Groundwater Depletion in the West Liaohe River Basin, China and Its Implications Revealed by GRACE and In Situ Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. TWSA Derived from GRACE
2.2. SMSA+SWESA Derived from GLDAS LSMs
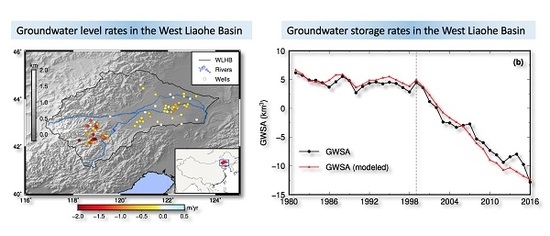
2.3. GWSA from In Situ Observations
2.4. RESSA from Ground Measurements
2.5. Precipitation Data and Climate Indices
2.6. Climate-Driven Water Storage Variability
2.7. Regression Analysis between Groundwater Flux and Precipitation Anomalies
2.8. Uncertainty Assessment
3. Results
3.1. GWSA from 2005 to 2015
3.2. GWSA from 1980 to 2015
3.3. Groundwater Flux (GWF) from 1980 to 2015
4. Discussion
4.1. Interannual Variablity of GWS from 2012 to 2015
4.2. Uncertainties in GRACE-Derived GWS Rates
4.3. Comparison with Other Studies
4.4. ENSO’s Effect on Groundwater from a Long-Term Perspective
4.5. Groundwater Recharge and Discharge
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konikow, L.F.; Kendy, E. Groundwater depletion: A global problem. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Velicogna, I.; Famiglietti, J.S. Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in India. Nature 2009, 460, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Longuevergne, L.; Long, D. Ground referencing GRACE satellite estimates of groundwater storage changes in the California Central Valley, USA. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 04520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourian, M.J.; Elmi, O.; Chen, Q.; Devaraju, B.; Roohi, S.; Sneeuw, N. A spaceborne multisensor approach to monitor the desiccation of Lake Urmia in Iran. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Yu, J.J.; Eloise, K. Groundwater exploitation and its impact on the environment in the North China Plain. Water Int. 2001, 26, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Strassberg, G.; Scanlon, B.R.; Chambers, D. Evaluation of groundwater storage monitoring with the GRACE satellite: Case study of the High Plains aquifer, central United States. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W05410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.Y.; Green, R.; Rodell, M.; Swenson, S. Inferring aquifer storage parameters using satellite and in situ measurements: Estimation under uncertainty. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, P.; Hoffmann-Dobrev, H.; Portmann, F.T.; Siebert, S.; Eicker, A.; Rodell, M.; Strassberg, G.; Scanlon, B.R. Impact of water withdrawals from groundwater and surface water on continental water storage variations. J. Geodyn. 2012, 59–60, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapley, B.D.; Bettadpur, S.; Ries, J.C.; Thompson, P.F.; Watkins, M.M. GRACE measurements of mass variability in the Earth system. Science 2004, 305, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahr, J.; Swenson, S.; Zlotnicki, V.; Velicogna, I. Time-variable gravity from GRACE: First results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L11501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Hou, X.Y.; Hong, Y.; Scanlon, B.R.; Longueyergne, L. Global analysis of spatiotemporal variability in merged total water storage changes using multiple GRACE products and global hydrological models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Chen, J.L.; Kato, H.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Nigro, J.; Wilson, C.R. Estimating groundwater storage changes in the Mississippi River basin (USA) using GRACE. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassberg, G.; Scanlon, B.R.; Rodell, M. Comparison of seasonal terrestrial water storage variations from GRACE with groundwater-level measurements from the High Plains Aquifer (USA). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Chen, X.; Scanlon, B.R.; Wada, Y.; Hong, Y.; Singh, V.P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Han, Z.; Yang, W. Have GRACE satellites overestimated groundwater depletion in the Northwest India Aquifer? Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Ni, S.N. Long-term groundwater variations in Northwest India from satellite gravity measurements. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 116, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.M.; Wahr, J.; Swenson, S. Dwindling groundwater resources in northern India, from satellite gravity observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L18401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanja, S.N.; Mukherjee, A.; Saha, D.; Velicogna, I.; Famiglietti, J.S. Validation of GRACE based groundwater storage anomaly using in-situ groundwater level measurements in India. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S.; Lo, M.; Ho, S.L.; Bethune, J.; Anderson, K.J.; Syed, T.H.; Swenson, S.C.; de Linage, C.R.; Rodell, M. Satellites measure recent rates of groundwater depletion in California’s Central Valley. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L03403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Faunt, C.C.; Longuevergne, L.; Reedy, R.C.; Alley, W.M.; McGuire, V.L.; McMahon, P.B. Groundwater depletion and sustainability of irrigation in the US High Plains and Central Valley. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9320–9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, W.; Zhong, M.; Lemoine, J.M.; Biancale, R.; Hsu, H.T.; Xia, J. Evaluation of groundwater depletion in North China using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data and ground-based measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Pan, Y.; Gong, H.L.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Li, X.J.; Zhou, D.M.; Zhao, W.J. Subregional-scale groundwater depletion detected by GRACE for both shallow and deep aquifers in North China Plain. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiwo, J.P.; Tao, F.L.; Lu, W.X. Analysis of satellite-based and in situ hydro-climatic data depicts water storage depletion in North China Region. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joodaki, G.; Wahr, J.; Swenson, S. Estimating the human contribution to groundwater depletion in the Middle East, from GRACE data, land surface models, and well observations. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 2679–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yu, M.W.; Zhang, L.L.; Liu, B.S.; Long, W.H.; Wang, A.S.; Feng, B.A.; Huo, G.L. Investigation and Assessment of Groundwater Resources and Their Environmental Issues in the West Liaohe Plain; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009; p. 313. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.Y. Changes of Light, Heat, Water Resources and Effect on Corn Potential Productivity in Xiliao River Plain; Inner Mongolia University for Nationalities: Tongliao, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Tang, Y.; Tang, K.W. Groundwater vulnerability assessment in Tongliao Plain, Inner Mongolia. J. China Inst. Water Resour. Hydrop. Res. 2015, 13, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Songliao Water Resources Commission (SLWRC). Songliao Basin Water Resources Bulletin; Songliao Water Resources Commission: Changchun, China, 2013.
- Inner Mongolia Water Resources Protection and Project Group (IMWRPPG). Inner Mongolia Songliao Basin Groundwater Protection and Project; Hydrological Bur. of Inner Mongolia; Inner Mongolia Water Resources Protection and Project Group: Hohhot, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K. Study on Water Cycle Regulation in West Liao River Basin and Ecosystem Stability of West Liao River Plain. D; China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Sun, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Li, J.F. Precipitation and streamflow changes in China: Changing patterns, causes and implications. J. Hydrol. 2011, 410, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y. Research on the Response of Groundwater Depth Change and the Vegetation Ecosystem in the West Liao River Plain Based on RS/GIS D; Jilin University: Changchun, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hydrological Bureau of Inner Mongolia (HBIM). Inner Mongolia Water Resources Bulletin; Department of Water Resources of Inner Mongolia: Hohhot, China, 2013.
- Yang, H.S.; Liu, J.; Liang, H.Y. Change characteristics of climate and water resources in West Liaohe River Plain. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 20, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.T.; Hai, J.Y. Brief discussion about water resource in Tongliao. J. Inner Mon. Univ. Natl. 2008, 14, 97–98. [Google Scholar]
- Long, W.H.; Chen, H.H.; Li, Z.; Pan, H.J. Evaluation of the groundwater intrinsic vulnerability in West Liaohe Plain, Inner Mongolia, China. Geol. Bull. China 2010, 29, 598–602. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Z.; Lin, A.W.; Feng, J.D.; Yang, Q.; Zou, L. Analysis of water resources in Horqin Sandy land using multisource data from 2003 to 2010. Sustainability 2016, 8, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, G.X.; Wu, Y.X. Spatial-temporal variation of precipitation in West Liao River Basin during 1961–2014. S. N. Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 15, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Save, H.; Bettadpur, S.; Tapley, B.D. High-resolution CSR GRACE RL05 mascons. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 7547–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Save, H.; Wiese, D.N.; Landerer, F.W.; Long, D.; Longuevergne, L.; Chen, J.L. Global evaluation of new GRACE mascon products for hydrologic applications. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 9412–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek, M.; Mitchell, K.; Lin, Y.; Rogers, E.; Grunmann, P.; Koren, V.; Gayno, G.; Tarpley, J. Implementation of Noah land surface model advances in the National Centers for Environmental Prediction operational mesoscale Eta model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 8851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.J.; Zeng, X.B.; Dickinson, R.E.; Baker, I.; Bonan, G.B.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Denning, A.S.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Houser, P.R.; Niu, G.Y.; et al. The Common Land Model. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, R.D.; Suarez, M.J. Modeling the land surface boundary in climate models as a composite of independent vegetation stands. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 2697–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Wood, E.F.; Burges, S.J. A simple hydrologically based model of land surface water and energy fluxes for general circulation models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 14415–14428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M.; et al. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Institute of Geological Environment Monitoring (CIGEM). China Geological Environment Monitoring: Groundwater Yearbook; China Land Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.Y.; He, X.F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ferreira, V.G.; Chang, L. Monitoring groundwater variations from satellite gravimetry and hydrological models: A comparison with in-situ measurements in the mid-Atlantic region of the United States. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 686–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songliao Water Resources Commission (SLWRC). Songliao Basin Groundwater Bulletin; Songliao Water Resources Commission: Changchun, China, 2013.
- Humphrey, V.; Gudmundsson, L.; Seneviratne, S.I. A global reconstruction of climate-driven subdecadal water storage variability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2300–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, V.; Gudmundsson, L.; Seneviratne, S.I. Assessing Global Water Storage Variability from GRACE: Trends, Seasonal Cycle, Subseasonal Anomalies and Extremes. Surv. Geophys. 2016, 37, 357–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Sun, W.K.; Feng, W.; Chen, J.L. Anthropogenic and climate-driven water depletion in Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 9061–9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landerer, F.W.; Swenson, S.C. Accuracy of scaled GRACE terrestrial water storage estimates. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W04531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.B.; Nie, Q.H.; He, X.D.; Chang, X.L.; He, H.L. Tactic phase and potential of grass plantation in Horqin sand land Taking Tongliao city of inner mongolia autonomous region as an example. J. Des. Res. 2003, 23, 242–245. [Google Scholar]
- Vondrák, J. Problem of smoothing observational data II. Bull. Astron. Inst. Czech. 1977, 28, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.W.; Zhong, P.; Ding, X.L.; Chen, W. Filtering GPS time-series using a Vondrak filter and cross-validation. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.J. Dynamic Simulation Evaluation about Water Resource System and Optimal Allocation Model of Macro-Economy Water Resource in Tong Liao City; Inner Mongolia Agricultural University: Hohhot, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Longuevergne, L.; Wilson, C.R.; Scanlon, B.R.; Cretaux, J.F. GRACE water storage estimates for the Middle East and other regions with significant reservoir and lake storage. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 4817–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, S.; Song, C.Q.; Wang, Q.Y.; Wang, L.S.; Heki, K.; Sun, W.K. The potential of GRACE gravimetry to detect the heavy rainfall-induced impoundment of a small reservoir in the upper Yellow River. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 6562–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, D.N.; Landerer, F.W.; Watkins, M.M. Quantifying and reducing leakage errors in the JPL RL05M GRACE Mascon solution. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 7490–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthcke, S.B.; Sabaka, T.J.; Loomis, B.D.; Arendt, A.A.; McCarthy, J.J.; Camp, J. Antarctica, Greenland and Gulf of Alaska land-ice evolution from an iterated GRACE global mascon solution. J. Glaciol. 2013, 59, 613–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusche, J.; Schmidt, R.; Petrovic, S.; Rietbroek, R. Decorrelated GRACE time-variable gravity solutions by GFZ, and their validation using a hydrological model. J. Geodesy 2009, 83, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, R.; Liu, W.; Fu, G.; Liu, C.; Hu, L.; Wang, H. Linkages between ENSO/PDO signals and precipitation, streamflow in China during the last 100 years. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3651–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Jiang, T.; Wu, Y.J. Possible influence of ENSO on annual maximum streamflow of the Yangtze River, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Ren, L.L.; Jiang, S.H.; Yuan, S.S.; Shi, L. Analysis of trend and influencing factors of runoff variation in headwater basin of West Liaohe River. J. Hohai Univ. 2012, 40, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Pail, R.; Bingham, R.; Braitenberg, C.; Dobslaw, H.; Eicker, A.; Güntner, A.; Horwath, M.; Ivins, E.; Longuevergne, L.; Panet, I. Science and user needs for observing global mass transport to understand global change and to benefit society. Surv. Geophys. 2015, 36, 743–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panet, I.; Flury, J.; Biancale, R.; Gruber, T.; Johannessen, J.; van den Broeke, M.; van Dam, T.; Gegout, P.; Hughes, C.; Ramillien, G. Earth system mass transport mission (e.motion): A concept for future earth gravity field measurements from space. Surv. Geophys. 2013, 34, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Type | Data Name | Data Version/Source | Spatial and Temporal Resolution, Ttime Period | Data Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satellite | TWSA | CSR Mascons | 1° × 1°, monthly, 2005–2015 | http://www2.csr.utexas.edu/grace/RL05_mascons.html |
| Models | SMSA+SWESA | GLDAS-1 LSMs | 1° × 1°, monthly, 2005–2015 | http://mirador.gsfc.nasa.gov/ |
| In situ | GWSA | CIGEM+HBIM | 122 wells, monthly, 2005–2015 | Groundwater yearbook and Hydrological Bureau of Inner Mongolia |
| GWLA | Region mean, annual, 1980–2015 | http://116.113.33.52:8989/ and Xu [29] | ||
| RESSA | Region sum, annual, 1997–2015 | http://116.113.33.52:8989/ | ||
| Precipitation | CMDC | 0.5° × 0.5°, monthly, 1961–2015 | http://data.cma.cn/ | |
| 0.5° × 0.5°, daily, 1961–2013 | http://data.cma.cn/ | |||
| Climate indices | ONI | Time series, monthly, 1980–2015 | http://origin.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/ensostuff/ONI_v5.php |
| GRACE Solutions | Rate (km3/yr) | Rate (km3/yr) |
|---|---|---|
| January 2005–December 2011 | January 2005–December 2015 | |
| CSR-M | −0.92 ± 0.49 | −0.43 ± 0.26 |
| JPL-M.dsf | −1.54 ± 0.42 | −0.45 ± 0.21 |
| GSFC-M | −1.47 ± 0.46 | −0.62 ± 0.23 |
| CSRT-GSH | −0.84 ± 0.47 | −0.51 ± 0.24 |
| CSR-DDK3 | −1.67 ± 0.65 | −0.65 ± 0.33 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.; Zhong, M.; Feng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wu, D. Groundwater Depletion in the West Liaohe River Basin, China and Its Implications Revealed by GRACE and In Situ Measurements. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040493
Zhong Y, Zhong M, Feng W, Zhang Z, Shen Y, Wu D. Groundwater Depletion in the West Liaohe River Basin, China and Its Implications Revealed by GRACE and In Situ Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(4):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040493
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Yulong, Min Zhong, Wei Feng, Zizhan Zhang, Yingchun Shen, and Dingcheng Wu. 2018. "Groundwater Depletion in the West Liaohe River Basin, China and Its Implications Revealed by GRACE and In Situ Measurements" Remote Sensing 10, no. 4: 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040493
APA StyleZhong, Y., Zhong, M., Feng, W., Zhang, Z., Shen, Y., & Wu, D. (2018). Groundwater Depletion in the West Liaohe River Basin, China and Its Implications Revealed by GRACE and In Situ Measurements. Remote Sensing, 10(4), 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10040493