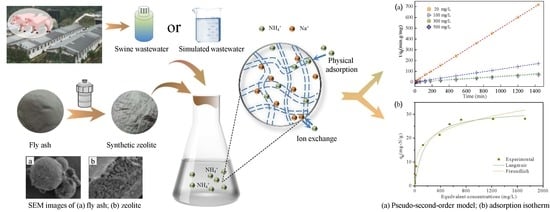
Removal of Ammonium from Swine Wastewater Using Synthesized Zeolite from Fly Ash
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pretreatment of Fly Ash
2.3. Hydrothermal Zeolite Synthesis
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Adsorption Experiments
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Materials
3.2. Pre-Treatment and Synthetic Parameters
3.3. Parameters Affecting Ammonium Adsorption
3.3.1. Effect of pH
3.3.2. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
3.3.3. Effect of Coexisting Ions
3.4. Kinetic Analysis
3.5. Equilibrium Adsorption Isotherms
3.6. Thermodynamics
3.7. Adsorption Mechanism
3.8. Removal of Ammonium from Real Swine Wastewater
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, Z.-L.; Ghyselbrecht, K.; Monballiu, A.; Pinoy, L.; Meesschaert, B. Fractionating various nutrient ions for resource recovery from swine wastewater using simultaneous anionic and cationic selective-electrodialysis. Water Res. 2019, 160, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadivelu, V.M.; Keller, J.; Yuan, Z. Effect of free ammonia and free nitrous acid concentration on the anabolic and catabolic processes of an enriched Nitrosomonas culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 95, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Li, J.; He, J.; Li, J.; Deng, K.; Nan, J. Nutrient removal from high ammonium swine wastewater in upflow microaerobic biofilm reactor suffered high hydraulic load. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Dong, J.; Shen, Z.; Mou, R.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Fu, X.; Yang, C. Nitrogen removal of anaerobically digested swine wastewater by pilot-scale tidal flow constructed wetland based on in-situ biological regeneration of zeolite. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, R.; Chen, C.-L.; Lin, J.-Y.; Tzeng, J.-H.; Huang, C.-P.; Dong, C.; Huang, C.P. Adsorption characteristics of ammonium ion onto hydrous biochars in dilute aqueous solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zeng, X.; Wen, X.; Yang, C.; Ouyang, S.; Li, P.; Gu, Z.; Wu, D.; Frost, R.L. Insights into efficient removal and mechanism for ammonium from aqueous solution on tricalcium aluminate. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, J.J.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Lei, S.; Xiao, R. Simultaneous capture removal of phosphate, ammonium and organic substances by MgO impregnated biochar and its potential use in swine wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, H.; Wang, J.; Garg, A.; Lin, X.; Zheng, Q.; Sharma, S. Potential of Novel Biochars Produced from Invasive Aquatic Species Outside Food Chain in Removing Ammonium Nitrogen: Comparison with Conventional Biochars and Clinoptilolite. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitrogiannis, D.; Psychoyou, M.; Koukouzas, N.; Tsoukalas, N.; Palles, D.; Kamitsos, E.; Pantazidis, A.; Oikonomou, G.; Baziotis, I. Phosphate recovery from real fresh urine by Ca(OH)(2) treated natural zeolite. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-R.; Soe, J.T.; Zhang, S.; Ahn, J.-W.; Park, M.B.; Ahn, W.-S. Synthesis of nanoporous materials via recycling coal fly ash and other solid wastes: A mini review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 821–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, R.; Hernandez, S.; Andres, J.M.; Ruiz, C. Ion exchange uptake of ammonium in wastewater from a Sewage Treatment Plant by zeolitic materials from fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Gong, H.; Fang, K.; Peng, F.; Wang, K. Revealing the effect of preparation parameters on zeolite adsorption performance for low and medium concentrations of ammonium. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 85, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivalingam, S.; Sen, S. Optimization of synthesis parameters and characterization of coal fly ash derived microporous zeolite X. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P. Clean & Sustainable process for Zeolite Synthesis: Effect of Acidic Pretreatment and Double Fusion on the Characteristics. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 10484–10488. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, F.; Song, H.; Zheng, N.; Wang, X. Application of Modified Coal Fly Ash as an Absorbent for Ammonia-Nitrogen Wastewater Treatment. In Advances in Environmental Science and Engineering, Pts 1–6; Iranpour, R., Zhao, J., Wang, A., Yang, F.L., Li, X., Eds.; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 2380–2384. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Xu, S.; Han, R.; Wang, Q. Nutrient sequestration from wastewater by using zeolite Na-P1 synthesized from coal fly ash. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.M.; Horn, M.B.; Ferret, L.S.; Azevedo, C.M.N.; Pires, M. Integrated synthesis of zeolites 4A and Na-P1 using coal fly ash for application in the formulation of detergents and swine wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 287, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Xu, D.; Han, L.; Niu, D.; Zhang, L.; Wu, W.; Tian, B. Ammonium removal from aqueous solution by zeolites synthesized from low-calcium and high-calcium fly ashes. Desalination 2011, 277, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, G.; Cardenas, E.; Cabrera, S.; Hedlund, J.; Mouzon, J. Synthesis of zeolite Y from diatomite as silica source. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 219, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Na, P. Synthesis and characterization of zeolite from coal fly ash. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.M.; Paprocki, A.; Ferret, L.S.; Azevedo, C.M.N.; Pires, M. Synthesis of zeolite Na-P1 under mild conditions using Brazilian coal fly ash and its application in wastewater treatment. Fuel 2015, 139, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franus, W.; Wdowin, M.; Franus, M. Synthesis and characterization of zeolites prepared from industrial fly ash. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 5721–5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Luo, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. The thermodynamics and kinetics for the removal of copper and nickel ions by the zeolite Y synthesized from fly ash. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Sun, H. A novel silica alumina-based backfill material composed of coal refuse and fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, W.; Han, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Gong, X.; Zhai, C.; Song, H. In-situ synthesis of NaP zeolite doped with transition metals using fly ash. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 7665–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, R.; Hernandez, S.; Andres, J.M.; Ruiz, C. Synthesis of granular zeolitic materials with high cation exchange capacity from agglomerated coal fly ash. Fuel 2007, 86, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Boyd, C.E. Total ammonia nitrogen removal from aqueous solutions by the natural zeolite, mordenite: A laboratory test and experimental study. Aquaculture 2014, 432, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, X.; Yan, B.; Yang, L. Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by using natural Chinese (Chende) zeolite as adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizito, S.; Wu, S.; Kirui, W.K.; Lei, M.; Lu, Q.; Bah, H.; Dong, R. Evaluation of slow pyrolyzed wood and rice husks biochar for adsorption of ammonium nitrogen from piggery manure anaerobic digestate slurry. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; Yan, C.; Al-Ani, Y.; Dawood, A.S.; Ibrahim, A.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H. An investigation into the adsorption removal of ammonium by salt activated Chinese (Hulaodu) natural zeolite: Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, D.; Pang, R.; Han, C.; Ding, L. Simultaneous removal of nutrients from simulated swine wastewater by adsorption of modified zeolite combined with struvite crystallization. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherley, L.R.; Miladinovic, N.D. Comparison of the ion exchange uptake of ammonium ion onto New Zealand clinoptilolite and mordenite. Water Res. 2004, 38, 4305–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Zhang, M.; Zou, X.; Zhao, X.; Deng, T.; Chen, T.; Huang, X. The investigation into the adsorption removal of ammonium by natural and modified zeolites: Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics. Water SA 2019, 45, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Lei, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, C.; Lee, D.-J.; Tay, J.H. Adsorption mechanisms of high-levels of ammonium onto natural and NaCl-modified zeolites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 103, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Jin, H.; Liu, W.; Su, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, J. Study on regeneration of waste powder activated carbon through pyrolysis and its adsorption capacity of phosphorus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Wu, L. Synthesis of zeolite P1 from fly ash under solvent-free conditions for ammonium removal from water. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Khunjar, W.; Zhao, K. Enhanced nutrient sequestration from swine wastewater using zeolite synthesized from fly ash integrated with surface amendment technique. Fuel 2013, 111, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, F.; Pang, W. Removal of ammonium ions from wastewater using modified zeolites. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2007, 16, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lalley, J.; Han, C.; Mohan, G.R.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Speth, T.F.; Garland, J.; Nadagouda, M.N. Phosphate removal using modified Bayoxide (R) E33 adsorption media. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2015, 1, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Han, L.; Ma, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Liang, S. Adsorption characteristics of ammonium ion by zeolite 13X. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, R. Removal of Ammonium from Wastewater by Pure Form Low-Silica Zeolite Y Synthesized tfrom Halloysite Mineral. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, R. Preparation of highly ordered cubic NaA zeolite from halloysite mineral for adsorption of ammonium ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesinghe, D.T.N.; Dassanayake, K.B.; Scales, P.; Sommer, S.G.; Chen, D. Removal of excess nutrients by Australian zeolite during anaerobic digestion of swine manure. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2018, 53, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J. Adsorption characteristics and mechanisms of high-levels of ammonium from swine wastewater using natural and MgO modified zeolites. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 5452–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.K.; Hayashi, S. Modification on natural clinoptilolite zeolite for its NH4+ retention capacity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belova, T.P. Adsorption of heavy metal ions (Cu2+, Ni2+, Co2+ and Fe2+) from aqueous solutions by natural zeolite. Heliyon 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wang, J.; Xiang, S.; Huang, Z.; Ruan, R.; Liu, Y. Nutrient removal from digested swine wastewater by combining ammonia stripping with struvite precipitation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6725–6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dote, Y.; Sekito, T.; Ueda, K.; Sakamoto, R.; Suzuki, T.; Sano, S. Removal of ammonia from aqueous solution for swine wastewater with swine manure compost-based char. Water Pract. Technol. 2015, 10, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-B.; Lin, H. Ammonia nitrogen removal from aqueous solution using zeolite modified by microwave-sodium acetate. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, I.M.S.; Gurgel, G.C.S.; Medeiros, A.M.; Zonta, E.; Ruiz, J.A.C.; Paskocimas, C.A.; Motta, F.V.; Bomio, M.R.D. The use of clinoptilolite as carrier of nitrogened fertilizer with controlled release. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4171–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameters | Unit | Raw Swine Wastewater | Effluent from the Biochemical Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | / | 7.84 | 6.32 |
| NH4+-N | mg/L | 584 | 189 |
| Total nitrogen | mg/L | 605 | 199 |
| PO43−-P | mg/L | 56 | 50 |
| Total phosphorus | mg/L | 269 | 61 |
| Chemical oxygen demand | mg/L | 3600 | 256 |
| Na | mg/L | 569 | 332 |
| K | mg/L | 702 | 437 |
| Ca | mg/L | 310 | 195 |
| Mg | mg/L | 413 | 289 |
| Zn | mg/L | 1.20 | 0.32 |
| Cu | mg/L | 0.30 | 0.16 |
| Components | Raw | Water-Washing | Pickling |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 58.00% | 58.17% | 58.69% |
| Al2O3 | 30.00% | 30.41% | 38.42% |
| Fe2O3 | 4.30% | 4.31% | 1.20% |
| CaO | 1.50% | 1.42% | 0.59% |
| MgO | 2.80% | 2.84% | 0.49% |
| Na2O | 3.20% | 2.63% | 0.35% |
| Impurity | 0.20% | 0.22% | 0.26% |
| Si/Al | 1.70 | 1.69 | 1.34 |
| Models | Parameters | Temperature (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 25 | 35 | ||
| Langmuir | qm(mg/g) | 33.39 | 32.16 | 31.68 |
| kl | 0.0079 | 0.0063 | 0.0055 | |
| r2 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.95 | |
| Freundlich | kf((mg/g)/ (mg/L)n) | 6.77 | 5.32 | 4.73 |
| n | 4.68 | 4.17 | 3.97 | |
| r2 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.93 | |
| Temperature (K) | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (kJ/mol /K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 288 | −2.13 | −22.72 | −0.071 |
| 298 | −1.42 | ||
| 308 | −0.70 |
| Dosage (g/L) | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical removal efficiency a (%) | 24.44 | 46.76 | 55.40 | 60.84 | 64.99 | 70.63 |
| Actual removal efficiency a (%) | 21.64 | 42.07 | 51.57 | 59.94 | 60.66 | 64.34 |
| Effluent concentration a (mg/L) | 457.62 | 338.31 | 282.83 | 233.95 | 229.75 | 208.25 |
| Theoretical removal efficiency b (%) | 73.42 | 83.58 | 86.63 | - | - | - |
| Actual removal efficiency b (%) | 66.18 | 78.15 | 79.61 | - | - | - |
| Effluent concentration b (mg/L) | 63.92 | 41.30 | 38.54 | - | - | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, B.; Lv, C.; Shi, D. Removal of Ammonium from Swine Wastewater Using Synthesized Zeolite from Fly Ash. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083423
Tang H, Xu X, Wang B, Lv C, Shi D. Removal of Ammonium from Swine Wastewater Using Synthesized Zeolite from Fly Ash. Sustainability. 2020; 12(8):3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083423
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Hui, Xiaoyi Xu, Bin Wang, Chenpei Lv, and Dezhi Shi. 2020. "Removal of Ammonium from Swine Wastewater Using Synthesized Zeolite from Fly Ash" Sustainability 12, no. 8: 3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083423
APA StyleTang, H., Xu, X., Wang, B., Lv, C., & Shi, D. (2020). Removal of Ammonium from Swine Wastewater Using Synthesized Zeolite from Fly Ash. Sustainability, 12(8), 3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083423