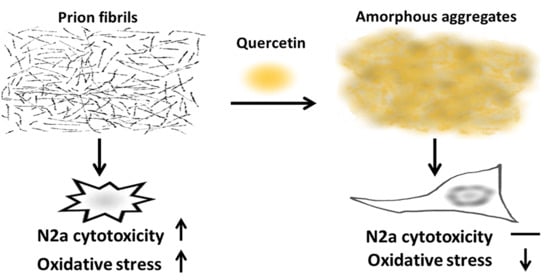
Quercetin Disaggregates Prion Fibrils and Decreases Fibril-Induced Cytotoxicity and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Expression and Purification of Recombinant moPrP
2.2. Fibril Conversion and Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.3. Protease K Digestion
2.4. Immunostaining and Fluorescence Imaging
2.5. Hemolytic Assay
2.6. Cell Viability and ROS Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Quercetin on Morphology of moPrP Fibrils
3.2. Effect of Quercetin on Structure and Protease-Resistance of moPrP Fibrils
3.3. Effect of Quercetin-Bound moPrP Fibrils on Hemolysis
3.4. Effect of Quercetin on moPrP Fibril Induced Cytotoxicity and ROS Level of N2a Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. 100 years of Lewy pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cooper, G.J.; Willis, A.C.; Clark, A.; Turner, R.C.; Sim, R.B.; Reid, K.B. Purification and characterization of a peptide from amyloid-rich pancreases of type 2 diabetic patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 8628–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desport, E.; Bridoux, F.; Sirac, C.; Delbes, S.; Bender, S.; Fernandez, B.; Quellard, N.; Lacombe, C.; Goujon, J.M.; Lavergne, D.; et al. Al amyloidosis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2012, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, P.; Will, R.G.; Bradley, R.; Asher, D.M.; Detwiler, L. Bovine spongiform encephalopathy and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Background, evolution, and current concerns. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milanesi, L.; Sheynis, T.; Xue, W.F.; Orlova, E.V.; Hellewell, A.L.; Jelinek, R.; Hewitt, E.W.; Radford, S.E.; Saibil, H.R. Direct three-dimensional visualization of membrane disruption by amyloid fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20455–20460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novitskaya, V.; Bocharova, O.V.; Bronstein, I.; Baskakov, I.V. Amyloid fibrils of mammalian prion protein are highly toxic to cultured cells and primary neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 13828–13836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambadi Thody, S.; Mathew, M.K.; Udgaonkar, J.B. Mechanism of aggregation and membrane interactions of mammalian prion protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 1927–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caughey, B.; Baron, G.S.; Chesebro, B.; Jeffrey, M. Getting a grip on prions: Oligomers, amyloids, and pathological membrane interactions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 177–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutala, W.A.; Weber, D.J.; Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Guideline for disinfection and sterilization of prion-contaminated medical instruments. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2010, 31, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glynn, C.; Sawaya, M.R.; Ge, P.; Gallagher-Jones, M.; Short, C.W.; Bowman, R.; Apostol, M.; Zhou, Z.H.; Eisenberg, D.S.; Rodriguez, J.A. Cryo-EM structure of a human prion fibril with a hydrophobic, protease-resistant core. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.; Kalita, S.; Kalita, S.; Sukumar, P.; Mandal, B. Disaggregation of amylin aggregate by novel conformationally restricted aminobenzoic acid containing alpha/beta and alpha/gamma hybrid peptidomimetics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, C.; Sigurdsson, E.M.; Morelli, L.; Kumar, R.A.; Castano, E.M.; Frangione, B. Beta-sheet breaker peptides inhibit fibrillogenesis in a rat brain model of amyloidosis: Implications for Alzheimer’s therapy. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolarinwa, O.; Li, C.; Khadka, N.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Pan, J.; Cai, J. γ-AApeptides-based small molecule ligands that disaggregate human islet amyloid polypeptide. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.; Ghormade, V.; Kolge, H.; Paknikar, K.M. Dual effect of chitosan-based nanoparticles on the inhibition of beta-amyloid peptide aggregation and disintegration of the preformed fibrils. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 3362–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.; Sorribas, A.; Howes, M.J. Natural products as a source of Alzheimer’s drug leads. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 48–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Misawa, K.; Nishimura, H.; Misawa, K.; Ota, N.; Shimotoyodome, A. Coffee polyphenols prevent cognitive dysfunction and suppress amyloid beta plaques in APP/PS2 transgenic mouse. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 154, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrich, K.; Bieschke, J. The effect of (-)-epigallo-catechin-(3)-gallate on amyloidogenic proteins suggests a common mechanism. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 863, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.F.; Yu, K.H.; Jheng, C.P.; Chung, R.; Lee, C.I. Curcumin reduces amyloid fibrillation of prion protein and decreases reactive oxidative stress. Pathogens 2013, 2, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyssin, A.; Page, G.; Fauconneau, B.; Rioux Bilan, A. Natural polyphenols effects on protein aggregates in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s prion-like diseases. Neural Regener. Res. 2018, 13, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossy-Wetzel, E.; Schwarzenbacher, R.; Lipton, S.A. Molecular pathways to neurodegeneration. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S2–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milhavet, O.; Lehmann, S. Oxidative stress and the prion protein in transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Brain Res. Rev. 2002, 38, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative Stress: A key modulator in neurodegenerative diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nijveldt, R.J.; van Nood, E.; van Hoorn, D.E.; Boelens, P.G.; van Norren, K.; van Leeuwen, P.A. Flavonoids: A review of probable mechanisms of action and potential applications. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 74, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boots, A.W.; Haenen, G.R.; Bast, A. Health effects of quercetin: From antioxidant to nutraceutical. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 585, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, A.; Ashida, H.; Terao, J. Multitargeted cancer prevention by quercetin. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Liu, Q.; Qin, S.; Zong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S.; Yang, N.; Guan, T.; Guo, S. Synthesis and cardiovascular protective effects of quercetin 7-O-sialic acid. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, Y.D.; Choi, C.H.; Bark, H.; Son, H.Y.; Park, H.H.; Lee, S.; Park, J.W.; Park, E.K.; Shin, H.I.; Kim, S.H. Quercetin inhibits expression of inflammatory cytokines through attenuation of NF-kappa B and p38 MAPK in HMC-1 human mast cell line. Inflamm. Res. 2007, 56, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.N.; Kim, J.H.; Kwak, J.H.; Jeong, C.H.; Jeong, H.R.; Lee, U.; Heo, H.J. Effect of quercetin on learning and memory performance in ICR mice under neurotoxic trimethyltin exposure. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabogal-Guaqueta, A.M.; Munoz-Manco, J.I.; Ramirez-Pineda, J.R.; Lamprea-Rodriguez, M.; Osorio, E.; Cardona-Gomez, G.P. The flavonoid quercetin ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease pathology and protects cognitive and emotional function in aged triple transgenic Alzheimer’s disease model mice. Neuropharmacology 2015, 93, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ono, K.; Yoshiike, Y.; Takashima, A.; Hasegawa, K.; Naiki, H.; Yamada, M. Potent anti-amyloidogenic and fibril-destabilizing effects of polyphenols in vitro: Implications for the prevention and therapeutics of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2003, 87, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Aliaga, K.; Bermejo-Bescos, P.; Benedi, J.; Martin-Aragon, S. Quercetin and rutin exhibit antiamyloidogenic and fibril-disaggregating effects in vitro and potent antioxidant activity in APPswe cells. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Han, S.; Fink, A.L. Oxidized quercetin inhibits alpha-synuclein fibrillization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 2872–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharova, O.V.; Breydo, L.; Parfenov, A.S.; Salnikov, V.V.; Baskakov, I.V. In vitro conversion of full-length mammalian prion protein produces amyloid form with physical properties of PrP(Sc). J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 346, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.J.; Yu, K.H.; Wu, J.R.; Lee, C.F.; Jheng, C.P.; Chen, H.R.; Lee, C.I. Liberation of GPI-anchored prion from phospholipids accelerates amyloidogenic conversion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17943–17957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novitskaya, V.; Makarava, N.; Bellon, A.; Bocharova, O.V.; Bronstein, I.B.; Williamson, R.A.; Baskakov, I.V. Probing the conformation of the prion protein within a single amyloid fibril using a novel immunoconformational assay. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 15536–15545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haurowitz, F. Hemoglobin, anhydro-hemoglobin, and oxyhemoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 443–452. [Google Scholar]
- Gibellini, L.; Pinti, M.; Nasi, M.; Montagna, J.P.; De Biasi, S.; Roat, E.; Bertoncelli, L.; Cooper, E.L.; Cossarizza, A. Quercetin and cancer chemoprevention. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med 2011, 2011, 591356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayin, V.I.; Ibrahim, M.X.; Larsson, E.; Nilsson, J.A.; Lindahl, P.; Bergo, M.O. Antioxidants accelerate lung cancer progression in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 221ra215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, S.; Shanmuganathan, B.; Balasubramaniam, B.; Balamurugan, K.; Devi, K.P. Phytol loaded PLGA nanoparticles regulate the expression of Alzheimer’s related genes and neuronal apoptosis against amyloid-beta induced toxicity in Neuro-2a cells and transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 110962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, R.; Kawabata, K.; Otsuka, S.; Ishisaka, A.; Kawai, Y.; Ji, Z.S.; Tsuboi, H.; Terao, J. Effect of quercetin and its glucuronide metabolite upon 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative damage in Neuro-2a cells. Free Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haney, C.M.; Cleveland, C.L.; Wissner, R.F.; Owei, L.; Robustelli, J.; Daniels, M.J.; Canyurt, M.; Rodriguez, P.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Baumgart, T.; et al. Site-specific fluorescence polarization for studying the disaggregation of alpha-synuclein fibrils by small molecules. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moss, M.A.; Varvel, N.H.; Nichols, M.R.; Reed, D.K.; Rosenberry, T.L. Nordihydroguaiaretic acid does not disaggregate beta-amyloid(1-40) protofibrils but does inhibit growth arising from direct protofibril association. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.F.; Hellewell, A.L.; Gosal, W.S.; Homans, S.W.; Hewitt, E.W.; Radford, S.E. Fibril fragmentation enhances amyloid cytotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 34272–34282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malishev, R.; Nandi, S.; Kolusheva, S.; Shaham-Niv, S.; Gazit, E.; Jelinek, R. Bacoside-A, an anti-amyloid natural substance, inhibits membrane disruption by the amyloidogenic determinant of prion protein through accelerating fibril formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 2208–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Sabareesan, A.T.; Mathew, M.K.; Udgaonkar, J.B. Development of the structural core and of conformational heterogeneity during the conversion of oligomers of the mouse prion protein to worm-like amyloid fibrils. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 423, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheignon, C.; Tomas, M.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C.; Collin, F. Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, H.I.; Lin, Z.Y.; Guo, J.X.; Lee, C.I. The effects of divalent cation-chelated prion fibrils on the immune response of EOC 13.31 microglia cells. Cells 2020, 9, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams-Koeppen, H.P.; Foster, J.S.; Hackenbrack, N.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M.; Donohoe, D.; Williams, A.; Macy, S.; Wooliver, C.; Wortham, D.; Morrell-Falvey, J.; et al. Light chain amyloid fibrils cause metabolic dysfunction in human cardiomyocytes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demuro, A.; Mina, E.; Kayed, R.; Milton, S.C.; Parker, I.; Glabe, C.G. Calcium dysregulation and membrane disruption as a ubiquitous neurotoxic mechanism of soluble amyloid oligomers. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 17294–17300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clapham, D.E. Calcium signaling. Cell 2007, 131, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gorlach, A.; Bertram, K.; Hudecova, S.; Krizanova, O. Calcium and ROS: A mutual interplay. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brennan-Minnella, A.M.; Won, S.J.; Swanson, R.A. NADPH oxidase-2: Linking glucose, acidosis, and excitotoxicity in stroke. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, K.-H.; Lee, C.-I. Quercetin Disaggregates Prion Fibrils and Decreases Fibril-Induced Cytotoxicity and Oxidative Stress. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111081
Yu K-H, Lee C-I. Quercetin Disaggregates Prion Fibrils and Decreases Fibril-Induced Cytotoxicity and Oxidative Stress. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(11):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111081
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Kun-Hua, and Cheng-I Lee. 2020. "Quercetin Disaggregates Prion Fibrils and Decreases Fibril-Induced Cytotoxicity and Oxidative Stress" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 11: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111081
APA StyleYu, K. -H., & Lee, C. -I. (2020). Quercetin Disaggregates Prion Fibrils and Decreases Fibril-Induced Cytotoxicity and Oxidative Stress. Pharmaceutics, 12(11), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111081