Ground Calcium Carbonate as a Low Cost and Biosafety Excipient for Solubility and Dissolution Improvement of Praziquantel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
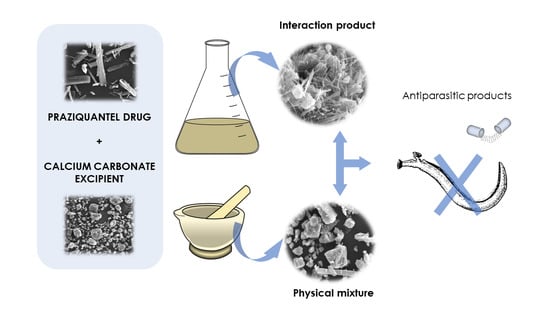
2.2. Preparation of the PZQ and GCC Physical Mixture
2.3. Preparation of the PZQ and GCC Interaction Product (IP)
2.4. Solid State Characterization of Calcium Carbonate/Praziquantel Systems
2.4.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.4.2. Thermal Analysis
2.4.3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.4.4. Particle Size Analysis
2.4.5. Fourier Transform Infrared and Raman Spectroscopies
2.5. Solubility Studies
2.6. Dissolution Studies
2.7. HPLC Analysis
2.8. Computational Methods
2.9. Cell Culture
2.10. Cytotoxicity Studies
2.11. Cell Cycle Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solid State Characterization of Calcium Carbonate/Praziquantel Systems
3.2. Solubility Studies
3.3. Dissolution Studies
3.4. Modeling Approach
3.5. Cytotoxicity Studies
3.6. Cell Cycle Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowe, R.C.; Sheskey, P.J.; Weller, P.J. Calcium Carbonate. In Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 6th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, Y.; Futagawa, H.; Takagi, Y.; Ueno, A.; Mizushima, Y. Drug-incorporating calcium carbonate nanoparticles for a new delivery system. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preisig, D.; Haid, D.; Varum, F.J.; Bravo, R.; Alles, R.; Huwyler, J.; Puchkov, M. Drug loading into porous calcium carbonate microparticles by solvent evaporation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzine Costa, L.M.; Molina de Olyveira, G.; Salomão, R. Precipitated Calcium Carbonate Nano-Microparticles: Applications in Drug Delivery. Adv. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 3, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Dizaj, S.M.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Zarrintan, M.H.; Adibkia, K.; Lotfipour, F. Calcium carbonate nanoparticles as cancer drug delivery system. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, W.; Lin, Q.; Han, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y. Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin functionalized calcium carbonate microparticles as a potential carrier for enhancing oral delivery of water-insoluble drugs. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3291–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islan, G.A.; Cacicedo, M.L.; Bosio, V.E.; Castro, G.R. Development and characterization of new enzymatic modified hybrid calcium carbonate microparticles to obtain nano-architectured surfaces for enhanced drug loading. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 439, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.-S.; Zong, J.-Y.; Zhao, D.; Li, F.; Zhuo, R.-X.; Cheng, S.-X. Calcium Carbonate/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hybrid Microspheres and Nanospheres for Drug Delivery. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 18940–18945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Gao, Q.; Liu, X.; Tong, Z. Alginate-calcium carbonate porous microparticle hybrid hydrogels with versatile drug loading capabilities and variable mechanical strengths. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kong, Y.; Liu, F.; Shou, D.; Tao, Y.; Qin, Y. Construction of pH-responsive drug delivery platform with calcium carbonate microspheres induced by chitosan gels. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 7902–7907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergaro, V.; Papadia, P.; Leporatti, S.; De Pascali, S.A.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Ciccarella, G. Synthesis of biocompatible polymeric nano-capsules based on calcium carbonate: A potential cisplatin delivery system. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 153, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, R.; Schoelkopf, J.; Huwyler, J.; Puchkov, M. Functionalized calcium carbonate microparticles for the delivery of proteins. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 122, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svenskaya, Y.; Parakhonskiy, B.; Haase, A.; Atkin, V.; Lukyanets, E.; Gorin, D.; Antolini, R. Anticancer drug delivery system based on calcium carbonate particles loaded with a photosensitizer. Biophys. Chem. 2013, 182, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trofimov, A.D.; Ivanova, A.A.; Zyuzin, M.V.; Timin, A.S. Porous Inorganic carriers Based on Silica, Calcium Carbonate and Calcium Phosphate for Controlled/Modulated Drug Delivery: Fresh Outlook and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trastullo, R.; Dolci, L.S.; Passerini, N.; Albertini, B. Development of flexible and dispersible oral formulations containing praziquantel for potential schistosomiasis treatment of pre-school age children. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO, World Health Organization. Schistosomiasis. Available online: http://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schistosomiasis (accessed on 12 October 2019).
- Lindenberg, M.; Kopp, S.; Dressman, J.B. Classification of orally administered drugs on the World Health Organization Model list of Essential Medicines according to the biopharmaceutics classification system. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Subbagh, H.I.; Al-Badr, A.A. Praziquantel. In Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances and Excipients; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 25, pp. 463–500. [Google Scholar]
- Zanolla, D.; Perissutti, B.; Passerini, N.; Chierotti, M.R.; Hasa, D.; Voinovich, D.; Gigli, L.; Demitri, N.; Geremia, S.; Keiser, J.; et al. A new soluble and bioactive polymorph of praziquantel. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourao, S.C.; Costa, P.I.; Salgado, H.R.N.; Gremiao, M.P.D. Improvement of antischistosomal activity of praziquantel by incorporation into phosphatidylcholine-containing liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 295, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Sánchez, A.; Carazo, E.; Aguzzi, C.; Viseras, C.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I. Biopharmaceutical improvement of praziquantel by interaction with montmorillonite and sepiolite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.G.; Chaves, I.S.; Melo, N.F.S.; de Jesus, M.B.; Fraceto, L.F.; Fernandes, S.A.; de Paula, E.; de Freitas, M.P.; Pinto, L.M.A. Computational analysis and physico-chemical characterization of an inclusion compound between praziquantel and methyl-β-cyclodextrin for use as an alternative in the treatment of schistosomiasis. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2011, 70, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maragos, S.; Archontaki, H.; Macheras, P.; Valsami, G. Effect of Cyclodextrin Complexation on the Aqueous Solubility and Solubility/Dose Ratio of Praziquantel. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2009, 10, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becket, G.; Schep, L.J.; Tan, M.Y. Improvement of the in vitro dissolution of praziquantel by complexation with α-, β-, and γ-cyclodextrins. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 179, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Torre, P.; Torrado, S.; Torrado, S. Preparation, Dissolution and Characterization of Praziquantel Solid Dispersions. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 1629–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Arini, S.K.; Leuenberger, H. Dissolution properties of praziquantel-PVP systems. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1998, 73, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.D.; Priotti, J.; Orlandi, S.; Leonardi, D.; Lamas, M.C.; Nunes, T.G.; Diogo, H.P.; Salomon, C.J.; Ferreira, M.J. Unexpected solvent impact in the crystallinity of praziquantel/poly(vinylpyrrolidone) formulations. A solubility, DSC and solid-state NMR study. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passerini, N.; Albertini, B.; Perissutti, B.; Rodriguez, L. Evaluation of melt granulation and ultrasonic spray congealing as techniques to enhance the dissolution of praziquantel. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 318, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Ding, W.; Dong, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Dissolution and oral bioavailability enhancement of praziquantel by solid dispersions. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Lei, L.; Guo, S. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of praziquantel loaded implants based on PEG/PCL blends. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 387, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaud, M.V.; Lima, A.C.; Vila, M.M.D.C.; Paganelli, M.O.; Paula, F.C.; Pedreiro, L.N.; Gremião, M.P.D. Development and evaluation of praziquantel solid dispersions in sodium starch glycolate. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissutti, B.; Passerini, N.; Trastullo, R.; Keiser, J.; Zanolla, D.; Zingone, G.; Voinovich, D.; Albertini, B. An explorative analysis of process and formulation variables affecting comilling in a vibrational mill: The case of praziquantel. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Sánchez, A.; Carazo, E.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N.; Perissutti, B.; Cerezo, P.; Viseras, C.; Aguzzi, C.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I. Conformational polymorphic changes in the crystal structure of the chiral antiparasitic drug praziquantel and interactions with calcium carbonate. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 132, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Ramos, J.D. XPowder software. 2005. Available online: http://www.xpowder.com (accessed on 12 October 2019).
- Borrego-Sánchez, A.; Viseras, C.; Aguzzi, C.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I. Molecular and crystal structure of praziquantel. Spectroscopic properties and crystal polymorphism. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 92, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H. COMPASS: An ab Initio Force-Field Optimized for Condensed-Phase Applications-Overview with Details on Alkane and Benzene Compounds. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 7338–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accelrys Materials Studio, version v 6.0; Accelrys Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012.
- Borrego-Sánchez, A.; Hernández-Laguna, A.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I. Molecular modeling and infrared and Raman spectroscopy of the crystal structure of the chiral anti-parasitic drug praziquantel. J. Mol. Model. 2017, 23, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.P.; Traganos, F.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. A selective procedure for DNA extraction from apoptotic cells applicable for gel electrophoresis and flow cytometry. Anal. Biochem. 1994, 218, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanolla, D.; Perissutti, B.; Passerini, N.; Invernizzi, S.; Voinovich, D.; Bertoni, S.; Melegari, C.; Millotti, G.; Albertini, B. Milling and comilling Praziquantel at cryogenic and room temperatures: Assessment of the process-induced effects on drug properties. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 153, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sample | HCl 0.001 M Medium, pH = 3 | SIF Medium, pH = 6.8 |
|---|---|---|
| PZQ | 0.50 mg/mL | 0.45 mg/mL |
| PM PZQ-GCC | 0.52 mg/mL | 0.50 mg/mL |
| IP PZQ-GCC | 1.42 mg/mL | 0.73 mg/mL |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borrego-Sánchez, A.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N.; Cerezo, P.; Viseras, C.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I. Ground Calcium Carbonate as a Low Cost and Biosafety Excipient for Solubility and Dissolution Improvement of Praziquantel. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100533
Borrego-Sánchez A, Sánchez-Espejo R, Albertini B, Passerini N, Cerezo P, Viseras C, Sainz-Díaz CI. Ground Calcium Carbonate as a Low Cost and Biosafety Excipient for Solubility and Dissolution Improvement of Praziquantel. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(10):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100533
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorrego-Sánchez, Ana, Rita Sánchez-Espejo, Beatrice Albertini, Nadia Passerini, Pilar Cerezo, César Viseras, and C. Ignacio Sainz-Díaz. 2019. "Ground Calcium Carbonate as a Low Cost and Biosafety Excipient for Solubility and Dissolution Improvement of Praziquantel" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 10: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100533
APA StyleBorrego-Sánchez, A., Sánchez-Espejo, R., Albertini, B., Passerini, N., Cerezo, P., Viseras, C., & Sainz-Díaz, C. I. (2019). Ground Calcium Carbonate as a Low Cost and Biosafety Excipient for Solubility and Dissolution Improvement of Praziquantel. Pharmaceutics, 11(10), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100533