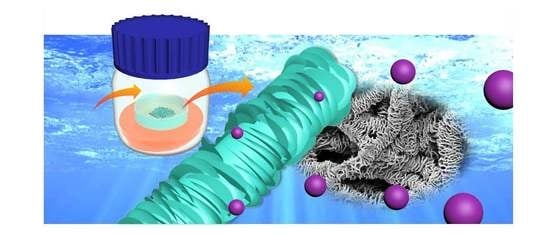
The Effect of Solvent Vapor Annealing on Drug-Loaded Electrospun Polymer Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrospinning
2.3. Solvent Vapor Annealing
2.4. Drug Loading and In Vitro Drug Release
2.5. Structure Analysis and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fiber Fabrication
3.2. Aging
3.3. Physical Form Characterisation
3.4. Drug Loading and In Vitro Release
3.5. Annealing and Release Mechanisms
3.6. Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, K. Controlled drug delivery systems: Past forward and future back. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monfared, M.; Taghizadeh, S.; Zare-Hoseinabadi, A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Ranjbar, S.; Amani, A.M. Emerging frontiers in drug release control by core–shell nanofibers: A review. Drug Metab. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.S. The origins and evolution of “controlled” drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrich, K.E.; Cannizzaro, S.M.; Langer, R.S.; Shakesheff, K.M. Polymeric systems for controlled drug release. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 3181–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauldbeck, H.; Le Hellaye, M.; Long, M.; Kennedy, S.M.; Williams, R.L.; Kearns, V.R.; Rannard, S.P. Controlling drug release from non-aqueous environments: Moderating delivery from ocular silicone oil drug reservoirs to combat proliferative vitreoretinopathy. J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Sang, Q.; Wu, J.; Williams, G.R.; Wang, H.; Niu, S.; Wu, J.; Zhu, L.-M. Dual-responsive drug delivery systems prepared by blend electrospinning. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 543, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, G.R.; Chatterton, N.P.; Nazir, T.; Yu, D.-G.; Zhu, L.-M.; Branford-White, C.J. Electrospun nanofibers in drug delivery: Recent developments and perspectives. Ther. Deliv. 2012, 3, 515–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleeton, C.; Keirouz, A.; Chen, X.; Radacsi, N. Electrospun nanofibers for drug delivery and biosensing. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 4183–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L. Electrospinning jets and polymer nanofibers. Polymer 2008, 49, 2387–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Xu, C.; He, H. Electrospinning of silica nanoparticles-entrapped nanofibers for sustained gentamicin release. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 516, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipour, M.; Mansouri, A.M.; Moradipour, P. Temozolomide conjugated carbon quantum dots embedded in core/shell nanofibers prepared by coaxial electrospinning as an implantable delivery system for cell imaging and sustained drug release. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.-Z.; Li, J.-J.; Yu, D.-G.; He, M.-F.; Yang, J.-H.; Williams, G.R. Nanosized sustained-release drug depots fabricated using modified tri-axial electrospinning. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.-G.; Li, X.-Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.-H.; Bligh, S.W.A.; Williams, G.R. Nanofibers fabricated using triaxial electrospinning as zero order drug delivery systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18891–18897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ismail, H.M.; Zamani, S.; Elrayess, M.A.; Kafienah, W.; Younes, H.M. New Three-dimensional poly(decanediol-co-tricarballylate) elastomeric fibrous mesh fabricated by photoreactive electrospinning for cardiac tissue engineering applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, K.; Kuang, H.; You, Z.; Morsi, Y.; Mo, X. Electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering with drug loading and release. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.Z.; Bauer, A.J.P.; Li, B.B. Solvent vapor annealing: An efficient approach for inscribing secondary nanostructures onto electrospun fibers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2014, 35, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Chiu, Y.J.; Lai, Y.C.; Fan, P.W.; Kuo, T.Y.; Liau, I.; Chen, J.T. Rayleigh-instability-driven morphology transformation of electrospun polymer fibers imaged by in situ optical microscopy and stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 51884–51892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-J.; Tseng, H.-F.; Lo, Y.-C.; Wu, B.-H.; Chen, J.-T. From Electrospun polymer core–shell fibers to polymer hemispheres and spheres: Two types of transformation processes and tearing films with linearly arranged cavities. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 9024–9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Olsen, B.C.; Luber, E.J.; Buriak, J.M. Nanopatterning via solvent vapor annealing of block copolymer thin films. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinturel, C.; Vayer, M.; Morris, M.; Hillmyer, M.A. Solvent vapor annealing of block polymer thin films. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 5399–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-J.; Chiu, H.-L.; Tseng, H.-F.; Wu, B.-H.; Li, J.-W.; Lu, T.-C.; Chen, J.-T. Fabrication and thermal insulation properties of bamboo-shaped polymer fibers by selective solvent vapor annealing. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1800424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.-J.; Liu, C.-T.; Weng, C.-C.; Chiu, T.-Y.; Li, J.-W.; Chen, J.-T. Sunny-Side-Up Egg-Shaped Structures: Surface Modification to Form Anisotropic Polymer Particles Driven by the Plateau–Rayleigh Instability as Fluorescence Manipulation Platforms. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedalwafa, M.; Wang, F.J.; Wang, L.; Li, C.J. Biodegradable poly-epsilon-caprolactone (pcl) for tissue engineering application: A review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2013, 34, 123–140. [Google Scholar]
- Malikmammadov, E.; Tanir, T.E.; Kiziltay, A.; Hasirci, V.; Hasirci, N. PCL and PCL-based materials in biomedical applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. 2018, 29, 863–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusu, M.; Ursu, M.; Rusu, D. Poly(vinyl chloride) and poly(e-caprolactone) blends for medical use. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2006, 19, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.J.P.; Grim, Z.B.; Li, B. Hierarchical polymer blend fibers of high structural regularity prepared by facile solvent vapor annealing treatment. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1700489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, C.G.; Chasalow, F.I.; Hibionada, Y.M.; Klimas, D.M.; Schindler, A. Aliphatic polyesters. I. The degradation of poly(ϵ-caprolactone) in vivo. J. Appl. Poly. Sci. 1981, 26, 3779–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A. Spironolactone: Disposition, metabolism, pharmacodynamics, and bioavailability. Drug Metab. Rev. 1978, 8, 151–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodzha, S.N.; Surmeneva, M.A.; Surmenev, R.A. Fabrication and characterization of polycaprolactone cross- linked and highly-aligned 3-D artificial scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration via electrospinning technology. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 98, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Resende, R.C.; Viana, O.; Freitas, J.T.J.; Bonfilio, R.; Ruela, A.L.M.; de Araujo, M.B. Analysis of spironolactone polymorphs in active pharmaceutical ingredients and their effect on tablet dissolution profiles. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 52, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Song, R.; Zhao, Y. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun polycaprolactone blended with chitosan-gelatin complex nanofibrous mats. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkarina, S.; Shkarin, R.; Weinhardt, V.; Melnik, E.; Vacun, G.; Kluger, P.J.; Loza, K.; Epple, M.; Ivlev, S.I.; Baumbach, T.; et al. 3D biodegradable scaffolds of polycaprolactone with silicate-containing hydroxyapatite microparticles for bone tissue engineering: High-resolution tomography and in vitro study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, J.; Saeedi, M.; Morteza-Semnani, K.; Kelidari, H.R.; Sadegh Moghanlou, F.; Zareh, G.; Rostamkalaei, S. The effect of Tween 20, 60, and 80 on dissolution behavior of sprionolactone in solid dispersions prepared by PEG 6000. Adv. Pharm. Bull 2015, 5, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lemos Barbosa, T.W.; Doriguetto, A.C.; Benjamim de Araújo, M.; Bonfilio, R. Solid-state characterization of spironolactone 1/3 Hydrate. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 2458–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, X.; Nguyen, T.X.; Tang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G. Nano-cellulose 3D-networks as controlled-release drug carriers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2976–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, D.A.; Colgan, S.T.; Langer, C.S.; Bandi, N.T.; Likar, M.D.; Van Alstine, L. Dissolution similarity requirements: How similar or dissimilar are the global regulatory expectations? AAPS J. 2016, 18, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample Name | Polymer Conc. (% w/v) | Drug Loading Conc. (% w/w) a | Annealing Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCL-0 | 13 | -- | -- |
| PCL-6 | 13 | -- | 6 |
| PCL-48 | 13 | -- | 48 |
| PCL-72 | 13 | -- | 72 |
| PCL-SPL-0 | 13 | 15 | -- |
| PCL-SPL-6 | 13 | 15 | 6 |
| PCL-SPL-48 | 13 | 15 | 48 |
| PCL-SPL-72 | 13 | 15 | 72 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, Y.-J.; Zhang, Z.; Dziemidowicz, K.; Nikoletopoulos, C.-G.; Angkawinitwong, U.; Chen, J.-T.; Williams, G.R. The Effect of Solvent Vapor Annealing on Drug-Loaded Electrospun Polymer Fibers. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12020139
Chiu Y-J, Zhang Z, Dziemidowicz K, Nikoletopoulos C-G, Angkawinitwong U, Chen J-T, Williams GR. The Effect of Solvent Vapor Annealing on Drug-Loaded Electrospun Polymer Fibers. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(2):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12020139
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, Yu-Jing, Ziwei Zhang, Karolina Dziemidowicz, Christos-Georgios Nikoletopoulos, Ukrit Angkawinitwong, Jiun-Tai Chen, and Gareth R. Williams. 2020. "The Effect of Solvent Vapor Annealing on Drug-Loaded Electrospun Polymer Fibers" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 2: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12020139
APA StyleChiu, Y. -J., Zhang, Z., Dziemidowicz, K., Nikoletopoulos, C. -G., Angkawinitwong, U., Chen, J. -T., & Williams, G. R. (2020). The Effect of Solvent Vapor Annealing on Drug-Loaded Electrospun Polymer Fibers. Pharmaceutics, 12(2), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12020139