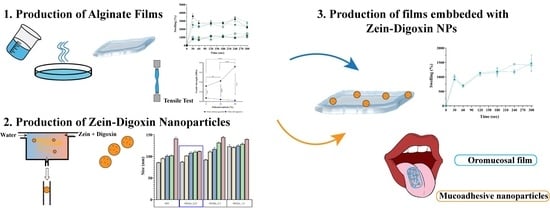
Oromucosal Alginate Films with Zein Nanoparticles as a Novel Delivery System for Digoxin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Sodium Alginate Films
2.3. Characterization of Films
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
2.3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.3. Thickness
2.3.4. Mechanical Properties
2.3.5. Swelling Profile
2.3.6. Dissolution Time
2.4. Preparation of Zein Nanoparticles with Embedded Digoxin
2.5. Particle Size, Zeta Potential and Polydispersity Index (PDI)
2.6. Determination of Standard Calibration Curve and Encapsulation Efficiency of Digoxin into Nanoparticles
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
3.3. Thickness
3.4. Mechanical Properties
3.5. Swelling Profile
3.6. Dissolution Time
3.7. Characterization of Zein Nanoparticles
3.8. Digoxin Encapsulation Efficiency
3.9. Characterization of SA Films Embedded with Zein-Digoxin Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Groenewegen, A.; Rutten, F.H.; Mosterd, A.; Hoes, A.W. Epidemiology of heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 1342–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Sanchis-Gomar, F. Global epidemiology and future trends of heart failure. AME Med. J. 2020, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghiade, M.; Adams, K.F.; Colucci, W.S. Digoxin in the management of cardiovascular disorders. Circulation 2004, 109, 2959–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.W.M.; Rybak, I. Use of digoxin for heart failure and atrial fibrillation in elderly patients. Am. J. Geriatr. Pharmacother. 2010, 8, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.; Adams, R.J.; Brown, T.M.; Carnethon, M.; Dai, S.; De Simone, G.; Ferguson, T.B.; Ford, E.; Furie, K.; Gillespie, C.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2010 update: A report from the American heart association. Circulation 2010, 121, e46–e215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angraal, S.; Nuti, S.V.; Masoudi, F.A.; Freeman, J.V.; Murugiah, K.; Shah, N.D.; Desai, N.R.; Ranasinghe, I.; Wang, Y.; Krumholz, H.M. Digoxin Use and Associated Adverse Events Among Older Adults. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewy, G.A. Digoxin: The art and science. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 1272–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renom-Guiteras, A.; Meyer, G.; Thürmann, P.A. The EU(7)-PIM list: A list of potentially inappropriate medications for older people consented by experts from seven European countries. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 861–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Idrees, H.; Zaidi, S.Z.J.; Sabir, A.; Khan, R.U.; Zhang, X.; Hassan, S.U. A review of biodegradable natural polymer-based nanoparticles for drug delivery applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, G.; Paderni, C.; Saccone, R.; Fede, O.; Wolff, A.; Giannola, L. Human Buccal Mucosa as an Innovative Site of Drug Delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Naik, P.K.; Pradhan, D.; Ghosh, G.; Rath, G. Mucoadhesive formulations: Innovations, merits, drawbacks, and future outlook. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2020, 25, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shojaei, A.H. Buccal mucosa as a route for systemic drug delivery: A review. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 1, 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- Boddupalli, B.M.; Mohammed, Z.N.K.; Nath, A.R.; Banji, D. Mucoadhesive drug delivery system: An overview. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2010, 1, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mansuri, S.; Kesharwani, P.; Jain, K.; Tekade, R.K.; Jain, N.K. Mucoadhesion: A promising approach in drug delivery system. React. Funct. Polym. 2016, 100, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavkova, M.; Breitkreutz, J. Orodispersible drug formulations for children and elderly. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 75, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yir-Erong, B.; Bayor, M.T.; Ayensu, I.; Gbedema, S.Y.; Boateng, J.S. Oral thin films as a remedy for noncompliance in pediatric and geriatric patients. Ther. Deliv. 2019, 10, 443–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, R.; Singh, T.R.R.; Garland, M.J.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, E.T.L.; Steadman, K.J.; Cichero, J.A.Y.; Nissen, L.M. Dosage form modification and oral drug delivery in older people. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 135, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irfan, M.; Rabel, S.; Bukhtar, Q.; Qadir, M.I.; Jabeen, F.; Khan, A. Orally disintegrating films: A modern expansion in drug delivery system. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arya, A.; Chandra, A.; Sharma, V.; Pathak, K. Fast dissolving oral films: An innovative drug delivery system and dosage form. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2010, 2, 576–583. [Google Scholar]
- Kadajji, V.G.; Betageri, G.V. Water soluble polymers for pharmaceutical applications. Polymers 2011, 3, 1972–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sellimi, S.; Younes, I.; Ayed, H.B.; Maalej, H.; Montero, V.; Rinaudo, M.; Dahia, M.; Mechichi, T.; Hajji, M.; Nasri, M. Structural, physicochemical and antioxidant properties of sodium alginate isolated from a Tunisian brown seaweed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, P.M.; Sousa, F.; Magalhães, R.; Ruiz-Henestrosa, V.M.P.; Pilosof, A.M.R.; Madureira, A.R.; Sarmento, B.; Pintado, M.E. Incorporation of beads into oral films for buccal and oral delivery of bioactive molecules. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 194, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morales, J.O.; McConville, J.T. Manufacture and characterization of mucoadhesive buccal films. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 77, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, F.; Uzunsoy, İ.; Baştürk, E.; Kahraman, M.V. Antimicrobial agent-free hybrid cationic starch/sodium alginate polyelectrolyte films for food packaging materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 170, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puscaselu, R.; Gutt, G.; Amariei, S. The use of edible films based on sodium alginate in meat product packaging: An eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastic materials. Coatings 2020, 10, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, D.; Bar-Shalom, D. Alginate drug delivery systems: Application in context of pharmaceutical and biomedical research. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grottkau, B.; Cai, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Lin, Y. Polymeric Nanoparticles for a Drug Delivery System. Curr. Drug Metab. 2013, 14, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczewska, A.Z.; Niemirowicz, K.; Markiewicz, K.H.; Car, H. Nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 1020–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argos, P.; Pedersen, K.; Marks, M.D.; Larkins, B.A. A structural model for maize zein proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 9984–9990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Zein-based micro- and nano-particles for drug and nutrient delivery: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoli, M.; de Lima, R.; Fraceto, L.F. Zein nanoparticles and strategies to improve colloidal stability: A mini-review. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, R.; Palakurthi, S. Zein in controlled drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2014, 189, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardi, A.; Bisharat, L.; AlKhatib, H.S.; Cespi, M. Zein as a Pharmaceutical Excipient in Oral Solid Dosage Forms: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 2009–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia-Hernández, J.A.; Rodríguez-Felix, F.; Juárez-Onofre, J.E.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Robles-García, M.A.; Borboa-Flores, J.; Wong-Corral, F.J.; Cinco-Moroyoqui, F.J.; Castro-Enríquez, D.D.; Del-Toro-Sánchez, C.L. Zein-polysaccharide nanoparticles as matrices for antioxidant compounds: A strategy for prevention of chronic degenerative diseases. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 451–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Rosa, C.G.; de Oliveira Brisola Maciel, M.V.; de Carvalho, S.M.; de Melo, A.P.Z.; Jummes, B.; da Silva, T.; Martelli, S.M.; Villetti, M.A.; Bertoldi, F.C.; Barreto, P.L.M. Characterization and evaluation of physicochemical and antimicrobial properties of zein nanoparticles loaded with phenolics monoterpenes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 481, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhakamy, N.A.; Ahmed, O.A.A.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Eid, B.G.; Abdel-Naim, A.B.; Fahmy, U.A. Encapsulation of lovastatin in zein nanoparticles exhibits enhanced apoptotic activity in hepg2 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boateng-Marfo, Y.; Dong, Y.; Ng, W.K.; Lin, H.S. Artemether-loaded zein nanoparticles: An innovative intravenous dosage form for the management of severe malaria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Wang, B.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Q.; Qian, J.; Zha, L.; Chen, W.; Hong, L. Preparation and preliminary pharmacokinetics study of GNA-loaded zein nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Dong, X.; Zhou, L.; Xiao, H.; Ho, P.Y.; Wong, M.S.; Wang, Y. Doxorubicin-loaded biodegradable self-assembly zein nanoparticle and its anti-cancer effect: Preparation, in vitro evaluation, and cellular uptake. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 140, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.F.; Guo, H.X. Preparation of new 5-fluorouracil-loaded zein nanoparticles for liver targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 404, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Kang, N.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.H.; Chae, J.W.; Lee, W.; Song, G.Y.; Cho, C.W.; Kim, D.D.; Lee, J.Y. Chondroitin sulfate-hybridized zein nanoparticles for tumor-targeted delivery of docetaxel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, P.; Agraval, H.; Srivastav, A.K.; Yadav, U.C.S.; Kumar, U. Physico-chemical characterization of carvacrol loaded zein nanoparticles for enhanced anticancer activity and investigation of molecular interactions between them by molecular docking. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 588, 119795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wu, H.; Hu, H.; Dong, Z.; Dang, Y.; Qi, Q.; Wang, Y.; Du, S.; Lu, Y. Zein nanoparticles as nontoxic delivery system for maytansine in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reboredo, C.; González-Navarro, C.J.; Martínez-Oharriz, C.; Martínez-López, A.L.; Irache, J.M. Preparation and evaluation of PEG-coated zein nanoparticles for oral drug delivery purposes. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 597, 120287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.P.; Geckeler, K.E. Polymer nanoparticles: Preparation techniques and size-control parameters. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 887–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gültekin, H.E.; Deǧim, Z. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles are effective systems for controlled drug delivery. Fabad J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 38, 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Kamaly, N.; Yameen, B.; Wu, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. Degradable controlled-release polymers and polymeric nanoparticles: Mechanisms of controlling drug release. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2602–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez, A.; Mejía, S.P.; Orozco, J. Recent advances in polymeric nanoparticle-encapsulated drugs against intracellular infections. Molecules 2020, 25, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, M.L.; De Freitas, O. Oral bioadhesive drug delivery systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2005, 31, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, X. Improving surface and mechanical properties of alginate films by using ethanol as a co-solvent during external gelation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alopaeus, J.F.; Hellfritzsch, M.; Gutowski, T.; Scherließ, R.; Almeida, A.; Sarmento, B.; Škalko-Basnet, N.; Tho, I. Mucoadhesive buccal films based on a graft co-polymer—A mucin-retentive hydrogel scaffold. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 142, 105142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, M.R.C.; Loebenberg, R.; Almukainzi, M. Simulated biological fluids with possible application in dissolution testing. Dissolution Technol. 2011, 18, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhu, Z.; Qian, H.; Wohl, A.R.; Beaman, C.J.; Hoye, T.R.; Macosko, C.W. A simple confined impingement jets mixer for flash nanoprecipitation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 4018–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milenković, M.Z.; Marinković, V.D.; Sibinović, P.S.; Palić, R.M.; Milenović, D.M. An HPLC method for the determination of digoxin in dissolution samples. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2010, 75, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.Y.; Jia, X.W.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B.H.; Wang, H. Fast dissolving oral films for drug delivery prepared from chitosan/pullulan electrospinning nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.D.; Shen, C.Y.; Yuan, X.D.; Bai, J.X.; Lv, Q.Y.; Xu, H.; Dai, L.; Yu, C.; Han, J.; Yuan, H.L. Development and characterization of an orodispersible film containing drug nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.A.; Stefano, J.S.; Janegitz, B.C. Sensing Materials: Nanomaterials Definition. In Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wasilewska, K.; Winnicka, K. How to assess orodispersible film quality? A review of applied methods and their modifications. Acta Pharm. 2019, 69, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helmiyati; Aprilliza, M. Characterization and properties of sodium alginate from brown algae used as an ecofriendly superabsorbent. IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 188, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Hsieh, Y. Lo Biocompatible sodium alginate fibers by aqueous processing and physical crosslinking. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurikov, P.; Smirnova, I. Non-conventional methods for gelation of alginate. Gels 2018, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tkalec, G.; Knez, Ž.; Novak, Z. Formation of polysaccharide aerogels in ethanol. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 77362–77371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, M.A.; Souza, B.W.S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vicente, A.A. Effect of glycerol and corn oil on physicochemical properties of polysaccharide films—A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nair, A.B.; Kumria, R.; Harsha, S.; Attimarad, M.; Al-Dhubiab, B.E.; Alhaider, I.A. In vitro techniques to evaluate buccal films. J. Control. Release 2013, 166, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, R.H.; Shah, D.A.; Patel, P.G. Development and Evaluation of High Loading Oral Dissolving Film of Aspirin and Acetaminophen. J. Pharm. Sci. Pharmacol. 2014, 1, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitencourt, C.M.; Fávaro-Trindade, C.S.; Sobral, P.J.A.; Carvalho, R.A. Gelatin-based films additivated with curcuma ethanol extract: Antioxidant activity and physical properties of films. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 40, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevinç Özakar, R.; Özakar, E. Current overview of oral thin films. Turkish J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 18, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafee, N.A.; Ismail, F.A.; Boraie, N.A.; Mortada, L.M. Mucoadhesive delivery systems. I. Evaluation of mucoadhesive polymers for buccal tablet formulation. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2004, 30, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mogherah, A.I.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Hassan, M.A. Optimization and evaluation of venlafaxine hydrochloride fast dissolving oral films. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilhotra, R.M.; Ikram, M.; Srivastava, S.; Gilhotra, N. A clinical perspective on mucoadhesive buccal drug delivery systems. J. Biomed. Res. 2014, 28, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, A.F.; Silva, C.; Coelho, J.F.J.; Simões, S. Oral films: Current status and future perspectives: I-Galenical development and quality attributes. J. Control. Release 2015, 206, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Leng, P.; Liu, Y. Oral drug delivery with nanoparticles into the gastrointestinal mucosa. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Kuang, H.; Wang, X. Annonaceous acetogenins (ACGs) nanosuspensions based on a self-assembly stabilizer and the significantly improved anti-tumor efficacy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Tang, X.; Pan, W.; Han, J.; He, Z. Development of a chemically stable 10-hydroxycamptothecin nanosuspensions. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and zeta potential—What they are and what they are not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, A.; Paolino, D.; Iannone, M.; Palma, E.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Sodium deoxycholate-decorated zein nanoparticles for a stable colloidal drug delivery system. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lakshmi, P.; Kumar, G.A. Nanosuspension technology: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 2, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, C.F.; Chiang, M.Y.; Chan, H.; Shoemaker, J.E.E.; Mirabelli, C.K. Cationic lipids enhance cellular uptake and activity of phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides. Mol. Pharmacol. 1992, 41, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Panyam, J.; Prabha, S.; Labhasetwar, V. Residual polyvinyl alcohol associated with poly (D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles affects their physical properties and cellular uptake. J. Control. Release 2002, 82, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Stellacci, F. Effect of surface properties on nanoparticle-cell interactions. Small 2010, 6, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punitha, S.; Girish, Y. Polymers in mucoadhesive buccal drug delivery system—A review. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 1, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, D.; Conte, C.; d’Angelo, I.; Miro, A.; Ungaro, F.; Quaglia, F. Mucoadhesive zein/beta-cyclodextrin nanoparticles for the buccal delivery of curcumin. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghalei, S.; Asadi, H.; Ghalei, B. Zein nanoparticle-embedded electrospun PVA nanofibers as wound dressing for topical delivery of anti-inflammatory diclofenac. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jing, Y.; Han, C.; Zhang, H.; Tian, Y. Encapsulation of curcumin in zein/ caseinate/sodium alginate nanoparticles with improved physicochemical and controlled release properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Teng, Z.; Wang, Q. Development of zein nanoparticles coated with carboxymethyl chitosan for encapsulation and controlled release of vitamin D3. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuselvi, L.; Dhathathreyan, A. Simple coacervates of zein to encapsulate Gitoxin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2006, 51, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albekairi, N.A.; Al-Enazy, S.; Ali, S.; Rytting, E. Transport of digoxin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles across BeWo cells, an in vitro model of human placental trophoblast. Ther. Deliv. 2015, 6, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Chaudhury, A. Recent advances in lipid nanoparticle formulations with solid matrix for oral drug delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuan, Y.L.; Navin Sivanasvaran, S.; Pui, L.P.; Yusof, Y.A.; Senphan, T. Physicochemical properties of sodium alginate edible film incorporated with mulberry (Morus australis) leaf extract. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2020, 43, 359–376. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamad, S.A.; Salem, H.; Yassin, H.A.; Mansour, H.F. Bucco-adhesive film as a pediatric proper dosage form for systemic delivery of propranolol hydrochloride: In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 4277–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwan, A.W.; Berania, J.E.; Liu, X. A comparative study on the effects of amphiphilic and hydrophilic polymers on the release profiles of a poorly water-soluble drug. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2016, 21, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Formulation | Film Composition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3% SA Solution (mL) | Ethanol (mL) | Water (mL) | Glycerol (g/L) | |
| SA EtOH0 | 15.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| SA EtOH10 | 10.00 | 1.50 | 3.50 | 0.00 |
| SA EtOH20 | 10.00 | 3.00 | 2.00 | 0.00 |
| SA_Glyc EtOH0 | 15.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 12.00 |
| SA_Glyc EtOH10 | 10.00 | 1.50 | 3.50 | 12.00 |
| SA_Glyc EtOH20 | 10.00 | 3.00 | 2.00 | 12.00 |
| Formulation | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|
| SA EtOH0 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 5.15 ± 0.70 |
| SA_Glyc EtOH0 | 0.35 ± 0.02 | 41.97 ± 0.72 |
| SA EtOH10 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 7.83 ± 1.27 |
| SA_Glyc EtOH10 | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 27.85 ± 4.59 |
| SA EtOH20 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 6.38 ± 1.17 |
| SA_Glyc EtOH20 | 0.72 ± 0.03 | 26.19 ± 1.96 |
| Formulation | Dissolution Time (min) |
|---|---|
| SA EtOH0 | 7.10 ± 0.41 |
| SA_Glyc EtOH0 | 6.27 ± 0.18 |
| SA EtOH10 | 8.88 ± 0.04 |
| SA_Glyc EtOH10 | 11.36 ± 0.68 |
| SA EtOH20 | 10.38 ± 0.05 |
| SA_Glyc EtOH20 | 9.00 ± 0.65 |
| Formulation | Mean Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zein 2.5 mg/mL | Digoxin 0.00 mg/mL | 85.72 ± 0.36 | 0.22 ± 0.00 | 24.23 ± 0.39 |
| Digoxin 0.25 mg/mL | 87.20 ± 0.88 | 0.23 ± 0.00 | 21.23 ± 0.07 | |
| Digoxin 0.50 mg/mL | 92.16 ± 0.77 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 23.40 ± 1.72 | |
| Digoxin 1.00 mg/mL | 123.20 ± 2.42 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 22.30 ± 0.25 | |
| Formulation | Thickness (mm) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Dissolution Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA_Glyc EtOH10 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 27.85 ± 4.59 | 11.36 ± 0.68 |
| SA_Glyc EtOH10_ZnDx0.25 | 0.08 ± 0.90 | 0.40 ± 0.04 | 5.72 ± 0.58 | 13.75 ± 0.37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, D.A.; Miguel, S.P.; Loureiro, J.; Ribeiro, M.; Roque, F.; Coutinho, P. Oromucosal Alginate Films with Zein Nanoparticles as a Novel Delivery System for Digoxin. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122030
Rodrigues DA, Miguel SP, Loureiro J, Ribeiro M, Roque F, Coutinho P. Oromucosal Alginate Films with Zein Nanoparticles as a Novel Delivery System for Digoxin. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(12):2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122030
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Daniela A., Sónia P. Miguel, Jorge Loureiro, Maximiano Ribeiro, Fátima Roque, and Paula Coutinho. 2021. "Oromucosal Alginate Films with Zein Nanoparticles as a Novel Delivery System for Digoxin" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 12: 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122030
APA StyleRodrigues, D. A., Miguel, S. P., Loureiro, J., Ribeiro, M., Roque, F., & Coutinho, P. (2021). Oromucosal Alginate Films with Zein Nanoparticles as a Novel Delivery System for Digoxin. Pharmaceutics, 13(12), 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122030