Elucidating the Influence of Tumor Presence on the Polymersome Circulation Time in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Polymersome Preparation
2.3. Radiolabeling and Radionuclide Retention
2.4. Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopy (Cryo-TEM) and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.5. Cellular Uptake Experiments
2.6. Animals
2.7. Blood Clearance
2.8. Clodronate Liposomes
2.9. Immunohistochemistry
3. Results and Discussion
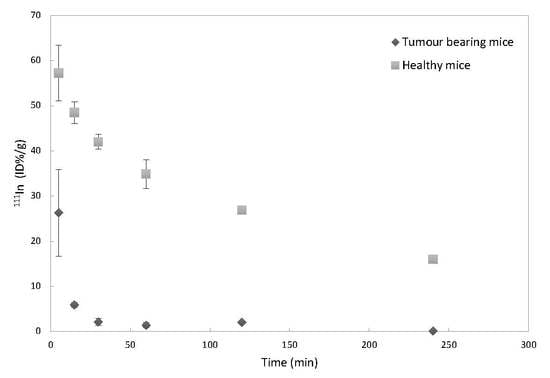
3.1. Circulation Time in Healthy Versus Tumor-Bearing Mice
3.2. Influence of Macrophages on Circulation Time
3.2.1. Cell Experiments
3.2.2. Animal Experiments
3.2.3. Comparison to Other Nanoparticle Systems
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Gu, F.; Chan, J.; Wang, A.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O. Nanoparticles in medicine: Therapeutic applications and developments. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. Nanoparticles in the clinic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2016, 1, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, M.E.R.; Wigler, N.; Inbar, M.; Rosso, R.; Grischke, E.; Santoro, A.; Catane, R.; Kieback, D.G.; Tomczak, P.; Ackland, S.P.; et al. Reduced cardiotoxicity and comparable efficacy in a phase III trial of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin HCl (CAELYX™/Doxil®) versus conventional doxorubicin for first-line treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerich, D.F.; Thanos, C.G. Targeted nanoparticle-based drug delivery and diagnosis. J. Drug Target. 2007, 15, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, H.; Baluk, P.; Morikawa, S.; McLean, J.W.; Thurston, G.; Roberge, S.; Jain, R.K.; McDonald, D.M. Openings between defective endothelial cells explain tumor vessel leakiness. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 1363–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Al Zaki, A.; Hui, J.Z.; Muzykantov, V.R.; Tsourkas, A. Multifunctional nanoparticles: Cost versus benefit of adding targeting and imaging capabilities. Science 2012, 338, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolkestein, M.; de Blois, E.; Koelewijn, S.J.; Eggermont, A.M.M.; Grosveld, F.; de Jong, M.; Koning, G.A. Investigation of factors determining the enhanced permeability and retention effect in subcutaneous xenografts. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, D.B.; Amiji, M.M. Poly(ethylene oxide)-modified poly(e-caprolactone) nanoparticles for targeted delivery of tamoxifen in breast cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 293, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Pakunlu, R.I.; Brannan, A.; Bates, F.; Minko, T.; Discher, D.E. Biodegradable polymersomes loaded with both paclitaxel and doxorubicin permeate and shrink tumors, inducing apoptosis in proportion to accumulated drug. J. Control. Release 2006, 116, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrois, G.J.R.; Allen, T.M. Drug release rate influences the pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, therapeutic activity, and toxicity of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin formulations in murine breast cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2004, 1663, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sawant, R.R.; Torchilin, V.P. Enhanced cytotoxicity of TATp-bearing paclitaxel-loaded micelles in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 374, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexis, F.; Pridgen, E.; Molnar, L.K.; Farokhzad, O.C. Factors affecting the clearance and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigger, I.; Dubernet, C.; Couvreur, P. Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-D.; Huang, L. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasic, D.D.; Needham, D. The “Stealth” liposome: A prototypical biomaterial. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 2601–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-W.; Chambers, E.; Mitragotri, S. Factors that control the circulation time of nanoparticles in blood: Challenges, solutions and future prospects. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 2298–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.-L.; Qi, X.-R.; Zhang, Q.; Li, R.-Y.; Wang, G.-L.; Zhang, R.-J.; Wei, S.-L. A PEGylated liposomal platform: Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and toxicity in mice using doxorubicin as a model drug. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 95, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klibanov, A.L.; Maruyama, K.; Torchilin, V.P.; Huang, L. Amphipathic polyethyleneglycols effectively prolong the circulation time of liposomes. FEBS Lett. 1990, 268, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litzinger, D.C.; Buiting, A.M.J.; van Rooijen, N.; Huang, L. Effect of liposome size on the circulation time and intraorgan distribution of amphipathic poly(ethylene glycol)-containing liposomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 1994, 1190, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkhuis, R.P.; Stojanov, K.; Laverman, P.; Eilander, J.; Zuhorn, I.S.; Rutjes, F.P.; Van Hest, J.C. Size dependent biodistribution and SPECT imaging of 111In-labeled polymersomes. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; de Kruijff, R.M.; Abou, D.; Ramos, N.; Mendes, E.; Franken, L.E.; Wolterbeek, H.T.; Denkova, A.G. Pharmacokinetics of polymersomes composed of poly(butadiene-ethylene oxide); Healthy versus tumor-bearing mice. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, M.P.; Brighton, H.E.; Fromen, C.A.; Shen, T.W.; Luft, J.C.; Luft, Y.E.; Keeler, A.W.; Robbins, G.R.; Ting, J.P.Y.; Zamboni, W.C.; et al. Tumor presence induces global immune changes and enhances nanoparticle clearance. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; de Kruijff, R.M.; Rol, A.; Thijssen, L.; Mendes, E.; Morgenstern, A.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Stuart, M.C.A.; Wolterbeek, H.T.; Denkova, A.G. Retention studies of recoiling daughter nuclides of 225Ac in polymer vesicles. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2014, 85, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kruijff, R.M.; Drost, K.; Thijssen, L.; Morgenstern, A.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Lathouwers, D.; Wolterbeek, H.T.; Denkova, A.G. Improved 225Ac daughter retention in InPO4 containing polymersomes. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2017, 128, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; de Kruijff, R.M.; Stuart, M.C.A.; Mendes, E.; Wolterbeek, H.T.; Denkova, A.G. Polymersomes as radionuclide carriers loaded via active ion transport through the hydrophobic bilayer. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Photos, P.J.; Bacakova, L.; Discher, B.; Bates, F.S.; Discher, D.E. Polymer vesicles in vivo: Correlations with PEG molecular weight. J. Control. Release 2003, 90, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rideau, E.; Dimova, R.; Schwille, P.; Wurm, F.R.; Landfester, K. Liposomes and polymersomes: A comparative review towards cell mimicking. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8571–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Discher, B.M.; Won, Y.-Y.; Ege, D.S.; Lee, J.C.-M.; Bates, F.S.; Discher, D.E.; Hammer, D.A. Polymersomes: Tough vesicles made from diblock copolymers. Science 1999, 284, 1143–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisberger, S.M.; Odermatt, B.; Marty, C.; Zehnder-Fjällman, A.H.M.; Ballmer-Hofer, K.; Schwendener, R.A. Clodronate-liposome-mediated depletion of tumor-associated macrophages: A new and highly effective antiangiogenic therapy approach. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: A review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kruijff, R.M.; van der Meer, A.J.G.M.; Windmeijer, C.A.A.; Kouwenberg, J.J.M.; Morgenstern, A.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Sminia, P.; Denkova, A.G. The therapeutic potential of polymersomes loaded with 225Ac evaluated in 2D and 3D in vitro glioma models. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiessling, R.; Wasserman, K.; Horiguchi, S.; Kono, K.; Sjoè Berg, J.; Pisa, P.; Petersson, M. Tumor-induced immune dysfunction. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 1999, 48, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.W.; Roberts, R.A.; Robbins, G.R.; Perry, J.L.; Kai, M.P.; Chen, K.; Bo, T.; Napier, M.E.; Ting, J.P.Y.; DeSimone, J.M.; et al. Nanoparticle clearance is governed by Th1/Th2 immunity and strain background. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 3061–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Owens, D.E., III; Peppas, N.A. Opsonization, biodistribution, and pharmacokinetics of polymeric nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 307, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgoustakis, K.; Beletsi, A.; Panagi, Z.; Klepetsanis, P.; Livaniou, E.; Evangelatos, G.; Ithakissios, D.S. Effect of copolymer composition on the physicochemical characteristics, in vitro stability, and biodistribution of PLGA-mPEG nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 259, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, C.J.H.; Moghimi, S.M.; Illum, L.; Davis, S.S. The polyoxyethylene/polyoxypropylene block co-polymer Poloxamer-407 selectively redirects intravenously injected microspheres to sinusoidal endothelial cells of rabbit bone marrow. FEBS Lett. 1992, 305, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsoi, K.M.; MacParland, S.A.; Ma, X.-Z.; Spetzler, V.N.; Echeverri, J.; Ouyang, B.; Fadel, S.M.; Sykes, E.A.; Goldaracena, N.; Kaths, J.M.; et al. Mechanism of hard-nanomaterial clearance by the liver. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terry, S.Y.A.; Boerman, O.C.; Gerrits, D.; Franssen, G.M.; Metselaar, J.M.; Lehmann, S.; Oyen, W.J.G.; Gerdes, C.A.; Abiraj, K. 111In-anti-F4/80-A3-1 antibody: A novel tracer to image macrophages. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, N.; Leroux, J.-C. The journey of a drug-carrier in the body: An anatomo-physiological perspective. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooijen, N.; Sanders, A. Liposome mediated depletion of macrophages: Mechanism of action, preparation of liposomes and applications. J. Immunol. Methods 1994, 174, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooijen, N.; Bakker, J.; Sanders, A. Transient suppression of macrophage functions by liposome-encapsulated drugs. Trends Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichele, P.; Zinke, J.; Grode, L.; Schwendener, R.A.; Kaufmann, S.H.E.; Seiler, P. Macrophages of the splenic marginal zone are essential for trapping of blood-borne particulate antigen but dispensable for induction of specific T cell responses. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demoy, M.; Gibaud, S.; Andreux, J.P.; Weingarten, C.; Gouritin, B.; Couvreur, P. Splenic trapping of nanoparticles: Complementary approaches for in situ studies. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demoy, M.; Andreux, J.P.; Weingarten, C.; Gouritin, B.; Guilloux, V.; Couvreur, P. Splenic capture of nanoparticles: Influence of animal species and surface characteristics. Pharm. Res. 1999, 16, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.; Pluddemann, A.; Martinez Estrada, F. Macrophage heterogeneity in tissues: Phenotypic diversity and functions. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 262, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawidczyk, C.M.; Russell, L.M.; Hultz, M.; Searson, P.C. Tumor accumulation of liposomal doxorubicin in three murine models: Optimizing delivery efficiency. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.D.; Ye, M.; Ulmschneider, M.B.; Searson, P.C. Quantitative analysis of the enhanced permeation and retention (EPR) effect. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0123461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoune, R.; Peters, A.; von Elverfeldt, D.; Winkler, K.; Pütz, G. Accumulating nanoparticles by EPR: A route of no return. J. Control. Release 2016, 238, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gref, R.; Minamitake, Y.; Peracchia, M.; Trubetskoy, V.; Torchilin, V.; Langer, R. Biodegradable long-circulating polymeric nanospheres. Science 1994, 263, 1600–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peracchia, M.T. Stealth nanoparticles for intravenous administration. STP Pharma Sci. 2003, 13, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Gabizon, A.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Liposome formulations with prolonged circulation time in blood and enhanced uptake by tumors (phospholipid vesicles/drug delivery systems/cancer therapy/glycolipids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 6949–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Kruijff, R.M.; Raavé, R.; Kip, A.; Molkenboer-Kuenen, J.; Roobol, S.J.; Essers, J.; Heskamp, S.; Denkova, A.G. Elucidating the Influence of Tumor Presence on the Polymersome Circulation Time in Mice. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050241
de Kruijff RM, Raavé R, Kip A, Molkenboer-Kuenen J, Roobol SJ, Essers J, Heskamp S, Denkova AG. Elucidating the Influence of Tumor Presence on the Polymersome Circulation Time in Mice. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(5):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050241
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Kruijff, Robin M., René Raavé, Annemarie Kip, Janneke Molkenboer-Kuenen, Stefan J. Roobol, Jeroen Essers, Sandra Heskamp, and Antonia G. Denkova. 2019. "Elucidating the Influence of Tumor Presence on the Polymersome Circulation Time in Mice" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 5: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050241
APA Stylede Kruijff, R. M., Raavé, R., Kip, A., Molkenboer-Kuenen, J., Roobol, S. J., Essers, J., Heskamp, S., & Denkova, A. G. (2019). Elucidating the Influence of Tumor Presence on the Polymersome Circulation Time in Mice. Pharmaceutics, 11(5), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050241