Accuracy of CHIRPS Satellite-Rainfall Products over Mainland China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology and Datasets
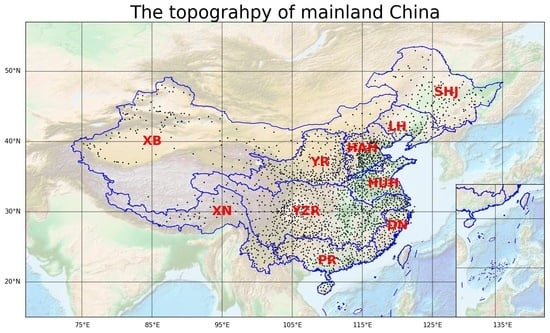
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Observation and Satellite Retrieval Precipitation Production
2.3. Methodology for Evaluation
2.3.1. Statistical Metrics
2.3.2. Evaluation Indices
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Gridded Observation (CN05.1) with In Situ Point Observation
3.2. Evaluation of CHIRPS with the Gridded Observation (CN05.1)
3.2.1. Evaluation on Monthly Scale
3.2.2. Evaluation of CHIRPS in Sub-Regions
3.3. Evaluation of CHIRPS with In Situ Point Observation
3.3.1. Evaluation on Monthly Scale
3.3.2. Evaluation of Technical Skill Indices
3.4. Interannual Variation of Statistic Metrics
3.5. Evaluation of Precipitation Intensity
3.6. Evaluations with Typical Cases
3.6.1. Snowfall
3.6.2. Typhoon Events
4. Discussion and Future Work
5. Conclusions
- Limited to the resolution, the gridded observations do not completely agree with the data from high-density rain gauge networks across mainland, China, especially in complex terrain areas (e.g., XN). Overall, the gridded observation, CN05.1, has an r value above 0.90 over the course of a seasonal cycle. However, the evaluation results are quite different when comparing point evaluation and grid evaluation.
- The CHIRPS precipitation is mainly based on the statistical model based on IR data and TRMM 3B42’s precipitation in pentad time. In mainland China, the CHIRPS QPEs have better performance in DN and PR, in southern China, and poor performance in XB, YR, SHJ, LH, and HAH. The ME and RSME exhibits significant variation with seasonal change, which are caused by the limitations of TRMM, which is suitable only for tropical regions, not middle-latitude regions. Thus, CHIRPS exhibits good performance in southern China.
- CHIRPS also exhibits better performance for areas that experience large amounts of precipitation (e.g., southern China) as compared to areas characterized by arid and semi-arid land (e.g., northwest China). In addition, the change in good performance zones change is strongly related to monsoon movement.
- Generally, the accuracy of CHIRPS is better in warm seasons than in Winter. It has limited ability to detect snowfall of any intensity.
- CHIRPS is moderately sensitive to the precipitation from typhoon weather systems.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, D.-H.; Han, D.-M.; Wang, G.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Fang, H.-Y. The evolution analysis of flood and drought in Huai River Basin of China based on monthly precipitation characteristics. Nat. Hazards 2014, 73, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, S.W.; de Paiva, R.C.D.; Espinoza, J.C.; Collischonn, W. Multi-decadal Hydrological Retrospective: Case study of Amazon floods and droughts. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gu, X.; Singh, V.P.; Kong, D.; Chen, X. Spatiotemporal behavior of floods and droughts and their impacts on agriculture in China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2015, 131, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, I.; Hinnerichsen, M. The Impact of Climate Change on Precipitation-related Insurance Risk: A Study of the Effect of Future Scenarios on Residential Buildings in Norway. Geneva Pap. Risk Insur. Issues Pract. 2012, 37, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yang, Q.; Mao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X. Precipitation trend-Elevation relationship in arid regions of the China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 143, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, S. Temporal and spatial variations of precipitation in Northwest China during 1960–2013. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G.; Nelkin, E.J.; Bowman, K.P.; Hong, Y.; Stocker, E.F.; Wolff, D.B. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P.P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.-l.; Gao, X.; Gupta, H.V.; Imam, B.; Braithwaite, D. Evaluation of PERSIANN System Satellite-Based Estimates of Tropical Rainfall. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Hashizume, H.; Aonashi, K.; Takahashi, N.; Seto, S.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Ushio, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Iwanami, K. Global Precipitation Map Using Satellite-Borne Microwave Radiometers by the GSMaP Project: Production and Validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J. A high spatiotemporal gauge-satellite merged precipitation analysis over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Xie, P.; Xu, M.; Jiang, L.; Shi, C.; You, R. A Validation of Passive Microwave Rain-Rate Retrievals from the Chinese FengYun-3B Satellite. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 1886–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.; Hu, J.; Yang, B.; Stepanian, P.M. Comprehensive Evaluation of High-Resolution Satellite-Based Precipitation Products over China. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.; Behrangi, A.; Hong, Y.; Ndayisaba, F.; Hu, J.; Stepanian, P.M. Early assessment of Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement over China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 176, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, Y. Evaluating the performance of remote sensing precipitation products CMORPH, PERSIANN, and TMPA, in the arid region of northwest China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 118, 429–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Hao, Z. Evaluation of satellite precipitation retrievals and their potential utilities in hydrologic modeling over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhai, P. Validation of daily precipitation from two high-resolution satellite precipitation datasets over the Tibetan Plateau and the regions to its east. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2012, 26, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.-Y. Assessing the performance of satellite-based precipitation products and its dependence on topography over Poyang Lake basin. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 713–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Hong, Y. Multi-scale evaluation of high-resolution multi-sensor blended global precipitation products over the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2013, 500, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.H.; Zhou, M.; Ren, L.L.; Cheng, X.R.; Zhang, P.J. Evaluation of latest TMPA and CMORPH satellite precipitation products over Yellow River Basin. Water Sci. Eng. 2016, 9, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Rutten, M.M.; Droogers, P. Spatial downscaling of TRMM precipitation using vegetative response on the Iberian Peninsula. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Zhu, W.; Lu, A.; Yan, T. A statistical spatial downscaling algorithm of TRMM precipitation based on NDVI and DEM in the Qaidam Basin of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3069–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.F.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.P.; Rowland, J.; Romero, B.E.; Husak, G.; Michaelsen, J.C.; Verdin, A. A Quasi-Global Precipitation Time Series for Drought Monitoring; USGS Professional Paper; Data Series 832; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2014.
- Paredes-Trejo, F.J.; Barbosa, H.A.; Kumar, T.V.L. Validating CHIRPS-based satellite precipitation estimates in Northeast Brazil. J. Arid Environ. 2017, 139, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, D.; Retalis, A.; Michaelides, S. Validation of a high-resolution precipitation database (CHIRPS) over Cyprus for a 30-year period. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, J.; Pricope, N.G. High-resolution spatial assessment of population vulnerability to climate change in Nepal. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 82, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Y.; Duan, Z.; Disse, M.; Chiogna, G. Evaluation of precipitation input for SWAT modeling in Alpine catchment: A case study in the Adige river basin (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tote, C.; Patricio, D.; Boogaard, H.; van der Wijngaart, R.; Tarnavsky, E.; Funk, C. Evaluation of Satellite Rainfall Estimates for Drought and Flood Monitoring in Mozambique. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1758–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Bao, A.; Liu, T.; Ndayisaba, F.; He, D.; Kurban, A.; de Maeyer, P. Meteorological Drought Analysis in the Lower Mekong Basin Using Satellite-Based Long-Term CHIRPS Product. Sustainability 2017, 9, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Yuan, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X. Evaluation of the latest satellite-gauge precipitation products and their hydrologic applications over the Huaihe River basin. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.; Hu, J.; Gebregiorgis, A.S.; Xue, X.; Zhang, X. Inter-Comparison of High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Products over Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7181–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirpa, F.A.; Gebremichael, M.; Hopson, T. Evaluation of High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Products over Very Complex Terrain in Ethiopia. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Ibrahim, A.L.; Duan, Z.; Cracknell, A.P.; Chaplot, V. Evaluation of Six High-Resolution Satellite and Ground-Based Precipitation Products over Malaysia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1504–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, D.; Lagouvardos, K.; Kotroni, V.; Huffmann, G.J. Statistical evaluation of MPA-RT high-resolution precipitation estimates from satellite platforms over the central and eastern Mediterranean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Cao, Q.; Hong, Y.; Wu, B.; Huang, M.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; et al. Evaluation of Version-7 TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis Product during the Beijing Extreme Heavy Rainfall Event of 21 July 2012. Water 2014, 6, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Arancibia, J.L.; van Dijk, A.I.; Renzullo, L.J.; Mulligan, M. Evaluation of Precipitation Estimation Accuracy in Reanalyses, Satellite Products, and an Ensemble Method for Regions in Australia and South and East Asia. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.L.; Duan, Z. Assessment of GPM and TRMM Precipitation Products over Singapore. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Hong, Y.; Limaye, A.S.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Khan, S.I.; Dorji, C.; Chen, S. Statistical and hydrological evaluation of TRMM-based Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis over the Wangchu Basin of Bhutan: Are the latest satellite precipitation products 3B42V7 ready for use in ungauged basins? J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qin, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation Project Daily Precipitation Estimates over the Chinese Mainland. Adv. Meteorol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, Q. Combining satellite precipitation and long-term ground observations for hydrological monitoring in China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2015, 120, 6426–6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cong, Z. Trends of precipitation intensity and frequency in hydrological regions of China from 1956 to 2005. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 117, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wu, B.; Scaife, A.A.; Broennimann, S.; Cherchi, A.; Fereday, D.; Fischer, A.M.; Folland, C.K.; Jin, K.E.; Kinter, J.; et al. The CLIVAR C20C project: which components of the Asian-Australian monsoon circulation variations are forced and reproducible? Clim. Dyn. 2009, 33, 1051–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bothe, O.; Fraedrich, K.; Zhu, X. Precipitation climate of Central Asia and the large-scale atmospheric circulation. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 108, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatagai, A.; Kamiguchi, K.; Arakawa, O.; Hamada, A.; Yasutomi, N.; Kitoh, A. APHRODITE Constructing a Long-Term Daily Gridded Precipitation Dataset for Asia Based on a Dense Network of Rain Gauges. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, X.-J. A gridded daily observation dataset over China region and comparison with the other datasets. Chin. J. Geophys.-Chin. 2013, 56, 1102–1111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; He, J.; Tang, W.; Qin, J.; Cheng, C.C.K. On downward shortwave and longwave radiations over high altitude regions: Observation and modeling in the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhou, T. Assessing the Quality of APHRODITE High-Resolution Daily Precipitation Dataset over Contiguous China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 36, 361–373. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Eylander, J.B.; Joyce, R.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Hsu, K.-L.; Turk, F.J.; Garcia, M.; Zeng, J. Component analysis of errors in satellite-based precipitation estimates. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Fan, J.; Sun, J.; Weipeng, L. Accuracy validation of TRMM 3B42 data in Sichuan basin and the surrounding areas. J. Meteorol. Sci.-Chin. 2013, 5, 526–535. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, R. Evaluation of Satellite Rainfall Estimates over the Chinese Mainland. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11649–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalck, J.; Meng, J.; Rodell, M.; Houser, P. Analysis of multiple precipitation products and preliminary assessment of their impact on global land data assimilation system land surface states. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 573–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D. A global map of uncertainties in satellite-based precipitation measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidment, R.I.; Grimes, D.; Allan, R.P.; Tarnavsky, E.; Stringer, M.; Hewison, T.; Roebeling, R.; Black, E. The 30 year TAMSAT African Rainfall Climatology and Time series (TARCAT) data set. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 10619–10644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, M.W.; Hoedjes, J.C.B.; Su, Z. An Assessment of Satellite-Derived Rainfall Products Relative to Ground Observations over East Africa. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, V.; Singh, C. Evaluation of error in TRMM 3B42V7 precipitation estimates over the Himalayan region. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2015, 120, 12458–12473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Li, L.; Hu, J.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, K. Accuracy validation of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis daily precipitation products in the Lancang River Basin of China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 112, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yatagai, A. Evaluation of TRMM 3B42 product using a new gauge-based analysis of daily precipitation over China. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 2749–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Cao, Q.; Gourley, J.J.; Kirstetter, P.-E.; Yong, B.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. Similarity and difference of the two successive V6 and V7 TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis performance over China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 13060–13074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Chen, B.; Tian, Y.; Yu, Z.; Hong, Y. Error-Component Analysis of TRMM-Based Multi-Satellite Precipitation Estimates over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Levizzani, V.; Schellekens, J.; Miralles, D.G.; Martens, B.; de Roo, A. MSWEP: 3-hourly 0.25 degrees global gridded precipitation (1979–2015) by merging gauge, satellite, and reanalysis data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 589–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Jin, C.; Wang, A.; Guan, D.; Wu, J.; Yuan, F.; Xu, L. Comprehensive precipitation evaluation of TRMM 3B42 with dense rain gauge networks in a mid-latitude basin, northeast, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 126, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Win, K.W.W.; Ren, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Assessment of GPM and TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Products in Streamflow Simulations in a Data-Sparse Mountainous Watershed in Myanmar. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Neilson, R.P.; Phillips, D.L. A Statistical-Topographic Model for Mapping Climatological Precipitation Over Mountain Terrain. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.-C.; Tong, K.; Liu, X.-L.; Zhang, L.-L. Capability of TMPA products to simulate streamflow in upper Yellow and Yangtze River basins on Tibetan Plateau. Water Sci. Eng. 2014, 7, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| QPEs | Temporal Coverage | Temporal and Spatial Resolution | Websites |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRMM 3B42 | 1998-present | 0.25°/3 h | https://pmm.nasa.gov/data-access/downloads/TRMM |
| CMORPH | 1998-present | 0.07°/30 min | ftp://ftp.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/precip/CMORPH_V1.0/RAW/8km-30min/ |
| PERSIANN-CRT | 1983-present | 0.25°/1 d | ftp://persiann.eng.uci.edu/CHRSdata/PERSIANN-CDR/daily/ |
| GsMaP | 2000-present | 0.10°/30 min | ftp://hokusai.eorc.jaxa.jp/reanalysis/v6/ |
| GPM IMERGE | 2014-present | 0.10°/30 min | https://pmm.nasa.gov/data-access/downloads/gpm |
| CHIRPS | 1981-present | 0.05°/1 d | ftp://ftp.chg.ucsb.edu/pub/org/chg/products/CHIRPS-2.0/global_daily/netcdf/p05/ |
| Basin | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Annual | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | ME | r | ME | r | ME | r | ME | r | ME | |
| SHJ | 0.302 | −0.044 | 0.249 | 0.085 | 0.332 | −0.024 | 0.226 | −0.039 | 0.277 | −0.006 |
| LH | 0.320 | −0.048 | 0.288 | 0.324 | 0.354 | 0.024 | 0.158 | 0.051 | 0.280 | 0.088 |
| XB | 0.145 | 0.018 | 0.160 | −0.138 | 0.182 | −0.040 | 0.111 | 0.023 | 0.150 | −0.034 |
| HAH | 0.299 | −0.068 | 0.310 | 0.071 | 0.304 | −0.111 | 0.166 | 0.013 | 0.270 | −0.024 |
| YR | 0.269 | −0.003 | 0.268 | 0.051 | 0.326 | −0.014 | 0.206 | −0.018 | 0.267 | 0.004 |
| YZR | 0.278 | 0.035 | 0.336 | 0.078 | 0.339 | 0.011 | 0.271 | −0.034 | 0.306 | 0.023 |
| HUH | 0.336 | 0.053 | 0.382 | 0.081 | 0.327 | −0.092 | 0.296 | 0.057 | 0.335 | 0.025 |
| DN | 0.352 | 0.460 | 0.512 | 0.802 | 0.415 | 0.204 | 0.362 | 0.013 | 0.410 | 0.370 |
| XN | 0.219 | 0.100 | 0.272 | 0.551 | 0.348 | 0.136 | 0.248 | −0.017 | 0.272 | 0.193 |
| PR | 0.400 | 0.211 | 0.472 | 0.407 | 0.418 | −0.055 | 0.353 | −0.104 | 0.411 | 0.115 |
| Regions | DN | HAH | HUH | LH | SHJ | YR | YZR | XN | PR | XB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05° | 0.44 | 0.34 | 0.39 | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.46 | 0.21 |
| 0.25° | 0.41 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.41 | 0.15 |
| Difference | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, L.; Shi, C.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J. Accuracy of CHIRPS Satellite-Rainfall Products over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030362
Bai L, Shi C, Li L, Yang Y, Wu J. Accuracy of CHIRPS Satellite-Rainfall Products over Mainland China. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(3):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030362
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Lei, Chunxiang Shi, Lanhai Li, Yanfen Yang, and Jing Wu. 2018. "Accuracy of CHIRPS Satellite-Rainfall Products over Mainland China" Remote Sensing 10, no. 3: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030362
APA StyleBai, L., Shi, C., Li, L., Yang, Y., & Wu, J. (2018). Accuracy of CHIRPS Satellite-Rainfall Products over Mainland China. Remote Sensing, 10(3), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030362