Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of a Novel Donepezil-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle Patch in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
2.3. Dissolving Microneedle Patch
2.4. Microneedle Patch Mechanical Properties
2.5. Determination of Drug Content in the Donepezil-Loaded DMN Patch
2.6. Dissolution of Microneedles after Application of DMN Patches in Rats
2.7. Skin Irritation Test following DMN Patch Application in Rats
2.8. In Vitro Drug Release from DMN Patches
2.9. Analysis of Donepezil in Rat Plasma
2.10. Pharmacokinetic Study
2.10.1. Application of DMN Patch to the Rats
2.10.2. Subcutaneous Administration of Donepezil to the Rats
2.10.3. Application of Transdermal Needleless Donepezil Patch to Rats
2.10.4. Oral Administration of Donepezil to Rats
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dissolving Microneedle Patch
3.2. Dissolution of Microneedles after Application of DMN Patches
3.3. Skin Irritation Test following DMN Patch Application in Rats
3.4. Microneedle Patch Mechanical Properties
3.5. Determination of Drug Content in Donepezil-Loaded DMN Patch
3.6. In Vitro Drug Release from the Dissolving Microneedle Patch
3.7. Analytical Method Validation
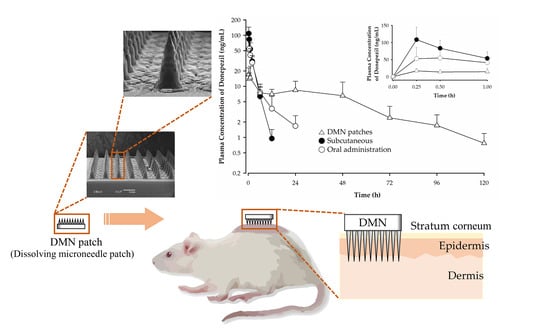
3.8. Pharmacokinetic Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeong, W.Y.; Kwon, M.; Choi, H.E.; Kim, K.S. Recent advances in transdermal drug delivery systems: A review. Biomater. Res. 2021, 25, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, R.H.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, E.; Lara, M.F.; Speaker, T.J.; Contag, C.H.; Kaspar, R.L.; Coulman, S.A.; Hargest, R.; Birchall, J.C. Gene silencing following siRNA delivery to skin via coated steel microneedles: In vitro and in vivo proof-of-concept. J. Control. Release 2013, 166, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Indermun, S.; Luttge, R.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kumar, P.; du Toit, L.C.; Modi, G.; Pillay, V. Current advances in the fabrication of microneedles for transdermal delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, A.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Mitragotri, S. Micro-scale devices for transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larrañeta, E.; Lutton, R.E.M.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle arrays as transdermal and intradermal drug delivery systems: Materials science, manufacture and commercial development. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. 2016, 104, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lahiji, S.F.; Dangol, M.; Jung, H. A patchless dissolving microneedle delivery system enabling rapid and efficient transdermal drug delivery. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Terry, R.N.; Tang, J.; Feng, M.H.R.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Rapidly separable microneedle patch for the sustained release of a contraceptive. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoesly, F.J.; Borovicka, J.; Gordon, J.; Nardone, B.; Holbrook, J.S.; Pace, N.; Ibrahim, O.; Bolotin, D.; Warycha, M.; Kwasny, M.; et al. Safety of a novel microneedle device applied to facial skin: A subject- and rater-blinded, sham-controlled, randomized trial. Arch. Dermatol. 2012, 148, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Park, J.H. Human studies with microneedles for evaluation of their efficacy and safety. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Dave, K.; Venuganti, V.V.K. Microneedles in the clinic. J. Control. Release 2017, 260, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affoo, R.H.; Foley, N.; Rosenbek, J.; Kevin Shoemaker, J.; Martin, R.E. Swallowing dysfunction and autonomic nervous system dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: A scoping review of the evidence. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2013, 61, 2203–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Petrov, D.; Ettcheto, M.; Abad, S.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Garcia, M.L.; Olloquequi, J.; Beas-Zarate, C.; Auladell, C.; Camins, A. Current research therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 8501693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neugroschl, J.; Sano, M. Current treatment and recent clinical research in Alzheimer’s disease. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 2010, 77, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farlow, M.R.; Evans, R.M. Pharmacologic treatment of cognition in Alzheimer’s dementia. Neurology 1998, 51, S36–S44; discussion S65–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlimoghaddam, A.; Neuendorff, M.; Roy, B.; Albensi, B.C. A review of clinical treatment considerations of donepezil in severe Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2018, 24, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maxwell, C.J.; Stock, K.; Seitz, D.; Herrmann, N. Persistence and adherence with dementia pharmacotherapy: Relevance of patient, provider, and system factors. Can. J. Psychiat. 2014, 59, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Saifi, N.; Moyle, W.; Jones, C.; Tuffaha, H. Medication adherence in older patients with dementia: A systematic literature review. J. Pharm. Pract. 2018, 31, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlt, S.; Lindner, R.; Rösler, A.; von Renteln-Kruse, W. Adherence to medication in patients with dementia: Predictors and strategies for improvement. Drugs Aging 2008, 25, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Shim, Y.S.; Domingueze, J.C.; Lee, C.N.; Kang, K.; Kim, H.J.; Jeong, S.K.; Jeong, J.H.; et al. Discontinuation rate of newly prescribed donepezil in alzheimer’s disease patients in Asia. J. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 17, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.L.; Geldmacher, D.; Farlow, M.; Sabbagh, M.; Christensen, D.; Betz, P. High-dose donepezil (23 mg/day) for the treatment of moderate and severe Alzheimer’s disease: Drug profile and clinical guidelines. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2013, 19, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozio, P.; Cerasa, L.S.; Marinelli, L.; Di Stefano, A. Transdermal donepezil on the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsych. Dis. Treat. 2012, 8, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhillon, S. Rivastigmine transdermal patch a review of its use in the management of dementia of the Alzheimer’s type. Drugs 2011, 71, 1209–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagenas, V.; Vlachos, G.S.; Vlachou, N.; Liakopoulos, D.; Kalaitzakis, M.E.; Vikelis, M. A prospective non-interventional study for evaluation of quality of life in patients with Alzheimer’s disease treated with rivastigmine transdermal patch. SAGE Open Med. 2015, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.H.; Wang, W.F.; Yip, B.S.; Yang, Y.W.; Peng, G.S.; Tsai, S.J.; Liao, Y.C. Real-world evaluation of compliance and preference in Alzheimer’s disease treatment: An observational study in Taiwan. Patient Prefer. Adher. 2016, 10, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Waghule, T.; Singhvi, G.; Dubey, S.K.; Pandey, M.M.; Gupta, G.; Singh, M.; Dua, K. Microneedles: A smart approach and increasing potential for transdermal drug delivery system. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larraneta, E.; Stewart, S.; Fallows, S.J.; Birkhauer, L.L.; McCrudden, M.T.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. A facile system to evaluate in vitro drug release from dissolving microneedle arrays. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 497, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation, Draft Guidance; US Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2013; pp. 4–24.
- Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyano, T.; Tobinaga, Y.; Kanno, T.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Takeda, H.; Wakui, M.; Hanada, K. Sugar micro needles as transdermic drug delivery system. Biomed. Microdevices 2005, 7, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuth, P.C.; Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Ai-Ling, M.L.; Hammond, P.T.; Irvine, D.J. Composite dissolving microneedles for coordinated control of antigen and adjuvant delivery kinetics in transcutaneous vaccination. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Polymer microneedles for controlled-release drug delivery. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.Q.; Yu, J.C.; Wang, C.; Nguyen, N.Y.; Walker, G.M.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Microneedles integrated with pancreatic cells and synthetic glucose-signal amplifiers for smart insulin delivery. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3115–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, S.P.; Koutsonanos, D.G.; Martin, M.D.; Lee, J.W.; Zarnitsyn, V.; Choi, S.O.; Murthy, N.; Compans, R.W.; Skountzou, I.; Prausnitz, M.R. Dissolving polymer microneedle patches for influenza vaccination. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Huang, S.F.; Lai, K.Y.; Ling, M.H. Fully embeddable chitosan microneedles as a sustained release depot for intradermal vaccination. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3077–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Choi, S.O.; Felner, E.I.; Prausnitz, M.R. Dissolving microneedle patch for transdermal delivery of human growth hormone. Small 2011, 7, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.K.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, B.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Sung, C.Y.; Jang, N.K.; Kim, J.D.; Jeong, D.H.; Ryu, H.Y.; Lee, S. A comparative study of dissolving hyaluronic acid microneedles with trehalose and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) for efficient peptide drug delivery. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 2566–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, C.; Hughes, H.; O’Reilly, N.J.; McLoughlin, P. Formulation and characterisation of dissolving microneedles for the transdermal delivery of therapeutic peptides. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, M.C.; Caffarel-Salvador, E.; Fallows, S.J.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle-mediated delivery of donepezil: Potential for improved treatment options in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 103, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Larraňeta, E. Slowly dissolving intradermal microneedles. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluja, S.; Kasha, P.C.; Paturi, J.; Anderson, C.; Morris, R.; Banga, A.K. A novel electronic skin patch for delivery and pharmacokinetic evaluation of donepezil following transdermal iontophoresis. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Compound | DH | PVP | TR | SR | ML | GL | PG | Needle Forming | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 27.3 | 54.5 | 18.2 | Yes | Suitable | ||||
| S2 | 27.3 | 54.5 | 18.2 | Yes | Poor | ||||
| S3 | 27.3 | 54.5 | 18.2 | No | - | ||||
| S4 | 27.3 | 54.5 | 18.2 | Yes | Poor | ||||
| S5 | 27.3 | 54.5 | 18.2 | Yes | Poor |
| Compound | F1 | F2 | F3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Donepezil HCl | 28.6 | 28.6 | 28.6 |
| PVP | 71.4 | 53.6 | 42.9 |
| Trehalose | - | 17.9 | 28.6 |
| Time (min) | A (%) | B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 75 | 25 |
| 5 | 55 | 45 |
| 5.5 | 10 | 90 |
| 6 | 10 | 90 |
| 6.5 | 75 | 25 |
| 8 | 75 | 25 |
| Compound | [M + H]+ (m/z) | MRM Transition | Fragmentor (V) | Collision Energy (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donepezil | 380.2 | 380.2 → 91.1 | 157 | 30 |
| Escitalopram | 325.2 | 325.2 → 109.1 | 80 | 25 |
| PK Parameters | SC 1 mg/kg | Oral 3 mg/kg | DMN Patch (1 h) 72 mg/kg | DMN Patch (1 Week) 43 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC0–∞ (ng·h/mL) | 213.64 ± 40.98 | 235.15 ± 79.17 | 273.64 ± 99.74 | 603.44 ± 320.39 2 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 108.32 ± 36.28 | 61.76 ± 27.50 | 100.46 ± 29.65 | 18.87 ± 8.36 3 |
| Tmax (h) 1 | 0.25 (0.00) | 0.5 (0.25–1) | 0.25 (0.25–0.50) | 0.25 (0.25–1) |
| t1/2 (h) | 2.02 ± 0.39 | 6.01 ± 1.87 | 4.35 ± 0.33 | 26.44 ± 6.36 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rehman, N.U.; Song, C.; Kim, J.; Noh, I.; Rhee, Y.-S.; Chung, H.J. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of a Novel Donepezil-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle Patch in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010005
Rehman NU, Song C, Kim J, Noh I, Rhee Y-S, Chung HJ. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of a Novel Donepezil-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle Patch in Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleRehman, Naveed Ur, Chanwoo Song, Junhyeong Kim, Inhwan Noh, Yun-Seok Rhee, and Hye Jin Chung. 2022. "Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of a Novel Donepezil-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle Patch in Rats" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010005
APA StyleRehman, N. U., Song, C., Kim, J., Noh, I., Rhee, Y. -S., & Chung, H. J. (2022). Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of a Novel Donepezil-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle Patch in Rats. Pharmaceutics, 14(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010005