Influence of Surface-Modification via PEGylation or Chitosanization of Lipidic Nanocarriers on In Vivo Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Profiles of Apixaban
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
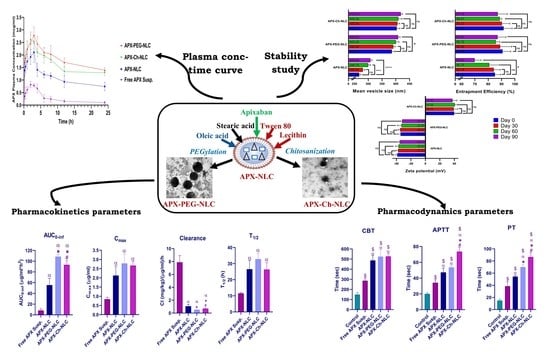
2.2.1. Development of APX-Loaded NLCs (APX-NLC) and APX-Loaded PEGylated NLCs (APX-PEG-NLC)
2.2.2. Elaboration of APX-Loaded Chitosan-Modified NLCs (APX-Ch-NLC)
2.2.3. Separation and Washing of APX-Loaded Nanovesicles
2.2.4. Characterization of APX-Loaded Nanovesicles
Particle Size and Zeta Potential Evaluation
Entrapment Efficiency (EE%) Determination
In Vitro APX Release Study and Mathematical Modeling of the Elaborated Nanovesicles
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.2.5. Stability Study
2.2.6. In Vivo Evaluation of the Prepared Nanovesicles
Protocol and Animal Preparation
Pharmacokinetics Study
- Chromatographic conditions
- Pharmacokinetics (PK)
Pharmacodynamics (PD) Study
- Cuticle Bleeding Time (CBT)
- Prothrombin Time (PT) and Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT)
2.2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the APX-Loaded Nanovesicles
3.1.1. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
3.1.2. Entrapment Efficiency
3.1.3. In Vitro Drug Release
3.1.4. Transmission Electron Microscope
3.1.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
3.2. Evaluation of Stability Parameters for the APX-Loaded Nanovesicles
3.3. In Vivo Characterization of Developed Nanovesicles
3.3.1. Pharmacokinetic Study
3.3.2. Pharmacodynamic Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ageno, W.; Haas, S.; Weitz, J.I.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Turpie, A.G.G.; Goto, S.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; Nielsen, J.D.; Kayani, G.; Pieper, K.S.; et al. Characteristics and Management of Patients with Venous Thromboembolism: The GARFIELD-VTE Registry. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raskob, G.E.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; Blanco, A.N.; Buller, H.; Gallus, A.; Hunt, B.J.; Hylek, E.M.; Kakkar, A.; Konstantinides, S.V.; McCumber, M.; et al. Thrombosis A Major Contributor to Global Disease Burden. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mekaj, Y.H.; Mekaj, A.Y.; Duci, S.B.; Miftari, E.I. New Oral Anticoagulants: Their Advantages and Disadvantages Compared with Vitamin K Antagonists in the Prevention and Treatment of Patients with Thromboembolic Events. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blann, A.D.; Lip, G.Y.H. Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) for the Management of Venous Thromboembolism. Heart 2016, 102, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, H.K.; Nikam, V.K. Formulation Development and Stability Indicating Hplc Assay of Tablets of Apixaban. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, P.C.; Pinto, D.J.P.; Zhang, D. Preclinical Discovery of Apixaban, a Direct and Orally Bioavailable Factor Xa Inhibitor. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2011, 31, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greig, S.L.; Garnock-Jones, K.P. Apixaban: A Review in Venous Thromboembolism. Drugs 2016, 76, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Yao, J.; Ma, Y.Y.; Chen, J.M.; Lu, T.B. Improving the Solubility and Bioavailability of Apixaban via Apixaban-Oxalic Acid Cocrystal. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 2923–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; He, K.; Herbst, J.J.; Kolb, J.; Shou, W.; Wang, L.; Balimane, P.V.; Han, Y.H.; Gan, J.; Frost, C.E.; et al. Characterization of Efflux Transporters Involved in Distribution and Disposition of Apixaban. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2013, 41, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheikh-Taha, M. Treatment of Apixaban- and Rivaroxaban-Associated Major Bleeding Using 4-Factor Prothrombin Complex Concentrate. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2019, 14, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeed, A.; Ågren, A.; Holmström, M.; Bruzelius, M.; Chaireti, R.; Odeberg, J.; Hempel, E.L.; Magnusson, M.; Frisk, T.; Schulman, S. Management of Rivaroxaban- or Apixaban-Associated Major Bleeding with Prothrombin Complex Concentrates: A Cohort Study. Blood 2017, 130, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadi, R.; Dand, N. BCS Class IV Drugs: Highly Notorious Candidates for Formulation Development. J. Control Release 2017, 248, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, S.; Zimmer, A.; Pardeike, J. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) for Pulmonary Application: A Review of the State of the Art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 86, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabelo, R.S.; Oliveira, I.F.; da Silva, V.M.; Prata, A.S.; Hubinger, M.D. Chitosan Coated Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) for Loading Vitamin D: A Physical Stability Study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloqui, A.; del Pozo-Rodríguez, A.; Isla, A.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Solinís, M.Á. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Oral Delivery Systems for Poorly Soluble Drugs. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 42, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Shaharyar, M.; Fazil, M.; Hassan, M.Q.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J. Tacrolimus-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Oral Delivery-in Vivo Bioavailability Enhancement. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 109, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Tang, B.; Chao, Y.; Xu, H.; Gou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Tang, X. Cysteine-Functionalized Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Oral Delivery of Docetaxel: A Permeability and Pharmacokinetic Study. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2384–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandpe, L.; Pokharkar, V. Quality by Design Approach to Understand the Process of Optimization of Iloperidone Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Oral Bioavailability Enhancement. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2015, 20, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, B.; Beg, S.; Kumar, R.; Katare, O.P.; Singh, B. Nanostructured Lipidic Carriers of Lopinavir for Effective Management of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Patel, M. Enhanced Oral Bioavailability of Nintedanib Esylate with Nanostructured Lipid Carriers by Lymphatic Targeting: In Vitro, Cell Line and in Vivo Evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 159, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, G.; Nahak, P.; Guha, P.; Roy, B.; Nath, R.K.; Panda, A.K. Role of PEG 2000 in the Surface Modification and Physicochemical Characteristics of Pyrazinamide Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 130, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Luo, Q.; Lin, T.; Li, R.; Zhu, T.; Zhou, K.; Ji, Z.; Song, J.; Jia, B.; Zhang, C.; et al. PEGylated Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (PEG–NLC) as a Novel Drug Delivery System for Biochanin A. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yostawonkul, J.; Surassmo, S.; Iempridee, T.; Pimtong, W.; Suktham, K.; Sajomsang, W.; Gonil, P.; Ruktanonchai, U.R. Surface Modification of Nanostructure Lipid Carrier (NLC) by Oleoyl-Quaternized-Chitosan as a Mucoadhesive Nanocarrier. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 149, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling Tan, J.S.; Roberts, C.J.; Billa, N. Mucoadhesive Chitosan-Coated Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Oral Delivery of Amphotericin B. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 24, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, Y.C.; Tran, P.; Kim, D.H.; Park, J.S. Chitosan-Coated Nanostructured Lipid Carriers of Fenofibrate with Enhanced Oral Bioavailability and Efficacy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 196, 111331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi Kumar, M.N.V. A Review of Chitin and Chitosan Applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasineh, S.; Akbarian, M.; Ebrahimi, H.A.; Behbudi, G. Tacrolimus-Loaded Chitosan-Coated Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Preparation, Optimization and Physicochemical Characterization. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 11, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; El-Bery, H.M.; Metwally, A.A.; Elshazly, M.; Hathout, R.M. Synthesis of CdS-Modified Chitosan Quantum Dots for the Drug Delivery of Sesamol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 214, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowaidar, M.; Nasser Abdelhamid, H.; Hällbrink, M.; Langel, Ü.; Zou, X. Chitosan Enhances Gene Delivery of Oligonucleotide Complexes with Magnetic Nanoparticles–Cell-Penetrating Peptide. J. Biomater. Appl. 2018, 33, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.D.; Huang, L. Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution of Nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Yin, L. Preparation and Evaluation of PEGylated Asiatic Acid Nanostructured Lipid Carriers on Anti-Fibrosis Effects. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, N. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Novel Carrier for Parenteral Delivery of Docetaxel. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 85, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Lin, Q.; Guo, L.; Fu, Y.; Han, J.; Ke, H.; Sun, X.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z. Rifampicin Loaded Mannosylated Cationic Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Alveolar Macrophage-Specific Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 1741–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaky, M.F.; Megahed, M.A.; Hammady, T.M.; Gad, S.; Ghorab, M.M.; El-Say, K.M. Tailoring Apixaban in Nanostructured Lipid Carrier Enhancing Its Oral Bioavailability and Anticoagulant Activity. Pharmaceutics 2022, 15, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenechukwu, F.C.; Isaac, G.T.; Nnamani, D.O.; Momoh, M.A.; Attama, A.A. Enhanced Circulation Longevity and Pharmacodynamics of Metformin from Surface-Modified Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Based on Solidified Reverse Micellar Solutions. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Ameeduzzafar; Alharbi, K.S.; Alruwaili, N.K.; Al-Abassi, F.A.; Al-Malki, A.A.L.; Kazmi, I.; Kumar, V.; Kamal, M.A.; Nadeem, M.S.; et al. Nanomedicine in Treatment of Breast Cancer—A Challenge to Conventional Therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 69, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, S.M.A.; Roslan, N.Z.I.; Muda, R.; Abdul-Aziz, A. Encapsulation of Ficus Deltoidea Extract in Nanostructured Lipid Carrier for Anti-Melanogenic Activity. Bionanoscience 2021, 11, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zuhairy, S.A.S.; Teaima, M.H.; Shoman, N.A.; Elasaly, M.; El-Nabarawi, M.A.; El-Sawy, H.S. PEGylated Tween 80-Functionalized Chitosan-Lipidic Nano-Vesicular Hybrids for Heightening Nose-to-Brain Delivery and Bioavailability of Metoclopramide. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2189112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, M.; Sammour, O.A.; Hammad, M.A.; Megrab, N.A. Effect of Some Formulation Parameters on Flurbiprofen Encapsulation and Release Rates of Niosomes Prepared from Proniosomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 361, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaabani, E.; Sharifiaghdam, M.; De Keersmaecker, H.; De Rycke, R.; De Smedt, S.; Faridi-Majidi, R.; Braeckmans, K.; Fraire, J.C. Layer by Layer Assembled Chitosan-Coated Gold Nanoparticles for Enhanced SiRNA Delivery and Silencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.D.; Nativo, P.; Smith, J.A.; Stirling, D.; Edwards, P.R.; Venugopal, B.; Flint, D.J.; Plumb, J.A.; Graham, D.; Wheate, N.J. Gold Nanoparticles for the Improved Anticancer Drug Delivery of the Active Component of Oxaliplatin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4678–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khames, A.; Khaleel, M.A.; El-Badawy, M.F.; El-Nezhawy, A.O.H. Natamycin Solid Lipid Nanoparticles—Sustained Ocular Delivery System of Higher Corneal Penetration against Deep Fungal Keratitis: Preparation and Optimization. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madan, J.R.; Waghmare, S.V.; Patil, R.B.; Awasthi, R.; Dua, K. Cocrystals of Apixaban with Improved Solubility and Permeability: Formulation, Physicochemical Characterization, Pharmacokinetic Evaluation, and Computational Studies. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2021, 19, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Paclitaxel Nanosuspension Using Novel Emulsification Method by Combining High Speed Homogenizer and High Pressure Homogenization. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 490, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shenawy, A.A.; Mahmoud, R.A.; Mahmoud, E.A.; Mohamed, M.S. Intranasal In Situ Gel of Apixaban-Loaded Nanoethosomes: Preparation, Optimization, and In Vivo Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; Application Number 202155—Clinical Pharmacology and Biopharmaceutical Review(S); US Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2012.
- Wójcik-Pastuszka, D.; Krzak, J.; Macikowski, B.; Berkowski, R.; Osiński, B.; Musiał, W. Evaluation of the Release Kinetics of a Pharmacologically Active Substance from Model Intra-Articular Implants Replacing the Cruciate Ligaments of the Knee. Materials 2019, 12, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, D.J.; Kumar, J.; Shakil, N.A.; Walia, S. Release Kinetics of Controlled Release Formulations of Thiamethoxam Employing Nano-Ranged Amphiphilic PEG and Diacid Based Block Polymers in Soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health—Part A Toxic/Hazardous Subst. Environ. Eng. 2012, 47, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaccorso, A.; Cimino, C.; Manno, D.E.; Tomasello, B.; Serra, A.; Musumeci, T.; Puglisi, G.; Pignatello, R.; Carbone, C. Essential Oil-loaded Nlc for Potential Intranasal Administration. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Renner, F.; Foster, K.; Oderinde, M.S.; Stefanski, K.; Mitra, S. Enhanced Aqueous Dissolution of Hydrophobic Apixaban via Direct Incorporation of Hydrophilic Nanographene Oxide. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 216, 112512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kong, D.; Wang, H.; Jiao, L.; Zhao, X.; Song, J.; Yang, D.; Yang, H.; Yang, S.; Du, G.; et al. Cocrystal of Apixaban–Quercetin: Improving Solubility and Bioavailability of Drug Combination of Two Poorly Soluble Drugs. Molecules 2021, 26, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Say, K.M.; Hosny, K.M. Optimization of Carvedilol Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: An Approach to Control the Release and Enhance the Oral Bioavailability on Rabbits. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cini, M.; Legnani, C.; Padrini, R.; Cosmi, B.; Dellanoce, C.; De Rosa, G.; Marcucci, R.; Pengo, V.; Poli, D.; Testa, S.; et al. DOAC Plasma Levels Measured by Chromogenic Anti-Xa Assays and HPLC-UV in Apixaban- and Rivaroxaban-Treated Patients from the START-Register. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2020, 42, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, F.; Bicker, J.; Santos, J.; Rocha, M.; Alves, G.; Falcão, A.; Fortuna, A. Development, Validation and Application of a New HPLC-DAD Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Apixaban, Dabigatran, Edoxaban and Rivaroxaban in Human Plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 181, 113109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankrom, W.; Wood, H.B.; Xu, J.; Geissler, W.; Bateman, T.; Chatterjee, M.S.; Feng, K.I.; Metzger, J.M.; Strapps, W.R.; Tadin-Strapps, M.; et al. Preclinical and Translational Evaluation of Coagulation Factor IXa as a Novel Therapeutic Target. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2016, 4, e00207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, R.; Fukushima, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Takahashi, H.; Hori, Y. The Correlations between Anti-Factor Xa Activity Values and PT/APTT at Peak and Trough Times in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism Using High Dose of Apixaban. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, ehaa946-2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Luo, B.; Cai, T.Q.; Thankappan, A.; Xu, Y.; Wu, W.; DiMuzio, J.; Lifsted, T.; DiPietro, M.; Disa, J.; et al. Proof-of-Concept Studies for SiRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing for Coagulation Factors in Rat and Rabbit. Mol. Ther.—Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghafar, O.A.M.A.; Helal, G.K.; Abo-Youssef, A.M. Apixaban Exhibits Anti-Arthritic Effects by Inhibiting Activated Factor X-Mediated JAK2/STAT3 and MAPK Phosphorylation Pathways. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 1253–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marianecci, C.; Paolino, D.; Celia, C.; Fresta, M.; Carafa, M.; Alhaique, F. Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles in Pulmonary Glucocorticoid Delivery: Characterization and Interaction with Human Lung Fibroblasts. J. Control Release 2010, 147, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeganroudsari, M.; Heydarinasab, A.; Akbarzadeh khiyavi, A.; Chen, P.; Soltani, M. In Vitro Investigation of Anticancer Efficacy of Carboplatin-Loaded PEGylated Nanoliposome Particles on Brain Cancer Cell Lines. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2019, 21, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, M.A.; El-Sawy, H.S.; Abd-Allah, F.I.; Abdelghany, T.M.; El-Say, K.M. Maximizing the Therapeutic Efficacy of Imatinib Mesylate–Loaded Niosomes on Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Using Box-Behnken Design. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardeike, J.; Weber, S.; Zarfl, H.P.; Pagitz, M.; Zimmer, A. Itraconazole-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) for Pulmonary Treatment of Aspergillosis in Falcons. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangtana-Anan, M.; Limmatvapirat, S.; Nunthanid, J.; Chalongsuk, R.; Yamamoto, K. Polyethylene Glycol on Stability of Chitosan Microparticulate Carrier for Protein. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1376–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bashiri, S.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Ayaseh, A.; Dehghannya, J.; Ehsani, A. Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan-Coated Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (CH-NLC) Containing Cinnamon Essential Oil for Enriching Milk and Anti-Oxidant Activity. LWT 2020, 119, 108836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, W.H.; Wang, Q. Preparation, Characterization and Evaluation of Selenite-Loaded Chitosan/TPP Nanoparticles with or without Zein Coating. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardakhty, A.; Varshosaz, J.; Rouholamini, A. In Vitro Study of Polyoxyethylene Alkyl Ether Niosomes for Delivery of Insulin. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 328, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Shi, Z.H.; Bian, X.H.; Xia, Q. Nanostructured-Lipid Carriers-Chitosan Hydrogel Beads Carrier System for Loading of Resveratrol: A New Method of Topical Application. J. Biomater. Appl. 2022, 36, 1444–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Asghar, S.; Gao, S.; Su, Z.; Song, J.; Huo, M.; Meng, W.; Ping, Q.; Xiao, Y. A Novel LDL-Mimic Nanocarrier for the Targeted Delivery of Curcumin into the Brain to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 134, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeyor, C.E.; Umeyor, I.C.; Uronnachi, E.M.; Nwakile, C.D. Formulation Design and Preclinical Evaluations of Surface Modified Lipid Nanoparticles-Coupled Gel Encapsulating Dihydroartemisinin for Treatment of Localized Inflammation. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci. 2021, 11, 3745–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; Li, Y.Z.; Chen, C.; Cao, Y.N.; Yu, M.M.; Xu, L.; He, B.; Jie, X.; Shen, W.W.; Wang, Y.N.; et al. G5-PEG PAMAM Dendrimer Incorporating Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Enhance Oral Bioavailability and Plasma Lipid-Lowering Effect of Probucol. J. Control Release 2015, 210, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Mäder, K.; Gohla, S. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) for Controlled Drug Delivery—A Review of the State of the Art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordillo-Galeano, A.; Mora-Huertas, C.E. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Review Emphasizing on Particle Structure and Drug Release. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 133, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil-Gadhe, A.; Pokharkar, V. Montelukast-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Part I Oral Bioavailability Improvement. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Imam, S.S.; Aqil, M.; Ahad, A.; Sultana, Y.; Ameeduzzafar; Ali, A. Carvedilol Nano Lipid Carriers: Formulation, Characterization and In-Vivo Evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, M.; Falkeborg, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, T.; Xu, X. Formulation and Characterization of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Containing a Mixed Lipids Core. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 430, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Varshosaz, J. Novel Hesperetin Loaded Nanocarriers for Food Fortification: Production and Characterization. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmowafy, M.; Shalaby, K.; Badran, M.M.; Ali, H.M.; Abdel-Bakky, M.S.; Ibrahim, H.M. Multifunctional Carbamazepine Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier (NLC) Formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohaib, M.; Shah, S.U.; Shah, K.U.; Shah, K.U.; Khan, N.R.; Irfan, M.M.; Niazi, Z.R.; Alqahtani, A.A.; Alasiri, A.; Walbi, I.A.; et al. Physicochemical Characterization of Chitosan-Decorated Finasteride Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Skin Drug Delivery. Biomed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 7792180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmowafy, M.; Al-Sanea, M.M. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) as Drug Delivery Platform: Advances in Formulation and Delivery Strategies. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021, 29, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Fang, Y.Q.; Liang, X.R.; Xu, Y.Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.H.; Fang, S.; Meng, Y.C. Influence of Polysorbates (Tweens) on Structural and Antimicrobial Properties for Microemulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 590, 119939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shete, H.; Chatterjee, S.; De, A.; Patravale, V. Long Chain Lipid Based Tamoxifen NLC. Part II: Pharmacokinetic, Biodistribution and in Vitro Anticancer Efficacy Studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Pan, W. Characterization and Evaluation of Nanostructured Lipid Carrier as a Vehicle for Oral Delivery of Etoposide. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 43, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.; Chavda, K.; Vyas, B.; Patel, S. Formulation Development of Linagliptin Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Bioavailability Enhancement: Role of P-Gp Inhibition. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 1166–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasir, M.; Gaur, P.K.; Puri, D.; Preeti, S.; Kumar, S.S. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Approach for Lymphatic Targeting through Intraduodenal Delivery of Quetiapine Fumarate. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2017, 15, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, R.; Pathak, K. Nanostructured Lipid Carrier versus Solid Lipid Nanoparticles of Simvastatin: Comparative Analysis of Characteristics, Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Uptake. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwanullah, M.; Amin, S.; Ahmad, J. Improved Pharmacokinetics and Antihyperlipidemic Efficacy of Rosuvastatin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. J. Drug Target. 2016, 25, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Higashi, K.; Watabe, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Limwikrant, W.; Yamamoto, K.; Moribe, K. Effects of the PEG Molecular Weight of a PEG-Lipid and Cholesterol on PEG Chain Flexibility on Liposome Surfaces. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 474, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, L.; Shen, J.; Zhang, D.; Duan, C.; Liu, G.; Zheng, D.; Tian, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Oridonin-Loaded Long Circulating Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, D.M.; Hoffman, M. A Mouse Bleeding Model to Study Oral Anticoagulants. Thromb. Res. 2014, 133, S6–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, S.; Hirai, N.; Shirai, M.; Ito, K.; Asai, F. Comparison of the Blood Coagulation Profiles of Ferrets and Rats. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2011, 73, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schumacher, W.A.; Bostwick, J.S.; Stewart, A.B.; Steinbacher, T.E.; Xin, B.; Wong, P.C. Effect of the Direct Factor Xa Inhibitor Apixaban in Rat Models of Thrombosis and Hemostasis. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2010, 55, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhong, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Xue, W. Effect of Chitosan and Carboxymethyl Chitosan on Fibrinogen Structure and Blood Coagulation. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 24, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Formulations | Mean Particle Size (nm) ± SD | Polydispersity Index | ZP * (mV) ± SD | Entrapment Efficiency (%) ± SD | Cumulative Release After 24 h (%) ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APX-NLC | 267.4 ± 5.5 | 0.4 | −38.7 ± 2.2 | 85.1 ± 4.1 | 82.1 ± 3.9 |
| APX-PEG-NLC | 385.9 ± 10.2 | 0.21 | −34.2 ± 4.4 | 90.8 ± 6.2 | 72.6 ± 2.1 |
| APX-Ch-NLC | 403.4 ± 11.5 | 0.26 | 39.7 ± 1.5 | 91.6 ± 6.4 | 65.9 ± 5.7 |
| Zero Order | First Order | Second Order | Higuchi Diffusion Model | Hixon | Baker | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APX-NLC | 0.7932 | −0.8336 | 0.8588 | 0.9093 | 0.8218 | 0.8386 |
| APX-PEG-NLC | 0.8388 | −0.8825 | 0.9174 | 0.9387 | 0.8687 | 0.8996 |
| APX-Ch-NLC | 0.8325 | −0.8659 | 0.8914 | 0.9344 | 0.8555 | 0.885 |
| Parameter | APX Suspension | APX-NLC | APX-PEG-NLC | APX-Ch-NLC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | SD | Average | SD | Average | SD | Average | SD | |
| Kel (1/h) | 0.053 | 0.0035 | 0.029 a | 0.009 | 0.0217 a | 0.0043 | 0.0268 a | 0.0045 |
| t1/2 (h) | 11.56 | 0.493 | 26.55 a | 5.35 | 32.83 a | 3.44 | 26.36 a | 4.217 |
| Tmax (h) | 2 | NA | 3 | NA | 3 | NA | 2 | NA |
| Cmax (μg/mL) | 0.841 | 0.101 | 2.127 a | 0.52 | 2.784 a | 0.518 | 2.671 a | 0.225 |
| AUC0-t (μg/mL·h) | 6.401 | 1.903 | 26.186 a | 5.053 | 43.99 a,b | 7.79 | 38.787 a,b | 2.226 |
| AUC0-inf (μg/mL·h) | 8.299 | 3.013 | 55.435 a | 12.33 | 108.59 a,b | 4.03 | 93.397 a,b,c | 7.284 |
| MRT0-inf (h) | 14.77 | 2.734 | 36.581 a | 12.8 | 47.193 a | 9.082 | 39.295 a | 5.512 |
| Vd ((mg/kg)/(μg/mL)) | 145.88 | 50.89 | 40.86 a | 2.98 | 26.306 a,b | 6.074 | 25.964 a,b | 2.597 |
| Cl ((mg/kg)/(μg/mL)/h) | 7.89 | 1.03 | 1.069 a | 0.28 | 0.515 a,b | 0.016 | 0.6898 a,c | 0.085 |
| PEGylation | Chitosanization | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | Significantly Enhanced Apixaban oral bioavailability over chitosanized and nonmodified NLCs through increasing AUC0-inf and Cmax. | Significantly Enhanced Apixaban anticoagulant activity over PEGylated and nonmodified NLCs through increasing PT and APTT. |
| Mechanisms | Increased NLC uptake through the gastrointestinal tract and the sustained release character of PEGylated NLCs. | Positively charged chitosan forms a complex with fibrinogen, resulting in conformational changes of its structure and thus blocking the last steps in the coagulation cascade |
| Protection and stability functions | Both protected the integrity of NLC, which was confirmed by the nonsignificant decrease in the entrapment efficiency % after 90 days compared to nonmodified. | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaky, M.F.; Hammady, T.M.; Gad, S.; Alattar, A.; Alshaman, R.; Hegazy, A.; Zaitone, S.A.; Ghorab, M.M.; Megahed, M.A. Influence of Surface-Modification via PEGylation or Chitosanization of Lipidic Nanocarriers on In Vivo Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Profiles of Apixaban. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061668
Zaky MF, Hammady TM, Gad S, Alattar A, Alshaman R, Hegazy A, Zaitone SA, Ghorab MM, Megahed MA. Influence of Surface-Modification via PEGylation or Chitosanization of Lipidic Nanocarriers on In Vivo Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Profiles of Apixaban. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(6):1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061668
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaky, Mohamed F., Taha M. Hammady, Shadeed Gad, Abdullah Alattar, Reem Alshaman, Ann Hegazy, Sawsan A. Zaitone, Mamdouh Mostafa Ghorab, and Mohamed A. Megahed. 2023. "Influence of Surface-Modification via PEGylation or Chitosanization of Lipidic Nanocarriers on In Vivo Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Profiles of Apixaban" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 6: 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061668
APA StyleZaky, M. F., Hammady, T. M., Gad, S., Alattar, A., Alshaman, R., Hegazy, A., Zaitone, S. A., Ghorab, M. M., & Megahed, M. A. (2023). Influence of Surface-Modification via PEGylation or Chitosanization of Lipidic Nanocarriers on In Vivo Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Profiles of Apixaban. Pharmaceutics, 15(6), 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061668