Effect of Lipid Additives and Drug on the Rheological Properties of Molten Paraffin Wax, Degree of Surface Drug Coating, and Drug Release in Spray-Congealed Microparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Melts for Rheological Tests and Spray Congealing
2.3. Preparation of Samples for Fourier Transform-Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.4. Rheological Tests
2.4.1. Continuous Ramping Tests
2.4.2. Temperature Ramping Tests
2.5. FTIR Spectroscopy
2.6. Rheological Tests with Drug
2.7. Thermal Analysis
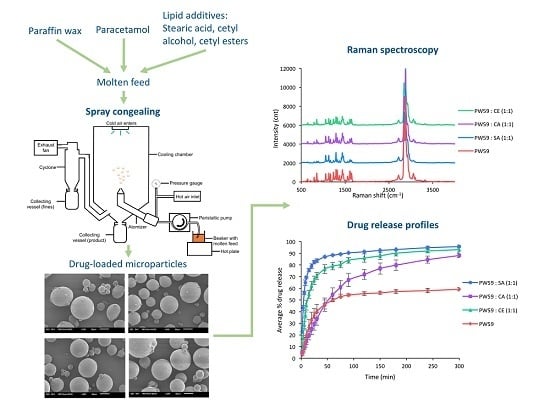
2.8. Production of Spray-Congealed Microparticles
2.9. Determination of Useful Yield and Total Yield of Spray-Congealed Microparticles
2.10. Surface Examination of Spray-Congealed Microparticles
2.11. Determination of Drug Content
2.12. Particle Size Analysis of Spray-Congealed Microparticles
2.13. Examination of Surface Solid-State Properties
2.14. Drug Release Study
2.15. Statistical Analyses of Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheological Tests
3.2. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.3. Conformations of Molecules under Shear
3.4. Modeling the Viscosity of Blends
3.5. Rheological Tests with Drug
3.6. Thermal Analysis
3.7. Total and Useful Yields of Spray-Congealed Microparticles
3.8. Surface Characteristics of Spray-Congealed Microparticles
3.9. Drug Content
3.10. Particle Size Characteristics
3.11. Surface Solid-State Properties
3.12. Drug Release Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albertini, B.; Passerini, N.; Pattarino, F.; Rodriguez, L. New spray congealing atomizer for the microencapsulation of highly concentrated solid and liquid substances. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passerini, N.; Albertini, B.; Perissutti, B.; Rodriguez, L. Evaluation of melt granulation and ultrasonic spray congealing as techniques to enhance the dissolution of praziquantel. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 318, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emås, M.; Nyqvist, H. Methods of studying aging and stabilization of spray-congealed solid dispersions with carnauba wax. 1. Microcalorimetric investigation. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 197, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanig, J.L. Properties of fused mannitol in compressed tablets. J. Pharm. Sci. 1964, 53, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felder, C.B.; Blanco-Príeto, M.J.; Heizmann, J.; Merkle, H.P.; Gander, B. Ultrasonic atomization and subsequent polymer desolvation for peptide and protein microencapsulation into biodegradable polyesters. J. Microencapsul. 2003, 20, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ilić, I.; Dreu, R.; Burjak, M.; Homar, M.; Kerč, J.; Srčič, S. Microparticle size control and glimepiride microencapsulation using spray congealing technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 381, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passerini, N.; Perissutti, B.; Albertini, B.; Franceschinis, E.; Lenaz, D.; Hasa, D.; Locatelli, I.; Voinovich, D. A new approach to enhance oral bioavailability of Silybum Marianum dry extract: Association of mechanochemical activation and spray congealing. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reithmeier, H.; Herrmann, J.; Göpferich, A. Development and characterization of lipid microparticles as a drug carrier for somatostatin. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 218, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N.; Cavallari, C.; Giovannelli, L. Hot air coating technique as a novel method to produce microparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2004, 30, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sabatino, M.; Albertini, B.; Kett, V.L.; Passerini, N. Spray congealed lipid microparticles with high protein loading: Preparation and solid state characterisation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 46, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarron, P.A.; Donnelly, R.F.; Al-Kassas, R. Comparison of a novel spray congealing procedure with emulsion-based methods for the micro-encapsulation of water-soluble drugs in low melting point triglycerides. J. Microencapsul. 2008, 25, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, R.M.; Siqueira, S.; Machado, M.O.; Freitas, L.A.P. The effect of homogenization method on the properties of carbamazepine microparticles prepared by spray congealing. J. Microencapsul. 2013, 30, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deasy, P.B. General Introduction to Microencapsulation and Related Drug Processes; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1984; Volume 20, ISBN 9780824771621. [Google Scholar]
- Tobío, M.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Guo, Y.; McIver, J.; Langer, R.; Alonso, M.J. Improved immunogenicity of a core-coated tetanus toxoid delivery system. Vaccine 1999, 18, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebre-Sellassie, I. Pellets: A General Overview; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1989; Volume 37. [Google Scholar]
- Thies, C. A Survey of Microencapsulation Processes; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 73. [Google Scholar]
- Maschke, A.; Becker, C.; Eyrich, D.; Kiermaier, J.; Blunk, T.; Göpferich, A. Development of a spray congealing process for the preparation of insulin-loaded lipid microparticles and characterization thereof. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 65, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, K.; Iwami, K.; Ibuki, F.; Kawabata, M. Oxidative stability of sardine oil embedded in spray-dried egg white powder and its use for n-3 unsaturated fatty acid fortification of cookies. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1992, 56, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-C.; Lin, S.-Y.; Hwang, L.S. Microencapsulation of squid oil with hydrophilic macromolecules for oxidative and thermal stabilization. J. Food Sci. 1995, 60, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanasundara, U.N.; Shahidi, F. Storage stability of microencapsulated seal blubber oil. J. Food Lipids 1995, 2, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.R.; Trehan, A. Biodegradable microspheres for protein delivery. J. Control. Release 2003, 90, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, Y.; Yoshioka, M.; Horibe, H.; Hirai, S.; Kitamori, N.; Toguchi, H. Novel oral controlled-release microspheres using polyglycerol esters of fatty acids. J. Control. Release 1993, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Tanigake, A.; Miyanaga, Y.; Matsuyama, K.; Kunitomo, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ikezaki, H.; Taniguchi, A. Evaluation of the bitterness of antibiotics using a taste sensor. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Deutsch, D.; Craig, D.Q.M. An investigation into the interaction between taste masking fatty acid microspheres and alkaline buffer using thermal and spectroscopic analysis. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajima, T.; Nogata, A.; Demachi, M.; Umeki, N.; Itai, S.; Yunoki, N.; Nemoto, M. Particle design for taste-masking using a spray-congealing technique. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1996, 44, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, T.; Umeki, N.; Itai, S. Optimum spray congealing conditions for masking the bitter taste of clarithromycin in wax matrix. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajima, T.; Fukushima, Y.; Itai, S.; Kawashima, Y. Method of evaluation of the bitterness of clarithromycin dry syrup. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajima, T.; Itai, S.; Takeuchi, H.; Kawashima, Y. Optimum heat treatment conditions for masking the bitterness of the clarithromycin wax matrix. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 1223–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quadir, M.A.; Rahman, M.S.; Karim, M.Z.; Akter, S.; Awkat, M.T.B.; Reza, M.S. Evaluation of hydrophobic materials as matrices for controlled-release drug delivery. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 16, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Savolainen, M.; Herder, J.; Khoo, C.; Lövqvist, K.; Dahlqvist, C.; Glad, H.; Juppo, A.M. Evaluation of polar lipid–hydrophilic polymer microparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 262, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savolainen, M.; Khoo, C.; Glad, H.; Dahlqvist, C.; Juppo, A.M. Evaluation of controlled-release polar lipid microparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 244, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspart, S.; Piel, G.; Delattre, L.; Evrard, B. Solid lipid microparticles: Formulation, preparation, characterisation, drug release and applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passerini, N.; Perissutti, B.; Moneghini, M.; Voinovich, D.; Albertini, B.; Cavallari, C.; Rodriguez, L. Characterization of carbamazepine-gelucire 50/13 microparticles prepared by a spray-congealing process using ultrasounds. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passerini, N.; Perissutti, B.; Albertini, B.; Voinovich, D.; Moneghini, M.; Rodriguez, L. Controlled release of verapamil hydrochloride from waxy microparticles prepared by spray congealing. J. Control. Release 2003, 88, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodmer, D.; Kissel, T.; Traechslin, E. Factors influencing the release of peptides and proteins from biodegradable parenteral depot systems. J. Control. Release 1992, 21, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodmer, D.; Fong, J.W.; Kissel, T.; Maulding, H.V.; Nagele, O.; Pearson, J.E. Sustained Release Formulations of Water Soluble Peptides. U.S. Patent US08470909, 6 June 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, L.; Passerini, N.; Cavallari, C.; Cini, M.; Sancin, P.; Fini, A. Description and preliminary evaluation of a new ultrasonic atomizer for spray-congealing processes. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 183, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B.; Kang, H.W.; Haam, S.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, W.S. Ca-alginate microspheres encapsulated in chitosan beads. J. Microencapsul. 2004, 21, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilati, U.; Allémann, E.; Doelker, E. Strategic approaches for overcoming peptide and protein instability within biodegradable nano- and microparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 59, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fini, A.; Rodriguez, L.; Cavallari, C.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N. Ultrasound-compacted and spray-congealed indomethacin/polyethyleneglycol systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 247, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.M.; Heng, P.W.S.; Chan, L.W. Influence of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose on metronidazole crystallinity in spray-congealed polyethylene glycol microparticles and its impact with various additives on metronidazole release. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, C.M.; Ru Shan Siow, C.; Wan Sia Heng, P.; Chan, L.W. Impact of HPMC on the physical properties of spray-congealed PEG microparticles and its swelling effect on rifampicin dissolution. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulthe, V.V.; Chaudhari, P.D. Effectiveness of spray congealing to obtain physically stabilized amorphous dispersions of a poorly soluble thermosensitive API. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallari, C.; Rodriguez, L.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N.; Rosetti, F.; Fini, A. Thermal and fractal analysis of diclofenac/gelucire 50/13 microparticles obtained by ultrasound-assisted atomization. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallari, C.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, M.; Tarterini, F.; Fini, A. Image analysis of lutrol/gelucire/olanzapine microspheres prepared by ultrasound-assisted spray congealing. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbakry, A.M.; Abd Al Haleem, E.N. Spray congealing for enhancement the solubility and pharmacological activity of methylprednisolone. J. Pharm. Sci. Pharmacol. 2015, 2, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.E.; Eshra, A.G.; Nada, A.H. Formulation of prolonged release lipid micropellets by emulsion congealing: Optimization of ketoprofen entrapment and release. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 121, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.Y.; Chan, L.W.; Heng, P.W.S. Investigation of the release of aspirin from spray-congealed micro-pellets. J. Microencapsul. 2005, 22, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consoli, L.; Grimaldi, R.; Sartori, T.; Menegalli, F.C.; Hubinger, M.D. Gallic acid microparticles produced by spray chilling technique: Production and characterization. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertini, B.; Passerini, N.; Di Sabatino, M.; Vitali, B.; Brigidi, P.; Rodriguez, L. Polymer–lipid based mucoadhesive microspheres prepared by spray-congealing for the vaginal delivery of econazole nitrate. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 36, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.C.H.; Heng, P.W.S.; Chan, L.W. Determination of solid state characteristics of spray-congealed ibuprofen solid lipid microparticles and their impact on sustaining drug release. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1592–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.C.H.; Heng, P.W.S.; Chan, L.W. Spray congealing as a microencapsulation technique to develop modified-release ibuprofen solid lipid microparticles: The effect of matrix type, polymeric additives and drug–matrix miscibility. J. Microencapsul. 2015, 32, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.P.; Gilligan, C.A.; Li Wan Po, A. Preparation and characterisation of sustained-release ibuprofen-cetostearyl alcohol spheres. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 83, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.C.H.; Wan Sia Heng, P.; Chan, L.W. A study on the solid state characteristics of spray-congealed glyceryl dibehenate solid lipid microparticles containing ibuprofen. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertini, B.; Passerini, N.; González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Perissutti, B.; Rodriguez, L. Effect of Aerosil® on the properties of lipid controlled release microparticles. J. Control. Release 2004, 100, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.W.; Robinson, M.J.; Pauls, J.F.; Lantz, R.J. Spray congealing: Particle size relationships using a centrifugal wheel atomizer. J. Pharm. Sci. 1964, 53, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer-Tropsch waxes. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6y1iQsOWT (accessed on 19 March 2018).
- Wong, P.C.H.; Heng, P.W.S.; Chan, L.W. Viscosity–temperature relationship of lipid-based excipients amenable for spray congealing: Derivation of a rheological parameter with good correlation to particle size. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.; Caldin, E.F. The association of carboxylic acids. Q. Rev. Chem. Soc. 1953, 7, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahashi, M.; Kasahara, Y. Dynamic molecular movements and aggregation structures of lipids in a liquid state. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithani, K.; Cuppok, Y.; Mostafa, S.; Slipper, I.J.; Snowden, M.J.; Douroumis, D. Diclofenac sodium sustained release hot melt extruded lipid matrices. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 19, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, R.M.; Siqueira, S.; Freitas, L.A.P. Spray congealing of pharmaceuticals: Study on production of solid dispersions using box-behnken design. Dry. Technol. 2012, 30, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, P. Chapter 8—Illustrated IR and Raman Spectra Demonstrating Important Functional Groups. In Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 135–176. ISBN 978-0-12-386984-5. [Google Scholar]











| Viscosity at Different Shear Stress (mPa.s) for 5% Drug Load | |||
| Shear Stress = 2 Pa | Shear Stress = 5 Pa | Shear Stress = 8 Pa | |
| PW59 | 36.6 | 22.9 | 20.3 |
| PW59:SA (1:1) | 37.2 | 29.6 | 30.7 |
| PW59:CA (1:1) | 33.0 | 27.4 | 25.3 |
| PW59:CE (1:1) | 29.5 | 24.1 | 24.7 |
| Viscosity at Different Shear Stress (mPa.s) for 10% Drug Load | |||
| Shear Stress = 2 Pa | Shear Stress = 5 Pa | Shear Stress = 8 Pa | |
| PW59 | 165.3 | 32.9 | 29.7 |
| PW59:SA (1:1) | 44.4 | 36.6 | 35.6 |
| PW59:CA (1:1) | 40.0 | 31.9 | 28.6 |
| PW59:CE (1:1) | 38.3 | 28.6 | 29.8 |
| Viscosity at Different Shear Stress (mPa.s) for 20% Drug Load | |||
| Shear Stress = 2 Pa | Shear Stress = 5 Pa | Shear Stress = 8 Pa | |
| PW59 | 1238.9 | 851.9 | 116.9 |
| PW59:SA (1:1) | 129.9 | 68.0 | 62.2 |
| PW59:CA (1:1) | 122.4 | 58.8 | 40.6 |
| PW59:CE (1:1) | 301.4 | 81.2 | 76.3 |
| Formulation | η0 (mPa.s) | η (mPa.s) | φ |
|---|---|---|---|
| PW59 | 5.836 | 116.9 | 7.61 |
| PW59:SA (1:1) | 6.446 | 62.2 | 3.46 |
| PW59:CA (1:1) | 5.691 | 40.6 | 2.45 |
| PW59:CE (1:1) | 5.692 | 76.3 | 4.96 |
| Formulation | Total Yield (%) | Useful Yield (%) | Fines (%) | Drug Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PW59 | 80.7 ± 4.8 | 74.5 ± 5.7 | 6.2 ± 0.9 | 21.8 ± 0.7 |
| PW59:SA (1:1) | 94.1 ± 2.1 | 87.5 ± 2.3 | 6.7 ± 0.3 | 21.6 ± 0.1 |
| PW59:CA (1:1) | 89.6 ± 4.5 | 81.1 ± 5.0 | 8.5 ± 0.6 | 21.6 ± 0.1 |
| PW59:CE (1:1) | 86.4 ± 0.3 | 81.5 ± 0.7 | 4.9 ± 0.5 | 21.9 ± 0.8 |
| Microparticle Size Characteristics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D10 (µm) | D50 (µm) | D90 (µm) | Span | |
| PW59 | 23.05 ± 1.54 | 46.81 ± 2.21 | 106.27 ± 8.49 | 1.79 ± 0.30 |
| PW59:SA (1:1) | 20.93 ± 1.94 | 44.33 ± 0.95 | 92.57 ± 5.98 | 1.62 ± 0.17 |
| PW59:CA (1:1) | 19.51 ± 1.28 | 42.25 ± 3.76 | 85.34 ± 10.84 | 1.55 ± 0.14 |
| PW59:CE (1:1) | 20.20 ± 0.54 | 45.57 ± 2.52 | 93.06 ± 8.07 | 1.60 ± 0.09 |
| Test Groups | Kruskal-Wallis p-Value | |||
| PW59, PW59:SA (1:1), PW59:CA (1:1), PW59:CE (1:1) | 0.000 | |||
| Test Groups | Wilcoxon Rank-Sum p-Value | |||
| PW59, PW59:SA (1:1) | 0.016 | |||
| PW59, PW59:CA (1:1) | 0.000 | |||
| PW59, PW59:CE (1:1) | 0.014 | |||
| PW59:SA (1:1), PW59:CA (1:1) | 0.058 | |||
| PW59:SA (1:1), PW59:CE (1:1) | 0.997 | |||
| PW59:CA (1:1), PW59:CE (1:1) | 0.056 | |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, H.; Zheng, A.Y.; Heng, P.W.S.; Chan, L.W. Effect of Lipid Additives and Drug on the Rheological Properties of Molten Paraffin Wax, Degree of Surface Drug Coating, and Drug Release in Spray-Congealed Microparticles. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030075
Ouyang H, Zheng AY, Heng PWS, Chan LW. Effect of Lipid Additives and Drug on the Rheological Properties of Molten Paraffin Wax, Degree of Surface Drug Coating, and Drug Release in Spray-Congealed Microparticles. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(3):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030075
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Hongyi, Audrey Yi Zheng, Paul Wan Sia Heng, and Lai Wah Chan. 2018. "Effect of Lipid Additives and Drug on the Rheological Properties of Molten Paraffin Wax, Degree of Surface Drug Coating, and Drug Release in Spray-Congealed Microparticles" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 3: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030075
APA StyleOuyang, H., Zheng, A. Y., Heng, P. W. S., & Chan, L. W. (2018). Effect of Lipid Additives and Drug on the Rheological Properties of Molten Paraffin Wax, Degree of Surface Drug Coating, and Drug Release in Spray-Congealed Microparticles. Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030075