Preparation, Characterization and Dermal Delivery of Methadone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Methadone Base
2.3. Thermal Analysis
2.4. HPLC Analysis
2.5. Log D
2.6. Solubility and Stability
2.7. In Vitro Permeation and Mass Balance Studies
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Methadone Free Base with NMR and IR Spectroscopy
3.2. Thermal Analysis
3.3. Log D Measurement
3.4. Stability and Solubility
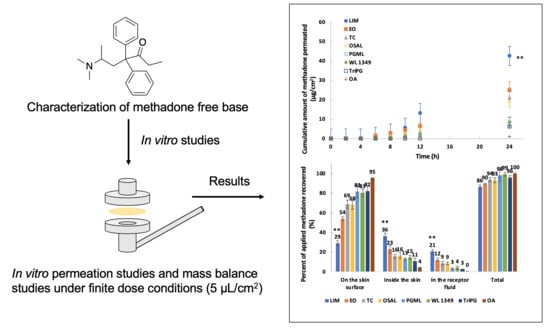
3.5. In Vitro Permeation and Mass Balance Studies of Methadone Base in Porcine Ear Skin
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1,3-BD | 1,3-butanediol |
| 1H-NMR | Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| ANOVA | One-way Analysis of Variance |
| CDCl3 | Chloroform-d |
| DiPG | Dipropylene Glycol |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| EO | Ethyl Oleate |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared |
| GRAS | Generally Recognized as Safe |
| HPLC | High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| IPM | Isopropyl Myristate |
| LIM | d-limonene |
| LOD | Limit of Detection |
| Log D | Logarithm to the Base 10 of Distribution Coefficient |
| Log P | Logarithm to the Base 10 of Partition Coefficient |
| LOQ | Limit of Quantification |
| Nav | Voltage-gated Sodium (Nav) Channels |
| NMDA | N-Methyl-d-aspartate |
| OA | Oleic Acid |
| OECD | Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development |
| OSAL | Octyl Salicylate |
| PBS | Phosphate Buffered Saline |
| PG | Propylene Glycol |
| PGMC | Propylene Glycol Monocaprylate |
| PGML | Propylene Glycol Monolaurate |
| pKa | Dissociation Constant |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| TC | Transcutol® |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| TriPG | Tripropylene Glycol |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| WL 1349 | Labrafac™ lipophile WL 1349 |
References
- O’Connor, A.B.; Dworkin, R.H. Treatment of neuropathic pain: An overview of recent guidelines. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, S22–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treede, R.-D.; Jensen, T.S.; Campbell, J.; Cruccu, G.; Dostrovsky, J.; Griffin, J.; Hansson, P.; Hughes, R.; Nurmikko, T.; Serra, J. Neuropathic pain redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 2008, 70, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.P.; Chodroff, M.J.; Dworkin, R.H. The impact of neuropathic pain on health-related quality of life Review and implications. Neurology 2007, 68, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hecke, O.; Austin, S.K.; Khan, R.A.; Smith, B.; Torrance, N. Neuropathic pain in the general population: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain 2014, 155, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colloca, L.; Ludman, T.; Bouhassira, D.; Baron, R.; Dickenson, A.H.; Yarnitsky, D.; Freeman, R.; Truini, A.; Attal, N.; Finnerup, N.B.; et al. Neuropathic pain. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altier, N.; Dion, D.; Boulanger, A.; Choinière, M. Management of chronic neuropathic pain with methadone: A review of 13 cases. Clin. J. Pain 2005, 21, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, J.A.; Furlan, A.D.; Mailis-Gagnon, A. Oral methadone for chronic noncancer pain: A systematic literature review of reasons for administration, prescription patterns, effectiveness, and side effects. Clin. J. Pain 2005, 21, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.S.; Bridson, J.; Nash, T.P.; Miles, J.B.; White, S.; Makin, M.K. Low-dose methadone has an analgesic effect in neuropathic pain: A double-blind randomized controlled crossover trial. Palliat. Med. 2003, 17, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, S.; Twomey, F. Methods of rotation from another strong opioid to methadone for the management of cancer pain: A systematic review of the available evidence. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2015, 50, 248–259.e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotgiu, M.L.; Valente, M.; Storchi, R.; Caramenti, G.; Biella, G.E.M. Cooperative N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonism and μ-opioid receptor agonism mediate the methadone inhibition of the spinal neuron pain-related hyperactivity in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol. Res. 2009, 60, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, V.; Christensen, D.; Kayser, V. The glycine/NMDA receptor antagonist (+)-HA966 enhances the peripheral effect of morphine in neuropathic rats. Pain 2002, 99, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoetzer, C.; Kistner, K.; Stüber, T.; Wirths, M.; Schulze, V.; Doll, T.; Foadi, N.; Wegner, F.; Ahrens, J.; Leffler, A. Methadone is a local anaesthetic-like inhibitor of neuronal Na+ channels and blocks excitability of mouse peripheral nerves. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 114, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullerton, A.; Christrup, L.; Bundgaard, H. Evaluation of the transdermal route for administration of narcotic analgesics: Human skin permeability studies of methadone and pethidine. Acta Pharm. Nord. 1991, 3, 181–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.K.; Bagherian, A. Development of a transdermal patch of methadone: In vitro evaluation across hairless mouse and human cadaver skin. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 1996, 1, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, M.; Castán, H.; Ruiz, M.; Morales, M. Design, development and characterization of transdermal patch of methadone. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 42, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICH. Q2 (R1). Validation of analytical procedures: Text and methodology. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Harmonization, Geneva, Switzerland, 10 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Test No. 107: Partition Coefficient (N-Octanol/Water): Shake Flask Method; Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Van Krevelen, D.W. Properties of Polymers: Their Correlation with Chemical Structure, Their Numerical Estimation and Prediction from Additive Group Contributions, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Scientific Pub. Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 200–225. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, P.; Watkinson, A.; Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M. Oxybutynin permeation in skin: The influence of drug and solvent activity. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 384, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, E.; Hua, P.; Webster, J.; Tompkins, W.; Pallas-Areny, R. Skin impedance measurements using simple and compound electrodes. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1992, 30, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronaugh, R.L.; Stewart, R.F. Methods for in vitro percutaneous absorption studies III: Hydrophobic compounds. J. Pharm. Sci. 1984, 73, 1255–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brain, K.R.; Walters, K.A.; Watkinson, A.C. Methods for Studying Percutaneous Absorption. In Dermatological and Transdermal Formulations; Walters, K.A., Roberts, M.S., Eds.; Marcel Dekker, lnc: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 197–270. [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb, H.E.; Kotlyar, V.; Nudelman, A. NMR chemical shifts of common laboratory solvents as trace impurities. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 7512–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemberg, K.; Kontinen, V.K.; Viljakka, K.; Kylänlahti, I.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J.; Kalso, E. Morphine, oxycodone, methadone and its enantiomers in different models of nociception in the rat. Anesth. Analg. 2006, 102, 1768–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, C.; Leo, A.; Hoekman, D.; Livingstone, D. Exploring QSAR: Hydrophobic, Electronic, and Steric Constants; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, D. Dissociation Constants of Organic Acids and Bases; Butterworths: London, UK, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Moffat, A.C.; Osselton, M.D.; Widdop, B.; Watts, J. Clarke’s Analysis of Drugs and Poisons; Pharmaceutical press London: London, UK, 2011; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil, M.J. The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, B.C.; York, P.; Rowe, R.C. The use of solubility parameters in pharmaceutical dosage form design. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 148, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrador, M.A.; González, A.G. Solubility prediction of caffeine in aqueous N,N-dimethylformamide mixtures using the extended Hildebrand solubility approach. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 156, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, P.; Navarro, J.; Romero, S.; Escalera, B. Thermodynamic origin of the solubility profile of drugs showing one or two maxima against the polarity of aqueous and nonaqueous mixtures: Niflumic acid and caffeine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, M.; Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M.E. Influence of membrane-solvent-solute interactions on solute permeation in model membranes. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 336, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Test No. 28: Guidance Document for the Conduct of Skin Absorption Studies; Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Terpenes and the lipid–protein–partitioning theory of skin penetration enhancement. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cal, K.; Janicki, S.; Sznitowska, M. In vitro studies on penetration of terpenes from matrix-type transdermal systems through human skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 224, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, A.; Herman, A.P. Essential oils and their constituents as skin penetration enhancer for transdermal drug delivery: A review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Inactive Ingredient Search for Approved Drug Products. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/iig/index.cfm (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- Small, D.M. Lateral chain packing in lipids and membranes. J. Lipid Res. 1984, 25, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Ongpipattanakul, B.; Burnette, R.R.; Potts, R.O.; Francoeur, M.L. Evidence that oleic acid exists in a separate phase within stratum corneum lipids. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.; Hadgraft, J. Oleic acid—A membrane “fluidiser” or fluid within the membrane? Int. J. Pharm. 1991, 71, R1–R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.; Watkinson, A.; Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M. Influence of penetration enhancer on drug permeation from volatile formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 439, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, T.; Rahman, K.M.; Thurston, D.E.; Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M.E. Topical delivery of anthramycin I. Influence of neat solvents. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 104, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| pH | Log D |
|---|---|
| 6.0 | 0.31 ± 0.01 |
| 6.5 | 0.80 ± 0.01 |
| 7.0 | 1.35 ± 0.01 |
| 7.4 | 1.82 ± 0.01 |
| 11.0 (free base) | 4.85 ± 0.03 |
| Solvent | Solubility of Methadone base (mg/mL) | Solubility of Methadone Hydrochloride (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| LIM | 342.38 ± 2.99 | 0.08 ± 0.002 |
| EO | 205.46 ± 1.69 | 0.08 ± 0.01 |
| IPM | 179.80 ± 0.89 | 0.03 ± 0.001 |
| WL 1349 | 217.66 ± 3.73 | 0.05 ± 0.001 |
| OA | 438.76 ± 2.56 | 2.53 ± 0.03 |
| PGML | 209.43 ± 0.54 | 19.68 ± 0.79 |
| PGMC | 250.74 ± 2.17 | 28.65 ± 0.46 |
| TC | 247.68 ± 0.95 | 21.96 ± 0.46 |
| OSAL | 277.20 ± 6.96 | 0.05 ± 0.001 |
| TriPG | 105.90 ± 0.25 | 18.03 ± 0.93 |
| DiPG | 85.94 ± 0.41 | 43.97 ± 1.28 |
| PG | 24.78± 0.49 | 201.33 ± 1.30 |
| 1,3-BD | 26.24 ± 0.05 | 88.40 ± 0.79 |
| PBS | 0.49 ± 0.01 | 86.66 ± 0.95 |
| PBS + 6% w/v Brij™ O20 | 2.61 ± 0.02 | 107.45 ± 1.35 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kung, C.-P.; Sil, B.C.; Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M.E.; Patel, B.; McCulloch, R. Preparation, Characterization and Dermal Delivery of Methadone. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100509
Kung C-P, Sil BC, Hadgraft J, Lane ME, Patel B, McCulloch R. Preparation, Characterization and Dermal Delivery of Methadone. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(10):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100509
Chicago/Turabian StyleKung, Chin-Ping, Bruno C. Sil, Jonathan Hadgraft, Majella E. Lane, Bhumik Patel, and Renée McCulloch. 2019. "Preparation, Characterization and Dermal Delivery of Methadone" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 10: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100509
APA StyleKung, C. -P., Sil, B. C., Hadgraft, J., Lane, M. E., Patel, B., & McCulloch, R. (2019). Preparation, Characterization and Dermal Delivery of Methadone. Pharmaceutics, 11(10), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100509