A NIR-Based Study of Desorption Kinetics during Continuous Spin Freeze-Drying
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Development of the Inline NIR-Based Moisture Quantification Model
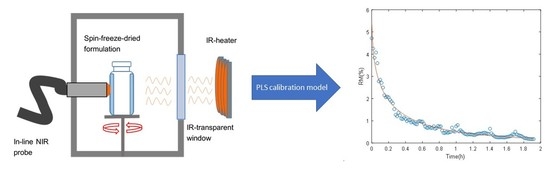
2.1.1. Sample Preparation and Spin Freeze-Drying Setup
2.1.2. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
2.1.3. PLS Calibration
2.2. Determination of the Influential Parameters on Desorption Kinetics
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2.2. NIR Measurement
2.2.3. Mathematical Description of the Desorption Process
2.2.4. Experimental Design
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Development and Validation of the PLS Calibration Model
3.2. Fitting of the Drying Curves and Validation of the Inline Predictions
3.3. Influence of Process Settings on the Desorption Process
3.4. Toward a Mechanistic Understanding of Desorption
3.5. Applicability of the Presented Approach
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Quality Considerations for Continuous Manufacturing Guidance for Industry; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2019.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: PAT—A Framework for Innovative Pharmaceutical Development, Manufacturing, and Quality Assurance; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2004.
- Pisano, R.; Arsiccio, A.; Capozzi, L.C.; Trout, B.L. Achieving continuous manufacturing in lyophilization: Technologies and approaches. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godawat, R.; Konstantinov, K.; Rohani, M.; Warikoo, V. End-to-end integrated fully continuous production of recombinant monoclonal antibodies. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 213, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J. Lyophilization in Review. 2020. Available online: https://pharmahub.org/resources/851 (accessed on 12 November 2021).
- AboulFotouh, K.; Cui, Z.; Williams, R.O. Next-Generation COVID-19 Vaccines Should Take Efficiency of Distribution into Consideration. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corver, J. Method and System for Freeze-Drying Injectable Compositions, in Particular Pharmaceutical Compositions. WIPO Patent WO2013036107, 14 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bockstal, P.j. The Development of a Continuous and Controlled Freeze-Drying Concept for Biopharmaceutical Unit Doses. Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University, Gent, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Leys, L.; Vanbillemont, B.; Van Bockstal, P.J.; Lammens, J.; Nuytten, G.; Corver, J.; Vervaet, C.; De Beer, T. A primary drying model-based comparison of conventional batch freeze-drying to continuous spin-freeze-drying for unit doses. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 157, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bockstal, P.J.; Mortier, S.T.F.; Corver, J.; Nopens, I.; Gernaey, K.V.; De Beer, T. Quantitative risk assessment via uncertainty analysis in combination with error propagation for the determination of the dynamic Design Space of the primary drying step during freeze-drying. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 121, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Bockstal, P.J.; Corver, J.; De Meyer, L.; Vervaet, C.; De Beer, T. Thermal Imaging as a Noncontact Inline Process Analytical Tool for Product Temperature Monitoring during Continuous Freeze-Drying of Unit Doses. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13591–13599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Meyer, L.; Lammens, J.; Mortier, S.T.F.; Vanbillemont, B.; Van Bockstal, P.J.; Corver, J.; Nopens, I.; Vervaet, C.; De Beer, T. Modelling the primary drying step for the determination of the optimal dynamic heating pad temperature in a continuous pharmaceutical freeze-drying process for unit doses. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Meyer, L. Evaluation of Spin Freezing versus Conventional Freezing as Part of a Continuous Pharmaceutical Freeze-Drying Concept for Unit Doses. Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University, Gent, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lammens, J.; Mortier, S.T.F.C.; De Meyer, L.; Vanbillemont, B.; Van Bockstal, P.J.; Van Herck, S.; Corver, J.; Nopens, I.; Vanhoorne, V.; De Geest, B.G.; et al. The relevance of shear, sedimentation and diffusion during spin freezing, as potential first step of a continuous freeze-drying process for unit doses. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 539, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikal, M.; Shah, S.; Roy, M.; Putman, R. The secondary drying stage of freeze drying: Drying kinetics as a function of temperature and chamber pressure. Int. J. Pharm. 1990, 60, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddone, I.; Barresi, A.A.; Pisano, R. Influence of controlled ice nucleation on the freeze-drying of pharmaceutical products: The secondary drying step. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 524, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geidobler, R.; Winter, G. Controlled ice nucleation in the field of freeze-drying: Fundamentals and technology review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assegehegn, G.; Brito-de la Fuente, E.; Franco, J.M.; Gallegos, C. The Importance of Understanding the Freezing Step and Its Impact on Freeze-Drying Process Performance. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1378–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, L.; Van Bockstal, P.J.; Corver, J.; Vervaet, C.; Remon, J.P.; De Beer, T. Evaluation of spin freezing versus conventional freezing as part of a continuous pharmaceutical freeze-drying concept for unit doses. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 496, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brouckaert, D.; De Meyer, L.; Vanbillemont, B.; Van Bockstal, P.J.; Lammens, J.; Mortier, S.; Corver, J.; Vervaet, C.; Nopens, I.; De Beer, T. Potential of Near-Infrared Chemical Imaging as Process Analytical Technology Tool for Continuous Freeze-Drying. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4354–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, R.; Fissore, D.; Barresi, A.A. Quality by Design in the Secondary Drying Step of a Freeze-Drying Process. Dry. Technol. 2012, 30, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, E.K.; Pikal, M.J. Modeling the Secondary Drying Stage of Freeze Drying: Development and Validation of an Excel-Based Model. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millman, M.J.; Liapis, A.; Marchello, J. An analysis of the lyophilization process using a sorption-sublimation model and various operational policies. Aiche J. 1985, 31, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trelea, I.C.; Fonseca, F.; Passot, S. Dynamic modeling of the secondary drying stage of freeze drying reveals distinct desorption kinetics for bound water. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, S.; van Boxtel, A. Thin Layer Drying of Black Tea. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1999, 74, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduola, K.; Oforkansi, B. Mathematical Model of Thin-Layer Drying Process in a Plantain Sample. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2016, 5, 364. [Google Scholar]
- Page, G.E. Factors Influencing the Maximum Rates of Air Drying Shelled Corn in Thin Layers. Ph.D. Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Simal, S.; Femenia, A.; Garau, M.; Rosselló, C. Use of exponential, Page’s and diffusional models to simulate the drying kinetics of kiwi fruit. J. Food Eng. 2005, 66, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Pisano, R.; Fissore, D.; Barresi, A.A.; Brayard, P.; Chouvenc, P.; Woinet, B. Quality by design: Optimization of a freeze-drying cycle via design space in case of heterogeneous drying behavior and influence of the freezing protocol. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nail, S.L. The Effect of Chamber Pressure on Heat Transfer in the Freeze Drying of Parenteral Solutions. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 1980, 34, 358–368. [Google Scholar]






| Run | Cooling Rate (°C/min) | Product Temperature (°C) | Filling Volume (mL) | Pressure (Pa) | kd (1/s0.5) | Cend (%) | CKF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | 30 | 2 | 10 | 0.017 | 1.30 | 1.19 |
| 2 | 50 | 30 | 2 | 30 | 0.028 | 0.59 | 0.63 |
| 3 | 9 | 40 | 2 | 30 | 0.026 | 0.72 | 0.69 |
| 4 | 50 | 40 | 2 | 10 | 0.053 | 0.05 | 0.22 |
| 5 | 9 | 30 | 4 | 30 | 0.012 | 2.20 | 2.00 |
| 6 | 50 | 30 | 4 | 10 | 0.021 | 1.34 | 1.72 |
| 7 | 9 | 40 | 4 | 10 | 0.023 | 0.74 | 0.85 |
| 8 | 50 | 40 | 4 | 30 | 0.041 | 0.17 | / |
| 9 | 29.5 | 35 | 3 | 20 | 0.023 | 0.88 | 0.99 |
| 10 | 29.5 | 35 | 3 | 20 | 0.024 | 0.67 | 0.90 |
| 11 | 29.5 | 35 | 3 | 20 | 0.021 | 0.70 | 0.70 |
| Wavelength Range (nm) | Latent Variables | RMSEcv (%—w/w) | RMSEP (%—w/w) | R2 (Cummulative) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1100–2200 | 2 | 0.254 | 0.229 | 0.990 |
| 1390–2200 | 2 | 0.170 | 0.220 | 0.996 |
| 1865–2200 | 2 | 0.161 | 0.216 | 0.996 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leys, L.; Nuytten, G.; Lammens, J.; Van Bockstal, P.-J.; Corver, J.; Vervaet, C.; De Beer, T. A NIR-Based Study of Desorption Kinetics during Continuous Spin Freeze-Drying. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122168
Leys L, Nuytten G, Lammens J, Van Bockstal P-J, Corver J, Vervaet C, De Beer T. A NIR-Based Study of Desorption Kinetics during Continuous Spin Freeze-Drying. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(12):2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122168
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeys, Laurens, Gust Nuytten, Joris Lammens, Pieter-Jan Van Bockstal, Jos Corver, Chris Vervaet, and Thomas De Beer. 2021. "A NIR-Based Study of Desorption Kinetics during Continuous Spin Freeze-Drying" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 12: 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122168
APA StyleLeys, L., Nuytten, G., Lammens, J., Van Bockstal, P. -J., Corver, J., Vervaet, C., & De Beer, T. (2021). A NIR-Based Study of Desorption Kinetics during Continuous Spin Freeze-Drying. Pharmaceutics, 13(12), 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122168