Raloxifene/SBE-β-CD Inclusion Complexes Formulated into Nanoparticles with Chitosan to Overcome the Absorption Barrier for Bioavailability Enhancement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Phase Solubility Study
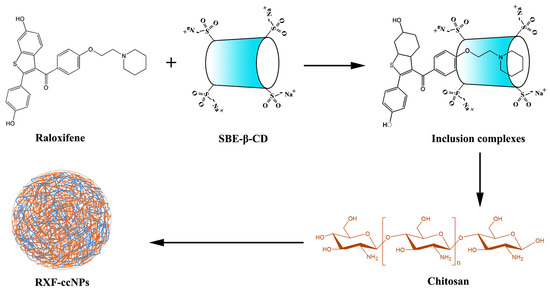
2.3. Preparation of Raloxifene -Loaded Cyclodextrin/Chitosan Nanoparticles (RXF-ccNPs)
2.4. Characterization of RXF-ccNPs
2.5. Quantification for Raloxifene (RXF)
2.6. In Vitro Release Study
2.7. Bioavailability Study
2.8. In Situ Single-Pass Intestinal Perfusion
2.9. Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity
2.10. Ex Vivo Imaging of Transepithelial Transport
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solubility Diagram of Raloxifene (RXF) vs. Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin (SBE-β-CD)
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of RXF-ccNPs
3.3. In Vitro Release of RXF-ccNPs
3.4. Enhanced Oral Bioavailability
3.5. Improved Intestinal Permeability
3.6. Excellent Cellular Uptake and Biocompatibility
3.7. Good Transepithelial Capacity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gizzo, S.; Saccardi, C.; Patrelli, T.S.; Berretta, R.; Capobianco, G.; Di Gangi, S.; Vacilotto, A.; Bertocco, A.; Noventa, M.; Ancona, E.; et al. Update on raloxifene: Mechanism of action, clinical efficacy, adverse effects, and contraindications. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2013, 68, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, S.; Hamaya, E.; Sato, M.; Graham-Clarke, P.; Flynn, J.A.; Burge, R. Systematic review of raloxifene in postmenopausal Japanese women with osteoporosis or low bone mass (osteopenia). Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 1879–1893. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Snyder, K.R.; Sparano, N.; Malinowski, J.M. Raloxifene hydrochloride. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2000, 57, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Varshosaz, J.; Minaiyan, M.; Dayyani, L. Poly(methyl vinyl ether-co-maleic acid) for enhancement of solubility, oral bioavailability and anti-osteoporotic effects of raloxifene hydrochloride. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 112, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikiaris, D.; Karavelidis, V.; Karavas, E. Effectiveness of various drug carriers in controlled release formulations of raloxifene HCl prepared by melt mixing. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, P.R.; Aditya, N.; Kathuria, H.; Malekar, S.; Vats, R. Lipid nanoparticles for oral delivery of raloxifene: Optimization, stability, in vivo evaluation and uptake mechanism. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsheikh, M.A.; Elnaggar, Y.S.; Gohar, E.Y.; Abdallah, O.Y. Nanoemulsion liquid preconcentrates for raloxifene hydrochloride: Optimization and in vivo appraisal. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3787–3802. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, W.; Sun, H.; Lu, D.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X. Glucose-based mesoporous carbon nanospheres as functional carriers for oral delivery of amphiphobic raloxifene: Insights into the bioavailability enhancement and lymphatic transport. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Kaur, R.; Beg, S.; Kushwah, V.; Jain, S.; Singh, B. Novel cationic supersaturable nanomicellar systems of raloxifene hydrochloride with enhanced biopharmaceutical attributes. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 670–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aditya, N.; Ravi, P.R.; Avula, U.S.; Vats, R. Poly (epsilon-caprolactone) nanocapsules for oral delivery of raloxifene: Process optimization by hybrid design approach, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Microencapsul. 2014, 31, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burra, M.; Jukanti, R.; Janga, K.Y.; Sunkavalli, S.; Velpula, A.; Ampati, S.; Jayaveera, K.N. Enhanced intestinal absorption and bioavailability of raloxifene hydrochloride via lyophilized solid lipid nanoparticles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansook, P.; Ogawa, N.; Loftsson, T. Cyclodextrins: Structure, physicochemical properties and pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmer, H.J.; Hamman, J.H. Paracellular drug absorption enhancement through tight junction modulation. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, T.; Connors, K.A. Phase solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 1965, 4, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, X. Enhanced bioavailability of raloxifene hydrochloride via dry suspensions prepared from drug/HP-beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Pharmazie 2015, 70, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Deng, W.; Yuan, X.; Wang, H.; Ma, Z.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X. Selenium-functionalized liposomes for systemic delivery of doxorubicin with enhanced pharmacokinetics and anticancer effect. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 122, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, T.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, B. Enhanced bioavailability of tripterine through lipid nanoparticles using broccoli-derived lipids as a carrier material. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.H.; Poudel, B.K.; Marasini, N.; Chi, S.C.; Choi, H.G.; Yong, C.S.; Kim, J.O. Preparation and evaluation of raloxifene-loaded solid dispersion nanoparticle by spray-drying technique without an organic solvent. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 443, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jiang, F.; Chi, Z.; Han, D.; Yu, L.; Liu, C. Development of Enteromorpha prolifera polysaccharide-based nanoparticles for delivery of curcumin to cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Yang, Y.; Ju, X.; Udenigwe, C.C.; He, R. Polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles from chitosan and acylated rapeseed cruciferin protein for curcumin delivery. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2685–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.M.; Calado, R.; Marto, J.; Bettencourt, A.; Almeida, A.J.; Goncalves, L.M.D. Chitosan nanoparticles as a mucoadhesive drug delivery system for ocular administration. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, R.E.; Gray, V.; Dorantes, A.; Gold, L.; Pham, L. Scientific and regulatory standards for assessing product performance using the similarity factor, f2. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Cao, W.; Sun, Y.; He, Z. Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation of formulation of repaglinide with hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Lan, Y.; Wu, B.; Shi, Z. Nanosuspensions containing oridonin/HP-beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes for oral bioavailability enhancement via improved dissolution and permeability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakeri-Milani, P.; Valizadeh, H.; Tajerzadeh, H.; Azarmi, Y.; Islambolchilar, Z.; Barzegar, S.; Barzegar-Jalali, M. Predicting human intestinal permeability using single-pass intestinal perfusion in rat. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 10, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schulz, J.D.; Gauthier, M.A.; Leroux, J.C. Improving oral drug bioavailability with polycations? Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 97, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trdan Lusin, T.; Mrhar, A.; Stieger, B.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Marc, J.; Ostanek, B.; Zavratnik, A.; Kristl, A.; Berginc, K.; Delic, K.; et al. Influence of hepatic and intestinal efflux transporters and their genetic variants on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of raloxifene in osteoporosis treatment. Transl. Res. 2012, 160, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Xia, D.; Yu, H.; Chen, D.; Fan, W.; Gan, Y. Lipid-based formulations for oral drug delivery: Effects on drug absorption and metabolism. Curr. Drug Metab. 2015, 16, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.S.; Cho, C.W. Surface modification of solid lipid nanoparticles for oral delivery of curcumin: Improvement of bioavailability through enhanced cellular uptake, and lymphatic uptake. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Parameter | RXF Suspensions | RXF-SICs Solution | RXF-ccNPs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 108.46 ± 12.62 | 227.78 ± 23.17 ** | 367.48 ± 26.22 ** |
| Tmax (h) | 4.13 ± 0.54 | 3.55 ± 0.46 | 3.87 ± 0.51 |
| T1/2 (h) | 5.66 ± 0.78 | 3.58 ± 0.39 * | 4.45 ± 0.43 * |
| AUC0-t (ng/mL·h) | 665.47 ± 39.62 | 1659.56 ± 74.02 ** | 2400.78 ± 83.26 ** |
| Relative BA (%) | / | 249.38 | 360.76 |
| Intestinal Segment | Peff (cm/s) | |
|---|---|---|
| Free RXF | RXF-ccNPs | |
| Duodenum | 2.051 ± 0.163 × 10−6 | 6.325 ± 0.472 × 10−5 ** |
| Jejunum | 4.469 ± 0.278 × 10−6 | 8.224 ± 0.396 × 10−5 ** |
| Ileum | 1.236 ± 0.107 × 10−5 | 2.005 ± 0.514 × 10−4 ** |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Raloxifene/SBE-β-CD Inclusion Complexes Formulated into Nanoparticles with Chitosan to Overcome the Absorption Barrier for Bioavailability Enhancement. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030076
Wang Z, Li Y. Raloxifene/SBE-β-CD Inclusion Complexes Formulated into Nanoparticles with Chitosan to Overcome the Absorption Barrier for Bioavailability Enhancement. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(3):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030076
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zaihua, and Yan Li. 2018. "Raloxifene/SBE-β-CD Inclusion Complexes Formulated into Nanoparticles with Chitosan to Overcome the Absorption Barrier for Bioavailability Enhancement" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 3: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030076
APA StyleWang, Z., & Li, Y. (2018). Raloxifene/SBE-β-CD Inclusion Complexes Formulated into Nanoparticles with Chitosan to Overcome the Absorption Barrier for Bioavailability Enhancement. Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030076