL | 96.8 | 89.8 | Amorphous |
| SDD HPMCAS-MF | 25% DL | 97.1 | 91.8 | Amorphous |
| SDD VA64 | 40% DL | 96.9 | 89.3 | Amorphous/Phase separation |
| SDD HPMCAS-LF | 25% DL under N2 | 98.8 | 95.4 | Amorphous |
| * SDD HPMCAS-LF | 25% DL under N2 antioxidants | 98.9 | 98.2 | Amorphous |
| HME HPMCAS-HF | 25% DL, 140 °C | 95.1 | 86.6 | Amorphous |
| HME HPMCAS-MF | 25% DL, 136 °C | 94.2 | 86.0 | Amorphous |
| Formulation | Dose (mpk) | AUC0–24 h (µM × h) | Cmax (µM) | Tmax (h) | AUC Ratio (Versus DFC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HME capsules (n = 6) | 15 | 12.4 ± 2.65 | 2.22 ± 0.42 | 2.0 (2.0–4.0) * | 1.33 |
| SDD capsules (n = 3) | 15 | 7.59 ± 1.44 | 1.19 ± 0.00 | 4.0 (4.0–4.0) * | 0.81 |
| SDD suspension (n = 6) | 15 | 14.7 ± 2.13 | 2.62 ± 0.19 | 2.0 (2.0–4.0) * | 1.58 |
| Solution (n = 3) | 15 | 22.4 ± 3.41 | 3.73 ± 0.38 | 2.0 (2.0–2.0) * | 2.40 |
| DFC (Benchmark, n = 6) | 15 | 9.35 ± 1.34 | 1.82 ± 0.34 | 2.0 (1.0–2.0) * | 1.00 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.; Lee, Y.-C.; Shabani, Z.; Frankenfeld Lamm, C.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Templeton, A. Processing Impact on Performance of Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030142
Zhang D, Lee Y-C, Shabani Z, Frankenfeld Lamm C, Zhu W, Li Y, Templeton A. Processing Impact on Performance of Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(3):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030142
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Dan, Yung-Chi Lee, Zaher Shabani, Celeste Frankenfeld Lamm, Wei Zhu, Yongjun Li, and Allen Templeton. 2018. "Processing Impact on Performance of Solid Dispersions" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 3: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030142
APA StyleZhang, D., Lee, Y. -C., Shabani, Z., Frankenfeld Lamm, C., Zhu, W., Li, Y., & Templeton, A. (2018). Processing Impact on Performance of Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030142