Impacts of Climate Change on Tibetan Lakes: Patterns and Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Environmental Conditions on the Tibetan Plateau
2.2. Lake Distribution and Extent
2.3. Climate Datasets
2.4. Glacier Cover
2.5. Permafrost Distribution
2.6. Watershed Delineation
3. Results
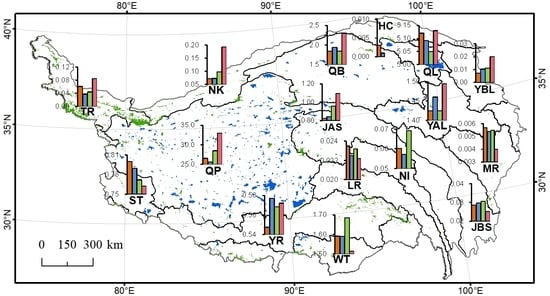
3.1. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of Changes in Tibetan Lakes
3.2. Spatially Variable Changes in Climate Factors, Glacier Extent, and Permafrost on the TP
3.3. Patterns and Processes in Impacts of Climate and Associated Changes on Tibetan Lakes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adrian, R.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Zagarese, H.; Baines, S.B.; Hessen, D.O.; Keller, W.; Livingstone, D.M.; Sommaruga, R.; Straile, D.; Donk, E.V.; et al. Lakes as sentinels of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williamson, C.E.; Saros, J.E.; Schindler, D.W. Sentinels of change. Science 2009, 323, 887–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J. China: The third pole. Nature 2008, 454, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Cao, J.; Hansen, J.; Yao, T.; Joswia, D.R.; Wang, N.; Wu, G.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Yang, W.; et al. Black soot and the survival of Tibetan glaciers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 106, 22114–22118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Yin, Y.; Zheng, D.; Yang, Q. Climatic trends over the Tibetan Plateau during 1971–2000. J. Geogr. Sci. 2007, 17, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Axel, T. Climatic change on the Tibetan Plateau: Potential evapotranspiration trends from 1961-2000. Clim. Chang. 2006, 76, 291–319. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B.; et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wu, T. Responses of permafrost to climate change and their environmental significance, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, F02S03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; Friedlingstein, P.; et al. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Pu, J.; Shen, Y.; Lu, A. Recent glacial retreat in High Asia and its impact on water resource in Northwest China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2004, 147, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Yu, S.; Yang, D.; Zhang, L. Climate warming and growth of high-elevation inland lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 67, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; Kang, S.; Yi, D.; Ackley, S.F. Monitoring lake level changes on the Tibetan Plateau using ICESat altimetry data (2003–2009). Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Song, C. A regional-scale assessment of Himalayan glacial lake changes using satellite observations from 1990 to 2015. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 189, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Nelson, F.E.; Shiklomanov, N.I.; Guo, D.; Wan, G. Permafrost degradation and its environmental effects on the Tibetan Plateau: A review of recent research. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 103, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Shen, G.; Li, Y. Lake variations in response to climate change in the Tibetan Plateau in the past 40 years. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 534–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liao, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, Z.; Shen, G. Patterns and potential drivers of dramatic changes in Tibetan lakes, 1972-2010. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 0111890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, J.J.; Prowse, T.D.; Peters, D.L. Hydroclimatic controls on water balance and water level variability in Great Slave Lake. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 4155–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Xu, Y.; You, Q.; Flügel, W.; Pepin, N.; Yao, T.D. Review of climate and cryosphere change in the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 015101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scherler, D.; Bookhagen, B.; Strecker, R. Spatially variable response of Himalayan glaciers to climate change affected by debris cover. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Ju, J.; Ma, Q.; Turner, F.; Guo, Q. Spatiotemporal variations in volume of closed lakes on the Tibetan Plateau and their climatic responses from 1976 to 2013. Clim. Chang. 2017, 140, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, B.; Sheng, Y.; Bird, B.W.; Zhang, G.; Tian, L. Response of inland lake dynamics over the Tibetan Plateau to climate change. Clim. Chang. 2014, 125, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Piao, S.; Bolch, T.; Xie, H.; Chen, D.; Gao, Y.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Shum, C.K.; Yang, K.; Yi, S.; et al. Extensive and drastically different alpine lake changes on Asia’s high plateaus during the past four decades. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kang, S.; Gong, T.; Lu, A. Growth of a high-elevation large inland lake, associated with climate change and permafrost degradation in Tibet. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yao, T.; Yang, K.; Sheng, Y.; Kleinherenbrink, M.; Yi, S.; Bird, B.W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, G. Lake seasonality across the Tibetan Plateau and their varying relationship with regional mass changes and local hydrology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.G.; Mosbrugger, V.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Y.; Luo, T.; Xu, B.; Yang, X.; Joswiak, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Third pole Environment (TPE). Environ. Dev. 2012, 3, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Graf, H. Recent land cover changes on the Tibetan Plateau: A review. Clim. Chang. 2009, 94, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Rao, S.; Zhao, S. Human-induced long-term changes in the lakes of the Jianghan Plain, Central Yangtze. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 3, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.E.; Anderson, R.S.; Chignell, S.M.; Vorster, A.G.; Lawrence, R.; Evangelista, P.H. A survival guide to Landsat preprocessing. Ecology 2017, 98, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, P.; Pons, X.; Sauri, D. Post-classification change detection with data from different sensors: Some accuracy considerations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 3311–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, T.A.; Campagna, D.J. Remote Sensing with IDRISI (R) Taiga: A Beginner’s Guide; Geocarto International Centre: Hong Kong, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dronova, I.; Gong, P.; Wang, L. Object-based analysis and change detection of major wetland cover types and their classification uncertainty during the low water period at Poyang Lake, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3220–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.S.; Kearney, M.S. Reducing signature variability in unmixing coastal marsh thematic mapper scenes using spectral indices. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2317–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davranche, A.; Lefebvre, G.; Poulin, B. Wetland monitoring using classification trees and SPOT-5 seasonal time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Lu, X. Drastic change in China’s lakes and reservoirs over the past decades. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Liu, M.; Zhuang, D.; Melillo, J.M.; Zhang, Z. China’s changing landscape during the 1990s: Large-scale land transformations estimated with satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L02405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yang, G.; Duan, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, X.; Li, A.; Kong, F.; Xue, B.; Wu, J.; et al. China’s lakes at present: Number, area, and spatial distribution. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Long, D.; Hong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xiao, P.; Duan, H.; Han, Z.; Gu, X. A lake data set for the Tibetan Plateau from the 1960s, 2005, and 2014. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, M.F. Anusplin Version 4.2 User Guide; Centre for Resource and Environmental Studies (CRES), The Australian National University: Canberra, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zu, J.; Zhang, J. The influences of climate change and human activities on vegetation dynamics in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Zong, J.; Tian, L.; Cogley, G.; Song, C.; Guo, W. Glacier changes on the Tibetan plateau derived from Landsat imagery: Mid-1970s-2000-13. J. Glaciol. 2017, 63, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, W.A.; Leung, A. Nature and fate of Hudson Bay permafrost. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2002, 2, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnocai, C.; Canadell, J.G.; Schuur, E.A.G.; Kuhry, P.; Mazhitova, G.; Zimov, S. Soil organic carbon pools in the northern circumpolar permafrost region. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2009, 23, GB2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, M.T.; Racine, C.H.; Walters, J.C.; Osterkap, T.E. Permafrost degradation and ecological changes associated with a warming climate in central Alaska. Clim. Chang. 2011, 48, 551–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapnick, S.B.; Delworth, T.L.; Ashfaq, M.; Malyshev, S.; Milly, P.C.D. Snowfall less sensitive to warming in Karakoram than in Himalayas due to a unique seasonal cycle. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liu, S.; Guo, W.; Yao, X.; Xu, J.; Bao, W.; Jiang, Z. Surface-area changes of glaciers in the Tibetan plateau interior area since the 1970s using recent Landsat images and historical maps. Ann. Glaciol. 2014, 55, 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.C.; Sheng, Y.; MacDonald, G.M.; Hinzman, L.D. Disappearing arctic lakes. Science 2005, 308, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Ju, J.; Daut, G. The warming of large lakes on the Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from a lake model simulation of Nam Co, China, during 1979–2012. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 13095–13107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donchyts, G.; Baart, F.; Winsemius, H.; Gerelick, N.; Kwadijk, J.; Giesen, N. Earth’s surface water change over the past 30 years. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Fang, H. Changes in the area of inland lakes in arid regions of central Asia during the past 30 years. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 178, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, S.; Fang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, S.; Shen, H.; Hu, H.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Q. Rapid loss of lakes on the Mongolian Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 112, 2281–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yin, Y.; Piao, S.; Zhao, F.; Engels, M.; Ciais, P. Disappearing lakes in semiarid northern China: Drivers and environmental impact. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12107–12114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Yao, X.; Luo, J.; Huang, Y.; Feng, Y. Changes of the three holy lakes in recent years and quantitative analysis of the influencing factors. Quat. Int. 2014, 349, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. Impact of land use and land cover change on environmental degradation in Lake Qinghai watershed, Northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2009, 20, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Flower, R.J.; Thompson, J.R. China’s new leaders offer green hope. Nature 2013, 493, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H. China must continue the momentum of green law. Nature 2014, 509, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; He, R.; Cheng, G.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Lv, L.; Chang, X. Changes in frozen ground in the source area of the Yellow River on the Qinhai-Tibet Plateau, China, and their eco-environmental impacts. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 045206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, J.; Shao, Q.; Liu, R. Changing inland lakes responding to climate warming in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 479–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, J.K.; Griffith, B.; Verbyla, D. Landscape influences on climate-related lake shrinkage at high latitudes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2276–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Flower, R.J.; Thompson, J.R. Sustaining China’s water resources. Science 2013, 339, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Watersheds | Number | Change | Area (km2) | Change | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1977 | 1990 | 2000 | 2014 | 1977–2014 | 1977 | 1990 | 2000 | 2014 | 1977–2014 | |
| QP (Inland Rivers on Qiangtang Plateau) | 695 | 677 | 846 | 824 | 18.6% | 26,539.7 | 25,595.1 | 28,472.8 | 32,994.9 | 24.3% |
| QL (Qinghai Lake) | 12 | 13 | 17 | 13 | 8.3% | 5120.5 | 5091.4 | 5049.7 | 5129.6 | 0.2% |
| QB (Qaidam Basin) | 36 | 58 | 49 | 59 | 63.9% | 1842.0 | 1940.8 | 1841.0 | 2304.0 | 25.1% |
| ST (South Tibet Rivers) | 46 | 52 | 47 | 47 | 2.2% | 1591.6 | 1590.2 | 1685.4 | 1514.1 | −4.9% |
| YAL (Yellow River above Longyangxia) | 45 | 46 | 40 | 47 | 4.4% | 1425.2 | 1460.4 | 1425.1 | 1494.3 | 4.8% |
| JAS (Jinsha River above stone drum) | 75 | 100 | 100 | 120 | 60.0% | 824.5 | 844.4 | 959.4 | 1095.0 | 32.8% |
| WT (West Tibet Rivers) | 15 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 6.7% | 799.9 | 789.7 | 771.9 | 762.6 | −4.7% |
| YR (Yarlung Zangbo River) | 70 | 84 | 87 | 78 | 11.4% | 547.5 | 577.1 | 568.4 | 572.0 | 4.5% |
| NK (Rivers on the North Foot of Mt. Kunlun) | 16 | 16 | 21 | 42 | 162.5% | 71.6 | 72.7 | 97.5 | 192.1 | 168.3% |
| TR (Tarim River) | 10 | 9 | 10 | 8 | −20.0% | 60.8 | 37.7 | 44 | 84.1 | 38.3% |
| NI (Nu and Irrawaddy Rivers) | 15 | 15 | 17 | 16 | 6.7% | 60.2 | 57.2 | 69.2 | 50.3 | −16.4% |
| JBS (Jinsha River below stone drum) | 12 | 14 | 15 | 13 | 8.3% | 28.6 | 29.7 | 30.6 | 25.2 | −11.9% |
| LR (Lantsang River) | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0.0% | 23.5 | 22.5 | 23.2 | 22.2 | −5.5% |
| YBL (Yellow River from Longyangxia to Lanzhou) | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 50% | 7.3 | 10.4 | 11.3 | 20.1 | 175.3% |
| MR (Mintuo River) | 4 | 3 | 4 | 3 | −25% | 5.7 | 5.4 | 5.5 | 4 | −29.8% |
| HC (Inland Rivers on Hexi Corridor) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | −100% | 3.1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | −100.0% |
| JR (Jialing River) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Total | 1056 | 1109 | 1275 | 1291 | 22.3% | 38,951.7 | 38,125.7 | 41,055.0 | 46,264.5 | 18.8% |
| Year or Period | Area Category (km2) | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–10 | 10–50 | 50–100 | 100–500 | 500–1000 | >1000 | |||
| Number of lakes | 1977 | 700 | 219 | 64 | 61 | 9 | 3 | 1056 |
| 1990 | 766 | 205 | 66 | 61 | 8 | 3 | 1109 | |
| 2000 | 889 | 234 | 71 | 70 | 8 | 3 | 1275 | |
| 2014 | 884 | 241 | 74 | 78 | 9 | 5 | 1291 | |
| Change in number (%) | 1977–1990 | 9.4 | −6.4 | 3.1 | 0 | −11.1 | 0.0 | 5.0 |
| 1990–2000 | 16.1 | 14.1 | 7.6 | 14.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 15.0 | |
| 2000–2014 | −0.6 | 3.0 | 4.2 | 11.4 | 12.5 | 66.7 | 1.3 | |
| 1977–2014 | 26.3 | 10.0 | 15.6 | 27.9 | 0 | 66.7 | 22.3 | |
| Lake area (km2) | 1977 | 2136.7 | 5292.9 | 4572.3 | 13,118.3 | 5822.6 | 8008.6 | 38,951.7 |
| 1990 | 2305.0 | 4818.6 | 4543.7 | 13,313.0 | 5200.6 | 7944.7 | 38,125.7 | |
| 2000 | 2617.6 | 5440.8 | 4877.8 | 14,342.4 | 5664.8 | 8111.6 | 41,055.0 | |
| 2014 | 2648.7 | 5459.6 | 5159.3 | 16,365.3 | 5877.9 | 10,753.8 | 46,264.5 | |
| Change in area (%) | 1977–1990 | 7.9 | −9.0 | −0.6 | 1.5 | −10.7 | −0.8 | −2.1 |
| 1990–2000 | 13.6 | 12.9 | 7.4 | 7.7 | 8.9 | 2.1 | 7.7 | |
| 2000–2014 | 1.2 | 0.3 | 5.8 | 14.1 | 3.8 | 32.6 | 12.7 | |
| 1977–2014 | 24.0 | 3.1 | 12.8 | 24.8 | 0.9 | 34.3 | 18.8 | |
| Lake Name from East to West | Area (km2) | Area Changes (km2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1977 | 1990 | 2000 | 2014 | 1977–1990 | 1990–2000 | 2000–2014 | 1977–2014 | |
| Nam Co | 1932 | 1947 | 1988 | 2024 | 15 | 41 | 36 | 92 |
| Siling Co | 1665 | 1681 | 1883 | 2369 | 16 | 202 | 486 | 704 |
| Gyaring Co | 475 | 468 | 480 | 478 | −7 | 12 | −2 | 3 |
| Ngangze Co | 421 | 393 | 421 | 462 | −28 | 28 | 41 | 41 |
| Tangra Yumco | 833 | 829 | 833 | 845 | −4 | 4 | 12 | 12 |
| Zhari Namco | 994 | 980 | 967 | 1003 | −14 | −13 | 36 | 9 |
| Taro Co | 483 | 486 | 481 | 486 | 3 | −5 | 5 | 3 |
| Ngangla Ringco | 511 | 520 | 495 | 496 | 9 | −25 | 1 | −15 |
| Mapam Yumco | 417 | 415 | 411 | 410 | −2 | −4 | −1 | −7 |
| La’nga Co | 272 | 270 | 260 | 255 | −2 | −10 | −5 | −17 |
| Modes | Definition | Number of Watershed Exhibiting Each Mode | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1977–1990 | 1990–2000 | 2000–2014 | 1977–2014 | ||
| 1 | −−−+ | 5 | 9 | 7 | 9 |
| 2 | +−−+ | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | +−−− | 4 | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| 4 | −−−− | 5 | 5 | 3 | 5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Thompson, J.R.; Li, L.; Song, K.; Chen, B.; Gao, H.; Wu, J. Impacts of Climate Change on Tibetan Lakes: Patterns and Processes. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030358
Mao D, Wang Z, Yang H, Li H, Thompson JR, Li L, Song K, Chen B, Gao H, Wu J. Impacts of Climate Change on Tibetan Lakes: Patterns and Processes. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(3):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030358
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Dehua, Zongming Wang, Hong Yang, Huiying Li, Julian R. Thompson, Lin Li, Kaishan Song, Bin Chen, Hongkai Gao, and Jianguo Wu. 2018. "Impacts of Climate Change on Tibetan Lakes: Patterns and Processes" Remote Sensing 10, no. 3: 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030358
APA StyleMao, D., Wang, Z., Yang, H., Li, H., Thompson, J. R., Li, L., Song, K., Chen, B., Gao, H., & Wu, J. (2018). Impacts of Climate Change on Tibetan Lakes: Patterns and Processes. Remote Sensing, 10(3), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030358