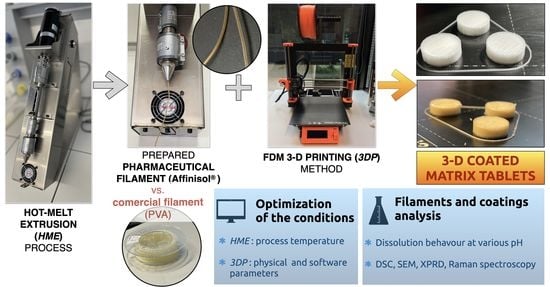
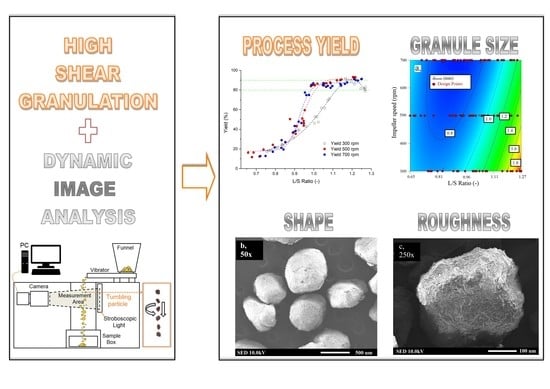
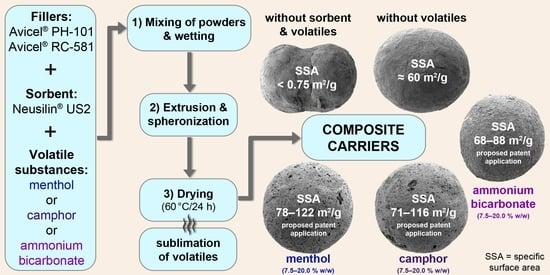
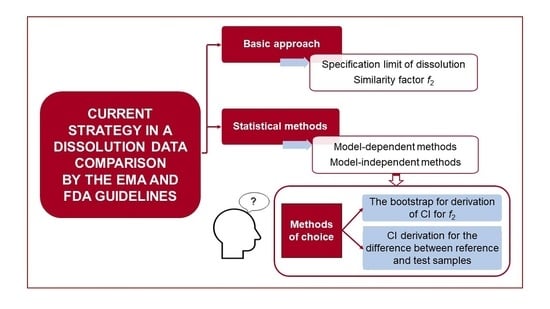
Advanced Pharmaceutical Research in the Czech Republic
A topical collection in Pharmaceutics (ISSN 1999-4923). This collection belongs to the section "Drug Delivery and Controlled Release".
Viewed by 56273Editors
Interests: dermal and transdermal application; skin barrier characterization; drug nanoformulation; drug targeting; application of biophysical techniques in pharmaceutics
Interests: microparticles for lung application; 2D and 3D printing of pharmaceutics; in situ forming gels; innovative processes and materials in pharmaceutical technology
Interests: microparticle/bead drug delivery systems; advanced drug delivery for veterinary use; biorelevant dynamic dissolution; controlled release formulation for oral drug delivery
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In recent decades, pharmaceutical sciences and engineering have come to represent a rapidly developing area in the Czech Republic. The aim of this regional issue is to bring an overview of the progress in this field. Researchers from both the academic and industrial spheres are welcome to submit their research or review articles focused on preformulation and formulation development, drug delivery, nanoparticulate formulation, polymer science, biopharmaceutics and pharmacokinetics, personalized medicine, or other related topics.
We intend to create a high-quality collection presenting novel results and attitudes. Moreover, we believe the issue will contribute to the discussion on these exciting topics and help to form new scientific collaborations.
Dr. Jarmila Zbytovska
Dr. Jan Gajdziok
Dr. Jakub Vysloužil
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Pharmaceutics is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- preformulation and formulation development
- drug delivery
- nanoparticulate formulation
- polymer science
- biopharmaceutics and pharmacokinetics
- personalized medicine
Related Special Issue
- Advanced Pharmaceutical Science and Technology in Pharmaceutics (3 articles)