Study on Air Pollution and Control Investment from the Perspective of the Environmental Theory Model: A Case Study in China, 2005–2014
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Study
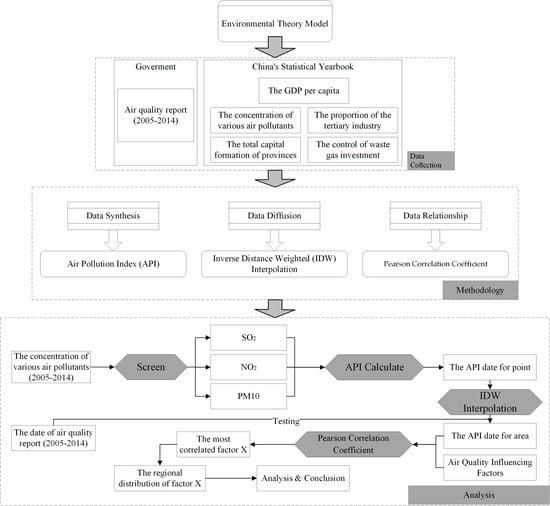
2.2. Basic Idea and Research Framework
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Environmental Theory Model
2.4.2. Air Pollution Index (API)
2.4.3. Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW) Interpolation
2.4.4. Pearson Correlation Coefficient
3. Results
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Changes in Air Quality in China
3.2. Temporal and Spatial Changes in Air Pollution Control Investment in China
3.3. China’s Average Air Pollution Index (API) and Average Air Pollution Control Investment
4. Discussion
4.1. Variable Selection and Applicability of the Environmental Kuznets Curve
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Tharby, R. (Ed.) Catching Gasoline and Diesel Adulteration (English); South Asia Urban Air Quality Management Briefing Note; NO. 7; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/223591468164352248/Catching-gasoline-and-diesel-adulteration (accessed on 13 June 2018).
- Ackermann-Liebrich, U.; Leuenberger, P.; Schwartz, J.; Schindler, C.; Monn, C.; Bolognini, G.; Bongard, J.; Brändli, O.; Domenighetti, G.; Elsasser, S. Lung function and long term exposure to air pollutants in Switzerland. Study on air pollution and lung diseases in adults (sapaldia) team. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Bai, L. Spatio-temporal characteristics of urban air pollutions and their causal relationships: Evidence from Beijing and its neighboring cities. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dockery, D.W.; Pope, C.A.; Xu, X.; Spengler, J.D.; Ware, J.H.; Fay, M.E.; Ferris, B.G., Jr.; Speizer, F.E. An association between air pollution and mortality in six US cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, R.N. Meteorological conditions for the persistent severe fog and haze event over eastern China in January 2013. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, W.; Luo, L.; Xu, Y.; Xie, H.; Xu, X. (Eds.) China Statistical Yearbook 2013; National Bureau of Statistics of People’s Republic of China, China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2013; Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2013/indexch.htm (accessed on 13 June 2018). (In Chinese)
- Ashbaugh, L.L. A statistical trajectory technique for determining air pollution source regions. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1983, 33, 1096–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, M.; Feng, F.; Yang, Y. Air pollution inequality and its sources in SO2 and NOx emissions among Chinese provinces from 2006 to 2015. Sustainability 2018, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; He, L. Are Chinese green transport policies effective? A new perspective from direct pollution rebound effect, and empirical evidence from the road transport sector. Sustainability 2017, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Niu, T.; Zhang, X.; Gong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J. Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China: Spatial/temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 779–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Cui, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, A.; Fu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Kong, L.; Chen, J. Spatial and temporal variation of particulate matter and gaseous pollutants in China during 2014–2016. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 161, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ma, W.; Dong, H.; Jiang, P. Analysis of co-effects on air pollutants and CO2 emissions generated by end-of-pipe measures of pollution control in China’s coal-fired power plants. Sustainability 2017, 9, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, B.Z.; Chevallier, J. Examining the factors affecting air pollution emission growth in China. Environ. Model. Assess. 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, X. Air pollution from industrial waste gas emissions is associated with cancer incidences in Shanghai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.; Pan, R.-H.; Chan, C.-K.; Wu, C.-Y.; Phan, D.-V.; Chan, C.-L. Application of a time-stratified case-crossover design to explore the effects of air pollution and season on childhood asthma hospitalization in cities of differing urban patterns: Big data analytics of government open data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zheng, S.; Nie, Y.; Weng, J.; Cheng, N.; Hu, X.; Ren, X.; Pei, H.; Bai, Y. Association between short-term exposure to air pollution and dyslipidemias among type 2 diabetic patients in northwest China: A population-based study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, G.S.; Spadaro, J.V.; Chapizanis, D.; Kendrovski, V.; Kochubovski, M.; Mudu, P. Health impacts and economic costs of air pollution in the metropolitan area of skopje. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Liu, X.; Geng, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, T. Effects of PM2.5 and haze event on hospital visiting of children in Ji’nan, 2013: A time series analysis. J. Environ. Health 2014, 6, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X. Influence of a severe dust storm on Chinese cities air quality. J. Desert Res. 2008, 28, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhu, B.; Zhou, T. An analysis of weather condition during a continuous air pollution process in Nanjing city. Environ. Monit. Forewarn. 2012, 1, 004. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ying, Q.; Zhang, H. Spatial and temporal variability of PM2.5 and PM10 over the North China plain and the Yangtze river delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, J. Characteristics of the transport of a typical pollution event in the Cengdu area based on remote sensing data and numerical simulations. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.K.; Pereira, N.C.; Hung, Y.-T. Air Pollution Control Engineering; Springer: New York, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zundel, T.; Rentz, O.; Dorn, R.; Jattke, A.; Wietschel, M. Control techniques and strategies for regional air pollution control from energy and industrial sectors. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1995, 85, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhani, H. Air pollution control by economic incentives in the US Policy, problems, and progress. Environ. Manag. 1982, 6, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; He, K.; Duan, L.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Air pollution and its control in China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2007, 1, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, C.; Murlis, J. Study on winter air pollution control in Lanzhou, China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 127, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, M. A new modeling technique for air pollution control. Environ. Manag. 1977, 1, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi, F.; Spinazzè, A.; Rovelli, S.; Campagnolo, D.; Del Buono, L.; Cattaneo, A.; Cavallo, D.M. Miniaturized monitors for assessment of exposure to air pollutants: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Q.W.R. Discussion on the influencing factors of the investment effect of air pollution control in China based on the logarithmic mean diels’ decomposition method. Environ. Pollut. Control 2012, 34, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Tisdell, C. Globalisation and sustainability: Environmental Kuznets curve and the WTO. Ecol. Econ. 2001, 39, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Environmental Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991; Available online: http://www.nber.org/papers/w3914 (accessed on 13 June 2018).
- Xiao, K.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Fu, B.; Zhu, Y. Spatiotemporal characteristics of air pollutants (PM10, PM2.5, SO2, NO2, O3, and CO) in the inland basin city of Chengdu, southwest China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ding, Y.; He, J.; Yu, J. An updating analysis of the climate change in China in recent 50 years. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2004, 62, 228–236. [Google Scholar]
- Holzworth, G.C. (Ed.) Mixing Heights, Wind Speeds, and Potential for Urban Air Pollution throughout the Contiguous United States; Epa Publication, EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1972; Available online: http://bases.bireme.br/cgi-bin/wxislind.exe/iah/online/?IsisScript=iah/iah.xis&src=google&base=REPIDISCA&lang=p&nextAction=lnk&exprSearch=163123&indexSearch=ID (accessed on 13 June 2018).
- Carslaw, D.C.; Ropkins, K. Openair—An r package for air quality data analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 27, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, C. Economic Analysis of the Health Effects of Air Pollution. Southwest. Univ. Finance Econ. 2012. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CDFD&dbname=CDFD1214&filename=1012509650.nh&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FhdXNXa0hIUUVQY0t2bElUUXNqQkhNaExMMmJRRT0=$9A4hF_YAuvQ5obgVAqNKPCYcEjKensW4ggI8Fm4gTkoUKaID8j8gFw!!&v=MDAwNTNDamxXcjNJVkYyNkhMYTRGOWZKcjVFYlBJUjhlWDFMdXhZUzdEaDFUM3FUcldNMUZyQ1VSTEtmWWVScUY= (accessed on 13 June 2018). (In Chinese).
- Li, G.; Zhai, Q.; Huan, R.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Zhuang, G. Monthly Air Quality Report 2013; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013. Available online: http://www.zhb.gov.cn/hjzl/dqhj/cskqzlzkyb/index_3.shtml (accessed on 13 June 2018).
- Shepard, D. A Two-Dimensional Interpolation Function for Irregularly-Spaced Data. In Proceedings of the 1968 23rd ACM National Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–29 August 1968; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 1968; pp. 517–524. [Google Scholar]
- Kethireddy, S.R.; Tchounwou, P.B.; Ahmad, H.A.; Yerramilli, A.; Young, J.H. Geospatial interpolation and mapping of tropospheric ozone pollution using geostatistics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 983–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, P.; Lei, M.; Yang, S.; Yang, J.; Guo, G.; Zhou, X. Comparing ordinary kriging and inverse distance weighting for soil as pollution in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 15597–15608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yu, C.; Li, X. The spatial-temporal characteristics of air pollution in China from 2001–2014. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 15875–15887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselin, L.; Le Gallo, J. Interpolation of air quality measures in hedonic house price models: Spatial aspects. Spat. Econ. Anal. 2006, 1, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhloom, H.M.; Al-Ansari, N.; Laue, J.; Chabuk, A. Modeling spatial distribution of some contamination within the lower reaches of diyala river using idw interpolation. Sustainability 2017, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ren, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M. Quantifying urban land sprawl and its driving forces in northeast China from 1990 to 2015. Sustainability 2018, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, W.; Duan, L.; Du, E.; Pan, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Atmospheric nitrogen emission, deposition, and air quality impacts in China: An overview. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2017, 3, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gong, Z. Spatiotemporal characteristics of urban air quality in China and geographic detection of their determinants. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. An Analysis and Research of Present Atmospheric Environment in Northwest Region (Gansu, Qinghai, Xinjiang). Lanzhou Univ. 2012. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201402&filename=1014301838.nh&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FhdXNXa0hIUUVQY0t2bElUUXNqQkhNaExMMmJRRT0=$9A4hF_YAuvQ5obgVAqNKPCYcEjKensW4ggI8Fm4gTkoUKaID8j8gFw!!&v=MjE2MzkxRnJDVVJMS2ZZZVJxRkNqbVZMN0tWRjI2R3JDNEg5blBwNUViUElSOGVYMUx1eFlTN0RoMVQzcVRyV00= (accessed on 13 June 2018). (In Chinese).
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J. Pollution haven hypothesis and environmental impacts of foreign direct investment: The case of industrial emission of sulfur dioxide (SO2) in Chinese provinces. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 60, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, S. Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: A survey. Ecol. Econ. 2004, 49, 431–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torras, M.; Boyce, J.K. Income, inequality, and pollution: A reassessment of the environmental Kuznets curve. Ecol. Econ. 1998, 25, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selden, T.M.; Song, D. Environmental quality and development: Is there a Kuznets curve for air pollution emissions? J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 1994, 27, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orubu, C.O.; Omotor, D.G. Environmental quality and economic growth: Searching for environmental Kuznets curves for air and water pollutants in Africa. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 4178–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, R.T.; Jeon, Y.; McCubbin, D.R. The relationship between air pollution emissions and income: US data. Environ. Dev. Econ. 1997, 2, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, D.I. The rise and fall of the environmental Kuznets curve. World Dev. 2004, 32, 1419–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Data Name | Data Content | Temporal Resolution | Data Sources and URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP (Gross Domestic Product) Per Person | Per capita GDP of provinces in China | 2005–2014 | China’s Statistical Yearbook, http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/ |
| Air Pollutants | China’s annual data of sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and fine particles (<10 μm) (PM10) | 2005–2014 | China’s Statistical Yearbook, http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/ |
| Industry Structure | Proportion of the tertiary industry in China | 2005–2014 | China’s Statistical Yearbook, http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/ |
| Control Investment | Investment completed for the treatment of waste gas which includes capital investment in the industrial air pollution sources and urban air governance infrastructure. | 2005–2014 | China’s Statistical Yearbook, http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/ |
| Total Capital Formation | Total capital formation of each province in China | 2005–2014 | China’s Statistical Yearbook, http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/ |
| Air Quality Composite Index | Air quality composite index for China for each month. | 2013,2014 | The Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, http://www.mep.gov.cn |
| Pollutant Concentrations (μg/m3) | API | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PM10 | SO2 | NO2 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 150 | 150 | 120 | 100 |
| 350 | 800 | 280 | 200 |
| 420 | 1600 | 565 | 300 |
| 500 | 2100 | 750 | 400 |
| 600 | 2620 | 940 | 500 |
| Group Name | |
|---|---|
| API (34sites) & AQCI (74sites) in 2013 | 0.942 ** |
| API (34sites) & AQCI (74sites) in 2014 | 0.917 ** |
| Statistical Data Related to API | |
|---|---|
| The GDP per capita (yuan) | 0.165 ** |
| The proportion of the tertiary industry (%) | −0.096 |
| The air pollution control investment (ten thousand yuan) | 0.466 ** |
| The total capital formation (ten million yuan) | 0.230 ** |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, P.; Lin, D.; Qian, C. Study on Air Pollution and Control Investment from the Perspective of the Environmental Theory Model: A Case Study in China, 2005–2014. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072181
Su P, Lin D, Qian C. Study on Air Pollution and Control Investment from the Perspective of the Environmental Theory Model: A Case Study in China, 2005–2014. Sustainability. 2018; 10(7):2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072181
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Peng, Degen Lin, and Chen Qian. 2018. "Study on Air Pollution and Control Investment from the Perspective of the Environmental Theory Model: A Case Study in China, 2005–2014" Sustainability 10, no. 7: 2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072181
APA StyleSu, P., Lin, D., & Qian, C. (2018). Study on Air Pollution and Control Investment from the Perspective of the Environmental Theory Model: A Case Study in China, 2005–2014. Sustainability, 10(7), 2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072181