Reconstructing Seabed Topography from Side-Scan Sonar Images with Self-Constraint
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Reconstruction Model of 3D Seabed Topography
3. Reconstructing Seabed Topography from SSS Image
3.1. Solution of Reconstruction Model
3.2. Bottom Tracking and Initial Seabed Topography
3.3. Assessment
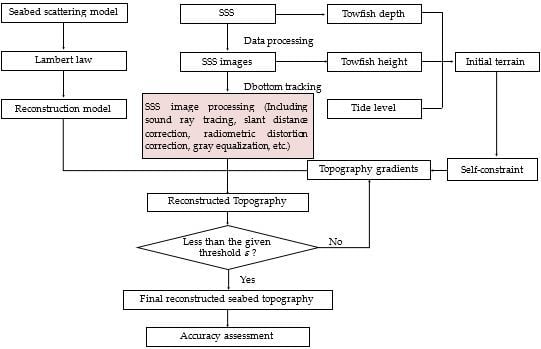
3.4. Process of Reconstructing 3D Seabed Topography
- (1)
- Detect the seabottom points from SSS waterfall images to get the towfish heights, and then obtain the initial seabed topography by that depicted in Figure 3.
- (2)
- (3)
- Compute the topography gradients by Equation (6), the angle ϕ by Equation (7), and the seabed topography by Equation (13) using the self-constraint.
- (4)
- Execute iteration until the difference of two adjacent iterations is less than the given threshold ε. In the iteration, the next calculation uses the last result as the initial condition, and step (2) and step (3) are repeated until the difference meets Equation (14).
- (5)
- Assess the reconstruction by referring to the actual bathymetry data.
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Area and Data Preparation
4.2. Reconstructing Seabed Topography
4.3. Seabed Topography Reconstruction of Surveying Area
5. Discussion
5.1. Noise in SSS Image
5.2. Eeffects of Refraction of Waves, Towfish Depth and Cross-Track Distance
5.2.1. Refraction of Waves in the Water Column
5.2.2. Towfish Depth and Across-Track Distance
5.3. Seabed Sediments
5.4. Bottom Tracking and Initial Seabed Topography
5.5. Determination of Iteration Termination Threshold
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- Sharma, R.; Khadge, N.H.; Jai Sankar, S. Assessing the distribution and abundance of seabed minerals from seafloor photographic data in the Central Indian Ocean Basin. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 1691–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakiris, E.; Papatheodorou, G.; Geraga, M.; Ferentinos, G. An automatic target detection algorithm for swath sonar backscatter imagery, using image texture and independent component analysis. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, R.; Ierodiaconou, D.; Monk, J. Evaluation of four supervised learning methods for benthic habitat mapping using backscatter from multi-beam sonar. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.; Brewer, S.K.; Long, J.M.; Campbell, T. Evaluating the use of side-scan sonar for detecting freshwater mussel beds in turbid river environments. Hydrobiologia 2015, 743, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.D.; Istenič, K.; Gracias, N.; Palomeras, N.; Campos, R.; Vidal, E.; García, R.; Carreras, M. Autonomous underwater navigation and optical mapping in unknown natural environments. Sensors 2016, 16, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, J.V.M. Analysis of Multibeam Sonar Data for the Characterization of Seafloor Habitats. Master’s Thesis, The University of New Brunswick, Fredericton & Saint John, NB, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, A. A new method for weakening the combined effect of residual errors on multibeam bathymetric data. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2014, 35, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canepa, G.; Bergem, O.; Pace, N.G. A new algorithm for automatic processing of bathymetric data. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2003, 28, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, P. The Handbook of Sidescan Sonar; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 35–77. ISBN 978-3-540-42641-7. [Google Scholar]
- Trucco, E.; Petillot, Y.R.; Ruiz, I.T.; Plakas, K.; Lane, D.M. Feature tracking in video and sonar subsea sequences with applications. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2000, 79, 92–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, B.K.P. Shape from Shading: A Method for Obtaining the Shape of a Smooth Opaque Object from One View. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Tsai, P.S.; Cryer, J.E.; Shah, M. Shape from shading: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1999, 21, 690–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragheb, H.; Hancock, E.R. Surface radiance correction for shape from shading. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 38, 1574–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.M.; Chantler, M.J.; Wittig, T. Sidescan sonar: A directional filter of seabed texture? IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 1999, 146, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.E. Incorporating different reflection models into surface reconstruction. In Proceedings of the Unmanned Untethered Submersible Technology Conference, Durham, UK, 27–29 September 1993; pp. 446–459. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.E.; Hebert, M. Seafloor map generation for autonomous underwater vehicle navigation. Auton. Robot. 1996, 3, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, D.; Hebert, M. Building qualitative elevation maps from side scan sonar data for autonomous underwater navigation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Sacramento, CA, USA, 9–11 April 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bikonis, K.; Moszynski, M.; Lubniewski, Z. Application of shape from shading technique for side scan sonar images. Pol. Marit. Res. 2013, 20, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shang, X.; Zhang, H. Recovering seabed topography from sonar image with constraint of sounding data. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2017, 46, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhao, J.; Shang, X.; Zhang, H. Recovery of seabed 3D micro-topography from side-scan sonar image constrained by single-beam soundings. J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 2017, 38, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dura, E.; Bell, J.; Lane, D. Reconstruction of textured seafloors from side-scan sonar images. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2004, 151, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiras, E.; Petillot, Y.; Lane, D.M. Multiresolution 3-d reconstruction from side-scan sonar images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckart, C. Principles of Underwater Sound, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 252–253. ISBN 0070660875. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.R.; Winebrenner, D.P.; Ishimaru, A. Application of the composite roughness model to high-frequency bottom backscattering. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1986, 79, 1410–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.M.; Linnett, L.M. Simulation and analysis of synthetic sidescan sonar images. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 1997, 144, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensane, M. A statistical study of acoustic signals backscattered from the sea bottom. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2002, 14, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Hsu, S.K.; Tsai, C.H. Sidescan sonar image processing: Correcting brightness variation and patching gaps. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2010, 18, 785–789. [Google Scholar]
- Ronald, W.; Marwood, N. Electro-Optics Handbook; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0-07-068716-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cervenka, P.; Moustier, C.D. Sidescan sonar image processing techniques. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1993, 18, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, P.S., Jr.; Isbrecht, J.A.; Galanis, P.; Gabel, G.L.; Sides, S.C.; Soltesz, D.L.; Ross, S.L.; Velasco, M.G. Processing, mosaicking and management of the monterey bay digital sidescan-sonar images. Mar. Geol. 2002, 181, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, H.; Meng, J. A new radiometric correction method for side-scan sonar images in consideration of seabed sediment variation. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping-Sing, T.; Shah, M. Shape from shading using linear approximation. Image Vis. Comput. 1994, 12, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, H.M.; Kurtis, D.F. Numerical Methods Using MATLAB, 4th ed.; Publishing House of Electronics Industry: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 136–138. ISBN 9787121314995. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, S.; Tena, R.I.; Capus, C.; Petillot, Y. The fusion of large scale classified side-scan sonar image mosaics. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 2049–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, A. A comprehensive bottom-tracking method for sidescan sonar image influenced by complicated measuring environment. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 42, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; John, E.H. Determination of precise instantaneous tidal level at vessel. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2006, 31, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, X. On-the-fly measurements of large-drop water level and high flow velocity in the closure gap. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2015, 45, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.; Mostafa, R. Seabed sub-bottom sediment classification using parametric sub-bottom profiler. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2016, 5, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, D.; Vassilvitskii, S. K-means++: The advantages of careful seeding. In Proceedings of the Advances in the Eighteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, New Orleans, LA, USA, 7–9 January 2007; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 1027–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Pinson, L.J.; Henstock, T.J.; Dix, J.K.; Bull, J.M. Estimating quality factor and mean grain size of sediments from high-resolution marine seismic data. Geophysics 2008, 73, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Max. (m) | Min. (m) | Mean (m) | STD (±m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.28 | −0.36 | 0.00 | 0.13 |
| Max. | Min. | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.30 | −0.43 | 0.00 | 0.12 |
| Line | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias | |||||||||
| Max./m | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.12 | 0.39 | 0.26 | 0.38 | 0.22 | 0.34 | |
| Min./m | −0.10 | −0.25 | −0.09 | −0.20 | −0.30 | −0.29 | −0.35 | −0.10 | |
| Mean/m | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.10 | |
| Std/m | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.08 | |
| Biases (m) | Max. | Min. | Mean | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | |||||
| Entire measurement area | 0. 47 | −0.54 | 0.00 | 0.12 | |
| Overlapping area of Strip I & II | 0.44 | −0.54 | −0.08 | 0.14 | |
| Overlapping area of Strip II & III | 0.49 | −0.38 | 0.03 | 0.10 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Shang, X.; Zhang, H. Reconstructing Seabed Topography from Side-Scan Sonar Images with Self-Constraint. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020201
Zhao J, Shang X, Zhang H. Reconstructing Seabed Topography from Side-Scan Sonar Images with Self-Constraint. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(2):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020201
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jianhu, Xiaodong Shang, and Hongmei Zhang. 2018. "Reconstructing Seabed Topography from Side-Scan Sonar Images with Self-Constraint" Remote Sensing 10, no. 2: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020201
APA StyleZhao, J., Shang, X., & Zhang, H. (2018). Reconstructing Seabed Topography from Side-Scan Sonar Images with Self-Constraint. Remote Sensing, 10(2), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020201