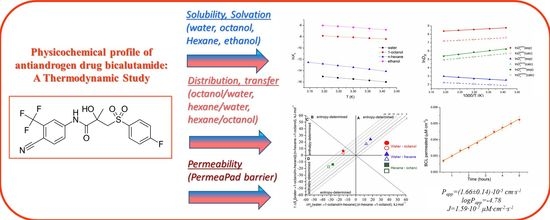
Physicochemical Profile of Antiandrogen Drug Bicalutamide: Solubility, Distribution, Permeability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| pKa | Ionization constant |
| S2 | Molar solubility of solute (M) |
| X2 | Mole fraction solubility of solute |
| M1 | Molar mass of pure solvent (g·mol−1) |
| M2 | Molar mass of solute (g·mol−1) |
| ρ | Density of pure solvents (g∙cm−3) |
| R | Universal gas constant (J⋅mol−1⋅K−1) |
| T | Temperature (K) |
| Tm | Melting point (K) |
| p | Pressure (kPa) |
| ,, | Standard dissolution enthalpy (kJ·mol−1), Gibbs free energy (kJ·mol−1), entropy (J⋅K−1⋅mol−1) |
| ,, | Standard solvation enthalpy (kJ·mol−1), Gibbs free energy (kJ·mol−1), entropy (J⋅K−1⋅mol−1) |
| ,, | Apparent distribution coefficient in 1-octanol/water, n-hexane/water, 1-octanol/n-hexane system (molarity scale) |
| ,, | Apparent distribution coefficient in 1-octanol/water, n-hexane/water, 1-octanol/n-hexane system (mole fraction scale) |
| , , | Thermodynamic functions (enthalpy, Gibbs free energy, entropy) of transferring |
| J | Steady state flux through the membrane (µmol∙cm−2∙sec−1) |
| Papp | Permeability coefficient (cm∙sec−1) |
| ur(S) | Relative standard uncertainties |
| u(T) | Standard uncertainty of temperature |
| u(p) | Standard uncertainty of pressure |
| Greek Letters | |
| , , | Partial solubility parameters of Hansen |
| Total solubility parameter | |
| Volume-dependent solubility parameter | |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Equilibrium Solubility Study: Dissolution and Solvation Thermodynamic Parameter Calculations
2.2.2. Solubility Modeling with the Modified Apelblat Equation
2.2.3. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
2.2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.2.5. Apparent Distribution Coefficients Determination and Transfer Thermodynamic Parameter Calculations
2.2.6. In Vitro Permeability Experiment
3. Results
3.1. Solubility of BCL in Water and Organic Solvents
3.2. Hansen Solubility Parameter for Solubility Prediction in Different Solvents
3.3. Modeling of Solubility Data by Van’t Hoff and Modified Apelblat Equations
3.4. Thermodynamics of Solubility, Solvation, and Transfer Processes
3.5. Apparent Distribution Coefficients in 1-Octanol/Water and n-Hexane/Water Systems
3.6. Transfer Thermodynamics
3.7. Permeation of BCL through the PermeaPad Barrier
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heidenreich, A.; Aus, G.; Bolla, M.; Joniau, S.; Matveev, V.B.; Schmid, H.P.; Zattoni, F. EAU Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2008, 53, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines: 21st List 2019; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Singh, S.M.; Gauthier, S.; Labrie, F. Androgen receptor antagonists (antiandrogens): Structure-activity relationships. Curr. Med. Chem. 2000, 7, 211–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lloyd, A.; Penson, D.; Dewilde, S.; Kleinman, L. Eliciting patient preferences for hormonal therapy options in the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2008, 11, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerns, E.H.; Di, L. Druglike Properties: Concepts, Structure Design and Methods; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zerara, M.; Brickmann, J.; Kretschmer, R.; Exner, T.E. Parameterization of an empirical model for the prediction of n-octanol, alkane and cyclohexane/water as well as brain/blood partition coefficient. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2009, 23, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glomme, A.; März, J.; Dressman, J.B. Comparison of a miniaturized shake-flask solubility method with automated potentiometric acid/base titrations and calculated solubilities. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestel, J.; Caldwell, D.; Constantine, L.; D’Aco, V.J.; Davidson, T.; Dolan, D.G.; Millard, S.P.; Murray-Smith, R.; Parke, N.J.; Ryan, J.J.; et al. Use of acute and chronic ecotoxicity data in environmental risk assessment of pharmaceuticals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 35, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiou, C.T.; Freed, V.H.; Schmedding, D.W.; Kohnert, R.L. Partition coefficient and bioaccumulation of selected organic chemicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1977, 11, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendyk, A.; Pacławski, A.; Szafraniec-Szczęsny, J.; Antosik, A.; Jamróz, W.; Paluch, M.; Jachowicz, R. Data-driven modeling of the bicalutamide dissolution from powder systems. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020, 21, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patil, A.L.; Pore, Y.V.; Kuchekar, B.S.; Late, S.G. Solid-state characterization and dissolution properties of bicalutamide-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Pharmazie 2008, 63, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlovich, G.L.; Blokhina, S.V.; Manin, N.G.; Volkova, T.V.; Tkachev, V.V. Polymorphism and solvatomorphism of bicalutamide. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 111, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, D.R.; Polla, G.; Martinez, A.; Mendioroz, E.; Reinoso, M. Conformational polymorphism in bicalutamide. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 328, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlovich, G.L.; Volkova, T.V.; Proshin, A.N.; Sergeev, Y.D.; Bui, C.-T.; Petrova, L.N.; Bachurin, S.O. Synthesis, pharmacology, crystal properties, and quantitative solvation studies from a drug transport perspective for three new 1,2,4-thiadiazoles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 3754–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkova, T.V.; Levshin, I.B.; Perlovich, G.L. New antifungal compound: Solubility thermodynamics and partitioning processes in biologically relevant solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 310, 113148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, T.V.; Simonova, O.R.; Levshin, I.B.; Perlovich, G.L. Physicochemical profile of new antifungal compound: pH-dependent solubility, distribution, permeability and ionization assay. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Connors, K. Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 1965, 4, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Bhesaniya, K.D.; Nandha, K.; Baluja, S. Measurement, correlation and dissolution thermodynamics of biological active chalcone in organic solvents at different temperatures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2014, 74, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarge, S.M.; Hemminger, W.; Gmelin, E.; Hohne, G.W.H.; Cammenga, H.K.; Eysel, W. Metrologically based procedures for the temperature. heat and heat flow rate calibration of DSC. J. Therm. Anal. 1997, 49, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, D.G.; Steffen, P.; Rudtsch, J. Enthalpy of fusion of indium: A certified reference material for differential scanning calorimetry. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 2003, 48, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Cagno, M.; Bibi, H.A.; Bauer-Brandl, A. New biomimetic barrier Permeapad™ for efficient investigation of passive permeability of drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 73, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, T.V.; Simonova, O.R.; Perlovich, G.L. New antifungal compound: Impact of cosolvency, micellization and complexation on solubility and permeability processes. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, K.A. The stability of cyclodextrin complexes in solution. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 1325–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cockshot, I.D. Bicalutamide clinical pharmacokinetics and metabolism. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 43, 855–878. [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt, C. Solvents and Solvent Effects in Organic Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Wiley-VCH Publishers: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fedors, R.F. A method for estimating both the solubility parameters and molar volumes of liquids. Polymer Eng. Sci. 1974, 14, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, S.; Sievert, F.; Thommes, M.; Breitkreutz, J. Improved group contribution parameter set for the application of solubility parameters to melt extrusion. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 5, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashimam, M. Hansen solubility parameters: A quick review in pharmaceutical aspect. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 597–599. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Afzal, O.; Altamimi, A.S.A.; Ali, A.; Ali, A.; Martinez, F.; Siddique, M.U.M.; Acree, W.E., Jr.; Ali, N. Preferential solvation study of (Z)-N-benzyl-2-{5-(4-hydroxybenzylidene)-2,4-dioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetamide (3) in {NMP (1) + Water (2)} co-solvent mixture and GastroPlus software based in vitro simulation. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 349, 118491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.A.; Alhalaweh, A.; Velaga, S.P. Hansen solubility parameter as a tool to predict cocrystal formation. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 407, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, T.V.; Drozd, K.V.; Surov, A.O. Effect of polymers and cyclodextrins on solubility, permeability and distribution of enzalutamide and apalutamide antiandrogens. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 322, 114937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters: A User’s Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Filimon, A.; Onofrei, M.-D. New insights on solvent implications in the design of materials based on cellulose derivatives using experimental and theoretical approaches. Materials 2021, 14, 6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, E.B.; Nelson, T.P.; Scigliano, J.M. Three-dimensional solubility parameters and their relationship to internal pressure measurements in polar and hydrogen bonding solvents. J. Paint Technol. 1971, 43, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Breitkreutz, J. Prediction of intestinal drug absorption properties by three dimensional solubility parameters. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Altamimi, M.A.; Afzal, O.; Altamimi, A.S.A.; Ali, A.; Ali, A.; Martinez, F.; Siddique, M.U.M.; Acree, W.E., Jr.; Jouyban, A. Preferential solvation study of the synthesized Aldose Reductase 2 inhibitor (SE415) in the {PEG 400 (1) + Water (2)} cosolvent mixture 3 and GastroPlus-based prediction. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avdeef, A. Absorbtion and drug developement. Solubility, Permeability, and Charge State, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, M.H.; Chadha, H.S.; Whiting, G.S.; Mitchell, R.C. Hydrogen bonding. 32. An analysis of water-octanol and water-alkane partitioning and the Δlog P parameter of Seiler. J. Pharm. Sci. 1994, 83, 1085–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avdeef, A.; Fuguet, E.; Llinàs, A.; Ràfols, C.; Bosch, E.; Völgyi, G.; Verbić, T.; Boldyreva, E.; Takács-Novák, K. Equilibrium solubility measurement of ionizable drugs—Consensus recommendations for improving data quality. ADMET DMPK 2016, 4, 117–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oja, M.; Maran, U. Quantitative structure–permeability relationships at various pH values for acidic and basic drugs and drug-like compounds. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2015, 26, 701–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| T (K) | Water | 1-Octanol | n-Hexane | Ethanol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X2 × 107 (S2 × 106) | X2 × 104 (S2 × 103) | X2 × 106 (S2 × 106) | X2 × 103 (S2 × 102) | |
| 293.15 | 1.12 (6.24) | 2.23 (1.42) | 0.74 (5.67) | 1.15 (1.95) |
| 298.15 | 1.47 (8.14) | 2.57 (1.62) | 1.07 (8.12) | 1.42 (2.40) |
| 303.15 | 1.90 (10.52) | 3.00 (1.88) | 1.50 (11.33) | 1.74 (2.91) |
| 308.15 | 2.35 (12.95) | 3.40 (2.13) | 2.04 (15.31) | 2.11 (3.49) |
| 313.15 | 2.97 (16.39) | 3.95 (2.46) | 2.76 (20.52) | 2.43 (3.99) |
| 318.15 | 3.63 (26.80) |
| Sample | V (cm3∙mol−1) | a (MPa0.5) | b (MPa0.5) | c (MPa0.5) | d (MPa0.5) | e | f (MPa0.5) | gRa (MPa0.5) | i RED |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCL | 339.7 | 15.8 | 13.5 | 9.0 | 22.6 | 20.8 | hR0 = 11.78 | ||
| water | 18.0 | 15.5 | 16.0 | 42.3 | 47.8 | 25.2 | 22.3 | 33.40 | 2.84 |
| 1-octanol | 157.7 | 17.0 | 3.3 | 11.9 | 21.0 | 1.6 | 17.3 | 10.87 | 0.92 |
| n-hexane | 131.6 | 14.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 14.9 | 7.7 | 14.9 | 16.32 | 1.39 |
| ethanol | 58.5 | 15.8 | 8.8 | 19.4 | 26.5 | 3.9 | 18.1 | 11.41 | 0.97 |
| Solvent | (kJ∙mol−1) | (kJ∙mol−1) | (kJ∙mol−1) | (J∙mol−1·K−1) | (kJ∙mol−1) | (kJ∙mol−1) | (kJ∙mol−1) | (J∙mol−1·K−1) | (%) | (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 1.47 × 10−7 | 39.0 | 36.8 ± 0.6 | −2.2 | −7.4 ± 0.3 | 24.7 | 87.9 | 63.2 | 212.0 | 58.2 | 41.8 |
| 1-Octanol | 2.51 × 10−4 | 20.5 | 21.6 ± 0.4 | 1.1 | 3.7 ± 3.6 | 43.2 | 103.1 | 59.9 | 200.9 | 63.3 | 36.7 |
| n-Hexane | 1.07 × 10−6 | 34.2 | 49.2 ± 0.7 | 15.0 | 50.3 ± 3.4 | 29.5 | 75.5 | 46.0 | 154.3 | 62.1 | 37.9 |
| Ethanol | 1.42 × 10−3 | 16.2 | 28.9 ± 0.9 | 12.7 | 42.6 ± 5.1 | 47.5 | 95.8 | 48.3 | 162.0 | 66.5 | 33.5 |
| ΔGtr (kJ⋅mol−1) | ΔHtr (kJ⋅mol−1) | TΔStr (kJ⋅mol−1) | ΔStr (J⋅mol−1⋅K−1) | a | b | c | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n-hexane → 1-octanol | |||||||
| −13.7 | −27.6 | −13.9 | −46.6 | 66.5 | 33.5 | 36.6 | 30.2 |
| n-hexane → water | |||||||
| 4.8 | −12.4 | −17.2 | −57.7 | 41.9 | 58.1 | 16.4 | 37.4 |
| n-hexane → ethanol | |||||||
| −18 | −20.3 | −2.3 | −7.7 | 89.8 | 10.2 | 68.8 | 5.0 |
| water → 1-octanol | |||||||
| −18.5 | −15.2 | 3.3 | 11.1 | 82.2 | 17.8 | - | - |
| 1-Octanol/Water System | n-Hexane/Water System | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| b Experimental Distribution Coefficients | ||||
| ∆logD | ||||
| 662.29 ± 20.22 | 2.82 ± 0.09 | 1.88 ± 0.04 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 2.55 |
| c Calculated distribution coefficients | ||||
| log | log | ∆logDcalc | ||
| 199.02 ± 12.00 | 2.30 ± 0.14 | 1.00 | 0 | 2.30 |
| (kJ∙mol−1) | (kJ∙mol−1) | (kJ∙mol−1) | (J⋅mol−1⋅K−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a 1-octanol/water system (water → 1-octanol) | ||||
| 5814.20 | −21.5 ± 0.4 | −15.0 ± 0.2 | 6.5 | 21.8 ± 0.7 |
| b n-hexane/water system (water → n-hexane) | ||||
| 13.67 | −6.5 ± 0.2 | 17.6 ± 1.8 | 24.1 | 80.8 ± 9.9 |
| c Δ parameter * (n-hexane → 1-octanol) | ||||
| 425.33 | −15.0 ± 0.4 | −32.5 ± 1.6 | −17.5 | −58.7 ± 4.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volkova, T.V.; Simonova, O.R.; Perlovich, G.L. Physicochemical Profile of Antiandrogen Drug Bicalutamide: Solubility, Distribution, Permeability. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030674
Volkova TV, Simonova OR, Perlovich GL. Physicochemical Profile of Antiandrogen Drug Bicalutamide: Solubility, Distribution, Permeability. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(3):674. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030674
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolkova, Tatyana V., Olga R. Simonova, and German L. Perlovich. 2022. "Physicochemical Profile of Antiandrogen Drug Bicalutamide: Solubility, Distribution, Permeability" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 3: 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030674
APA StyleVolkova, T. V., Simonova, O. R., & Perlovich, G. L. (2022). Physicochemical Profile of Antiandrogen Drug Bicalutamide: Solubility, Distribution, Permeability. Pharmaceutics, 14(3), 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030674