Emerging Trends of Nanomedicines in the Management of Prostate Cancer: Perspectives and Potential Applications
Abstract
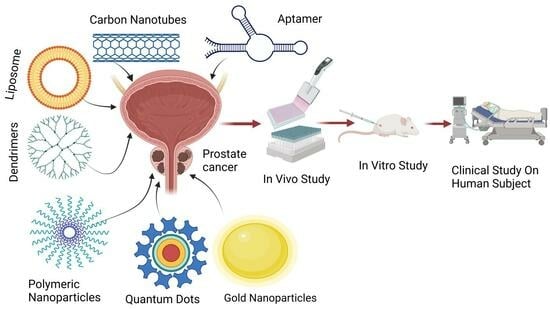
:1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology of Prostate Cancer
3. Beginning and Progression of the Prostate Cancer Process
4. Risk Factors of Prostate Cancer
4.1. Age
4.2. Diet
4.3. Family History and Genetic Factors
4.4. Medication
5. Diagnosis
6. Old Treatment Strategies for Prostate Cancer
7. Prostate Cancer Treatment by Novel Drug Delivery System
7.1. Nanoparticles
7.2. Novel Drug Delivery System on the Basis of Ingredients
7.2.1. Liposomes
7.2.2. Carbon Nanotubes
7.2.3. Quantum Dots
7.2.4. Dendrimers
7.2.5. Gold Nanoparticles
7.2.6. Micelles
7.3. Novel Drug Delivery System on the Basis of Shape
7.3.1. Nanorods
7.3.2. Nanosheets
7.4. Others
| Nanocarrier | Key Ingredient | Therapeutic Agent | Targeting Agent | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gold nanoparticles | Prostate-specific membrane antigen | Au and Gd [128] | MR guided | [129] |
| Gold nanoparticles | Polyethylene glycol | Docetaxel | Folic acid | [130] |
| Gold nanoparticles | Bioactive phytochemicals | Resveratrol | PC-3 cancer | [140] |
| Polymeric nanoparticles | Polylactic-co-glycolic acid | Docetaxel | Wy5a-aptamer | [87] |
| Polymeric nanoparticles | Prostate-specific membrane antigen | Docetaxel | Folic acid | [86] |
| Dendrimer | Gold nanocages | Lactoferrin | DNA | [141] |
| Liposome | Nanoliposome | Doxirubicine and resveratral | Capspase-3 enzyme | [102] |
| Liposome | Herceptin | DOX and simvastatine | Human epidermal growth factor 2 | [104] |
| Liposome | Polyethylenimine And polyethylene glycol | n-Butylidenephthalide | B16/F10 | [142] |
| Carbon nanotubes | Polyethyleneimine | Paclitaxel | LnCaP | [143] |
| CdSe/ZnS quantum dots | Mesoporous silica nanoparticles | Paclitaxel | Prostate cancer cells PSMA+ | [144] |
| Micelles | UniPR126 | Niclosamide | PC-3 cells | [145] |
| Nanorods | Zinc oxide | PC-3 cells | [135] |
8. Different Drug Delivery Routes for Targeting Prostate Cancer
8.1. Systemic Route
| Drug | Carrier | Targeting Moiety | Route of Administration | Dose | Animal Model | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mRNA | Polymeric nanoparticles | Death -1 | Tail vein | 700 μg/kg | Orthotopic model | [153] |
| PTEN mRNA | Polymer lipid hybrid nanoparticles | Anti–HA antibody | Tail vein | 700 μg/kg | Pc3 xenograft model | [154] |
| Docetaxel | PLGA nanoparticle | PCa | - | - | - | [155] |
| Curcumin and Cabazitaxel | Lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles | A10-3.2 aptamer | Intraperitoneally | 2 mg/kg–5 mg/kg | Xenograft model | [156] |
8.2. Locoregional Routes
Intraprostatic Route
8.3. Vas Deferens
8.4. Transrectal Route
9. Aptamers (Novel) Mediated Drug Delivery Systems
10. Future Prospect
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schatten, H. Brief Overview of Prostate Cancer Statistics, Grading, Diagnosis and Treatment Strategies. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1095, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorkowski, J.; Grzegorowska, O.; Kozień, M.S.; Kotela, I. Effects of Breast and Prostate Cancer Metastases on Lumbar Spine Biomechanics: Rapid In Silico Evaluation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1096, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Nielsen, M.; Borre, M. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies for Prostate Cancer. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2016, 46, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S. Advantages of Nanomedicine in Cancer Therapy: A Review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 22594–22610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohite, P.; Puri, A.; Pandhare, R.; Singh, S.; Prajapati, B. Current Trends in the Biomarker’sDiscovery for the Treatment and Management of Colorectal Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Prajapati, B.G.; Singh, S.; Anjum, M. Nanoparticles drug delivery for 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) in photodynamic therapy (PDT) for multiple cancer treatment: A critical review on biosynthesis, detection, and therapeutic applications. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 17607–17634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Malviya, R.; Prajapati, B.; Singh, S.; Yadav, D.; Kumar, A. Nanotechnology-Aided Advancement in Combating the Cancer Metastasis. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Malviya, R.; Prajapati, B.; Singh, S.; Goyal, P. Utilization of Stimuli-Responsive Biomaterials in the Formulation of Cancer Vaccines. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohite, P.; Rajput, T.; Pandhare, R.; Sangale, A.; Singh, S.; Prajapati, B.G. Nanoemulsion in Management of Colorectal Cancer: Challenges and Future Prospects. Nanomanufacturing 2023, 3, 139–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Prajapati, B.G.; Singh, S. A critical review on the dissemination of PH and stimuli-responsive polymeric nanoparticular systems to improve drug delivery in cancer therapy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2023, 185, 103961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumüller, G. Prostate Gland and Seminal Vesicles; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, M.; Salih, A.F.; Illzam, E.M.; Sharifa, A.M.; Suleiman, M.; Hussain, S.S. Prostate cancer: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and prognosis. IOSR J. Dent. Med. Sci. 2016, 15, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Scardino, P.T. The Gordon Wilson Lecture. Natural history and treatment of early stage prostate cancer. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2000, 111, 201–241. [Google Scholar]
- Theodorescu, D.; Ehdaie, B. Prostate Cancer, Clinical Oncology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 720–727. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, E.D. Understanding the Epidemiology, Natural History, and Key Pathways Involved in Prostate Cancer. Urology 2009, 73, S4–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate-Shen, C.; Shen, M.M. Molecular genetics of prostate cancer. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2410–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsing, A.W.; Chokkalingam, A.P. Prostate cancer epidemiology. Front. Biosci. A J. Virtual Libr. 2006, 11, 1388–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankey, B.F.; Feuer, E.J.; Clegg, L.X.; Hayes, R.B.; Legler, J.M.; Prorok, P.C.; Ries, L.A.; Merrill, R.M.; Kaplan, R.S. Cancer surveillance series: Interpreting trends in prostate cancer—Part I: Evidence of the effects of screening in recent prostate cancer incidence, mortality, and survival rates. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999, 91, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markozannes, G.; Tzoulaki, I.; Karli, D.; Evangelou, E.; Ntzani, E.; Gunter, M.J.; Norat, T.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Tsilidis, K.K. Diet, body size, physical activity and risk of prostate cancer: An umbrella review of the evidence. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 69, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, P.; Doll, R. The age distribution of cancer and a multi-stage theory of carcinogenesis. Br. J. Cancer 1954, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, P.; Doll, R. A two-stage theory of carcinogenesis in relation to the age distribution of human cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1957, 11, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, D.M.; Riffon, M.F.; Manning, B.; Taylor, A.; Emmas, C.; Kabadi, S.; Jiang, M.; Miller, R.S. Summary of the 12 Most Common Cancers in the CancerLinQ Discovery (CLQD) Database. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2021, 5, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.W.; Ritchey, J.; Devesa, S.S.; Quraishi, S.M.; Zhang, H.; Hsing, A.W. Prostate cancer incidence rates in Africa. Prostate Cancer 2011, 2011, 947870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, V.; Klotz, L.H. Diet and prostate cancer: Mechanisms of action and implications for chemoprevention. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2010, 7, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Key, T.J. Fruit and vegetables and cancer risk. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, D.D.; Mink, P.J.; Cushing, C.A.; Sceurman, B. A review and meta-analysis of prospective studies of red and processed meat intake and prostate cancer. Nutr. J. 2010, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigle, D.T.; Turner, M.C.; Gomes, J.; Parent, M.-E. Role of hormonal and other factors in human prostate cancer. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2008, 11, 242–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Cui, Y.; Shen, L.; Sun, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, B.; Xu, X.; Huo, Y.; et al. Folic acid supplementation and cancer risk: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, G.D.; Carter, B.S.; Beaty, T.H.; Childs, B.; Walsh, P.C. Family history and the risk of prostate cancer. Prostate 1990, 17, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, P.; Holm, N.V.; Verkasalo, P.K.; Iliadou, A.; Kaprio, J.; Koskenvuo, M.; Pukkala, E.; Skytthe, A.; Hemminki, K. Environmental and heritable factors in the causation of cancer—Analyses of cohorts of twins from Sweden, Denmark, and Finland. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeles, R.A.; Olama, A.A.; Benlloch, S.; Saunders, E.J.; Leongamornlert, D.A.; Tymrakiewicz, M.; Ghoussaini, M.; Luccarini, C.; Dennis, J.; Jugurnauth-Little, S.; et al. Identification of 23 new prostate cancer susceptibility loci using the iCOGS custom genotyping array. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, E.J.; Rodriguez, C.; Mondul, A.M.; Connell, C.J.; Henley, S.J.; Calle, E.E.; Thun, M.J. A large cohort study of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and prostate cancer incidence. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, J.; Tewoderos, S.; Garzotto, M.; Beer, T.M.; Derenick, R.; Palma, A.; Farris, P.E. Statins and prostate cancer risk: A case-control study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 162, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.L.; Harshman, L.C.; Presti, J.C., Jr. Impact of common medications on serum total prostate-specific antigen levels: Analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3951–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtola, T.J.; Syvälä, H.; Tolonen, T.; Helminen, M.; Riikonen, J.; Koskimäki, J.; Pakarainen, T.; Kaipia, A.; Isotalo, T.; Kujala, P.J.E.u. Atorvastatin versus placebo for prostate cancer before radical prostatectomy—A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Shin, H.-R.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melichar, B. PSA, PCA3 and the phi losophy of prostate cancer management. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2013, 51, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naji, L.; Randhawa, H.; Sohani, Z.; Dennis, B.; Lautenbach, D.; Kavanagh, O.; Bawor, M.; Banfield, L.; Profetto, J. Digital Rectal Examination for Prostate Cancer Screening in Primary Care: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Fam. Med. 2018, 16, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okotie, O.T.; Roehl, K.A.; Han, M.; Loeb, S.; Gashti, S.N.; Catalona, W.J. Characteristics of prostate cancer detected by digital rectal examination only. Urology 2007, 70, 1117–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scattoni, V.; Zlotta, A.; Montironi, R.; Schulman, C.; Rigatti, P.; Montorsi, F. Extended and saturation prostatic biopsy in the diagnosis and characterisation of prostate cancer: A critical analysis of the literature. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 1309–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, F.H.; van der Cruijsen-Koeter, I.; de Koning, H.J.; Vis, A.N.; Hoedemaeker, R.F.; Kranse, R. Prostate cancer detection at low prostate specific antigen. J. Urol. 2000, 163, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.J.; Jeun, M.; Jang, G.H.; Song, S.H.; Jeong, I.G.; Kim, C.S.; Searson, P.C.; Lee, K.H. Diagnosis of prostate cancer via nanotechnological approach. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 6555–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranav; Laskar, P.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C.; Yallapu, M.M. Biomolecule-functionalized nanoformulations for prostate cancer theranostics. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 51, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshirsagar, P.; Seshacharyulu, P.; Muniyan, S.; Rachagani, S.; Smith, L.M.; Thompson, C.; Shah, A.; Mallya, K.; Kumar, S.; Jain, M.; et al. DNA-gold nanoprobe-based integrated biosensing technology for non-invasive liquid biopsy of serum miRNA: A new frontier in prostate cancer diagnosis. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2022, 43, 102566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiczek, M.; Szylberg, Ł.; Kasperska, A.; Kowalewski, A.; Parol, M.; Antosik, P.; Radecka, B.; Marszałek, A. Immunotherapy as a Promising Treatment for Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 4861570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauman, G.; Rumble, R.B.; Chen, J.; Loblaw, A.; Warde, P. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy in the treatment of prostate cancer. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 24, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nader, R.; El Amm, J.; Aragon-Ching, J.B. Role of chemotherapy in prostate cancer. Asian J. Androl. 2018, 20, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDuffie, E.; D’Amico, A.V. Adjuvant vs Salvage Radiation Therapy for High-Risk Prostate Cancer Following Radical Prostatectomy. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1165–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brucić, L.J.; Juretić, A.; Solarić, M.; Bisof, V.; Basić-Koretić, M.; Rakusić, Z.; Santek, F. Hormonal therapy of prostate cancer: Are there any dilemmas left? Lijec. Vjesn. 2012, 134, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cox, R.L.; Crawford, E.D. Estrogens in the treatment of prostate cancer. J. Urol. 1995, 154, 1991–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissa, A.; Elsherbiny, A.; Coelho, R.F.; Rassweiler, J.; Davis, J.W.; Porpiglia, F.; Patel, V.R.; Prandini, N.; Micali, S.; Sighinolfi, M.C.; et al. The role of 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT scan in biochemical recurrence after primary treatment for prostate cancer: A systematic review of the literature. Minerva Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 70, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoli, A.; Alfieri, G.; Scipione, R.; Leonardi, A.; Fierro, D.; Panebianco, V.; De Nunzio, C.; Leonardo, C.; Catalano, C. High-intensity focused ultrasound for prostate cancer. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2020, 17, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaussy, C.G.; Thüroff, S. High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer: A Review. J. Endourol. 2017, 31, S30–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, J.; Graefen, M.; Huland, H. Basic principles of anatomy for optimal surgical treatment of prostate cancer. World J. Urol. 2007, 25, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lintz, K.; Moynihan, C.; Steginga, S.; Norman, A.; Eeles, R.; Huddart, R.; Dearnaley, D.; Watson, M. Prostate cancer patients’ support and psychological care needs: Survey from a non-surgical oncology clinic. Psychooncology 2003, 12, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, Z.; Parsons, J.K. Prostate Cancer Prevention: Concepts and Clinical Trials. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2016, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrylak, D.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Hussain, M.H.; Lara, P.N., Jr.; Jones, J.A.; Taplin, M.E.; Burch, P.A.; Berry, D.; Moinpour, C.; Kohli, M.; et al. Docetaxel and estramustine compared with mitoxantrone and prednisone for advanced refractory prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Rodriguez, B.L. Molecular targeting of liposomal nanoparticles to tumor microenvironment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ding, J.; Xiao, C.; Li, L.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Versatile preparation of intracellular-acidity-sensitive oxime-linked polysaccharide-doxorubicin conjugate for malignancy therapeutic. Biomaterials 2015, 54, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotté, F.; Ratta, R.; Beuzeboc, P. Side effects of immunotherapy: A constant challenge for oncologists. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2019, 31, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K. Intensity modulated radiotherapy: Advantages, limitations and future developments. Biomed. Imaging Interv. J. 2006, 2, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gill, A.A.S.; Nlooto, M.; Karpoormath, R. Prostate cancer biomarkers detection using nanoparticles based electrochemical biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 137, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xie, W.; Chen, J.; Zhao, L.; Wen, Y.; Xie, H.; Shu, Q.; Pan, F.; Lu, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Exploration: Nanoparticles in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Retinal Diseases. J. Nanomater. 2023, 2023, 9099778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddu, S.H.S.; Vaishya, R.; Jwala, J.; Vadlapudi, A.; Pal, D.; Mitra, A.K. Preparation and characterization of folate conjugated nanoparticles of doxorubicin using PLGA-PEG-FOL polymer. Med. Chem. 2012, 2, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, S.; Mahanta, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Maiti, P. Controlled drug delivery vehicles for cancer treatment and their performance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwabor, O.F.; Singh, S.; Wunnoo, S.; Lerwittayanon, K.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Facile deposition of biogenic silver nanoparticles on porous alumina discs, an efficient antimicrobial, antibiofilm, and antifouling strategy for functional contact surfaces. Biofouling 2021, 37, 538–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ontong, J.C.; Singh, S.; Nwabor, O.F.; Chusri, S.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Potential of antimicrobial topical gel with synthesized biogenic silver nanoparticle using Rhodomyrtus tomentosa leaf extract and silk sericin. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 2653–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, A.; Mohite, P.; Patil, S.; Chidrawar, V.R.; Ushir, Y.V.; Dodiya, R.; Singh, S. Facile green synthesis and characterization of Terminalia arjuna bark phenolic–selenium nanogel: A biocompatible and green nano-biomaterial for multifaceted biological applications. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1273360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Shah, S.R.; Jayeoye, T.J.; Kumar, A.; Parihar, A.; Prajapati, B.; Singh, S.; Kapoor, D.U. Biogenic metallic nanoparticles: Biomedical, analytical, food preservation, and applications in other consumable products. Front. Nanotechnol. 2023, 5, 1175149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayeoye, T.J.; Eze, F.N.; Singh, S.; Olatunde, O.O.; Benjakul, S.; Rujiralai, T. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles/polyaniline boronic acid/sodium alginate aqueous nanocomposite based on chemical oxidative polymerization for biological applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 179, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Nwabor, O.F.; Sukri, D.M.; Wunnoo, S.; Dumjun, K.; Lethongkam, S.; Kusolphat, P.; Hemtanon, N.; Klinprathum, K.; Sunghan, J.; et al. Poly (vinyl alcohol) copolymerized with xanthan gum/hypromellose/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose dermal dressings functionalized with biogenic nanostructured materials for antibacterial and wound healing application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syukri, D.M.; Nwabor, O.F.; Singh, S.; Ontong, J.C.; Wunnoo, S.; Paosen, S.; Munah, S.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Antibacterial-coated silk surgical sutures by ex situ deposition of silver nanoparticles synthesized with Eucalyptus camaldulensis eradicates infections. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 174, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Chunglok, W.; Nwabor, O.F.; Ushir, Y.V.; Singh, S.; Panpipat, W. Hydrophilic Biopolymer Matrix Antibacterial Peel-off Facial Mask Functionalized with Biogenic Nanostructured Material for Cosmeceutical Applications. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 938–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syukri, D.M.; Nwabor, O.F.; Singh, S.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Antibacterial functionalization of nylon monofilament surgical sutures through in situ deposition of biogenic silver nanoparticles. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 413, 127090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwabor, O.F.; Singh, S.; Ontong, J.C.; Vongkamjan, K.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Valorization of Wastepaper Through Antimicrobial Functionalization with Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles, a Sustainable Packaging Composite. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 3287–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagime, P.V.; Singh, S.; Shaikh, N.M.; Gomare, K.S.; Chitme, H.; Abdel-Wahab, B.A.; Alqahtany, Y.S.; Khateeb, M.M.; Habeeb, M.S.; Bakir, M.B. Biogenic Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles Using Calotropis procera Flower Extract with Enhanced Biomimetics Attributes. Materials 2023, 16, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Dodiya, T.R.; Dodiya, R.; Ushir, Y.V.; Widodo, S. Lipid Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery Systems: A Revolution in Dosage Form Design and Development. In Drug Carriers; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor, D.U.; Gaur, M.; Parihar, A.; Prajapati, B.G.; Singh, S.; Patel, R.J. Phosphatidylcholine (PCL) fortified nano-phytopharmaceuticals for improvement of therapeutic efficacy. EXCLI J. 2023, 22, 880–903. [Google Scholar]
- Mohite, P.; Singh, S.; Pawar, A.; Sangale, A.; Prajapati, B.G. Lipid-based oral formulation in capsules to improve the delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs. Front. Drug Deliv. 2023, 3, 1232012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A.D.; Claypool, S.E.; Liu, R. The smart targeting of nanoparticles. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 6315–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Biopolymers Towards Green and Sustainable Development; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.Y.; Wu, D.C.; Li, Z.J.; Chen, G.Q. Polymer nanoparticles. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2011, 104, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, A.; Kausar, A.; Younus, A. A review on preparation, properties and applications of polymeric nanoparticle-based materials. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2015, 54, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, Z.; Patel, A.; Butcher, T.; Banerjee, T.; Bean, R.; Santra, S. Pseudo-branched polyester copolymer: An efficient drug delivery system to treat cancer. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 1592–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Lin, S.; Yang, F.; Situ, J.; Lin, S.; Luo, Y. Aptamer-Conjugated Multifunctional Polymeric Nanoparticles as Cancer-Targeted, MRI-Ultrasensitive Drug Delivery Systems for Treatment of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 9186583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefiasl, S.; Manoochehri, H.; Makvandi, P.; Afshar, S.; Salahinejad, E.; Khosraviyan, P.; Saidijam, M.; Asl, S.S.; Sharifi, E. Chitosan/alginate bionanocomposites adorned with mesoporous silica nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2023, 13, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lei, H.; Yan, B.; Zhang, S.; Xu, B.; Lin, M.; Shuai, X.; Huang, J.; Pang, J. Tumor acidity-activatable macromolecule autophagy inhibitor and immune checkpoint blockade for robust treatment of prostate cancer. Acta Biomater. 2023, 168, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alserihi, R.F.; Mohammed, M.R.S.; Kaleem, M.; Khan, M.I.; Sechi, M.; Zughaibi, T.A.; Tabrez, S. Comparative efficacy of epigallocatechin gallate and its nano-formulation in prostate cancer 3D spheroids model. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2023, 35, 102627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, C.; Wu, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, C. Cascade targeting codelivery of ingenol-3-angelate and doxorubicin for enhancing cancer chemoimmunotherapy through synergistic effects in prostate cancer. Mater. Today Bio 2021, 13, 100189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.; Danışman-Kalındemirtaş, F.; Karakuş, S. Effective drug combinations of betulinic acid and ceranib-2 loaded Zn:MnO2 doped-polymeric nanocarriers against PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 225, 113278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengel-Turk, C.T.; Ozkan, E.; Bakar-Ates, F. Box-Behnken design optimization and in vitro cell based evaluation of piroxicam loaded core-shell type hybrid nanocarriers for prostate cancer. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 216, 114799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Gul, A.R.; Xu, P.; Lee, S.Y.; Rafique, R.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, T.J. Target delivery of photo-triggered nanocarrier for externally activated chemo-photodynamic therapy of prostate cancer. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 23, 100688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ontong, J.C.; Singh, S.; Siriyong, T.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Transferosomes stabilized hydrogel incorporated rhodomyrtone-rich extract from Rhodomyrtus tomentosa leaf fortified with phosphatidylcholine for the management of skin and soft-tissue infections. Biotechnol. Lett. 2024, 46, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittasupho, C.; Chaobankrang, K.; Sarawungkad, A.; Samee, W.; Singh, S.; Hemsuwimon, K.; Okonogi, S.; Kheawfu, K.; Kiattisin, K.; Chaiyana, W. Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Attenuating Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Activities of Nicotiana tabacum var. Virginia Leaf Extract Phytosomes and Shape Memory Gel Formulation. Gels 2023, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulbake, U.; Doppalapudi, S.; Kommineni, N.; Khan, W. Liposomal Formulations in Clinical Use: An Updated Review. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangham, A.D.; Standish, M.M.; Watkins, J.C. Diffusion of univalent ions across the lamellae of swollen phospholipids. J. Mol. Biol. 1965, 13, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Du, C.; Guo, N.; Teng, Y.; Meng, X.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Yu, P.; Galons, H. Composition design and medical application of liposomes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 164, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Kluzek, M.; Iuster, N.; Shimoni, E.; Kampf, N.; Goldberg, R.; Klein, J. Cartilage-inspired, lipid-based boundary-lubricated hydrogels. Science 2020, 370, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apolinário, A.C.; Hauschke, L.; Nunes, J.R.; Lopes, L.B. Lipid nanovesicles for biomedical applications: ‘What is in a name’? Prog. Lipid Res. 2021, 82, 101096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gao, D.; Wang, P.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Han, Y.; Yuan, H. Co-delivery of Docetaxel and Resveratrol by liposomes synergistically boosts antitumor efficiency against prostate cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 174, 106199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, J.; Metselaar, J.M.; Storm, G.; van der Pluijm, G. Liposomal nanomedicines in the treatment of prostate cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Xie, X.; Hu, Y.; He, H.; Fu, X.; Fang, T.; Li, C. Herceptin-conjugated liposomes co-loaded with doxorubicin and simvastatin in targeted prostate cancer therapy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 1255–1269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, M.; He, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Q.; et al. Liposomal Codelivery of Doxorubicin and Andrographolide Inhibits Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quick, J.; Dos Santos, N.; Cheng, M.H.Y.; Chander, N.; Brimacombe, C.A.; Kulkarni, J.; van der Meel, R.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Witzigmann, D.; Cullis, P.R. Lipid nanoparticles to silence androgen receptor variants for prostate cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2022, 349, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.; Ma, G.; Na, L.; Hudoklin, S.; Kreft, M.E.; Kostevsek, N.; Al-Jamal, W.T. Encapsulation of doxorubicin prodrug in heat-triggered liposomes overcomes off-target activation for advanced prostate cancer therapy. Acta Biomater. 2022, 140, 530–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Barkat, H.A.; Harwansh, R.K.; Deshmukh, R. Carbon-based Nanomaterials: Carbon Nanotubes, Graphene, and Fullerenes for the Control of Burn Infections and Wound Healing. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2022, 23, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, V.; Yadav, P.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Mishra, A.K.; Verma, N.; Verma, A.; Pandit, J.K. Carbon nanotubes: An emerging drug carrier for targeting cancer cells. J. Drug Deliv. 2014, 2014, 670815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, P.; Liu, C.; Xie, C.; Ke, J.; He, Y.; Wei, L.; Chen, L.; Jin, J. TiO2 nanotubes loaded with CdS nanocrystals as enhanced emitters of electrochemiluminescence: Application to an assay for prostate-specific antigen. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Deng, W.; Tan, Y.; Xie, Q. Electrocatalytic activity of Co3O4 quantum dots supported on aminated carbon nanotubes and their application for sensitive electrochemical immunosensing of prostate-specific antigen. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 862, 114023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Hu, C.; Xia, Q.; Gong, C.; Gao, S.; Chen, Z. Aptamer-conjugated multi-walled carbon nanotubes as a new targeted ultrasound contrast agent for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. J. Nanoparticle Res. Interdiscip. Forum Nanoscale Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; de Araújo Júnior, R.F.; Cruz, L.J.; Eich, C. Functionalized Nanoparticles Targeting Tumor-Associated Macrophages as Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargozar, S.; Hoseini, S.J.; Milan, P.B.; Hooshmand, S.; Kim, H.-W.; Mozafari, M. Quantum Dots: A Review from Concept to Clinic. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, e2000117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, A.A.H.; Younis, M.A.; Alsharidah, M.; Al Rugaie, O.; Tawfeek, H.M. Biomedical Applications of Quantum Dots: Overview, Challenges, and Clinical Potential. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 1951–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-M.; Huang, X.-Q.; Wang, A.-J.; Luo, X.; Liu, W.-D.; Yuan, P.-X.; Feng, J.-J. Construction of efficient “on-off-on” fluorescence aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of prostate specific antigen via covalent energy transfer between g-C3N4 quantum dots and palladium triangular plates. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1104, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jigyasu, A.K.; Siddiqui, S.; Jafri, A.; Arshad, M.; Lohani, M.; Khan, I.A. Biological Synthesis of CdTe Quantum Dots and Their Anti-Proliferative Assessment Against Prostate Cancer Cell Line. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 3398–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncapayi, V.; Ninan, N.; Lebepe, T.C.; Parani, S.; Girija, A.R.; Bright, R.; Vasilev, K.; Maluleke, R.; Tsolekile, N.; Kodama, T.; et al. Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer and Prostatitis Using near Infra-Red Fluorescent AgInSe/ZnS Quantum Dots. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, C.; Prajapati, B.G.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.; Maheshwari, S. Chapter 14—Dendrimers in the management of Alzheimer’s disease. In Alzheimer’s Disease and Advanced Drug Delivery Strategies; Prajapati, B.G., Chellappan, D.K., Kendre, P.N., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 235–251. [Google Scholar]
- Hawker, C.J.; Frechet, J.M.J. Preparation of polymers with controlled molecular architecture: A new convergent approach to dendritic macromolecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 7638–7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Lang, H.X.; Loh, J.S.; Chai, Y.L.; Tee, H.L.; Mayuren, J.; Candasamy, M.; Gorain, B.; Jain, N.; Gupta, G.; et al. Dendrimer platform against prostate cancer: Recent update on new horizon of treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 85, 104589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Yang, H.; Xue, S.; Qiao, J.; Salarian, M.; Hekmatyar, K.; Meng, Y.; Mukkavilli, R.; Pu, F.; Odubade, O.Y.; et al. Chemokine receptor 4 targeted protein MRI contrast agent for early detection of liver metastases. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaav7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedi-Gaballu, F.; Dehghan, G.; Ghaffari, M.; Yekta, R.; Abbaspour-Ravasjani, S.; Baradaran, B.; Dolatabadi, J.E.N.; Hamblin, M.R. PAMAM dendrimers as efficient drug and gene delivery nanosystems for cancer therapy. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 12, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Farnood, R.; Yan, N. Corn-derived dendrimer-like carbohydrate phytoglycogen nanoparticles as selective fluorescent sensor for silver ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, D.; Shi, K.; Ma, C.; Zhang, W.; Rocchi, P.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X. Self-assembly of amphiphilic phospholipid peptide dendrimer-based nanovectors for effective delivery of siRNA therapeutics in prostate cancer therapy. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2020, 322, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayeoye, T.J.; Sirimahachai, U.; Rujiralai, T. Sensitive colorimetric detection of ascorbic acid based on seed mediated growth of sodium alginate reduced/stabilized gold nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, J.N.; Hall, W.P.; Lyandres, O.; Shah, N.C.; Zhao, J.; van Duyne, R.P. Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirozzi, C.S.; Jones, B.E.; VanDerslice, J.A.; Zhang, Y.; Paine, R., III; Dean, N.C. Short-term air pollution and incident pneumonia. A case–crossover study. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2018, 15, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Johnson, A.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Erokwu, B.O.; Springer, S.; Lou, J.; Ramamurthy, G.; Flask, C.A.; Burda, C.; et al. Targeted Radiosensitizers for MR-Guided Radiation Therapy of Prostate Cancer. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 7159–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thambiraj, S.; Vijayalakshmi, R.; Shankaran, D.R. An effective strategy for development of docetaxel encapsulated gold nanoformulations for treatment of prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.; Syed, A.; Mohany, M.; Elgorban, A.M.; Khan, M.S.; Al-Rejaie, S.S. Survivin-targeted nanomedicine for increased potency of abiraterone and enzalutamide against prostate cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2023, 192, 88–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, H. PSMA1-mediated ultrasmall gold nanoparticles facilitate tumor targeting and MR/CT/NIRF multimodal detection of early-stage prostate cancer. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2023, 47, 102617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.; Syed, A.; Iram, S.; Elgorban, A.M.; Al-Harthi, H.F.; Al-Rejaie, S.S.; Kim, J.; Khan, M.S. AR independent anticancer potential of enza against prostate cancer. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 642, 128598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Guo, B.; Zhong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, G.; Yang, J.; Zhong, Z.; Meng, F. Integrin-targeting disulfide-crosslinked micellar docetaxel eradicates lung and prostate cancer patient-derived xenografts. Acta Biomater. 2023, 170, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Sadique, M.A.; Pal, M.; Khan, R.; Srivastava, A.K. Cytotoxicity and DNA fragmentation-mediated apoptosis response of hexagonal ZnO nanorods against human prostate cancer cells. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2022, 9, 100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Lin, X.; Li, Z.; Dou, T.; Gao, L.; Li, R.; Lai, K.P. Instrumental and transcriptome analysis reveals the chemotherapeutic effects of doxorubicin-loaded black phosphate nanosheets on abiraterone-resistant prostate cancer. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 137, 106583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Ruiz, S.; Armiñán, A.; Maso, K.; Gallon, E.; Zagorodko, O.; Movellan, J.; Rodríguez-Otormín, F.; Baues, M.; May, J.-N.; De Lorenzi, F.; et al. Poly-l-glutamic acid modification modulates the bio-nano interface of a therapeutic anti-IGF-1R antibody in prostate cancer. Biomaterials 2023, 301, 122280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, C.T.; Bloomquist, C.; Kim, I.; Knape, N.M.; Byrne, J.D.; Tu, L.; Wagner, K.; Mecham, S.; DeSimone, J.; Wang, A.Z. Continuous liquid interface production of 3D printed drug-loaded spacers to improve prostate cancer brachytherapy treatment. Acta Biomater. 2022, 148, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Liu, Y.; Hou, N.; Cui, S.; Liu, B.; Fan, S.; Yu, G.; Han, C.; Zheng, D.; Li, W.; et al. Tumor microenvironment pH-responsive pentagonal gold prism-based nanoplatform for multimodal imaging and combined therapy of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Acta Biomater. 2022, 141, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thipe, V.C.; Amiri, K.P.; Bloebaum, P.; Karikachery, A.R.; Khoobchandani, M.; Katti, K.K.; Jurisson, S.S.; Katti, K.V. Development of resveratrol-conjugated gold nanoparticles: Interrelationship of increased resveratrol corona on anti-tumor efficacy against breast, pancreatic and prostate cancers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4413–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almowalad, J.; Laskar, P.; Somani, S.; Meewan, J.; Tate, R.J.; Dufès, C. Lactoferrin- and Dendrimer-Bearing Gold Nanocages for Stimulus-Free DNA Delivery to Prostate Cancer Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 1409–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.-W.; Chang, K.-F.; Huang, X.-F.; Lin, Y.-L.; Weng, J.-C.; Liao, K.-W.; Tsai, N.-M. Antitumor Effect of n-Butylidenephthalide Encapsulated on B16/F10 Melanoma Cells In Vitro with a Polycationic Liposome Containing PEI and Polyethylene Glycol Complex. Molecules 2018, 23, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comparetti, E.J.; Romagnoli, G.G.; Gorgulho, C.M.; Pedrosa, V.d.A.; Kaneno, R. Anti-PSMA monoclonal antibody increases the toxicity of paclitaxel carried by carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 116, 111254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharkhiz, S.; Nasri, N.; Dini, G.; Yousefnia, S. Development of a new smart theranostic anti-PSMA-aptamer conjugated cationic-lipid coated mesoporous silica platform for targeted delivery of paclitaxel and CdSe/ZnS quantum dots to LNCaP cell line. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 104964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannu, A.K.; Puppala, E.R.; Gawali, B.; Syamprasad, N.P.; Alexander, A.; Marepally, S.; Chella, N.; Gangasani, J.K.; Naidu, V.G.M. Lithocholic acid-tryptophan conjugate (UniPR126) based mixed micelle as a nano carrier for specific delivery of niclosamide to prostate cancer via EphA2 receptor. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 605, 120819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Garg, S.; Swarnakar, N.K. Nanoparticles and prostate cancer. In Nano Drug Delivery Strategies for the Treatment of Cancers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 275–318. [Google Scholar]
- Arriaga, J.M.; Abate-Shen, C. Genetically Engineered Mouse Models of Prostate Cancer in the Postgenomic Era. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a030528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hine, C.M.; Seluanov, A.; Gorbunova, V. Rad51 promoter-targeted gene therapy is effective for in vivo visualization and treatment of cancer. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2012, 20, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yallapu, M.M.; Khan, S.; Maher, D.M.; Ebeling, M.C.; Sundram, V.; Chauhan, N.; Ganju, A.; Balakrishna, S.; Gupta, B.K.; Zafar, N.; et al. Anti-cancer activity of curcumin loaded nanoparticles in prostate cancer. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8635–8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadajkar, A.S.; Menon, J.U.; Tsai, Y.-S.; Gore, C.; Dobin, T.; Gandee, L.; Kangasniemi, K.; Takahashi, M.; Manandhar, B.; Ahn, J.M.; et al. Prostate cancer-specific thermo-responsive polymer-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3618–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Jiang, J.; Guan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, Y. In Vivo Molecular MRI Imaging of Prostate Cancer by Targeting PSMA with Polypeptide-Labeled Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9573–9587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Waterman, P.; Chen, S.; Marinelli, B.; Seaman, M.; Rodig, S.; Ross, R.W.; Josephson, L.; Weissleder, R.; Kelly, K.A. Development of Secreted Protein and Acidic and Rich in Cysteine (SPARC) Targeted Nanoparticles for the Prognostic Molecular Imaging of Metastatic Prostate Cancer. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 1000112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, J.; Jiang, A.; Wang, J.; Yu, M.; Blake, S.; Liu, S.; Bieberich, C.J.; Farokhzad, O.C.; et al. Reactivation of the tumor suppressor PTEN by mRNA nanoparticles enhances antitumor immunity in preclinical models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaba9772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.A.; Xu, Y.; Tao, W.; Ubellacker, J.M.; Lim, M.; Aum, D.; Lee, G.Y.; Zhou, K.; Zope, H.; Yu, M.; et al. Restoration of tumour-growth suppression in vivo via systemic nanoparticle-mediated delivery of PTEN mRNA. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 850–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saniee, F.; Ravari, N.S.; Goodarzi, N.; Amini, M.; Atyabi, F.; Moghadam, E.S.; Dinarvand, R. Glutamate-urea-based PSMA-targeted PLGA nanoparticles for prostate cancer delivery of docetaxel. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, C.; Xiang, C. Anti prostate cancer therapy: Aptamer-functionalized, curcumin and cabazitaxel co-delivered, tumor targeted lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitole, A.A.; Sharma, N.; Giram, P.; Khandwekar, A.; Baruah, M.; Garnaik, B.; Koratkar, S. LHRH-conjugated, PEGylated, poly-lactide-co-glycolide nanocapsules for targeted delivery of combinational chemotherapeutic drugs Docetaxel and Quercetin for prostate cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 114, 111035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolinsky, J.B.; Colson, Y.L.; Grinstaff, M.W. Local drug delivery strategies for cancer treatment: Gels, nanoparticles, polymeric films, rods, and wafers. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2012, 159, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linxweiler, J.; Körbel, C.; Müller, A.; Hammer, M.; Veith, C.; Bohle, R.M.; Stöckle, M.; Junker, K.; Menger, M.D.; Saar, M. A novel mouse model of human prostate cancer to study intraprostatic tumor growth and the development of lymph node metastases. Prostate 2018, 78, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wientjes, M.G.; Zheng, J.H.; Hu, L.; Gan, Y.; Au, J.L. Intraprostatic chemotherapy: Distribution and transport mechanisms. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 4204–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geißen, W.; Engels, S.; Aust, P.; Schiffmann, J.; Gerullis, H.; Wawroschek, F.; Winter, A. Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetometer-Guided Sentinel Lymphadenectomy After Intraprostatic Injection of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Intermediate- and High-Risk Prostate Cancer Using the Magnetic Activity of Sentinel Nodes. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koslov, D.S.; Andersson, K.E. Physiological and pharmacological aspects of the vas deferens—An update. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, S.K.; Chauhan, V.; Banerjee, S. Designed self assembly of nano–liposomes in the male reproductive tract for model drug delivery to the prostate. Open Nanosci. J. 2011, 5, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, P.K.; Dharanivasan, G.; Verma, R.S. Current prospects and challenges of nanomedicine delivery in prostate cancer therapy. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 2675–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutzer, M.E.; Orio, P.F.; Biagioli, M.C.; Asher, D.A.; Lomas, H.; Moghanaki, D. A review of rectal toxicity following permanent low dose-rate prostate brachytherapy and the potential value of biodegradable rectal spacers. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2015, 18, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, F.; Chen, R.; Zheng, W.; Yang, X. Recent advances in imaging-guided interventions for prostate cancers. Cancer Lett. 2014, 349, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.K.; Turkbey, B.; Valayil, S.G.; Muthigi, A.; Mertan, F.; Kongnyuy, M.; Pinto, P.A. A urologist’s perspective on prostate cancer imaging: Past, present, and future. Abdom. Radiol. 2016, 41, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meo, S.A.; Abukhalaf, A.A.; Alomar, A.A.; Alessa, O.M.; Sami, W.; Klonoff, D.C. Effect of environmental pollutants PM-2.5, carbon monoxide, and ozone on the incidence and mortality of SARS-COV-2 infection in ten wildfire affected counties in California. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimjee, S.M.; White, R.R.; Becker, R.C.; Sullenger, B.A. Aptamers as Therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 57, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhin, A.V.; Tarantul, V.Z.; Gening, L.V. Aptamers: Problems, solutions and prospects. Acta Naturae 2013, 5, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, H.; Dong, S.; Ge, L.; Zhang, Y. Progress in aptamer-mediated drug delivery vehicles for cancer targeting and its implications in addressing chemotherapeutic challenges. Theranostics 2014, 4, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrukh, S.; Jain, N.; Shah, S.; Famta, P.; Srinivasarao, D.A.; Khatri, D.K.; Asthana, A.; Singh, S.B.; Raghuvanshi, R.S.; Srivastava, S. Aptamer guided nanomedicine strategies in prostate cancer: Targeting and diagnosis. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 85, 104593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Qi, F.; Li, B.; Wu, S.; Chu, T.; Lu, Z.; Li, S.; Nie, G. Identification of protein kinase C beta as a therapeutic target for neuroendocrine prostate cancer and development of a nanoparticle-based therapeutic strategy. Nano Today 2023, 48, 101705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Interventions | Conditions | Characteristics | Population | NCT Number | Status | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phases | Study Type | Age | Sex | ||||
| Diagnostic test: Blood sample | PC | Not Applicable | IV | 40 years or above | Male | NCT04556916 | Recruiting |
| Drug: ODM- Drug: ADT | PC | 2 | IV | 18 years or above | Male | NCT02972060 | Active, not recruiting |
| Drug: cholecalciferol Other: placebo | PC | 2 | IV | 19 years to 90 years | Male | NCT02726113 | Completed |
| Diagnostic test: 18FPSMA | PC | 1 | IV | 40 years to 70 years | Male | NCT03558711 | Completed |
| Drug: Leuprolide | PC | 4 | IV | 18 years or above | Male | NCT03035032 | Completed |
| Diagnostic test: [18F] PSMA-11 | PC | 2 | IV | 18 years or above | Male | NCT03573011 | Completed |
| Drug: 18F-DCFPyL PET | Prostate Cancer Prostate Neoplasm | Early Phase 1 | IV | 18 years or above | Male | NCT03232164 | Recruiting |
| Dietary supplement: green tea capsules. Behavioral: Green tea drink. Other: Green tea placebo capsules. Other: Lycopene placebo capsules. Other: Tomato-rich diet. Dietary supplement: Lycopene capsules | PC | 2 and 3 | IV | 50 Years to 69 Years | Male | NCT01105338 | Completed |
| Drug: High-dose testosterone | Metastatic Prostate Cancer | 2 | IV | 18 years or above | Male | NCT05011383 | Recruiting |
| Drug: 18F-DCFBC | PC | 1 and 2 | IV | 18 years to 90 years | Male | NCT01496157 | Completed |
| Drug: ELIGARD | PC | 2 | IV | 18 years or above | Male | NCT02274779 | Active, not recruiting |
| Radiation: Radiation therapy | PC | 2 | IV | 18 years to 90 years | Male | NCT04984343 | Recruiting |
| Drug: Enzalutamide Drug: Leuprolide acetate Radiation: radiation | PC | 2 | IV | 18 years to 90 years | Male | NCT02064582 | Completed |
| Drug: PD1-PSMACART cells | PC | 1 | IV | 18 years to 75 years | Male | NCT04768608 | Completed |
| Drug: BR55 | PC | 1 and 2 | IV | 50 years to 70 years | Male | NCT02142608 | Completed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deshmukh, R.; Singh, V.; Harwansh, R.K.; Agrawal, R.; Garg, A.; Singh, S.; Elossaily, G.M.; Ansari, M.N.; Ali, N.; Prajapati, B.G. Emerging Trends of Nanomedicines in the Management of Prostate Cancer: Perspectives and Potential Applications. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030297
Deshmukh R, Singh V, Harwansh RK, Agrawal R, Garg A, Singh S, Elossaily GM, Ansari MN, Ali N, Prajapati BG. Emerging Trends of Nanomedicines in the Management of Prostate Cancer: Perspectives and Potential Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(3):297. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030297
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeshmukh, Rohitas, Vaibhav Singh, Ranjit K. Harwansh, Rutvi Agrawal, Akash Garg, Sudarshan Singh, Gehan M. Elossaily, Mohd Nazam Ansari, Nemat Ali, and Bhupendra G. Prajapati. 2024. "Emerging Trends of Nanomedicines in the Management of Prostate Cancer: Perspectives and Potential Applications" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 3: 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030297
APA StyleDeshmukh, R., Singh, V., Harwansh, R. K., Agrawal, R., Garg, A., Singh, S., Elossaily, G. M., Ansari, M. N., Ali, N., & Prajapati, B. G. (2024). Emerging Trends of Nanomedicines in the Management of Prostate Cancer: Perspectives and Potential Applications. Pharmaceutics, 16(3), 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030297