Structural and Spectral Analysis of Cereal Canopy Reflectance and Reflectance Anisotropy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The influence of plant and canopy architecture on nadir acquired cereal top-of-canopy reflectance between leaf development (BBCH 11-13, BBCH is the phenological scale system for plants developed by [45] and adapted by BBCH [46]) and senescence (BBCH 99) for the improvement of retrieval methods of soil and plant optical properties and
- The anisotropic behaviour of cereal top-of-canopy reflectance and its inter-annual variations as affected by varying biochemical properties and canopy structure of green phenological stages from tillering (BBCH 24-25) until inflorescence emergence (BBCH 51-53).
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Modelling of Top-of-Canopy Reflectance
2.2. Modelling of Top-of-Canopy BRDF
2.3. Development of Virtual Canopies
2.3.1. Geometrically
2.3.2. Spectrally
2.3.3. Computation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Nadir Top-of-Canopy Reflectance
3.1.1. Influence of Plant Structure Due to Phenology
3.1.2. Influence of Canopy Structure
3.2. Analysis of Top-of-Canopy BRDF
3.2.1. Influence of Plant Structure Due to Phenology
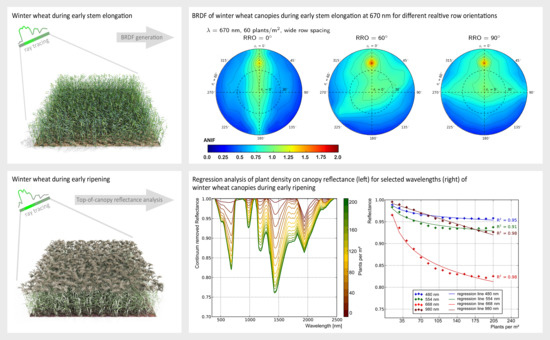
3.2.2. Influence of Row Spacing and Relative Row Orientation
3.2.3. Influence of Plant Density
4. Conclusions
4.1. Nadir Top-of-Canopy Reflectance
4.2. Top-of-Canopy BRDF
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bousbih, S.; Zribi, M.; Lili-Chabaane, Z.; Baghdadi, N.; Hajj, M.E.; Gao, Q.; Mougenot, B. Potential of Sentinel-1 Radar Data for the Assessment of Soil and Cereal Cover Parameter. Sensors 2017, 17, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erten, E.; M.Lopez-Sanchez, J.; Yuzugullu, O.; Hajnsek, I. Retrieval of agricultural crop height from space: A comparison of SAR techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 157, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Ballester-Berman, J.D. Potentials of polarimetric SAR interferometry for agriculture monitoring. Radio Sci. 2009, 44, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumberg, N.; Bollandsås, O.; Gobakken, T.; Næsset, E. Automatic Detection of Small Single Trees in the Forest-Tundra Ecotone Using Airborne Laser Scanning. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10152–10170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Defibaugh y Chàvez, J.; Tullis, J. Deciduous Forest Structure Estimated with LIDAR-Optimized Spectral Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sankey, J.; Munson, S.; Webb, R.; Wallace, C.; Duran, C. Remote Sensing of Sonoran Desert Vegetation Structure and Phenology with Ground-Based LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 342–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandois, J.; Ellis, E. Remote Sensing of Vegetation Structure Using Computer Vision. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 1157–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Næsset, E. Predicting forest stand characteristics with airborne scanning laser using a practical two-stage procedure and field data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefsky, M.; Cohen, W.; Acker, S.; Parker, G.; Spies, T.; Harding, D. Lidar Remote Sensing of the Canopy Structure and Biophysical Properties of Douglas-Fir Western Hemlock Forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 70, 339–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuusk, A. Determination of vegetation canopy parameters from optical measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P. Biophysical and biochemical sources of variability in canopy reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 64, 234–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onojeghuo, A.O.; Blackburn, G.A.; Wang, Q.; Atkinson, P.M.; Kindred, D.; Miao, Y. Rice crop phenology mapping at high spatial and temporal resolution using downscaled MODIS time-series. GISci. Remote Sens. 2018, 55, 659–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulsig, L.; Nichol, C.J.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Landis, D.R.; Middleton, E.M.; Lyapustin, A.I.; Mammarella, I.; Levula, J.; Porcar-Castell, A. Detecting Inter-Annual Variations in the Phenology of Evergreen Conifers Using Long-Term MODIS Vegetation Index Time Series. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuba, N.; Rogan, J.; Lawrence, D.; Williams, C. Cross-Scale Correlation between In Situ Measurements of Canopy Gap Fraction and Landsat-Derived Vegetation Indices with Implications for Monitoring the Seasonal Phenology in Tropical Forests Using MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkauskaite, P.; Tagesson, T.; Fensholt, R. Evaluation of the Plant Phenology Index (PPI), NDVI and EVI for Start-of-Season Trend Analysis of the Northern Hemisphere Boreal Zone. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, M.L.P.; Bustamante, J.; Soriguer, R.; Santamaría, L. Modeling Biomass Production in Seasonal Wetlands Using MODIS NDVI Land Surface Phenology. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, H.; Wu, B. Mapping Winter Wheat Biomass and Yield Using Time Series Data Blended from PROBA-V 100- and 300-m S1 Products. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Du, X.; Wu, B. Generation of high spatial and temporal resolution NDVI and its application in crop biomass estimation. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.B.; Li, Z.L.; Wu, H.; Tang, B.H.; Ma, L.; Zhao, E.; Li, C. Inversion of the PROSAIL model to estimate leaf area index of maize, potato, and sunflower fields from unmanned aerial vehicle hyperspectral data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosjen, P.P.; Brede, B.; Suomalainen, J.M.; Bartholomeus, H.M.; Kooistra, L.; Clevers, J.G. Improved estimation of leaf area index and leaf chlorophyll content of a potato crop using multi-angle spectral data—Potential of unmanned aerial vehicle imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 66, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haboudane, D.; Miller, J.; Pattey, E.; Zarco-Tejada, P.; Strachan, I. Hyperspectral vegetation indices and novel algorithms for predicting green LAI of crop canopies: Modeling and validation in the context of precision agriculture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenkabail, S.; Smith, R.; De Pauw, E. Hyperspectral Vegetation Indices and Their Relationships with Agricultural Crop Characteristics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 71, 158–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre-Carmona, P.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Alonso, L.; Moreno, J.F.; Pla, F.; Yan, Y. On Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of Leaf Biophysical Constituents: Decoupling Vegetation Structure and Leaf Optics Using CHRIS–PROBA Data Over Crops in Barrax. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1579–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorigo, W.A. Improving the Robustness of Cotton Status Characterisation by Radiative Transfer Model Inversion of Multi-Angular CHRIS/PROBA Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Woodcock, C.; Jupp, D. Variance in Bidirectional Reflectance over Discontinous Plant Canopies. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 69, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmeier, S.R.; Middleton, E.M.; Deering, D.W.; Qin, W. The potential of hyperspectral bidirectional reflectance distribution function data for grass canopy characterization. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 9547–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deering, D.W.; Middleton, E.M.; Irons, J.R.; Blad, B.L.; Walter-Shea, E.A.; Hays, C.J.; Walthall, C.; Eck, T.F.; Ahmad, S.P.; Banerjee, B.P. Prairie Grassland Bidirectional Reflectances Measured by Different Instruments at the FIFE Site. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 18887–18903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schill, S.; Jensen, J.; Raber, G.; Porter, D. Temporal Modeling of Bidirectional Reflection Distribution Function (BRDF) in Coastal Vegetation. GISci. Remote Sens. 2004, 41, 116–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Schopfer, J.; Oppelt, N.; Dorigo, W.; Vreeling, W.; Gege, P. GonioExp06—A Field Goniometer Intercomparison Campaign. In Support of Physical Model Inversion and Upscaling Methods for Hyperspectral, Multispectral RS Data. Proceedings of the Envisat Symposium, Montreux, Switzerland, 23–27 April 2007; ESA: Pairs, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Buchhorn, M.; Petereit, R.; Heim, B. A Manual Transportable Instrument Platform for Ground-Based Spectro-Directional Observations (ManTIS) and the Resultant Hyperspectral Field Goniometer System. Sensors 2013, 13, 16105–16128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burkart, A.; Aasen, H.; Alonso, L.; Menz, G.; Bareth, G.; Rascher, U. Angular Dependency of Hyperspectral Measurements over Wheat Characterized by a Novel UAV Based Goniometer. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 725–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ESA. Sentinel-2 Data Sheet, The operational Copernicus Optical High Resolution Land Misssion; ESA: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guanter, L.; Kaufmann, H.; Segl, K.; Foerster, S.; Rogass, C.; Chabrillat, S.; Kuester, T.; Hollstein, A.; Rossner, G.; Chlebek, C.; et al. The EnMAP Spaceborne Imaging Spectroscopy Mission for Earth Observation. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8830–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roosjen, P.; Suomalainen, J.; Bartholomeus, H.; Kooistra, L.; Clevers, J. Mapping reflectance anisotropy of a potato canopy using aerial images acquired with an unmanned aerial vehicle. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, P.; Loke, T.; Baarstad, I.; Fridman, A.; Hernandez, J. Real-time hyperspectral image processing for UAV applications, using HySpex Mjolnir-1024. Proc SPIE 2017, 10198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, C. Winter wheat geometry identification by bidirectional canopy reflected spectrum. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2008, 1, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Landis, B.; Aber, J. Low-cost field goniometer for multiangular reflectance measurements. Emporia State Res. Stud. 2007, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Peltoniemi, J.I.; Kaasalainen, S.; Näränen, J.; Rautiainen, M.; Stenberg, P.; Smolander, H.; Smolander, S.; Voipio, P. BRDF measurement of understory vegetation in pine forests: Dwarf shrubs, lichen, and moss. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, K.; Wang, J. Device for convenient measurement of spatially varying bidirectional reflectance. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2004, 21, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmeier, S. Acquisition of Bidirectional Reflectance Factor Data with Field Goniometers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasen, H.; Honkavaara, E.; Lucieer, A.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J. Quantitative Remote Sensing at Ultra-High Resolution with UAV Spectroscopy: A Review of Sensor Technology, Measurement Procedures, and Data Correction Workflows. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuester, T.; Spengler, D.; Barczi, J.F.; Segl, K.; Hostert, P.; Kaufmann, H. Modeling multitemporal and hyperspectral vegetation canopy bidirectional reflectance using detailed virtual 3D canopy models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 4, 2096–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P. Three-dimensional plant modelling for remote sensing simulation studies using the botanical plant modelling system. Agronomie 1999, 19, 185–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, P. Three-dimensional forest light interaction model using a Monte Carlo method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadoks, J.; Chang, T.T.; Konzak, C. A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res. 1974, 14, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, U. Growth Stages of Mono- and Dicotyledonous Plants: BBCH-Monograph; Blackwell Wissenschafts-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1997; p. 622. [Google Scholar]
- Barczi, J.F.; de Reffye, P.; Caraglio, Y. Essai sur l’identification et la mise en oevre des paramètres nécessaires a la simulation d’une architecture végétale: Le logiciel AmapSim. In Modélisation et Simulation de L’architecture des Végétaux; Bouchon, J., de Reffye, P., Barthélémy, D., Eds.; INRA: Paris, France, 1997; pp. 205–254. [Google Scholar]
- Barczi, J.F.; Rey, H.; Caraglio, Y.; de Reffye, P.; Barthélémy, D.; Dong, Q.; Fourcaud, T. AmapSim: A structural whole-plant simulator based on botanical knowledge and designed to host external functional models. Ann. Bot. 2008, 101, 1125–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicodemus, F.; Richmond, J.; Hsia, J.; Ginsberg, I.; Limperis, T. Geometrical Considerations and Nomenclature for Reflectance; Technical Report; National Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Spengler, D. Charakterisierung von Getreidearten aus Hyperspektralen Fernerkundungsdaten auf der Basis von 4D-Bestandsmodellen. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Berlin, FBerlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Disney, M.; Lewis, P.; Gomez-Dans, J.; Roy, D.; Wooster, M.; Lajas, D. 3D radiative transfer modelling of fire impacts on a two-layer savanna system. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1866–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disney, M.; Lewis, P.; Saich, P. 3D modelling of forest canopy structure for remote sensing simulations in the optical and microwave domains. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disney, M.; Lewis, P.; North, P. Monte Carlo ray tracing in optical canopy reflectance modelling. Remote Sens. Rev. 2000, 18, 163–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saich, P.; Lewis, P.; Disney, M. Biophysical parameter retrieval from forest and crop canopies in the optical and microwave domains using 3D models of canopy structure. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2003), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 6, pp. 3546–3548. [Google Scholar]
- Saich, P.; Lewis, P.; Disney, M.; Thackrah, G. Comparison of Hymap/E-SAR data with models for optial reflectance and microwave scattering from vegetation canopies. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Retrieval of Bio- and Geophysical Parameters from SAR Data for Land Applications; Wilson, A., Ed.; ESA: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Widlowski, J.L.; Taberner, M.; Pinty, B.; Bruniquel-Pinel, V.; Disney, M.; Fernades, R.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.P.; Gobron, N.; Kuusk, A.; Lavergne, T.; et al. The third RAdiation transfer Model Intercompariosn (RAMI) exercise: Documenting progress in canopy reflectance models. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küster, T. Modellierung von Getreidebestandsspektren zur Korrektur BRDF-Bedingter Einflüsse auf Vegetationsindizes im Rahmen der EnMAP-Mission. Ph.D. Thesis, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kuester, T.; Förster, S.; Chabrillat, S.; Spengler, D.; Guanter, L. Assessing The Influence Of Variable Fractional Vegetation Cover On Soil Spectral Features Using Simulated Canopy Reflectance Modeling. In Proceedings of the 10th EARSeL SIG Imaging Spectroscopy Workshop, Zurich, Switzerland, 19–21 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Spengler, D.; Kuester, T.; Frick, A.; Scheffler, D.; Kaufmann, H. Correcting the influence of vegetation on surface soil moisture indices by using hyperspectral artificial 3D-canopy models. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Dresden, Germany, 23–26 September 2013; Volume 8887, p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Spengler, D.; Frick, A.; Davey, C.; Peisker, T.; Kaufmann, H. Estimation of surface soil moisture content using imaging spectroscopy—A simulation case study. In Proceedings of the 7th EARSeL SIG Imaging Spectroscopy Workshop, Edinburgh, Scotland, UK, 11–13 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Peisker, T.; Spengler, D.; Segl, K.; Hostert, P.; Kaufmann, H. Simulation of EnMAP measured cereal canopy spectra—Challenges posed by varying observation geometry and plant phenology. In Proceedings of the Hyperspectral Workshop 2010, ESA-ESRIN, Frascati, Italy, 17–19 March 2010; ESA: Pairs, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Peisker, T.; Spengler, D.; Segl, K.; Kaufmann, H. On the spectral resolution requirements for the derivation of leaf area index from hyperspectral remote sensing data. In Imaging Spectroscopy: Innovative Tool for Scientific and Commercial Environmental Applications, Proceedings of the 6th EARSeL SIG IS Workshop, Ramat Aviv, Tel Aviv, Israel, 16–19 March 2009; Tel Aviv University: Tel Aviv, Israel, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Spengler, D.; Peisker, T.; Bochow, M.; Segl, K.; Kaufmann, H. Determination of cereal type and growth stage using simulated reflectance data. In Imaging Spectroscopy: Innovative Tool for Scientific and Commercial Environmental Applications, Proceedings of the 6th EARSeL SIG IS Workshop, Ramat Aviv, Tel Aviv, Israel, 16–19 March 2009; Tel Aviv University: Tel Aviv, Israel, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- BMELV—Bundesministerium Für Ernährung, Landwirtschaft und Verbraucherschutz. Ökologischer Landbau. Available online: http://www.bmelv.de (accessed on 12 June 2010).
- Sandmeier, S.; Müller, C.; Hosgood, B.; Andreoli, G. Physical Mechanisms in Hyperspectral BRDF Data of Grass and Watercress. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstl, S. The angular reflectance signature of the canopy hot spot in the optical regime. In Proceedings of the 4th International Colloquium Spectral Signatures of Objects in Remote Sensing, Aussois, France, 18–22 January 1988; pp. 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Gerstl, S.; Simmer, C. Radiation physics and modelling for off-nadir satellite sensing of non-lambertian surfaces. Remote Sens. Environ. 1986, 20, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, K. Effects of Reflection Properties of Natural Surfaces in Aerial Reconnaissance. Appl. Opt. 1966, 5, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandmeier, S.; Deering, D. Structure Analysis and Classification of Boreal Forests Using Airborne Hyperspectral BRDF Data from ASAS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 69, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdebout, J.; Jacquemoud, S.; Schmuck, G. Optical Properties of Leaves: Modelling and Experimental Studies. In Imaging Spectrometry—A Tool for Environmental Observations; ECSC, EEC, EAEC: Brussels, Luxembourg, 1994; pp. 169–191. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, L.; Schmidt, K.; Dury, S.; Skidmore, A. Imaging Spectrometry and Vegetation Science. In Imaging Spectrometry. Basic Principles and Prospective Applications; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 111–155. [Google Scholar]
- Knipling, E.B. Physical and physiological basis for the reflectance of visible and near-infrared radiation from vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1970, 1, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, C. Fernerkundung von Pflanzen, Ausbreitung, Gesundheitszustand und Produktivität. Naturwissenschaften 1993, 80, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffer, R. Biological and Physical Considerations in Applying Computer-Aided Analysis Techniques to Remote Sensor Data. In Remote Sensing: The Quantitative Approach; Mcgraw-Hill College: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 297–343. [Google Scholar]
- Belward, A. Spectral Characteristics of Vegetation, Soil And Water in Visible, Near Infrared and Middle-Infrared Wavelengths. In Remote Sensing and Geographical Information Systems of Resource Management in Developing Countries; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 31–53. [Google Scholar]
- GEOGLAM Crop Monitor. Available online: http://www.cropmonitor.org (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- Crop Watch. Available online: http://www.cropwatch.com (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- Loizzo, R.; Guarini, R.; Longo, F.; Scopa, T.; Formaro, R.; Facchinetti, C.; Varacalli, G. PRISMA: The Italian Hyperspectral Mission. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium on Observing, Understanding and Forecasting the Dynamics of our Planet (IGARSS), Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, T.; Iwasaki, A.; Tsuchida, S.; Iwao, K.; Tanii, J.; Kashimura, O.; Nakamura, R.; Yamamoto, H.; Kato, S.; Obata, K.; Mouri, K.; Tachikawa, T. HISUI Status toward FY2019 Launch. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium on Observing, Understanding and Forecasting the Dynamics of our Planet (IGARSS), Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Feingersh, T.; Ben Dor, E. SHALOM—A Commercial Hyperspectral Space Mission. In Optical Payloads for Space Missions; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 247–263. [Google Scholar]
- Carrere, V.; Briottet, X.; Jacquemoud, S.; Marion, R.; Bourguignon, A.; Chami, M.; Dumont, M.; Minghelli-Roman, A.; Weber, C.; Lefevre-Fonollosa, M.; et al. HYPXIM: A second generation high spatial resolution hyperspectral satellite for dual applications. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Gainesville, FL, USA, 26–28 June 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Nieke, J.; Rast, M. Towards the Copernicus Hyperspectral Imaging Mission for the Environment (CHIME). In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium on Observing, Understanding and Forecasting the Dynamics of our Planet (IGARSS), Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018. [Google Scholar]













| Radiant Power Quantities | Leaves | Stems | Ears | Soil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reflectance (R) | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.0 |
| Transmittance (T) | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | - |
| Absorptance (A) | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 1.0 |
| Scenario | Leaves | Stems | Ears | Soil | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | T | A | R | T | A | R | T | A | R | A | |
| 1 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 2 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 3 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 4 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 5 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 6 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 7 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 8 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 9 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 10 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Crop Types | Modelling Stages | Plant Appearance | RRO | RS | PD | Observations | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nadir Art. Opt. Prop. | 3 | 13 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 117 |
| Nadir Nat. Opt. Prop. | 3 | 13 | 1 | 36 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 12,636 |
| BRDF (mod. stage 4) | 3 | 1 | 4 (1) | 4 | 3 | 7 (5) | 113 | 35,652 |
| BRDF (mod. stage 3, 5 & 6) | 3 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 113 | 36,612 |
| Structure Features | Influence of Row Spacing and Row Orientation on BRDF | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RRO | RS | Plants/m | WB | WR | WW | WB | WR | WW |
| BRDF at = 670 nm | BRDF at = 800 nm | |||||||
| 0 | wide | 35–60 | + | + | + | * | − | * |
| 0 | medium | 60–100 | * | * | * | − | − | − |
| 0 | narrow | 90–150 | * | − | * | − | − | − |
| 30 | wide | 35–60 | + | * | + | + | + | + |
| 30 | medium | 60–100 | * | − | * | * | − | * |
| 30 | narrow | 90–150 | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 60 | wide | 35–60 | + | * | + | + | * | + |
| 60 | medium | 60–100 | * | − | * | * | − | * |
| 60 | narrow | 90–150 | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 90 | wide | 35–60 | * | * | * | * | * | * |
| 90 | medium | 60–100 | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 90 | narrow | 90–150 | − | − | − | − | − | − |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuester, T.; Spengler, D. Structural and Spectral Analysis of Cereal Canopy Reflectance and Reflectance Anisotropy. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111767
Kuester T, Spengler D. Structural and Spectral Analysis of Cereal Canopy Reflectance and Reflectance Anisotropy. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(11):1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111767
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuester, Theres, and Daniel Spengler. 2018. "Structural and Spectral Analysis of Cereal Canopy Reflectance and Reflectance Anisotropy" Remote Sensing 10, no. 11: 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111767
APA StyleKuester, T., & Spengler, D. (2018). Structural and Spectral Analysis of Cereal Canopy Reflectance and Reflectance Anisotropy. Remote Sensing, 10(11), 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111767