Resveratrol-Loaded Lipid-Core Nanocapsules Modulate Acute Lung Inflammation and Oxidative Imbalance Induced by LPS in Mice
Abstract
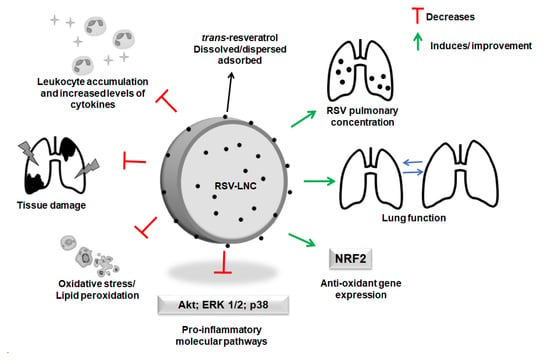
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of RSV-LNCs
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization of RSV-LNCs
2.3. Animals
2.4. Murine Model of LPS-Induced Lung Injury and Treatment Protocol
2.5. Assessment of Pulmonary Function and Airway Hyperreactivity
2.6. Cell Recovery from the Airway Lumen
2.7. Myeloperoxidase Activity Assay
2.8. Inflammatory Mediator Quantification
2.9. Pulmonary Tissue Analysis
2.10. Oxidative Imbalance Analysis
2.11. Quantification of RSV in the Lung Tissue
2.12. Western Blot Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of Polymeric Nanocapsules
3.2. Effect of RSV-LNCs on Airway Hyperreactivity (AHR) and Leukocyte Infiltration
3.3. Effect of RSV-LNCs on Pulmonary Structural Damage
3.4. Effect of RSV-LNCs on Inflammatory Mediator Levels in Lung Tissue
3.5. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of RSV
3.6. Effect of RSV-LNCs on Oxidative Imbalance
3.7. RSV Quantification in Lung Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diamond, M.; Peniston Feliciano, H.L.; Sanghavi, D.; Mahapatra, S. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS); StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, P.L.; Pelosi, P.; Rocco, P.R.M. Personalized pharmacological therapy for ARDS: A light at the end of the tunnel. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, T.J.; Hibbert, K.A. Recent advances in the understanding and management of ARDS. F1000Research 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffey, J.G.; Matthay, M.A. Fifty Years of Research in ARDS. Cell Based Therapy for ARDS: Biology and Potential Therapeutic Value. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, C.W.; Herrera Abreu, M.T.; Suzuki, T.; Downey, G.P. Oxidative stress and acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 29, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, P.; Zhao, P.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Guo, W.; Gao, H.; Jiao, Y. Pretreatment of ferulic acid attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharm. 2018, 32, 394632017750518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghasemian, M.; Owlia, S.; Owlia, M.B. Review of Anti-Inflammatory Herbal Medicines. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 2016, 9130979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, C.-Y.; Tain, Y.-L.; Yu, H.-R.; Huang, L.-T. The Effects of Resveratrol in the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malaguarnera, L. Influence of Resveratrol on the Immune Response. Nutrients 2019, 11, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kursvietiene, L.; Staneviciene, I.; Mongirdiene, A.; Bernatoniene, J. Multiplicity of effects and health benefits of resveratrol. Medicina 2016, 52, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, N.; Liu, J.B.; Wu, J.B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X. Protective effect of resveratrol against acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide via inhibiting the myd88-dependent Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghetaa, H.; Mohammed, A.; Sultan, M.; Busbee, P.; Murphy, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P. Resveratrol protects mice against SEB-induced acute lung injury and mortality by miR-193a modulation that targets TGF-β signalling. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 2644–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhuo, Y.; Cui, L.; Li, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, S.; Cui, N.; Wang, X.; Gao, H. Resveratrol alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by suppressing inflammation and apoptosis of alveolar macrophage cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 1961–1975. [Google Scholar]
- Chedea, V.S.; Vicas, S.I.; Sticozzi, C.; Pessina, F.; Frosini, M.; Maioli, E.; Valacchi, G. Resveratrol: From diet to topical usage. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3879–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirola, L.; Frojdo, S. Resveratrol: One molecule, many targets. IUBMB Life 2008, 60, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katekar, R.; Thombre, G.; Riyazuddin, M.; Husain, A.; Rani, H.; Praveena, K.S.; Gayen, J.R. Pharmacokinetics and brain targeting of trans-resveratrol loaded mixed micelles in rats following intravenous administration. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2020, 25, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Lee, S.H.; Chow, P.S.; Macbeath, C. Microemulsion composed of combination of skin beneficial oils as vehicle: Development of resveratrol-loaded microemulsion based formulations for skin care applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 194, 111161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J.R.; Weissleder, R. Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for targeted imaging and therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odeniyi, M.A.; Omoteso, O.A.; Adepoju, A.O.; Jaiyeoba, K.T. Starch nanoparticles in drug delivery: A review. Polim. Med. 2018, 48, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck, R.C.R.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Hoffmeister, C.; Gallas, M.R.; Collnot, E.; Schaefer, U.F.; Guterres, S.S.; Lehr, C.M. Dexamethasone-loaded nanoparticle-coated microparticles: Correlation between in vitro drug release and drug transport across Caco-2 cell monolayers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, S.; Hebeda, C.B.; Loiola, R.A.; Calgaroto, S.; Uchiyama, M.K.; Araki, K.; Frank, L.A.; Paese, K.; Guterres, S.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; et al. Direct effects of poly(epsilon-caprolactone) lipid-core nanocapsules on human immune cells. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1429–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Oliveira, M.T.P.; de Sa Coutinho, D.; Tenorio de Souza, E.; Staniscuaski Guterres, S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Silva, P.M.R.; Martins, M.A.; Bernardi, A. Orally delivered resveratrol-loaded lipid-core nanocapsules ameliorate LPS-induced acute lung injury via the ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5215–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frozza, R.L.; Bernardi, A.; Paese, K.; Hoppe, J.B.; da Silva, T.; Battastini, A.M.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S.; Salbego, C. Characterization of trans-resveratrol-loaded lipid-core nanocapsules and tissue distribution studies in rats. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2010, 6, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Almeida, A.P.L.; Pacheco de Oliveira, M.T.; de Souza, E.T.; de Sa Coutinho, D.; Ciambarella, B.T.; Gomes, C.R.; Terroso, T.; Guterres, S.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Silva, P.M.; et al. Alpha-bisabolol-loaded lipid-core nanocapsules reduce lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation in mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 4479–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coutinho, D.S.; Anjos-Valotta, E.A.; do Nascimento, C.; Pires, A.L.A.; Napimoga, M.H.; Carvalho, V.F.; Torres, R.C.; e Silva, P.M.R.; Martins, M.A. 15-Deoxy-Delta-12,14-Prostaglandin J2 Inhibits Lung Inflammation and Remodeling in Distinct Murine Models of Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petronilho, F.; Florentino, D.; Danielski, L.G.; Vieira, L.C.; Martins, M.M.; Vieira, A.; Bonfante, S.; Goldim, M.P.; Vuolo, F. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Attenuates Oxidative Damage in Organs After Sepsis. Inflammation 2016, 39, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, H.H.; Hadley, M. [43] Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid Peroxidation. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990; Volume 186, pp. 421–431. [Google Scholar]
- Insuela, D.B.R.; Azevedo, C.T.; Coutinho, D.S.; Magalhaes, N.S.; Ferrero, M.R.; Ferreira, T.P.T.; Cascabulho, C.M.; Henriques-Pons, A.; Olsen, P.C.; Diaz, B.L.; et al. Glucagon reduces airway hyperreactivity, inflammation, and remodeling induced by ovalbumin. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calixto, J.B. The role of natural products in modern drug discovery. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2019, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhrmann, C.; Popper, B.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Resveratrol downregulates inflammatory pathway activated by lymphotoxin alpha (TNF-beta) in articular chondrocytes: Comparison with TNF-alpha. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Huang, T.; Song, D.X.; Tao, H.R. Therapeutic potential of hyaluronic acid/chitosan nanoparticles for the delivery of curcuminoid in knee osteoarthritis and an in vitro evaluation in chondrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 2604–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Sá Coutinho, D.; Pires, J.; Gomes, H.; Raffin Pohlmann, A.; Stanisçuaski Guterres, S.; Rodrigues e Silva, P.M.; Martins, M.A.; Ferrarini, S.R.; Bernardi, A. Pequi (Caryocar brasiliense Cambess)-Loaded Nanoemulsion, Orally Delivered, Modulates Inflammation in LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhun, J.; Min, H.K.; Na, H.S.; Kwon, J.Y.; Ryu, J.; Cho, K.H.; Choi, J.; Jung, K.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Combinatmarion treatment with Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-1, vitamin B, and curcumin ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis by inhibiting the pro-inflammatory mediators. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 228, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koushki, M.; Amiri-Dashatan, N.; Ahmadi, N.; Abbaszadeh, H.-A.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M. Resveratrol: A miraculous natural compound for diseases treatment. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2473–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yehya, N. Lessons learned in acute respiratory distress syndrome from the animal laboratory. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, L.B.; Matthay, M.A. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1334–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran Rahimi, V.; Rakhshandeh, H.; Raucci, F.; Buono, B.; Shirazinia, R.; Samzadeh Kermani, A.; Maione, F.; Mascolo, N.; Askari, V.R. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Activity of Portulaca oleracea Extract on LPS-Induced Rat Lung Injury. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.H.; Liu, J.P.; Qu, R.; Ma, S.P. Tectorigenin inhibits the inflammation of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 12, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, S.; Florquin, S.; Golenbock, D.T.; van der Poll, T. Pulmonary Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Binding Protein Inhibits the LPS-Induced Lung Inflammation In Vivo. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 3189–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rittirsch, D.; Flierl, M.A.; Day, D.E.; Nadeau, B.A.; McGuire, S.R.; Hoesel, L.M.; Ipaktchi, K.; Zetoune, F.S.; Sarma, J.V.; Leng, L.; et al. Acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide is independent of complement activation. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 7664–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-M.; Lu, H.-C.; Tung, Y.-T.; Chen, W. Antiplatelet Therapy for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, L.; Kang, K.; Fei, D.; Gong, R.; Cao, Y.; Pan, S.; Zhao, M. Resveratrol ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury via NLRP3 inflammasome modulation. Biomed. Pharm. 2016, 84, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Q.; Yao, S.; Gui, P. Amelioration of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats by Na-H Exchanger-1 Inhibitor Amiloride Is Associated with Reversal of ERK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3560234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, M.J. Myeloperoxidase-derived oxidation: Mechanisms of biological damage and its prevention. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2011, 48, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bradley, P.P.; Priebat, D.A.; Christensen, R.D.; Rothstein, G. Measurement of Cutaneous Inflammation: Estimation of Neutrophil Content with an Enzyme Marker. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1982, 78, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Souza, A.P.; Vale, V.L.C.; da Costa Silva, M.; de Oliveira Araújo, I.B.; Trindade, S.C.; de Moura-Costa, L.F.; Rodrigues, G.C.; Sales, T.S.; dos Santos, H.A.; de Carvalho-Filho, P.C.; et al. MAPK involvement in cytokine production in response to Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis infection. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Liao, R.; Qiang, Z.; Zhang, C. Pro-inflammatory cytokine-driven PI3K/Akt/Sp1 signalling and H(2)S production facilitates the pathogenesis of severe acute pancreatitis. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20160483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Hu, Z.; Fu, Q.; Song, X.; Cui, Q.; Jia, R.; Zou, Y.; He, C.; Li, L.; Yin, Z. Resveratrol mitigates lipopolysaccharide-mediated acute inflammation in rats by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κBp65/MAPKs signaling cascade. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakus, P.B.; Kalman, N.; Antus, C.; Radnai, B.; Tucsek, Z.; Gallyas, F., Jr.; Sumegi, B.; Veres, B. TRAF6 is functional in inhibition of TLR4-mediated NF-kappaB activation by resveratrol. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakibaei, M.; Csaki, C.; Nebrich, S.; Mobasheri, A. Resveratrol suppresses interleukin-1beta-induced inflammatory signaling and apoptosis in human articular chondrocytes: Potential for use as a novel nutraceutical for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Biochem. Pharm. 2008, 76, 1426–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhrmann, C.; Mobasheri, A.; Matis, U.; Shakibaei, M. Curcumin mediated suppression of nuclear factor-κB promotes chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in a high-density co-culture microenvironment. Arthritis Res. 2010, 12, R127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Limagne, E.; Lançon, A.; Delmas, D.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M.; Latruffe, N. Resveratrol Interferes with IL1-β-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Paracrine Interaction between Primary Chondrocytes and Macrophages. Nutrients 2016, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Constanze, B.; Popper, B.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Evidence that TNF-β suppresses osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and resveratrol reverses it through modulation of NF-κB, Sirt1 and Runx2. Cell Tissue Res. 2020, 381, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, A.; Muñoz, M.F.; Argüelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: Production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchi, C.F.; Fioretto, J.R.; Ferreira, A.L.A.; Berchieri-Ronchi, C.B.; Correa, C.R.; Kurokawa, C.S.; Carpi, M.F.; Moraes, M.A.; Yeum, K.-J. Biomarkers for oxidative stress in acute lung injury induced in rabbits submitted to different strategies of mechanical ventilation. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, C.J.; Binder, C.J. Malondialdehyde epitopes as mediators of sterile inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Kokare, C. Chapter 11—Microbial Enzymes of Use in Industry. In Biotechnology of Microbial Enzymes; Brahmachari, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 267–298. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.X.; Duan, G.L.; Wang, C.N.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhu, X.Y.; Liu, Y.J. Protective effect of resveratrol against endotoxemia-induced lung injury involves the reduction of oxidative/nitrative stress. Pulm. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 27, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, O. Cerebroprotective effect of resveratrol through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in diabetic rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharm. 2013, 386, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovac, S.; Angelova, P.R.; Holmström, K.M.; Zhang, Y.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Abramov, A.Y. Nrf2 regulates ROS production by mitochondria and NADPH oxidase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2015, 1850, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.-N.; Ma, L.-Y.; Ji, H.; Qin, Y.-H.; Jin, S.-S.; Xu, L.-X. Resveratrol protects against oxidative stress by activating the Keap-1/Nrf2 antioxidant defense system in obese-asthmatic rats. Exp. Med. 2018, 16, 4339–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kode, A.; Rajendrasozhan, S.; Caito, S.; Yang, S.-R.; Megson, I.L.; Rahman, I. Resveratrol induces glutathione synthesis by activation of Nrf2 and protects against cigarette smoke-mediated oxidative stress in human lung epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 294, L478–L488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Planas, J.M.; Alfaras, I.; Colom, H.; Juan, M.E. The bioavailability and distribution of trans-resveratrol are constrained by ABC transporters. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 527, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karn, P.R.; Vanic, Z.; Pepic, I.; Skalko-Basnet, N. Mucoadhesive liposomal delivery systems: The choice of coating material. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 37, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plapied, L.; Duhem, N.; des Rieux, A.; Préat, V. Fate of polymeric nanocarriers for oral drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, A.C.; Elsom, J.; Wibroe, P.P.; Moghimi, S.M. Polymeric particulate technologies for oral drug delivery and targeting: A pathophysiological perspective. Nanomedicine 2012, 8 (Suppl. 1), S5–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohlmann, A.R.; Fonseca, F.N.; Paese, K.; Detoni, C.B.; Coradini, K.; Beck, R.C.R.; Guterres, S.S. Poly(ϵ-caprolactone) microcapsules and nanocapsules in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 623–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guterres, S.S.; Muller, C.B.; Michalowski, C.B.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Dalla Costa, T. Gastro-intestinal tolerance after oral administration of spray-dried diclofenac-loaded nanocapsules and nanospheres. STP Pharma Sci. 2001, 11, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi, A.; Zilberstein, A.C.C.V.; Jäger, E.; Campos, M.M.; Morrone, F.B.; Calixto, J.B.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S.; Battastini, A.M.O. Effects of indomethacin-loaded nanocapsules in experimental models of inflammation in rats. Br. J. Pharm. 2009, 158, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira, M.T.P.; Coutinho, D.d.S.; Guterres, S.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Silva, P.M.R.e.; Martins, M.A.; Bernardi, A. Resveratrol-Loaded Lipid-Core Nanocapsules Modulate Acute Lung Inflammation and Oxidative Imbalance Induced by LPS in Mice. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050683
de Oliveira MTP, Coutinho DdS, Guterres SS, Pohlmann AR, Silva PMRe, Martins MA, Bernardi A. Resveratrol-Loaded Lipid-Core Nanocapsules Modulate Acute Lung Inflammation and Oxidative Imbalance Induced by LPS in Mice. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(5):683. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050683
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira, Maria Talita Pacheco, Diego de Sá Coutinho, Sílvia Stanisçuaski Guterres, Adriana Raffin Pohlmann, Patrícia Machado Rodrigues e Silva, Marco Aurélio Martins, and Andressa Bernardi. 2021. "Resveratrol-Loaded Lipid-Core Nanocapsules Modulate Acute Lung Inflammation and Oxidative Imbalance Induced by LPS in Mice" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 5: 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050683
APA Stylede Oliveira, M. T. P., Coutinho, D. d. S., Guterres, S. S., Pohlmann, A. R., Silva, P. M. R. e., Martins, M. A., & Bernardi, A. (2021). Resveratrol-Loaded Lipid-Core Nanocapsules Modulate Acute Lung Inflammation and Oxidative Imbalance Induced by LPS in Mice. Pharmaceutics, 13(5), 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050683