L-Band Temporal Coherence Assessment and Modeling Using Amplitude and Snow Depth over Interior Alaska
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
3. Methods
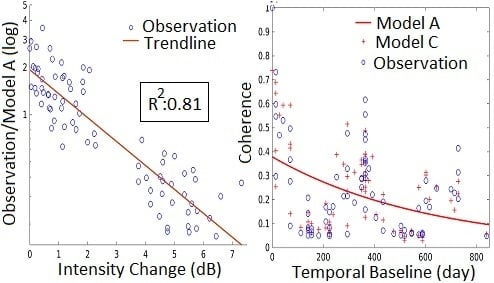
3.1. InSAR Coherence
3.2. Temporal Coherence Modeling
4. Discussion
4.1. Scatterers’ Type and Decorrelation Sources
4.2. The Effect of Seasonality on Temporal Coherence
4.3. Statistical Assessment on Models’ Performance
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgmann, R.; Rosen, P.A.; Fielding, E.J. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry to Measure Earth’s Surface Topography and Its Deformation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.; Rosen, P. Treatise on Geophysics: Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Geodesy. In Geodesy; Schubert, G., Ed.; Elsevier Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 3, pp. 391–446. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Dzurisin, D. InSAR imaging of Aleutian volcanoes: Monitoring a volcanic arc from space. In Geophysical Sciences; Springer Praxis Books: Chichester, UK, 2014; 390p. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Lu, Z.; Degrandpre, K. Ongoing Deformation of Sinkholes in Wink, Texas, Observed by Time-Series Sentinel-1A SAR Interferometry (Preliminary Results). Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, T.; Pierson, T.C.; Lu, Z.; Kim, J.; Cecere, T.H. Detecting seasonal landslide movement within the Cascade landslide complex (Washington) using time-series SAR imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykhus, R.; Lu, Z. InSAR detects possible thaw settlement in the Alaskan Arctic Coastal Plain. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 34, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Wahr, J. InSAR measurements of surface deformation over permafrost on the North Slope of Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, F03023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 45, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, D.; Bamler, R. Phase statistics of interferograms with applications to synthetic aperture radar. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 4361–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simard, M.; Hensley, S.; Lavalle, M. An empirical assessment of temporal decorrelation using the uninhabited aerial vehicle synthetic aperture radar over forested landscapes. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, F. Modeling Interferograms Stacks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3289–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Askne, J.; Smith, G.; Dammert, P. Coherence characteristics of RADAR signals from rough soil. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2001, 31, 68–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieback, S.; Hensley, S.; Hajnsek, I. Assessment of soil moisture effects on L-band radar interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zwieback, S.; Paulik, C.; Wagner, W. Frozen Soil Detection Based on Advanced Scatterometer Observations and Air Temperature Data as Part of Soil Moisture Retrieval. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3206–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieback, S.; Hensley, S.; Hajnsek, I. A Polarimetric First-Order Model of Soil Moisture Effects on the DInSAR Coherence. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7571–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavalle, M.; Simard, M.; Hensley, S. A Temporal Decorrelation Model for Polarimetric Radar Interferometers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2880–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, K. The estimation of dielectric constant of frozen soil-water mixture at microwave bands. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 2903–2905. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zeng, Q.; Li, Y.; Xiang, Y. Study on relation between InSAR coherence and soil moisture. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Congress, Beijing, China, 3–11 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Borgeaud, M.; Wegmueller, U. On the use of ERS SAR interferometry for the retrieval of geoand bio-physical information. In Proceedings of the ‘Fringe 96’ Workshop on ERS SAR Interferometry, Zurich, Switzerland, 30 September–2 October 1996; pp. 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Morishita, Y.; Hanssen, R.F. Temporal Decorrelation in L-, C-, and X-band Satellite Radar Interferometry for Pasture on Drained Peat Soils. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-K.; Kugler, F.; Papathanassiou, K.P.; Hajnsek, I. Quantification of Temporal Decorrelation Effects at L-Band for Polarimetric SAR Interferometry Applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1351–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homer, C.G.; Dewitz, J.A.; Yang, L.; Jin, S.; Danielson, P.; Xian, G.; Coulston, J.; Herold, N.D.; Wickham, J.D.; Megown, K. Completion of the 2011 National Land Cover Database for the conterminous United States-Representing a decade of land cover change information. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 81, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, K.P.; Kasischke, E.S.; Richter, D.D. Seasonal and decadal patterns of soil carbon uptake and emission along an age-sequence of burned black spruce stands in interior Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Freymueller, J. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry coherence analysis over Katmai volcano group, Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 29887–29894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzurisin, D.; Lu, Z. Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) (Chapter 5): Volcano Deformation: Geodetic Monitoring Techniques; Dzurisin, D., Ed.; Springer-Praxis Publishing Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2007; pp. 153–194. [Google Scholar]
- Hanssen, R. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bamler, R.; Hartl, P. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Inverse Prob. 1998, 14, R1–R54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Lopes, A.; Bruniquel, J.; Vachon, P. Coherence estimation for SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardini, F.; Griffiths, H. Effect of temporal decorrelation on 3D SAR imaging using multiple pass beamforming. In Proceedings of the IEE/EUREL Meeting Radar Sonar Signal Processing, Peebles, UK, 5–8 July 1998; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Bradley, G.A.; Dobson, M.C. Microwave backscatter dependence on surface roughness, soil moisture, and soil texture, II, Vegetation covered soil. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Electron. 1979, 17, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, M.; Gorrab, A.; Baghdadi, N. A new soil roughness parameter for the modelling of radar backscattering over bare soil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiel, C.; Schmullius, C. The potential of ALOS PALSAR backscatter and InSAR coherence for forest growing stock volume estimation in Central Siberia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 173, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Rignot, E.J.M.; Way, J.; Freeman, A.; Holt, J. Polarization signatures of frozen and thawed forests of varying environmental state. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Way, J.; Paris, J.; Kasischke, E.; Slaughter, C.; Viereck, L.; Christensen, N.; Weber, J. The effect of changing environmental-conditions on microwave signatures of forest ecosystems—Preliminary-results of the March 1988 Alaskan aircraft SAR experiment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1990, 11, 1119–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, M.G.; McDonald, K.; Ulaby, F.T. Effects of temperature on radar backscatter from boreal forests. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, College Park, MD, USA, 20–24 May 1990; Mills, R., Ed.; IEEE Publications: College Park, MD, USA, 1990; pp. 2481–2484. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, M.; Eriksson, L.; Fransson, J. Reviewing ALOS PALSAR backscatter observations for stem volume retrieval in Swedish forest. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4290–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, M.C. Diurnal and seasonal variations in the microwave dielectric constant of selected trees. In Proceedings of the International on Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Edinburgh, UK, 12–16 September 1988; Guyenne, T.D., Hunt, J.J., Eds.; ESA Publications Devision: Edinburgh, UK, 1988; p. 1754. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, K.C.; Zimmermann, R.; Kimball, J.S. Diurnal and spatial variation of xylem dielectric constant in Norway spruce (Picea abies [L.] karst.) as related to microclimate, xylem sap flow, and xylem chemistry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2063–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.C. Statistics and Data Analysis in Geology, 3rd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]










| Path-Frame | Orbit Direction | Number of Interferograms | Color of Frame on Figure 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0040-2330 | D | 4 | Yellow |
| 0041-2330 | D | 16 | Blue |
| 0042-2320 | D | 10 | Green |
| 0137-1280 | A | 10 | Magenta |
| 0138-1280 | A | 29 | Red |
| 0139-1270 | A | 6 | Cyan |
| Model | Land Cover | γ0 | τ (Day) | ρ | σ | RMS | f-Test | Cf (α = 0.01) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Forest | 0.37824 | 616.49 | - | - | 0.180 | - | - |
| Shrub | 0.444 | 629.53 | - | - | 0.186 | - | - | |
| B | Forest | 0.68885 | 861.07 | 2.5406 | - | 0.092 | 205.84 | 6.99 |
| Shrub | 0.74482 | 879.27 | 2.5467 | - | 0.121 | 102.38 | 6.99 | |
| C | Forest | 0.73842 | 903.7 | 3.3464 | 0.62062 | 0.083 | 16.23 | 7.00 |
| Shrub | 0.79153 | 913.47 | 5.6462 | 0.37348 | 0.101 | 29.64 | 7.00 |
| Land Cover | Group | Mean | SD | SD/Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest | S | 0.3433 | 0.0711 | 0.2070 |
| W | 0.3703 | 0.0680 | 0.1835 | |
| C | 0.0896 | 0.0407 | 0.4546 | |
| Shrub | S | 0.3905 | 0.0974 | 0.2495 |
| W | 0.4074 | 0.0836 | 0.2052 | |
| C | 0.1522 | 0.0566 | 0.3720 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eshqi Molan, Y.; Kim, J.-W.; Lu, Z.; Agram, P. L-Band Temporal Coherence Assessment and Modeling Using Amplitude and Snow Depth over Interior Alaska. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010150
Eshqi Molan Y, Kim J-W, Lu Z, Agram P. L-Band Temporal Coherence Assessment and Modeling Using Amplitude and Snow Depth over Interior Alaska. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(1):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010150
Chicago/Turabian StyleEshqi Molan, Yusuf, Jin-Woo Kim, Zhong Lu, and Piyush Agram. 2018. "L-Band Temporal Coherence Assessment and Modeling Using Amplitude and Snow Depth over Interior Alaska" Remote Sensing 10, no. 1: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010150
APA StyleEshqi Molan, Y., Kim, J.-W., Lu, Z., & Agram, P. (2018). L-Band Temporal Coherence Assessment and Modeling Using Amplitude and Snow Depth over Interior Alaska. Remote Sensing, 10(1), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010150