The Selective NMDA Receptor GluN2B Subunit Antagonist CP-101,606 with Antidepressant Properties Modulates Cytochrome P450 Expression in the Liver
Abstract
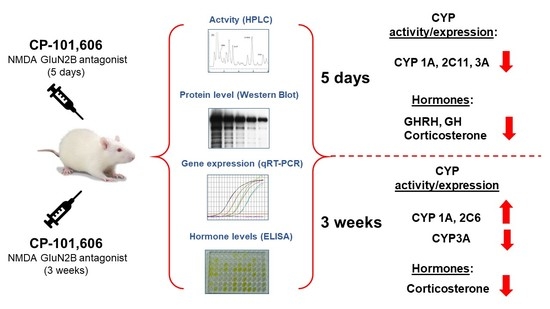
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Effect of CP-101,606 on the CYP1A Activity and Expression in Rat Liver after 5-Day and 3-Week Treatment
2.2. The Effect of CP-101,606 on the CYP2A Activity and Expression in Rat Liver after 5-Day and 3-Week Treatment
2.3. The Effect of CP-101,606 on the CYP2B Activity and Expression in Rat Liver after 5-Day and 3-Week Treatment
2.4. The Effect of CP-101,606 on the CYP2C6 Activity and Expression in Rat Liver after 5-Day and 3-Week Treatment
2.5. The Effect of CP-101,606 on the CYP2C11 Activity and Expression in Rat Liver after 5-Day and 3-Week Treatment
2.6. The Effect of CP-101,606 on the CYP3A Activity and Expression in Rat Liver after 5-Day and 3-Week Treatment
2.7. The Effect of CP-101,606 on Pituitary and Serum Hormone Levels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Materials
4.2. Collection of Pituitary, Liver and Serum Samples
4.3. Estimation of Cytochrome P450 Enzyme Activities in Rat Liver Microsomes
4.4. Estimation of the Cytochrome P450 Enzyme Protein Levels in Liver Microsomes
4.5. Determination of Hormone and Cytokine Levels
4.6. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wójcikowski, J.; Gołembiowska, K.; Daniel, W.A. The regulation of liver cytochrome P450 by the brain dopaminergic system. Curr. Drug Metab. 2007, 8, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcikowski, J.; Gołembiowska, K.; Daniel, W.A. Regulation of liver cytochrome P450 by activation of brain dopaminergic system: Physiological and pharmacological implications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcikowski, J.; Daniel, W.A. The brain dopaminergic system as an important center regulating liver cytochrome P450 in the rat. Exp. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadakierska-Chudy, A.; Haduch, A.; Rysz, M.; Gołembiowska, K.; Daniel, W.A. The role of brain noradrenergic system in the regulation of liver cytochrome P450 expression. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromek, E.; Wójcikowski, J.; Daniel, W.A. Involvement of the paraventricular (PVN) and arcuate (ARC) nuclei of the hypothalamus in the central noradrenergic regulation of liver cytochrome P450. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kot, M.; Sadakierska-Chudy, A.; Haduch, A.; Rysz, M.; Bromek, E.; Gołembiowska, K.; Daniel, W.A. The role of the dorsal noradrenergic pathway of the brain (locus coeruleus) in the regulation of liver cytochrome P450 activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 751, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rysz, M.; Bromek, E.; Haduch, A.; Sadakierska-Chudy, A.; Daniel, W.A. Damage to the brain serotonergic system increases the expression of liver cytochrome P450. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rysz, M.; Bromek, E.; Daniel, W.A. Activation of brain serotonergic system by repeated intracerebral administration of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) decreases the expression and activity of liver cytochrome P450. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 99, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rysz, M.; Bromek, E.; Haduch, A.; Liskova, B.; Wójcikowski, J.; Daniel, W.A. The reverse role of the hypothalamic paraventricular (PVN) and arcuate (ARC) nuclei in the central serotonergic regulation of the liver cytochrome P450 isoform CYP2C11. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 112, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromek, E.; Rysz, M.; Haduch, A.; Wójcikowski, J.; Daniel, W.A. Activation of 5-HT1A Receptors in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nuclei Negatively Regulates Cytochrome P450 Expression and Activity in Rat Liver. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bromek, E.; Rysz, M.; Haduch, A.; Daniel, W.A. Serotonin Receptors of 5-HT2 Type in the Hypothalamic Arcuate Nuclei Positively Regulate Liver Cytochrome P450 via Stimulation of the Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone/Growth Hormone Hormonal Pathway. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2019, 47, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bromek, E.; Rysz, M.; Haduch, A.; Daniel, W.A. Stimulation of 5-HT2C serotonin receptor subtype in the hypothalamic arcuate nuclei (ARC) increases the cytochrome P450 activity in the liver. Pharmacol. Rep. 2019, 71, 1210–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromek, E.; Daniel, W.A. The regulation of liver cytochrome P450 expression and activity by the brain serotonergic system in different experimental models. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2021, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Meeker, R.B.; Greenwood, R.S.; Hayward, J.N. Glutamate receptors in the rat hypothalamus and pituitary. Endocrinology 1994, 134, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csáki, A.; Kocsis, K.; Halász, B.; Kiss, J. Localization of glutamatergic/aspartatergic neurons projecting to the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus studied by retrograde transport of [3H]D-aspartate autoradiography. Neuroscience 2000, 101, 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, G.; Lechan, R.M.; Liposits, Z.; Fekete, C. Glutamatergic innervation of corticotropin-releasing hormone- and thyrotropin-releasing hormone-synthesizing neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of the rat. Brain Res. 2005, 1039, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, J.; Csaba, Z.; Csáki, Á.; Halász, B. Glutamatergic innervation of growth hormone-releasing hormone-containing neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus and somatostatin-containing neurons in the anterior periventricular nucleus of the rat. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 70, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabovszky, E.; Deli, L.; Turi, G.F.; Kallo, I.; Liposits, Z. Glutamatergic innervation of the hypothalamic median eminence and posterior pituitary of the rat. Neuroscience 2007, 144, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabovszky, E.; Liposits, Z. Novel aspects of glutamatergic signaling in the neuroendocrine system. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brann, D.W.; Mahesh, V.B. Excitatory amino acids: Function and significance in reproduction and neuroendocrine regulation. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 1994, 15, 3–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brann, D.W. Glutamate: A major excitatory transmitter in neuroendocrine regulation. Neuroendocrinology 1995, 61, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalobos, B.; Núnez, L.; Garcia-Sancho, J. Functional glutamate receptors in a subpopulation of anterion pituitary cells. Res. Commun. 1996, 10, 654–660. [Google Scholar]
- Evanson, N.K.; Van Hooren, D.C.; Herman, J.P. GluR5-mediated glutamate signaling regulates hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical stress responses at the paraventricular nucleus and median eminence. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aizawa, S.; Sakai, T.; Sakata, I. Glutamine and glutamic acid enhance thyroid-stimulating hormone β subunit mRNA expression in the rat pars tuberalis. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 212, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, M.; Durán, R.; Arufe, M.C. Effect of excitatory amino acids on serum TSH and thyroid hormone levels in freely moving rats. Horm. Res. 2000, 54, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arufe, M.C.; Durán, R.; Perez-Vences, D.; Alfonso, M. Endogenous excitatory amino acid neurotransmission regulates thyroid-stimulating hormone and thyroid hormone secretion in conscious freely moving male rats. Endocrine 2002, 17, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanson, N.K.; Herman, J.P. Role of Paraventricular Nucleus Glutamate Signaling in Regulation of HPA Axis Stress Responses. Interdiscip. Inf. Sci. 2015, 21, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguilar, E.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Pinilla, L. Role of excitatory amino acids in the control of growth hormone secretion. Endocrine 2005, 28, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henter, I.D.; de Sousa, R.T.; Zarate, C.A., Jr. Glutamatergic Modulators in Depression. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2018, 26, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.T.; Wei, L.; Chen, T.L.; Huang, C.J.; Chen, R.M. Regulation of cytochrome P450 gene expression by ketamine: A review. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, M.; Phillips, C.; Fahimi, A.; McNerney, M.W.; Salehi, A. Mechanisms of action and clinical efficacy of NMDA receptor modulators in mood disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 80, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, E.; Mallien, A.S.; Vasilescu, A.N.; Hefter, D.; Luoni, A.; Riva, M.A.; Borgwardt, S.; Sprengel, R.; Lang, U.E.; Gass, P.; et al. Molecular and cellular dissection of NMDA receptor subtypes as antidepressant targets. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 84, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochwat, B.; Nowak, G.; Szewczyk, B. An update on NMDA antagonists in depression. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.T.; Sanacora, G. A new generation of antidepressants: An update on the pharmaceutical pipeline for novel and rapid-acting therapeutics in mood disorders based on glutamate/GABA neurotransmitter systems. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adell, A. Brain NMDA Receptors in Schizophrenia and Depression. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chazot, P.L.; Lawrence, S.; Thompson, C.L. Studies on the subtype selectivity of CP-101,606: Evidence for two classes of NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology 2002, 42, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preskorn, S.H.; Baker, B.; Kolluri, S.; Menniti, F.S.; Krams, M.; Landen, J.W. An innovative design to establish proof of concept of the antidepressant effects of the NR2B subunit selective N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist, CP-101,606, in patients with treatment-refractory major depressive disorder. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2008, 28, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gass, N.; Becker, R.; Sack, M.; Schwarz, A.J.; Reinwald, J.; Cosa-Linan, A.; Zheng, L.; von Hohenberg, C.C.; Inta, D.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; et al. Antagonism at the NR2B subunit of NMDA receptors induces increased connectivity of the prefrontal and subcortical regions regulating reward behavior. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 1055–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, C.A.; Bartlett, J.M.; Arban, R.; Hengerer, B.; Robinson, E.S.J. Role of the medial prefrontal cortex in the effects of rapid acting antidepressants on decision-making biases in rodents. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 2278–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, D.J.; O’Connor, C. Growth hormone regulation of sex-dependent liver gene expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 2613–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, D.J.; Holloway, M.G. Sex differences in the expression of hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monostory, K.; Dvorak, Z. Steroid regulation of drug-metabolizing cytochromes P450. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monostory, K.; Pascussi, J.M.; Kóbori, L.; Dvorak, Z. Hormonal regulation of CYP1A expression. Drug Metab. Rev. 2009, 41, 547–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorak, Z.; Pavek, P. Regulation of drug-metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes by glucocorticoids. Drug Metab. Rev. 2010, 42, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brtko, J.; Dvorak, Z. Role of retinoids and thyroid hormone in the expression of cytochrome P450 enzymes. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójcikowski, J.; Daniel, W.A. The role of the nervous system in the regulation of liver cytochrome P450. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Tokarski, K.; Bobula, B.; Zajdel, J.; Jastrzębska, K.; Cieślak, P.E.; Zygmunt, M.; Sowa, J.; Smutek, M.; Kamińska, K.; et al. NMDA Receptors on Dopaminoceptive Neurons Are Essential for Drug-Induced Conditioned Place Preference. ENeuro 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cieślak, P.E.; Llamosas, N.; Kos, T.; Ugedo, L.; Jastrzębska, K.; Torrecilla, M.; Rodriguez Parkitna, J. The role of NMDA receptor-dependent activity of noradrenergic neurons in attention, impulsivity and exploratory behaviors. Genes Brain Behav. 2017, 16, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wójcikowski, J.; Daniel, W.A. Identification of factors mediating the effect of the brain dopaminergic system on the expression of cytochrome P450 in the liver. Pharmacol. Rep. 2008, 60, 966–971. [Google Scholar]
- Zidek, Z.; Anzenbacher, P.; Kmonickova, E. Current status and challenges of cytokine pharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 342–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loch, J.M.; Potter, J.; Bachmann, K.A. The influence of anesthetic agents on rat hepatic cytochromes P450 in vivo. Pharmacology 1995, 50, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.H.; Sun, W.Z.; Ueng, T.H. Induction of rat hepatic cytochrome P-450 by ketamine and its toxicological implications. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2005, 68, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, M.; Gruca, P.; Lason-Tyburkiewicz, M.; Willner, P. Antidepressant, anxiolytic and procognitive effects of subacute and chronic ketamine in the chronic mild stress model of depression. Behav. Pharmacol. 2017, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanos, P.; Moaddel, R.; Morris, P.J.; Georgiou, P.; Fischell, J.; Elmer, G.I.; Alkondon, M.; Yuan, P.; Pribut, H.J.; Singh, N.S.; et al. NMDAR inhibition-independent antidepressant actions of ketamine metabolites. Nature 2016, 533, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zanos, P.; Highland, J.N.; Stewart, B.W.; Georgiou, P.; Jenne, C.E.; Lovett, J.; Morris, P.J.; Thomas, C.J.; Moaddel, R.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; et al. (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine exerts mGlu2 receptor-dependent antidepressant actions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6441–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daniel, W.A.; Haduch, A.; Syrek, M.; Boksa, J. Direct and indirect interactions between antidepressant drugs and CYP2C6 in the rat liver during long-term treatment. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2006, 16, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.; Wojcik, T.; Baireddy, P.; Pieschl, R.; Newton, A.; Tian, Y.; Hong, Y.; Bristow, L.; Li, Y.W. Inhibition of in vivo [(3)H]MK-801 binding by NMDA receptor open channel blockers and GluN2B antagonists in rats and mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 766, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, W.A.; Haduch, A.; Wójcikowski, J. Inhibition and possibile induction of rat CYP2D after short- and long-term treatment with antidepressants. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2002, 54, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kot, M.; Daniel, W.A. Relative Contribution of Rat Cytochrome P450 Isoforms to the Metabolism of Caffeine: The Pathway and Concentration Dependence. Biochem. Pharm. 2008, 75, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcikowski, J.; Haduch, A.; Daniel, W.A. Effect of antidepressant drugs on cytochrome P450 2C11 (CYP2C11) in rat liver. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haduch, A.; Wójcikowski, J.; Daniel, W.A. The effect of tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and newer antidepressant drugs on the activity and level of rat CYP3A. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2006, 16, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haduch, A.; Wójcikowski, J.; Daniel, W.A. Effect of selected antidepressant drugs on cytochrome P450 2B (CYP2B) in rat liver. An in vitro and in vivo study. Pharmacol. Rep. 2008, 60, 957–965. [Google Scholar]









| CYPs | 5 Days | 3 Weeks | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activity | Protein | mRNA | Activity | Protein | mRNA | |||||
| 1A1/2 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | ||
| 2A1/2 |  |  |  |  |  | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. | ||
| 2B1/2 |  |  |  |  |  | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. | ||
| 2C6 |  | n.t. | n.t. |  |  |  | ||||
| 2C11 |  |  |  |  | n.t. | n.t. | ||||
| 3A1/2 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | ||
| Gene Name | Assay ID |
|---|---|
| CYP1A1 | Rn01418021_g1 |
| CYP1A2 | Rn00561082_m1 |
| CYP2A1 | Rn04219367_m1 |
| CYP2A2 | Rn00562207_m1 |
| CYP2B1 | Rn01457880_m1 |
| CYP2B2 | Rn02786833_m1 |
| CYP2C6 | Rn03417171_gH |
| CYP2C11 | Rn01502203_m1 |
| CYP3A1 | Rn03062228_m1 |
| CYP3A2 | Rn00756461_m1 |
| ACTB | Rn00667869_m1 |
| GAPDH | Rn01462662_g1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bromek, E.; Haduch, A.; Rysz, M.; Jastrzębska, J.; Pukło, R.; Wójcikowska, O.; Danek, P.J.; Daniel, W.A. The Selective NMDA Receptor GluN2B Subunit Antagonist CP-101,606 with Antidepressant Properties Modulates Cytochrome P450 Expression in the Liver. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101643
Bromek E, Haduch A, Rysz M, Jastrzębska J, Pukło R, Wójcikowska O, Danek PJ, Daniel WA. The Selective NMDA Receptor GluN2B Subunit Antagonist CP-101,606 with Antidepressant Properties Modulates Cytochrome P450 Expression in the Liver. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(10):1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101643
Chicago/Turabian StyleBromek, Ewa, Anna Haduch, Marta Rysz, Joanna Jastrzębska, Renata Pukło, Olga Wójcikowska, Przemysław Jan Danek, and Władysława Anna Daniel. 2021. "The Selective NMDA Receptor GluN2B Subunit Antagonist CP-101,606 with Antidepressant Properties Modulates Cytochrome P450 Expression in the Liver" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 10: 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101643
APA StyleBromek, E., Haduch, A., Rysz, M., Jastrzębska, J., Pukło, R., Wójcikowska, O., Danek, P. J., & Daniel, W. A. (2021). The Selective NMDA Receptor GluN2B Subunit Antagonist CP-101,606 with Antidepressant Properties Modulates Cytochrome P450 Expression in the Liver. Pharmaceutics, 13(10), 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101643