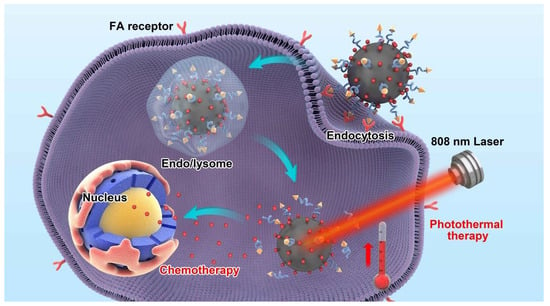
Folic Acid-Functionalized Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots for Targeted Chemo-Photothermal Combination Cancer Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots (BPQDs)
2.3. Modification with PEG-FA
2.4. DOX Loading
2.5. Characterization of BPQDs
2.6. Photothermal Effect of BPQDs-PEG-FA
2.7. pH and Photothermally-Triggered Drug Release Study
2.8. Cell Culture
2.9. In Vitro Cellular Uptake Assays
2.10. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assays
2.11. In Vitro Photothermal Therapy Study
2.12. Xenograft Tumor Models
2.13. In Vivo Photothermal Images
2.14. In Vivo Combined Therapy
2.15. Statistical Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizations of the Drug Delivery Platform
3.2. Drug Loading Capacity and Release Behavior Study
3.3. In Vitro NIR Photothermal Performances
3.4. In Vitro Cellular Uptake and Distribution Assay
3.5. In Vitro Combined Therapy Effect
3.6. In Vivo NIR Photothermal Performances
3.7. In Vivo Combined Therapy Effect
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, F.; Shen, Y.; Guo, S. A new NIR-triggered DOX and ICG co-delivery system for enhanced multidrug resistant cancer treatment through simultaneous chemo/photothermal/photodynamic therapy. Acta Biomater. 2017, 59, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Ma, J.; Lin, J.; Lin, H.; Su, G.; Chen, D.; Ye, S.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.; Hou, Z. Chemotherapeutic drug-photothermal agent co-self-assembling nanoparticles for near-infrared fluorescence and photoacoustic dual-modal imaging-guided chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy. J. Controlled Release 2017, 258, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabner, B.A.; Roberts, T.G. Timeline—Chemotherapy and the war on cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Liang, C.; Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Gao, N.; Tao, W.; Luo, L.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. TPGS-functionalized polydopamine-modified mesoporous silica as drug nanocarriers for enhanced lung cancer chemotherapy against multidrug resistance. Small 2017, 13, 1700623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, Y.Y.C.; Chen, S.; Cullis, P.R. Advances in lipid nanoparticles for siRNA delivery. Pharmaceutics 2013, 5, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzur, A.; Oluwasanmi, A.; Moss, D.; Curtis, A.; Hoskins, C. Nanotechnologies in pancreatic cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y.-F.; He, R.-R.; Liu, M. Enhanced therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin for breast cancer using chitosan oligosaccharide-modified halloysite nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2016, 8, 26578–26590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, A.; Li, A.; Tian, W.; Li, Z.; Wei, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, M. A target-directed chemo-photothermal system based on transferrin and copolymer modified MoS₂ nanoplates with pH-activated drug release. Chemistry 2017, 23, 11346–11356. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Yin, W.; Zheng, X.; Tian, G.; Zhang, X.; Bao, T.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Gu, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y. Smart MoS2/Fe3O4 nanotheranostic for magnetically targeted photothermal therapy guided by magnetic resonance/photoacoustic imaging. Theranostics 2015, 5, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Xi, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Mayr, T.; Shi, L.; Sun, L. In situ crystal growth of gold nanocrystals on upconversion nanoparticles for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 12885–12896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Cai, K. Mesoporous polydopamine nanoparticles with co-delivery function for overcoming multidrug resistance via synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 8781–8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-M.J.; Zhang, L. Nanoparticle-based combination therapy toward overcoming drug resistance in cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Yin, W.; Yu, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y. TPGS-stabilized NaYbF4:Er upconversion nanoparticles for dual-modal fluorescent/CT imaging and anticancer drug delivery to overcome multi-drug resistance. Biomaterials 2015, 40, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xie, H.; Tang, S.; Yu, X.-F.; Guo, Z.; Shao, J.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Chu, P.K. Ultrasmall black phosphorus quantum dots: Synthesis and use as photothermal agents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11526–11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, C.; Feng, L.; Yang, K.; Liu, Z. Functional nanomaterials for phototherapies of cancer. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10869–10939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavuz, M.S.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Cobley, C.M.; Zhang, Q.; Rycenga, M.; Xie, J.; Kim, C.; Song, K.H.; Schwartz, A.G.; et al. Gold nanocages covered by smart polymers for controlled release with near-infrared light. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ye, K.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, J.; Zou, R.; Xu, K.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X.; Hu, J. Photothermal theragnosis synergistic therapy based on bimetal sulphide nanocrystals rather than nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F.; Yin, Y.; Mei, L.; Song, F.; Tao, M.; Yue, W.; Zhong, W. Overcoming multidrug resistance by a combination of chemotherapy and photothermal therapy mediated by carbon nanohorns. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 6043–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Yin, W.; Ruan, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Yan, L.; Li, S.; Gu, Z.; et al. Multifunctional RbxWO3 nanorods for simultaneous combined chemo-photothermal therapy and photoacoustic/CT imaging. Small 2014, 10, 4160–4170. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, D.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z. Targeted cancer imaging and photothermal therapy via monosaccharide-imprinted gold nanorods. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 6716–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Xie, H.; Huang, H.; Li, Z.; Sun, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Yu, X.-F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Biodegradable black phosphorus-based nanospheres for in vivo photothermal cancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Neal, A.T.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Xu, X.; Tomanek, D.; Ye, P.D. Phosphorene: An unexplored 2D semiconductor with a high hole mobility. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4033–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Yang, G.; Fei, X.; Zhao, H.; Guo, Y.; Su, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, H.; et al. A multifunctional nanoplatform based on black phosphorus quantum dots for bioimaging and photodynamic/photothermal synergistic cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2017, 9, 25098–25106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childers, D.L.; Corman, J.; Edwards, M.; Elser, J.J. Sustainability challenges of phosphorus and food: Solutions from closing the human phosphorus cycle. Bioscience 2011, 61, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Shao, W.; Chen, S.; Xie, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, Y. Ultrathin black phosphorus nanosheets for efficient singlet oxygen generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11376–11382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Nie, J.; Xu, L.; Liang, C.; Peng, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, T.; Mei, L.; Huang, L.; Zeng, X. pH-sensitive delivery vehicle based on folic acid-conjugated polydopamine-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2017, 9, 18462–18473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, F.; Lamers, G.E.M.; Morrhayim, J.; Chatzopoulou, A.; Schaaf, M.; den Dulk, H.; Backendorf, C.; Zink, J.I.; Kros, A. Folic acid-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cellular and nuclear targeted drug delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Felidj, N.; Boubekeur-Lecaque, L.; Lau-Truong, S.; Gam-Derouich, S.; Decorse, P.; Lamouri, A.; Mangeney, C. Water-soluble plasmonic nanosensors with synthetic receptors for label-free detection of folic acid. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9678–9681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Zhu, X.; Yu, X.; Zeng, X.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ji, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Black phosphorus nanosheets as a robust delivery platform for cancer theranostics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Sun, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Yu, J.C. A black-red phosphorus heterostructure for efficient visible-light-driven photocatalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 3285–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wen, L.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Deng, L.; Zhao, C.; Li, Z. One-pot solventless preparation of PEGylated black phosphorus nanoparticles for photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy of cancer. Biomaterials 2016, 91, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Yan, S.; Shi, Y.; Xiao, M. Ultrafast carrier dynamics and efficient triplet generation in black phosphorus quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 12972–12978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Wang, J.-Y.; Bai, X.; Xu, F.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Jing, Y.; Liu, L.; Xue, X.; Dai, H.; et al. Black phosphorus quantum dot induced oxidative stress and toxicity in living cells and mice. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2017, 9, 20399–20409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Zeng, X.W.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X.; Yu, X.H.; Zhang, X.D.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, G.; Mei, L. Polydopamine-based surface modification of novel nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates for in vivo breast cancer targeting and enhanced therapeutic effects. Theranostics 2016, 6, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Li, W.; Luo, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Kong, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Zhu, C.; Du, Y.; et al. External magnetic field-enhanced chemo-photothermal combination tumor therapy via iron oxide nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2017, 9, 16581–16593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, C.; Gu, X.; Gong, H.; Cheng, L.; Shi, X.; Feng, L.; Sun, B.; Liu, Z. Drug delivery with PEGylated MoS2 nano-sheets for combined photothermal and chemotherapy of cancer. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3433–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, L.; He, D.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Cheng, H.; Huang, X.; Shangguan, J. Facile fabrication of a resveratrol loaded phospholipid@reduced graphene oxide nanoassembly for targeted and near-infrared laser-triggered chemo/photothermal synergistic therapy of cancer in vivo. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 5783–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, M.; Cheng, W.; Zeng, X.; Mei, L.; Liu, G.; Deng, W. Folic Acid-Functionalized Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots for Targeted Chemo-Photothermal Combination Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050242
Luo M, Cheng W, Zeng X, Mei L, Liu G, Deng W. Folic Acid-Functionalized Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots for Targeted Chemo-Photothermal Combination Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(5):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050242
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Miaomiao, Wei Cheng, Xiaowei Zeng, Lin Mei, Gan Liu, and Wenbin Deng. 2019. "Folic Acid-Functionalized Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots for Targeted Chemo-Photothermal Combination Cancer Therapy" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 5: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050242
APA StyleLuo, M., Cheng, W., Zeng, X., Mei, L., Liu, G., & Deng, W. (2019). Folic Acid-Functionalized Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots for Targeted Chemo-Photothermal Combination Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics, 11(5), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050242