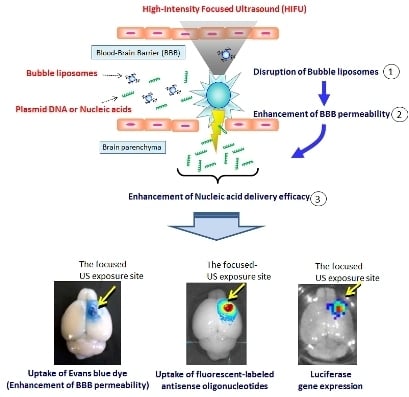
Enhancement of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability and Delivery of Antisense Oligonucleotides or Plasmid DNA to the Brain by the Combination of Bubble Liposomes and High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Preparation of Bubble Liposomes (BLs)
2.2. Ultrasound Experimental Setup
2.3. Extravasation of Evans Blue Dye (EB)
2.4. Delivery of Fluorescent-Labeled Dextrans
2.5. Delivery of Phosphorodiamidate Morpholino Oligomers (PMOs)
2.6. Delivery of Plasmid DNA into the Brain
2.7. Evaluation of Tissue Damage
2.8. In Vivo Studies
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Permeability of BBB by the Combination of BL and HIFU Exposure





3.2. Delivery of Phosphorodiamidate Morpholino Oligomers (PMOs) into the Brain Using a Combination of BLs and HIFU Exposure

3.3. Delivery of Plasmid DNA into the Brain Using a Combination of BLs and HIFU Exposure


4. Conclusions
Acknowledgement
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hynynen, K. Ultrasound for drug and gene delivery to the brain. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christine, C.W.; Starr, P.A.; Larson, P.S.; Eberling, J.L.; Jagust, W.J.; Hawkins, R.A.; VanBrocklin, H.F.; Wright, J.F.; Bankiewicz, K.S.; Aminoff, M.J. Safety and tolerability of putaminal AADC gene therapy for Parkinson disease. Neurology 2009, 73, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingozzi, F.; High, K.A. Therapeutic in vivo gene transfer for genetic disease using AAV: Progress and challenges. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeWitt, P.A.; Rezai, A.R.; Leehey, M.A.; Ojemann, S.G.; Flaherty, A.W.; Eskandar, E.N.; Kostyk, S.K.; Thomas, K.; Sarkar, A.; Siddiqui, M.S.; et al. AAV2-GAD gene therapy for advanced Parkinson’s disease: A double-blind, sham-surgery controlled, randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungta, R.L.; Choi, H.B.; Lin, P.J.; Ko, R.W.; Ashby, D.; Nair, J.; Manoharan, M.; Cullis, P.R.; Macvicar, B.A. Lipid Nanoparticle Delivery of siRNA to Silence Neuronal Gene Expression in the Brain. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2013, 2, e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, J.L.; Yi, X.; Quan, L.; Kabanov, A.V. Novel nanomaterials for clinical neuroscience. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2008, 3, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluffo, H.; Unzueta, U.; Negro-Demontel, M.L.; Xu, Z.; Váquez, E.; Ferrer-Miralles, N.; Villaverde, A. BBB-targeting, protein-based nanomedicines for drug and nucleic acid delivery to the CNS. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenleaf, W.J.; Bolander, M.E.; Sarkar, G.; Goldring, M.B.; Greenleaf, J.F. Artificial cavitation nuclei significantly enhance acoustically induced cell transfection. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1998, 24, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechheimer, M.; Boylan, J.F.; Parker, S.; Sisken, J.E.; Patel, G.L.; Zimmer, S.G. Transfection of mammalian cells with plasmid DNA by scrape loading and sonication loading. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 84, 8463–8467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamics-based transfection in animals by systemic administration of plasmid DNA. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvshani-Eshet, M.; Machluf, M. Therapeutic ultrasound optimization for gene delivery: A key factor achieving nuclear DNA localization. J. Control. Release 2005, 108, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schratzberger, P.; Krainin, J.G.; Schratzberger, G.; Silver, M.; Ma, H.; Kearney, M.; Zuk, R.F.; Brisken, A.F.; Losordo, D.W.; Isner, J.M. Transcutaneous ultrasound augments naked DNA transfection of skeletal muscle. Mol. Ther. 2002, 6, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, R.P.; Yeaman, L.D.; Taylor, R.G.; McCullough, D.L. Altered neutrophil permeability following shock wave exposure in vitro. J. Urol. 1992, 147, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Tachibana, K.; Kuroki, M.; Kuroki, M. Gene transfer with echo-enhanced contrast agents: Comparison between Albunex, Optison, and Levovist in mice—Initial results. Radiology 2003, 229, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, S.; Tachibana, K.; Uchino, E.; Okubo, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Sakoda, K.; Hisatomi, T.; Sonoda, K.H.; Negishi, Y.; Izumi, Y.; et al. Gene transfer to corneal epithelium and keratocytes mediated by ultrasound with microbubbles. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniyama, Y.; Tachibana, K.; Hiraoka, K.; Namba, T.; Yamasaki, K.; Hashiya, N.; Aoki, M.; Ogihara, T.; Yasufumi, K.; Morishita, R. Local delivery of plasmid DNA into rat carotid artery using ultrasound. Circulation 2002, 105, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, E.C.; Porter, T.; Culp, W.; Labell, R.; Matsunaga, T.; Zutshi, R. Therapeutic applications of lipid-coated microbubbles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1291–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynynen, K.; McDannold, N.; Vykhodtseva, N.; Jolesz, F.A. Noninvasive MR imaging-guided focal opening of the blood–brain barrier in rabbits. Radiology 2001, 220, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Kennedy, A.M.; Christensen, D.A.; Rapoport, N.Y. Drug-loaded nano/microbubbles for combining ultrasonography and targeted chemotherapy. Ultrasonics 2008, 48, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.M.; Hansen, C.; Martin, F.; Redemann, C.; Yau-Young, A. Liposomes containing synthetic lipid derivatives of poly(ethylene glycol) show prolonged circulation half-lives in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1066, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, G.; Cevc, G. Liposomes for the sustained drug release in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1029, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Ishida, O.; Kasaoka, S.; Takizawa, T.; Utoguchi, N.; Shinohara, A.; Chiba, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Eriguchi, M.; Yanagie, H. Intracellular targeting of sodium mercaptoun-decahydrododecaborate (BSH) to solid tumors by transferrin-PEG liposomes, for boron neutron-capture therapy (BNCT). J. Control. Release 2004, 98, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, K.; Yuda, T.; Okamoto, A.; Kojima, S.; Suginaka, A.; Iwatsuru, M. Prolonged circulation time in vivo of large unilamellar liposomes composed of distearoyl phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol containing amphipathic poly(ethylene glycol). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1128, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Takizawa, T.; Negishi, Y.; Hagisawa, K.; Tanaka, K.; Sawamura, K.; Utoguchi, N.; Nishioka, T.; Maruyama, K. Gene delivery by combination of novel liposomal bubbles with perfluoropropane and ultrasound. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Takizawa, T.; Negishi, Y.; Utoguchi, N.; Maruyama, K. Effective gene delivery with novel liposomal bubbles and ultrasonic destruction technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 354, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negishi, Y.; Endo, Y.; Fukuyama, T.; Suzuki, R.; Takizawa, T.; Omata, D.; Maruyama, K.; Aramaki, Y. Delivery of siRNA into the cytoplasm by liposomal bubbles and ultrasound. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negishi, Y.; Omata, D.; Iijima, H.; Takabayashi, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Endo, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Nomizu, M.; Aramaki, Y. Enhanced laminin-derived peptide AG73-mediated liposomal gene transfer by Bubble liposomes and ultrasound. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negishi, Y.; Matsuo, K.; Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Matsuki, Y.; Takagi, N.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Aramaki, Y. Delivery of an angiogenic gene into ischemic muscle by novel Bubble liposomes followed by ultrasound exposure. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negishi, Y.; Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Matsuki, Y.; Kato, Y.; Takagi, N.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Aramaki, Y. Systemic delivery systems of angiogenic gene by novel Bubble liposomes containing cationic lipid and ultrasound exposure. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.Y.; Lin, Y.S.; Kang, K.H.; Chao, T.K. Reversible blood-brain barrier disruption by repeated transcranial focused ultrasound allows enhanced extravasation. J. Control. Release 2011, 150, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.Y.; Lee, P.Y. Efficiency of drug delivery enhanced by acoustic pressure during blood–brain barrier disruption induced by focused ultrasound. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 2573–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinali, M.; Arechavala-Gomeza, V.; Feng, L.; Cirak, S.; Hunt, D.; Adkin, C.; Guglierim, M.; Ashton, E.; Abbs, S.; Nihoyannopoulos, P.; et al. Local restoration of dystrophin expression with the morpholino oligomer AVI-4658 in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: A single-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation, proof-of-concept study. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goemans, N.M.; Tulinius, M.; van den Akker, J.T.; Burm, B.E.; Ekhart, P.F.; Heuvelmans, N.; Holling, T.; Janson, A.A.; Platenburg, G.J.; Sipkens, J.A.; et al. Systemic administration of PRO051 in Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirak, S.; Arechavala-Gomeza, V.; Guglieri, M.; Feng, L.; Torelli, S.; Anthony, K.; Abbs, S.; Garralda, M.E.; Bourke, J.; Wells, D.J.; et al. Exon skipping and dystrophin restoration in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy after systemic phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer treatment: An open-label, phase 2, dose-escalation study. Lancet 2011, 378, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, Y.; Ishii, Y.; Shiono, H.; Akiyama, S.; Sekine, S.; Kojima, T.; Mayama, S.; Kikuchi, T.; Hamano, N.; Endo-Takahashi, Y.; et al. Bubble liposomes and ultrasound exposure improve localized morpholino oligomer delivery into the skeletal muscles of dystrophic mdx mice. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaillend, C.; Perronnet, C.; Ros, C.; Gruszczynski, C.; Goyenvalle, A.; Laroche, S.; Danos, O.; Garcia, L.; Peltekian, E. Rescue of a dystrophin-like protein by exon skipping in vivo restores GABAA-receptor clustering in the hippocampus of the mdx mouse. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1683–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallérac, G.; Perronnet, C.; Chagneau, C.; Leblanc-Veyrac, P.; Samson-Desvignes, N.; Peltekian, E.; Danos, O.; Garcia, L.; Laroche, S.; Billard, J.M.; et al. Rescue of a dystrophin-like protein by exon skipping normalizes synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus of the mdx mouse. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 43, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyenvalle, A.; Griffith, G.; Babbs, A.; El Andaloussi, S.; Ezzat, K.; Avril, A.; Dugovic, B.; Chaussenot, R.; Ferry, A.; Voit, T.; et al. Functional correction in mouse models of muscular dystrophy using exon-skipping tricyclo-DNA oligomers. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, J.P.; French, B.A.; Klibanov, A.L.; Kaul, S.; Lindner, J.R. Targeted tissue transfection with ultrasound destruction of plasmid-bearing cationic microbubbles. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2003, 29, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, L.C.; Klibanov, A.L.; Bowles, D.K.; Ragosta, M.; Hossack, J.A.; Wamhoff, B.R. Focused in vivo delivery of plasmid DNA to the porcine vascular wall via intravascular ultrasound destruction of microbubbles. J. Vasc. Res. 2010, 47, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, L.C.; Klibanov, A.L.; Wamhoff, B.R.; Hossack, J.A. Targeted gene transfection from microbubbles into vascular smooth muscle cells using focused, ultrasound-mediated delivery. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Negishi, Y.; Kato, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Aramaki, Y. Efficient siRNA delivery using novel siRNA-loaded Bubble liposomes and ultrasound. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 422, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Negishi, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Suzuki, D.; Ukai, S.; Sugimoto, K.; Moriyasu, F.; Takagi, N.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; et al. pDNA-loaded Bubble liposomes as potential ultrasound imaging and gene delivery agents. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2807–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Negishi, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Ukai, S.; Ooaku, K.; Oda, Y.; Sugimoto, K.; Moriyasu, F.; Takagi, N.; Suzuki, R.; et al. Systemic delivery of miR-126 by miRNA-loaded Bubble liposomes for the treatment of hindlimb ischemia. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, Y.; Hamano, N.; Tsunoda, Y.; Oda, Y.; Choijamts, B.; Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Omata, D.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K.; Nomizu, M.; et al. AG73-modified Bubble liposomes for targeted ultrasound imaging of tumor neovasculature. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.D.; Sagare, A.P.; Friedman, A.E.; Bedi, G.S.; Holtzman, D.M.; Deane, R.; Zlokovic, B.V. Transport pathways for clearance of human Alzheimer’s amyloid β-peptide and apolipoproteins E and J in the mouse central nervous system. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 27, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, T.; Agashe, H.B.; Garg, M.; Balasubramanium, P.; Kabra, M.; Jain, N.K. Poly (propyleneimine) dendrimer based nanocontainers for targeting of efavirenz to human monocytes/macrophages in vitro. J. Drug Target. 2007, 15, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and its receptors in Alzheimer’s disease: Pathways, pathogenesis and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Choi, W.I.; Kim, Y.H.; Tae, G. Brain-targeted delivery of protein using chitosan- and RVG peptide-conjugated, pluronic-based nano-carrier. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaru, M.; Akita, H.; Kajimoto, K.; Sato, Y.; Hatakeyama, H.; Harashima, H. An apolipoprotein E modified liposomal nanoparticle: Ligand dependent efficiency as a siRNA delivery carrier for mouse-derived brain endothelial cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 465, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negishi, Y.; Yamane, M.; Kurihara, N.; Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Sashida, S.; Takagi, N.; Suzuki, R.; Maruyama, K. Enhancement of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability and Delivery of Antisense Oligonucleotides or Plasmid DNA to the Brain by the Combination of Bubble Liposomes and High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 344-362. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030344
Negishi Y, Yamane M, Kurihara N, Endo-Takahashi Y, Sashida S, Takagi N, Suzuki R, Maruyama K. Enhancement of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability and Delivery of Antisense Oligonucleotides or Plasmid DNA to the Brain by the Combination of Bubble Liposomes and High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound. Pharmaceutics. 2015; 7(3):344-362. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030344
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegishi, Yoichi, Masaya Yamane, Naho Kurihara, Yoko Endo-Takahashi, Sanae Sashida, Norio Takagi, Ryo Suzuki, and Kazuo Maruyama. 2015. "Enhancement of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability and Delivery of Antisense Oligonucleotides or Plasmid DNA to the Brain by the Combination of Bubble Liposomes and High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound" Pharmaceutics 7, no. 3: 344-362. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030344
APA StyleNegishi, Y., Yamane, M., Kurihara, N., Endo-Takahashi, Y., Sashida, S., Takagi, N., Suzuki, R., & Maruyama, K. (2015). Enhancement of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability and Delivery of Antisense Oligonucleotides or Plasmid DNA to the Brain by the Combination of Bubble Liposomes and High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound. Pharmaceutics, 7(3), 344-362. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7030344