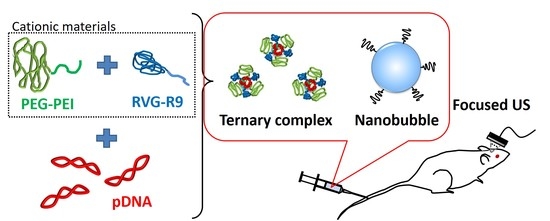
Ternary Complexes of pDNA, Neuron-Binding Peptide, and PEGylated Polyethyleneimine for Brain Delivery with Nano-Bubbles and Ultrasound
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Ternary Complexes
2.3. Cell Cultures
2.4. Gene Transfection with Ternary Complexes In Vitro
2.5. Cellular Specific Binding of Ternary Complexes
2.6. Preparation of Liposomes and NBs
2.7. Extravasation of Evans Blue Dye
2.8. In Vivo Gene Delivery to the Brain Tissue
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. The Formation of Ternary Complexes Composed of pDNA, PEG-PEI, and RVG-R9 Peptide
3.2. The Transfection Effects of Various Ternary Complexes In Vitro
3.3. Cellular Specificity of Ternary Complexes
3.4. Permeability of the BBB Induced by NBs and FUS
3.5. In Vivo Gene Transfection by Ternary Complexes with NBs and FUS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, S.; Fu, J.; Liu, D.; Chen, D.; Hu, H. The Blood-Brain Barrier Cell-Targeted Gene Delivery System to Enhance Nerve Growth Factor Protein Secretion in the Brain. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 6207–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Schlachetzki, F.; Pardridge, W.M. Global Non-Viral Gene Transfer to the Promate Brain Following Intravenous Administration. Mol. Ther. 2003, 7, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Shao, K.; Huang, R.; Han, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Kuang, Y.; Ye, L.; Lou, J.; Jiang, C. Gene Delivery Targeted to the Brain Using an Angiopep-Conjugated Polyethyleneglycol-Modified Polyamidoamine Dendrimer. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6976–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.; Lapierre, J.; Ojha, C.R.; Kaushik, A.; Batrakova, E.; Kashanchi, F.; Dever, S.M.; Nair, M.; El-Hage, N. Intranasal Drug Delivery of Small Interfering RNA Targeting Beclin1 Encapsulated with Polyethylenimine (PEI) in Mouse Brain to Achieve HIV Attenuation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aly, A.E.E.; Harmon, B.; Padegimas, L.; Sesenoglu-Laird, O.; Cooper, M.J.; Yurek, D.M.; Waszczak, B.L. Intranasal Delivery of HGDNF Plasmid DNA Nanoparticles Results in Long-Term and Widespread Transfection of Perivascular Cells in Rat Brain. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 16, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamei, N.; Shingaki, T.; Kanayama, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Zochi, R.; Hasegawa, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Takeda-Morishita, M. Visualization and Quantitative Assessment of the Brain Distribution of Insulin through Nose-to-Brain Delivery Based on the Cell-Penetrating Peptide Noncovalent Strategy. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, T.; Akiyama, F.; Kakizaki, S.; Takashima, Y.; Seta, Y. Delivery of SiRNA to the Brain Using a Combination of Nose-to-Brain Delivery and Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Modified Nano-Micelles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 9220–9226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anraku, Y.; Kuwahara, H.; Fukusato, Y.; Mizoguchi, A.; Ishii, T.; Nitta, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Toh, K.; Miyata, K.; Uchida, S.; et al. Glycaemic Control Boosts Glucosylated Nanocarrier Crossing the BBB into the Brain. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hynynen, K.; McDannold, N.; Vykhodtseva, N.; Jolesz, F.A. Noninvasive MR Imaging-Guided Focal Opening of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Rabbits. Radiology 2001, 220, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H.; Harvey, B.K.; Borden, M.A. State-of-the-Art of Microbubble-Assisted Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4393–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, D.; Maruyama, T.; Unga, J.; Hagiwara, F.; Munakata, L.; Kageyama, S.; Shima, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Suzuki, R. Effects of Encapsulated Gas on Stability of Lipid-Based Microbubbles and Ultrasound-Triggered Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2019, 311–312, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Hsieh, H.Y.; Chen, C.M.; Wu, S.R.; Tsai, C.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Hua, M.Y.; Wei, K.C.; Yeh, C.K.; Liu, H.L. Non-Invasive, Neuron-Specific Gene Therapy by Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening in Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Model. J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, B.P.; Kim, N.; Miller, G.W.; Hodges, D.; Mastorakos, P.; Klibanov, A.L.; Mandell, J.W.; Hirsh, J.; Suk, J.S.; Hanes, J.; et al. Novel Focused Ultrasound Gene Therapy Approach Noninvasively Restores Dopaminergic Neuron Function in a Rat Parkinson’s Disease Model. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 3533–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Feng, L.Y.; Chai, W.Y.; Lin, C.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Wei, K.C.; Yeh, C.K.; Chen, C.M.; Liu, H.L. Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood Brain-Barrier Opening Enhanced Vascular Permeability for GDNF Delivery in Huntington’s Disease Mouse Model. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, B.P.; Mastorakos, P.; Suk, J.S.; Klibanov, A.L.; Hanes, J.; Price, R.J. Targeted Gene Transfer to the Brain via the Delivery of Brain-Penetrating DNA Nanoparticles with Focused Ultrasound. J. Control. Release 2016, 223, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, P.H.; Wei, K.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Wen, C.J.; Yen, T.C.; Liu, C.L.; Lin, Y.T.; Chen, J.C.; Shen, C.R.; Liu, H.L. Noninvasive and Targeted Gene Delivery into the Brain Using Microbubble-Facilitated Focused Ultrasound. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xhima, K.; Nabbouh, F.; Hynynen, K.; Aubert, I.; Tandon, A. Noninvasive Delivery of an α-Synuclein Gene Silencing Vector with Magnetic Resonance–Guided Focused Ultrasound. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, K.; Fuchigami, Y.; Hagimori, M.; Fumoto, S.; Miura, Y.; Kawakami, S. Efficient Gene Transfection to the Brain with Ultrasound Irradiation in Mice Using Stabilized Bubble Lipopolyplexes Prepared by the Surface Charge Regulation Method. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2309–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negishi, Y.; Yamane, M.; Kurihara, N.; Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Sashida, S.; Takagi, N.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K. Enhancement of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability and Delivery of Antisense Oligonucleotides or Plasmid DNA to the Brain by the Combination of Bubble Liposomes and High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negishi, Y.; Endo, Y.; Fukuyama, T.; Suzuki, R.; Takizawa, T.; Omata, D.; Maruyama, K.; Aramaki, Y. Delivery of SiRNA into the Cytoplasm by Liposomal Bubbles and Ultrasound. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Takizawa, T.; Negishi, Y.; Hagisawa, K.; Tanaka, K.; Sawamura, K.; Utoguchi, N.; Nishioka, T.; Maruyama, K. Gene Delivery by Combination of Novel Liposomal Bubbles with Perfluoropropane and Ultrasound. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Takizawa, T.; Negishi, Y.; Utoguchi, N.; Sawamura, K.; Tanaka, K.; Namai, E.; Oda, Y.; Matsumura, Y.; Maruyama, K. Tumor Specific Ultrasound Enhanced Gene Transfer in Vivo with Novel Liposomal Bubbles. J. Control. Release 2008, 125, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, Y.; Matsuo, K.; Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Matsuki, Y.; Takagi, N.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Aramaki, Y. Delivery of an Angiogenic Gene into Ischemic Muscle by Novel Bubble Liposomes Followed by Ultrasound Exposure. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, Y.; Tsunoda, Y.; Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Oda, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Aramaki, Y. Local Gene Delivery System by Bubble Liposomes and Ultrasound Exposure into Joint Synovium. J. Drug Deliv. 2011, 2011, 203986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Negishi, Y.; Kato, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Aramaki, Y. Efficient SiRNA Delivery Using Novel SiRNA-Loaded Bubble Liposomes and Ultrasound. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 422, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Negishi, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Ukai, S.; Ooaku, K.; Oda, Y.; Sugimoto, K.; Moriyasu, F.; Takagi, N.; Suzuki, R.; et al. Systemic Delivery of MiR-126 by MiRNA-Loaded Bubble Liposomes for the Treatment of Hindlimb Ischemia. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, Y.; Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Matsuki, Y.; Kato, Y.; Takagi, N.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Aramaki, Y. Systemic Delivery Systems of Angiogenic Gene by Novel Bubble Liposomes Containing Cationic Lipid and Ultrasound Exposure. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Negishi, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Suzuki, D.; Ukai, S.; Sugimoto, K.; Moriyasu, F.; Takagi, N.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; et al. PDNA-Loaded Bubble Liposomes as Potential Ultrasound Imaging and Gene Delivery Agents. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2807–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negishi, Y.; Tsunoda, Y.; Hamano, N.; Omata, D.; Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Nomizu, M.; Aramaki, Y. Ultrasound-Mediated Gene Delivery Systems by AG73-Modified Bubble Liposomes. Biopolymers 2013, 100, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, T.L.; Burrage, T.G.; Smith, A.L.; Crick, J.; Tignor, G.H. Is the Acetylcholine Receptor a Rabies Virus Receptor? Science 1982, 215, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafon, M. Rabies Virus Receptors. J. Neurovirol. 2005, 11, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Wu, H.; McBride, J.L.; Jung, K.E.; Hee Kim, M.; Davidson, B.L.; Kyung Lee, S.; Shankar, P.; Manjunath, N. Transvascular Delivery of Small Interfering RNA to the Central Nervous System. Nature 2007, 448, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M.J.A. Delivery of SiRNA to the Mouse Brain by Systemic Injection of Targeted Exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.W.; Son, S.; Jang, J.; Youn, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.; Lee, Y.S.; Jeong, J.M.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, D.S. A Brain-Targeted Rabies Virus Glycoprotein-Disulfide Linked PEI Nanocarrier for Delivery of Neurogenic MicroRNA. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4968–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald, M.; Geissler, S.; Goepferich, A. Targeting the Central Nervous System (CNS): A Review of Rabies Virus-Targeting Strategies. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 2177–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, R.; Han, L.; Ke, W.; Shao, K.; Ye, L.; Lou, J.; Jiang, C. Brain-Targeting Gene Delivery and Cellular Internalization Mechanisms for Modified Rabies Virus Glycoprotein RVG29 Nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4195–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa-Cedillo, S.A.; Rodríguez-Rocha, H.; Zavala-Flores, L.M.; Montes-de-Oca-Luna, R.; García-García, A.; de Jesus Loera-Arias, M.; Saucedo-Cárdenas, O. Asn194Lys Mutation in RVG29 Peptide Increases GFP Transgene Delivery by Endocytosis to Neuroblastoma and Astrocyte Cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 69, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Cedillo, S.A.; Soto-Domínguez, A.; Rodríguez-Rocha, H.; García-García, A.; de Jesús Loera-Arias, M.; Rivera-Chávez, L.F.; Acosta-Espinoza, E.J.; Valdés, J.; Zavala-Flores, L.M.; Montes-de-Oca-Luna, R.; et al. The MRVG-9R Peptide as a Potential Therapeutic Vector to the Central Nervous System Cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kong, C.; Cho, J.S.; Lee, J.; Koh, C.S.; Yoon, M.S.; Na, Y.C.; Chang, W.S.; Chang, J.W. Focused Ultrasound-Mediated Noninvasive Blood-Brain Barrier Modulation: Preclinical Examination of Efficacy and Safety in Various Sonication Parameters. Neurosurg. Focus 2018, 44, E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









| N/P | Mean Size (nm) | PDI * | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 320.0 ± 55.4 | 0.203 ± 0.03 | 4.4 ± 3.0 |
| 4 | 106.3 ± 12.9 | 0.159 ± 0.01 | 13.2 ± 4.4 |
| 6 | 100.7 ± 6.0 | 0.181 ± 0.11 | 14.6 ± 3.8 |
| 8 | 101.5 ± 23.6 | 0.149 ± 0.07 | 12.0 ± 0.9 |
| 10 | 115.4 ± 19.4 | 0.253 ± 0.08 | 13.6 ± 6.1 |
| PEG-PEI:RVG-R9 | Mean Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2:8 | 100.3 ± 3.5 | 0.277 ± 0.15 | 14.7 ± 9.0 |
| 5:5 | 115.4 ± 19.4 | 0.253 ± 0.08 | 13.6 ± 6.1 |
| 8:2 | 123.9 ± 32.2 | 0.188 ± 0.04 | 12.0 ± 2.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Kurokawa, R.; Sato, K.; Takizawa, N.; Katagiri, F.; Hamano, N.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Nomizu, M.; Takagi, N.; et al. Ternary Complexes of pDNA, Neuron-Binding Peptide, and PEGylated Polyethyleneimine for Brain Delivery with Nano-Bubbles and Ultrasound. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071003
Endo-Takahashi Y, Kurokawa R, Sato K, Takizawa N, Katagiri F, Hamano N, Suzuki R, Maruyama K, Nomizu M, Takagi N, et al. Ternary Complexes of pDNA, Neuron-Binding Peptide, and PEGylated Polyethyleneimine for Brain Delivery with Nano-Bubbles and Ultrasound. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(7):1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071003
Chicago/Turabian StyleEndo-Takahashi, Yoko, Ryo Kurokawa, Kanako Sato, Nao Takizawa, Fumihiko Katagiri, Nobuhito Hamano, Ryo Suzuki, Kazuo Maruyama, Motoyoshi Nomizu, Norio Takagi, and et al. 2021. "Ternary Complexes of pDNA, Neuron-Binding Peptide, and PEGylated Polyethyleneimine for Brain Delivery with Nano-Bubbles and Ultrasound" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 7: 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071003
APA StyleEndo-Takahashi, Y., Kurokawa, R., Sato, K., Takizawa, N., Katagiri, F., Hamano, N., Suzuki, R., Maruyama, K., Nomizu, M., Takagi, N., & Negishi, Y. (2021). Ternary Complexes of pDNA, Neuron-Binding Peptide, and PEGylated Polyethyleneimine for Brain Delivery with Nano-Bubbles and Ultrasound. Pharmaceutics, 13(7), 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071003