Development and Comparison of Various Coated Hard Capsules Suitable for Enteric Administration to Small Patient Cohorts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
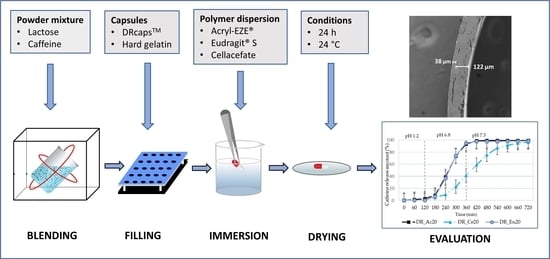
2.2. Preparation of Enteric-Coated Capsules
2.3. Viscosity Measurement
2.4. Weight Gain of the Coating
2.5. Capsule Structure Images
2.6. Disintegration Test
2.7. Dissolution Test
2.8. Comparison of Dissolution Profiles
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Viscosity Measurement
3.2. Characteristics of Polymer Coating: Weight Gain of Coating; Thickness of Coating; Capsule Structure Images
3.3. Disintegration Test
3.4. Dissolution Test. Similarity Factor f2 and Dissolution Efficiency (Expressed as ΔDE) of Compared Dissolution Profiles
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murachanian, D. Two-piece hard capsules for pharmaceutical formulation. J. GXP Compliance 2010, 14, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tuleu, C.; Khela, M.K.; Evans, D.F.; Jones, B.E.; Nagata, S.; Basit, A.W. A scintigraphic investigation of the disintegration behaviour of capsules in fasting subjects: A comparison of hypromellose capsules containing carrageenan as a gelling agent and standard gelatin capsules. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 30, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalani, R.; Samant, R.; Mistra, A. Applications of polymers in small intestinal drug delivery. In Applications of Polymers in Drug Delivery, 2nd ed.; Mistra, A., Shahiwala, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nober, C.; Manini, G.; Carlier, E.; Raquez, J.M.; Benali, S.; Dubois, P.; Amighi, K.; Goole, J. Feasibility study into the potential use of fused-deposition modeling to manufacture 3D-printed enteric capsules in compounding pharmacies. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, M.; Ball, K.; Scholz, E.; Schneider, F.; Sivert, A.; Benameur, H.; Kromrey, M.L.; Kühn, J.P.; Weitschies, W. Characterization of the gastrointestinal transit and disintegration behavior of floating and sinking acid-resistant capsules using a novel MRI labeling technique. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 129, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořáčková, K.; Franc, A.; Kejdušová, M. Drug delivery to the large intestine. Chemické Listy 2013, 107, 522–529. Available online: http://chemicke-listy.cz/ojs3/index.php/chemicke-listy/article/view/6455 (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Dvořáčková, K.; Rabišková, M.; Gajdziok, J.; Vetchý, D.; Muselík, J.; Bernatoniene, J.; Bajerová, M.; Drottnerová, P. Coated capsules for drug targeting to proximal and distal part of human intestine. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Amidon, S.; Brown, J.E.; Dave, V.S. Colon-targeted oral drug delivery systems: Design trends and approaches. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Kuo, C.H.; Kuo, F.C.; Wang, Y.K.; Hsu, W.H.; Yu, F.J.; Hu, H.M.; Hsu, P.I.; Wang, J.Y.; Wu, D.C. Fecal microbiota transplantation: Review and update. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyghebaert, N.; Vermeire, A.; Remon, J.P. Alternative method for enteric coating of HPMC capsules resulting in ready-to-use enteric-coated capsules. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 21, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wening, K.; Breitkreutz, J. Oral drug delivery in personalized medicine: Unmet needs and novel approaches. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 404, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benameur, H. Enteric Capsule Drug Delivery Technology–Achieving Protection without Coating. Drug Dev. Deliv. 2015, 15, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jančálková, M. Capsule Coating for Faecal Transplant Transport. Master’s Thesis, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- DRcapsTM Capsules. Available online: https://s3.amazonaws.com/cpsl-web/kc/library/c1a-32029_DRCaps-A4_FIN.PDF (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Youngster, I.; Russell, G.H.; Pindar, C.; Ziv-Baran, T.; Sauk, J.; Hohmann, E.L. Oral, capsulized, frozen fecal microbiota transplantation for relapsing Clostridium difficile infection. JAMA 2014, 312, 1772–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Tabakha, M.M.; Arida, A.I.; Fahelelbom, K.M.S.; Sadek, B.; Jarad, R.A.A. Performances of New Generation of Delayed Release Capsules. J. Young Pharm. 2015, 7, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AR CAPS® Enteric Capsules. Available online: https://www.cphi-online.com/ar-caps-enteric-capsules-prod476709.html (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- European Pharmacopoeia, 9th ed.; Ph. Eur. MMXVII; European Pharmacopoeia Commission: Strasbourg, France, 2017.
- EMBO CAPS® AP capsules. Available online: https://www.cphi-online.com/embo-capsap-prod907236.html (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Acid Resistant Hypromellose Capsules. EMBO CAPS® AP. Available online: https://www.capromax.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/EMBOCAPS_AP.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2022).
- BioVXR®. Available online: https://www.dfc.com.tw/archive/product/item/files/BioVXR%20brochure%202022.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Chang, R.J.; Wu, C.J.; Lin, Y.H. Acid Resistant Capsule Shell Composition, Acid Resistant Capsule Shell and Its Preparing Process. U.S. Patent No. 9,452,141 B1, 27 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hussan, S.D.; Santanu, R.; Verma, P.; Bhandari, V. A review on recent advances of enteric coating. IOSR J. Pharm. 2012, 2, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, E.T.; Scott, R.A.; Connor, A.L.; Wilding, I.R.; Petereit, H.U.; Schminke, C.; Beckert, T.; Cadé, D. Enteric coated HPMC capsules designed to achieve intestinal targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 231, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUDRAGIT® L 100 and EUDRAGIT® S 100—Technical Information. Available online: https://studylib.net/doc/25298564/evonik-eudragit-l-100-and-eudragit-s-100-specification-sheet (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- AcrylEZE®—Product Information. Available online: https://www.colorcon.com/products-formulation/all-products/film-coatings/enteric-release/acryl-eze/download/543/2025/34 (accessed on 13 November 2021).
- Saikh, M.A.A. Aqueous film coating the current trend. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2021, 11, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, K.; Bechtold, K. Enteric Coated Hard Gelatin Capsules. 2018. Available online: https://cpsl-web.s3.amazonaws.com/kc/library/enteric-coated-hard-gelatin-capsules.pdf?mtime=20170701121845 (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Moghimipour, E.; Rezaei, M.; Kouchak, M.; Fatahiasl, J.; Angali, K.A.; Ramezani, Z.; Amini, M.; Dorkoosh, F.A.; Handali, S. Effects of coating layer and release medium on release profile from coated capsules with Eudragit FS 30D: An in vitro and in vivo study. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonaje, K.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, H.L.; Wey, S.P.; Juang, J.H.; Nguyen, H.N.; Hsu, C.W.; Lin, K.J.; Sung, H.W. Enteric-coated capsules filled with freeze-dried chitosan/poly(γ-glutamic acid) nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3384–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vattanagijying, Y.; Kulvanich, P.; Chatchawalsaisin, J. Fabrication of delayed release hard capsule shells from zein/methacrylic acid copolymer blends. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 171, 106124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullapalli, R.P.; Mazzitelli, C.L. Gelatin and non-gelatin capsule dosage forms. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodmeier, R.; Paeratakul, O. The distribution of plasticizers between aqueous and polymer phases in aqueous colloidal polymer dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 1994, 103, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.C.; Sheskey, P.J.; Weller, P.J. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients; The Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Brookfield DV-II+PRO Viscometer Manual. Available online: https://www.brookfieldengineering.com/-/media/ametekbrookfield/manuals/obsolete%20manuals/dviipro%20m03165f0612.pdf?la=en&fbclid=IwAR2sRzHX9LS4LzT6khm0enZi6cKau4k06x3lJVi6zP3NapN1u6Iap29dv9M (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Costa, P.; Lobo, J.M.S. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.H.; Bauer, M.; Boussac, N.; Khan-Malek, R.; Munden, P.; Sardaro, M. An evaluation of fit factors and dissolution efficiency for the comparison of in vitro dissolution profiles. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1998, 17, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, S.A.; Bedaiwy, H.M.E. In vitro dissolution similarity as a surrogate for in vivo bioavailability and therapeutic equivalence. Dissolution Technol. 2016, 23, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Khalafvandi, S.A.; Pazokian, M.A.; Fathollahi, E. The Investigation of Viscometric properties of the most reputable types of viscosity index improvers in different lubricant case oils: API groups I, II and III. Lubricants 2022, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, L.A. Mechanisms of polymeric film formation. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, C.D.; Fegely, K.A.; Rajabi-Siahboomi, A.R.; McGinity, J.W. The influence of heterogeneous nucleation on the surface crystallization of guaifenesin from melt extrudates containing Eudragit® L10055 or Acryl-EZE®. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 75, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, L.A.; McGinity, J.W. Adhesion of polymeric films to pharmaceutical solids. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1999, 47, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořáčková, K.; Rabišková, M.; Muselík, J.; Gajdziok, J.; Bajerová, M. Coated hard capsules as the pH-dependent drug transport systems to ileo-colonic compartment. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 37, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acryl-EZE®. Aqueous Acrylic Enteric System, Colorcon. Available online: https://www.colorcon.com/search/item/2035-crs-2007-the-influence-of-plasticizer-type-and-concentration-on-acid-resistance-of-coated-tablets (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- Fu, M.; Al-Gousous, J.; Blechar, J.A.; Langguth, P. Enteric hard capsules for targeting the small intestine: Positive correlation between in vitro disintegration and dissolution times. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deasy, P.B.; O’Connell, M.J.M. Correlation of surface characteristics with ease of production and in vitro release of sodium salicylate from various enteric coated microcapsules prepared by pan coating. J. Microencapsul. 1984, 1, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Sample ** | Coating | The Practical Content of Caffeine per Capsule ± SD (mg) | Mean Weight of Uncoated Capsules ± SD (mg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | % | Solvent | |||
| DR_Eu10 | Eudragit® S | 10 | Ethanol (96%) | 101.50 ± 4.63 | 500.71 ± 10.96 |
| DR_Eu15 | 15 | 98.40 ± 5.54 | 497.10 ± 9.38 | ||
| DR_Eu20 | 20 | 103.40 ± 6.51 | 510.93 ± 3.16 | ||
| DR_Ac10 | Acryl-EZE® | 10 | Purified Water | 99.20 ± 4.96 | 498.20 ± 10.05 |
| DR_Ac15 | 15 | 102.10 ± 5.47 | 499.37 ± 10.60 | ||
| DR_Ac20 | 20 | 95.60 ± 3.56 | 518.78 ± 8.58 | ||
| DR_Ce10 | Cellacefate | 10 | Acetone | 97.80 ± 5.96 | 456.37 ± 4.49 |
| DR_Ce15 | 15 | 103.40 ± 2.91 | 528.25 ± 7.97 | ||
| DR_Ce20 | 20 | 99.30 ± 4.47 | 432.36 ± 6.45 | ||
| Ge_Eu10 | Eudragit® S | 10 | Ethanol (96%) | 102.80 ± 5.19 | 511.18 ± 11.03 |
| Ge_Eu15 | 15 | 105.90 ± 5.82 | 509.95 ± 7.58 | ||
| Ge_Eu20 | 20 | 101.10 ± 4.59 | 514.89 ± 7.55 | ||
| Ge_Ac10 | Acryl-EZE® | 10 | Purified Water | 100.60 ± 5.43 | 501.83 ± 10.57 |
| Ge_Ac15 | 15 | 103.30 ± 4.96 | 504.73 ± 8.52 | ||
| Ge_Ac20 | 20 | 98.10 ± 4.87 | 520.10 ± 8.74 | ||
| Ge_Ce10 | Cellacefate | 10 | Acetone | 103.90 ± 5.86 | 423.63 ± 9.05 |
| Ge_Ce15 | 15 | 103.70 ± 5.59 | 529.19 ± 8.05 | ||
| Ge_Ce20 | 20 | 105.50 ± 5.28 | 439.06 ± 8.29 | ||
| Polymer/Solvent | Dispersion Concentration (%) | Viscosity ± SD (cP) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eudragit® S/Ethanol 96% (w/w) | 10 | 36.1 ± 1.25 | |
| 15 | 142.8 ± 4.35 | ||
| 20 | 216.3 ± 6.60 | ||
| Acryl-EZE®/Purified Water | 10 | 1.3 ± 0.12 | |
| 15 | 2.0 ± 0.00 | ||
| 20 | 3.5 ± 0.00 | ||
| Cellacefate/Acetone | 10 | 28.8 ± 2.16 | |
| 15 | 67.9 ± 8.83 | ||
| 20 | 176.2 ± 21.23 |
| Sample | Mean Weight of the Coating ± SD (mg) | Mean Weight Gain of the Coating * ± SD (%) | The Average Thickness of Coating ± SD (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DR_Eu10 | 7.99 ± 0.93 | 7.98 ± 1.21 | 5.70 ± 0.73 |
| DR_Eu15 | 16.93 ± 2.90 | 17.36 ± 2.84 | 17.00 ± 2.15 |
| DR_Eu20 | 23.78 ± 4.47 | 23.90 ± 4.81 | 37.75 ± 2.67 |
| DR_Ac10 | 9.49 ± 2.44 | 10.53 ± 2.76 | 19.40 ± 3.79 |
| DR_Ac15 | 13.17 ± 2.29 | 13.21 ± 2.58 | 29.0 ± 6.34 |
| DR_Ac20 | 17.18 ± 1.80 | 17.60 ± 2.14 | 35.60 ± 7.97 |
| DR_Ce10 | 6.28 ± 0.86 | 6.48 ± 0.96 | 28.35 ± 3.12 |
| DR_Ce15 | 10.50 ± 0.99 | 8.15 ± 0.99 | 29.65 ± 4.96 |
| DR_Ce20 | 18.49 ± 1.91 | 13.17 ± 2.10 | 70.00 ± 2.71 |
| Ge_Eu10 | 4.28 ± 0.48 | 3.84 ± 0.50 | 11.10 ± 2.20 |
| Ge_Eu15 | 5.37 ± 0.37 | 4.87 ± 0.42 | 11.20 ± 1.82 |
| Ge_Eu20 | 9.85 ± 1.29 | 8.71 ± 1.39 | 19.80 ± 2.55 |
| Ge_Ac10 | 5.47 ± 1.76 | 5.81 ± 1.90 | 12.50 ± 3.12 |
| Ge_Ac15 | 11.18 ± 2.09 | 11.79 ± 2.31 | 40.70 ± 5.03 |
| Ge_Ac20 | 15.09 ± 1.82 | 15.88 ± 1.94 | 57.90 ± 6.83 |
| Ge_Ce10 | 3.39 ± 0.68 | 3.13 ± 0.73 | 8.35 ± 1.14 |
| Ge_Ce15 | 7.40 ± 1.78 | 5.30 ± 1.91 | 21.75 ± 1.59 |
| Ge_Ce20 | 18.44 ± 1.74 | 11.90 ± 1.89 | 23.20 ± 3.74 |
| (A) Polymer Concentration | |||||
| Compared samples | f2/ΔDE (%) | Compared samples | f2/ΔDE (%) | ||
| DR_Ce10 */DR_Ce15 | 15.28/−75.78 | Ge_Ce10 */Ge_Ce15 | 35.32/−29.61 | ||
| DR_Ce10 */DR_Ce20 | 15.89/−73.47 | Ge_Ce10 */Ge_Ce20 | 26.51/−52.17 | ||
| DR_Ce15 */DR_Ce20 | 79.44/9.53 ** | Ge_Ce15 */Ge_Ce20 | 46.44/−32.05 | ||
| DR_Eu10 */DR_Eu15 | 66.12/11.35 ** | Ge_Eu10 */Ge_Eu15 | 53.72/−0.64 ** | ||
| DR_Eu10 */DR_Eu20 | 37.87/48.4 | Ge_Eu10 */Ge_Eu20 | 18.69/−45.69 | ||
| DR_Eu15 */DR_Eu20 | 42.12/33.27 | Ge_Eu15 */Ge_Eu20 | 20.6/−45.34 | ||
| DR_Ac10 */DR_Ac15 | 46.25/−11.64 | Ge_Ac10 */Ge_Ac15 | 28.04/−10.84 | ||
| DR_Ac10 */DR_Ac20 | 16.3/−47.28 | Ge_Ac10 */Ge_Ac20 | 19.06/−26.76 | ||
| DR_Ac15 */DR_Ac20 | 22.49/−40.33 | Ge_Ac15 */Ge_Ac20 | 36.31/−17.86 | ||
| (B) Polymer Type | |||||
| Compared samples | f2/ΔDE (%) | Compared samples | f2/ΔDE (%) | ||
| DR_Eu10 */DR_Ce10 | 25.05/91.94 | Ge_Eu10 */Ge_Ce10 | 28.78/−29.79 | ||
| DR_Ce10 */DR_Ac10 | 23.95/25.84 | Ge_Ce10 */Ge_Ac10 | 14.23/74.88 | ||
| DR_Eu10 */DR_Ac10 | 13.34/141.54 | Ge_Eu10 */Ge_Ac10 | 28.9/22.79 | ||
| DR_Eu15 */DR_Ce15 | 32.43/−58.25 | Ge_Eu15 */Ge_Ce15 | 19.0/−50.26 | ||
| DR_Ce15 */DR_Ac15 | 12.3/359.04 | Ge_Ce15 */Ge_Ac15 | 14.17/121.53 | ||
| DR_Eu15 */DR_Ac15 | 20.7/91.66 | Ge_Eu15 */Ge_Ac15 | 45.77/10.19 | ||
| DR_Eu20 */DR_Ce20 | 22.62/−65.69 | Ge_Eu20 */Ge_Ce20 | 40.66/−38.17 | ||
| DR_Ce20 */DR_Ac20 | 28.63/150.07 | Ge_Ce20 */Ge_Ac20 | 17.39/167.8 | ||
| DR_Eu20 */DR_Ac20 | 52.19/−14.19 ** | Ge_Eu20 */Ge_Ac20 | 24.91/65.6 | ||
| (C) Capsule Type | |||||
| Compared samples | f2/ ΔDE (%) | Compared samples | f2/ ΔDE (%) | Compared samples | f2/ ΔDE (%) |
| DR_Ce10 */Ge_Ce10 | 15.28/ 160.21 | DR_Eu10 */Ge_Eu10 | 6.14/ 753.98 | DR_Ac10 */Ge_Ac10 | 12.97/ 49.85 |
| DR_Ce15 */Ge_Ce15 | 8.54/ 1546.18 | DR_Eu15 */Ge_Eu15 | 6.22/ 557.71 | DR_Ac15 */Ge_Ac15 | 13.63/ 83.04 |
| DR_Ce20 */Ge_Ce20 | 10.42/ 1102.78 | DR_Eu20 */Ge_Eu20 | 11.52/ 392.4 | DR_Ac20 */Ge_Ac20 | 7.97/ 464.25 |
| Factor | Dispersion | Capsules | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | The Released Amount of API at 120 min | Weight Gain from the Coating | Coating Thickness | |
| Polymer type (A) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Polymer concentration (B) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Capsule type (C) | NA | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| A × B | <0.001 | 0.096 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| A × C | NA | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| B × C | NA | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| A × B × C | NA | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fülöpová, N.; Pavloková, S.; DeBono, I.; Vetchý, D.; Franc, A. Development and Comparison of Various Coated Hard Capsules Suitable for Enteric Administration to Small Patient Cohorts. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14081577
Fülöpová N, Pavloková S, DeBono I, Vetchý D, Franc A. Development and Comparison of Various Coated Hard Capsules Suitable for Enteric Administration to Small Patient Cohorts. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(8):1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14081577
Chicago/Turabian StyleFülöpová, Nicole, Sylvie Pavloková, Ivan DeBono, David Vetchý, and Aleš Franc. 2022. "Development and Comparison of Various Coated Hard Capsules Suitable for Enteric Administration to Small Patient Cohorts" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 8: 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14081577
APA StyleFülöpová, N., Pavloková, S., DeBono, I., Vetchý, D., & Franc, A. (2022). Development and Comparison of Various Coated Hard Capsules Suitable for Enteric Administration to Small Patient Cohorts. Pharmaceutics, 14(8), 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14081577