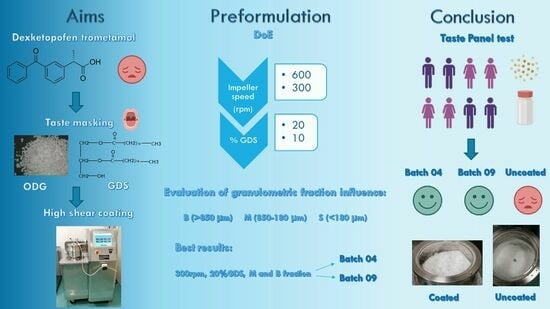
Taste Masking of Dexketoprofen Trometamol Orally Disintegrating Granules by High-Shear Coating with Glyceryl Distearate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Wet Granulation in a High-Shear Mixer (HSM)
2.3. Design of Experiments (DoEs)
2.4. Coating in a High-Shear Mixer
2.5. UV-Vis Spectrophotometry
2.6. Dissolution in Simulated Saliva (SS)
2.7. Solid-State Characterization
2.8. Human Taste Panel Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Evaluation
3.2. Production and Characterization of DXKT Granules
3.3. Production of Coated Granules
3.3.1. Preliminary Test
3.3.2. Experiments according to the DoE
3.3.3. Additional Experiments
3.4. Characterization of Coated Granules
3.5. Taste Panel Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salunke, S.; Tuleu, C. ‘Formulating Better Medicines for Children’—The Leap Forward. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 469, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, E.A.; Adeleke, O.A. Orally Disintegrating Drug Carriers for Paediatric Pharmacotherapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 182, 106377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, D.; Koberle, M. From Bitter to Sweet: Developing a User-Friendly Painkiller. Pharm. Tech. Eur. 2016, 40, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Cornilă, A.; Iurian, S.; Tomuță, I.; Porfire, A. Orally Dispersible Dosage Forms for Paediatric Use: Current Knowledge and Development of Nanostructure-Based Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, A.; Sala, J.; Vallés, J.; Ballarin, M. Bioavailability of Dexketoprofen Trometamol Granules for Oral Solution: New Formulation for the Treatment of Acute Pain. Eur. J. Pain 2006, 10, S170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICH Harmonized Guideline Addendum to ICH E11: Clinical Investigation of Medicinal Products in the Pediatric Population E11 (R1). 2018. Available online: https://admin.ich.org/sites/default/files/inline-files/ICH_E11_R1_Step_2_25Aug2016_Final.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- FDA Food and Drug Administration; CDER Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Use of Liquids and/or Soft Foods as Vehicles for Drug Administration: General Considerations for Selection and In Vitro Methods for Product Quality Assessments. 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/use-liquids-andor-soft-foods-vehicles-drug-administration-general-considerations-selection-and-vitro (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Hu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Quan, D. An Overview of Taste-Masking Technologies: Approaches, Application, and Assessment Methods. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavras, F.-M.; Partheniadis, I.; Nikolakakis, I. Formulation of Taste-Masked Orodispersible Famotidine Tablets by Sequential Spray Drying and Direct Compression—Bitterness Evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 81, 104290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-kasmi, B.; Alsirawan, M.H.D.B.; Bashimam, M.; El-zein, H. Mechanical Microencapsulation: The Best Technique in Taste Masking for the Manufacturing Scale–Effect of Polymer Encapsulation on Drug Targeting. J. Control. Release 2017, 260, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V. (Ed.) Encapsulation Nanotechnologies; Wiley Scrivener Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA; Salem, MA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-118-34455-2. [Google Scholar]
- Passerini, N.; Calogerà, G.; Albertini, B.; Rodriguez, L. Melt Granulation of Pharmaceutical Powders: A Comparison of High-Shear Mixer and Fluidised Bed Processes. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 391, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannin, V.; Cuppok, Y. Hot-Melt Coating with Lipid Excipients. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Salar-Behzadi, S.; Zimmer, A. Solvent-Free Melting Techniques for the Preparation of Lipid-Based Solid Oral Formulations. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 1519–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosiaux, Y.; Forest, A.; Girard, J.-M.; Deleglise, C.; Sheehan, L.; Marchaud, D. High Shear Blending with Glyceryl Distearate Provides Individually Coated Drug Particles for Effective Taste Masking. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellberg, E.; Westberg, A.; Appelblad, P.; Mattsson, S. Evaluation of Dissolution Techniques for Orally Disintegrating Mini-Tablets. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittings, S.; Turnbull, N.; Roberts, C.J.; Gershkovich, P. Dissolution Methodology for Taste Masked Oral Dosage Forms. J. Control. Release 2014, 173, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council of Europe. European Pharmacopoeia, 7th ed.; Granules; Council of Europe: London, UK, 2017; pp. 912–913. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, S.; Kleinebudde, P. A Review of Regime Maps for Granulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 587, 119660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, C.; Pein, M.; Reimann, J.; Breitkreutz, J. Taste Evaluation of Multicomponent Mixtures Using a Human Taste Panel, Electronic Taste Sensing Systems and HPLC. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 182, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Joshi, U.; Singh, A.; Saharan, V.A. Lipids for Taste Masking and Taste Assessment in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2021, 235, 105031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Mangal, S.; Denman, J.; Gengenbach, T.; Lee Bonar, K.; Khan, R.I.; Qu, L.; Li, T.; Zhou, Q. Effects of Coating Materials and Processing Conditions on Flow Enhancement of Cohesive Acetaminophen Powders by High-Shear Processing With Pharmaceutical Lubricants. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 3022–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llusa, M.; Sturm, K.; Sudah, O.; Stamato, H.; Goldfarb, D.J.; Ramachandruni, H.; Hammond, S.; Smith, M.R.; Muzzio, F.J. Effect of High Shear Blending Protocols and Blender Parameters on the Degree of API Agglomeration in Solid Formulations. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, M.; Gerbaud, V.; Hemati, M. Effect of Operating Conditions and Physico–Chemical Properties on the Wet Granulation Kinetics in High Shear Mixer. Powder Technol. 2009, 190, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattefossè pharma Process Sheet_high Shear Coating for Taste Masking 2018. Gattefossé Pharma, Application Laboratories. Available online: www.gattefosse.com (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Rossi, P.; Paoli, P.; Chelazzi, L.; Milazzo, S.; Biagi, D.; Valleri, M.; Ienco, A.; Valtancoli, B.; Conti, L. Relationships between Anhydrous and Solvated Species of Dexketoprofen Trometamol: A Solid-State Point of View. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Batch | Impeller Speed (rpm) | GDS % | Time to Reach 42 °C (min) | % Dissolved at 1 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 300 | 10 | 43.8 | 41.5 |
| 02 | 450 | 15 | 20.6 | 35.6 |
| 03 | 600 | 20 | 9.4 | 44.1 |
| 04 | 300 | 20 | 45.4 | 12.1 |
| 05 | 600 | 10 | 11.1 | 60.9 |
| Batch | Impeller Speed (rpm) | GDS % | Time to Reach 42 °C (min) | % Dissolved at 1 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02 | 450 | 15 | 20.6 | 35.6 |
| 06 | 450 | 20 | 16.5 | 35.3 |
| 07 | 450 | 25 | 15.2 | 34.6 |
| Batch | Fraction | Impeller Speed (rpm) | GDS % | Time to Reach 42 °C (min) | % Dissolved at 1 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 08 | S | 300 | 20 | 101.3 | 87.9 |
| 04 | M | 300 | 20 | 45.4 | 12.1 |
| 09 | B | 300 | 20 | 34.6 | 7.1 |
| Batch | Fraction | GDS % | Time to Reach 42 °C (min) | % Dissolved at 1 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04 | M | 20 | 45.4 | 12.1 |
| 09 | B | 20 | 34.6 | 7.1 |
| 10 | M | 25 | 40.8 | 11.8 |
| 11 | B | 25 | 32.0 | 6.6 |
| Uncoated Granules | Coated Granules | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fraction | (m2/g) | Batch | (m2/g) |
| S | 0.8 | 08 | 0.7 |
| M | 0.6 | 04 | 0.6 |
| B | 0.5 | 09 | 0.5 |
| Batch | Mean Residence Time in Oral Cavity before Burning Sensation (s) | Standard Error of the Mean |
|---|---|---|
| 04 | 51.6 | 3.8 |
| 09 | 55.6 | 2.9 |
| Uncoated granules | 13.9 | 2.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiarugi, I.; Biagi, D.; Nencioni, P.; Maestrelli, F.; Valleri, M.; Mura, P.A. Taste Masking of Dexketoprofen Trometamol Orally Disintegrating Granules by High-Shear Coating with Glyceryl Distearate. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020165
Chiarugi I, Biagi D, Nencioni P, Maestrelli F, Valleri M, Mura PA. Taste Masking of Dexketoprofen Trometamol Orally Disintegrating Granules by High-Shear Coating with Glyceryl Distearate. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(2):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020165
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiarugi, Ilaria, Diletta Biagi, Paolo Nencioni, Francesca Maestrelli, Maurizio Valleri, and Paola Angela Mura. 2024. "Taste Masking of Dexketoprofen Trometamol Orally Disintegrating Granules by High-Shear Coating with Glyceryl Distearate" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 2: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020165
APA StyleChiarugi, I., Biagi, D., Nencioni, P., Maestrelli, F., Valleri, M., & Mura, P. A. (2024). Taste Masking of Dexketoprofen Trometamol Orally Disintegrating Granules by High-Shear Coating with Glyceryl Distearate. Pharmaceutics, 16(2), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020165