Satellite Images and Gaussian Parameterization for an Extensive Analysis of Urban Heat Islands in Thailand
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Satellite Data
3.2. Estimation of the SUHI
- -
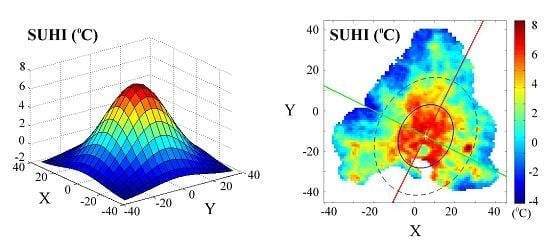
- the magnitude a0 (°C) of the SUHI maximum intensity of the study area;
- -
- the spatial extent (ax, ay) (km), central location (x0, y0) (km), and orientation (φ) (degree) of the SUHI pattern.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Gaussian Fitting of SUHI Maps
4.2. Fitting Parameter Comparison
4.3. Yearly Trend of SUHI Footprint and Magnitude
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fallmann, J.; Forkel, R.; Emeis, S. Secondary Effects of Urban Heat Island Mitigation Measures on Air Quality. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 125, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, A.; Lakmini, S.; Bhargava, S. Urban Heat Island Effect: It’s Relevance in Urban Planning. J. Biodivers. Endanger. Spec. 2017, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ridder, K.; Maiheu, B.; Lauwaet, D.; Daglis, I.; Keramitsoglou, I.; Kourtidis, K.; Manunta, P.; Paganini, M. Urban Heat Island Intensification during Hot Spells—The Case of Paris during the Summer of 2003. Urban Sci. 2016, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Pengwang, C.; Gao, W. Evaluation of Urbanization Dynamics and Its Impacts on Surface Heat Islands: A Case Study of Beijing, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, H. Urban Climates and Heat Islands: Albedo, Evapotranspiration, and Anthropogenic Heat. Energy Build. 1997, 25, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Rybski, D.; Kropp, J.P. The Role of City Size and Urban Form in the Surface Urban Heat Island. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oke, T.R. City Size and the Urban Heat Island. Atmos. Environ. 1973, 7, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M. Analysing the heat island magnitude and characteristics in one hundred Asian and Australian cities and region. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, J.; Chapman, L.; Muller, C. Quantifying the Daytime and Night-Time Urban Heat Island in Birmingham, UK: A Comparison of Satellite Derived Land Surface Temperature and High Resolution Air Temperature Observations. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anniballe, R.; Bonafoni, S.; Pichierri, M. Spatial and Temporal Trends of the Surface and Air Heat Island over Milan Using MODIS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 150, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtidis, K.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Rapsomanikis, S.; Amiridis, V.; Keramitsoglou, I.; Hooyberghs, H.; Maiheu, B.; Melas, D. A Study of the Hourly Variability of the Urban Heat Island Effect in the Greater Athens Area during Summer. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 517, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasul, A.; Balzter, H.; Smith, C.; Remedios, J.; Adamu, B.; Sobrino, J.; Srivanit, M.; Weng, Q. A Review on Remote Sensing of Urban Heat and Cool Islands. Land 2017, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, U.; Weng, Q. Spatio-Temporal Modelling and Analysis of Urban Heat Islands by Using Landsat TM and ETM+ Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 3531–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Myint, S.W.; Kaplan, S.; Middel, A.; Zheng, B.; Rahman, A.; Huang, H.P.; Brazel, A.; Blumberg, D.G. Understanding the Impact of Urbanization on Surface Urban Heat Islands-A Longitudinal Analysis of the Oasis Effect in Subtropical Desert Cities. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haashemi, S.; Weng, Q.; Darvishi, A.; Alavipanah, S. Seasonal Variations of the Surface Urban Heat Island in a Semi-Arid City. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichierri, M.; Bonafoni, S.; Biondi, R. Satellite Air Temperature Estimation for Monitoring the Canopy Layer Heat Island of Milan. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 127, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Sparrow, M.; Yang, J.; Chen, H. Influences of urbanization on surface characteristics as derived from the Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer: A case study for the Beijing metropolitan area. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D22S06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Bonafoni, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R. Remote sensing of the urban heat island effect in a highly populated urban agglomeration area in East China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deilami, K.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Hayes, J. Correlation or Causality between Land Cover Patterns and the Urban Heat Island Effect? Evidence from Brisbane, Australia. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, A.; Cao, X.; Ito, T.; Shi, F.; Imura, H. Evaluating the Potential for Urban Heat-Island Mitigation by Greening Parking Lots. Urban For. Urban Green. 2010, 9, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavipanah, S.; Wegmann, M.; Qureshi, S.; Weng, Q.; Koellner, T. The Role of Vegetation in Mitigating Urban Land Surface Temperatures: A Case Study of Munich, Germany during the Warm Season. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4689–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongtanom, Y.; Kositanont, C.; Baulert, S. Temporal Variations of Urban Heat Island Intensity in Three Major Cities, Thailand. Mod. Appl. Sci. 2011, 5, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifwidodo, S.D.; Tanaka, T. The Characteristics of Urban Heat Island in Bangkok, Thailand. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifwidodo, S.; Chandrasiri, O. Urban Heat Island and Household Energy Consumption in Bangkok, Thailand. Energy Proc. 2015, 79, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivanit, M.; Hokao, K. Effects of Urban Development and Spatial Characteristics on Urban Thermal Environment in Chiang Mai Metropolitan, Thailand. Lowl. Technol. Int. 2012, 14, 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Laosuwan, T.; Sangpradit, S. Urban Heat Island Monitoring and Analysis by Using Integration of Satellite Data and Knowledge Based Method. Int. J. Dev. Sustain. 2012, 1, 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, H.; Uchihama, D.; Ochi, S.; Yasuoka, Y. Assessment with satellite data of the urban heat island effects in Asian mega cities. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2006, 8, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeratikasikorn, C.; Bonafoni, S. Urban Heat Island Analysis over the Land Use Zoning Plan of Bangkok by Means of Landsat 8 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distributed Active Archive Center DAAC ORNL. Available online: https://daac.ornl.gov/get_data/ (accessed on 1 September 2017).
- US Geological Survey USGS. Available online: http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov (accessed on 12 December 2017).
- Bolstad, P.V.; Lillesand, T.M. Rapid Maximum Likelihood Classification. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1991, 57, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Phiri, D.; Morgenroth, J. Developments in Landsat Land Cover Classification Methods: A Review. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data. Principles and Practices; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Streutker, D. Satellite-Measured Growth of the Urban Heat Island of Houston, Texas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anniballe, R.; Bonafoni, S. A Stable Gaussian Fitting Procedure for the Parameterization of Remote Sensed Thermal Images. Algorithms 2015, 8, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quan, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhan, W.; Wang, J.; Voogt, J.; Wang, M. Multi-temporal trajectory of the urban heat island centroid in Beijing, China based on a Gaussian volume model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, J.; Weng, Q.H.; Yi, W.B. A volume model for urban heat island based on remote sensing imagery and its application: A case study in Beijing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 12, 734–742. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Dong, J.; Liu, J.; Zhai, J.; Cui, Y.; He, T.; Xiao, X. Different Patterns in Daytime and Nighttime Thermal Effects of Urbanization in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Public Works and Town & Country Planning. Available online: https://dpt.go.th/en/ (accessed on 5 February 2018).
- McGrath, B.; Sangawongse, S.; Thaikatoo, D.; Corte, M.B. The Architecture of the Metacity: Land Use Change, Patch Dynamics and Urban Form in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Urban Plan. 2017, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulou, M.; Cartalis, C.; Keramitsoglou, I. Mapping Micro-Urban Heat Islands Using NOAA/AVHRR Images and CORINE Land Cover: An Application to Coastal Cities of Greece. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2301–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.S.; Kessomkiat, W.; Pereira, G. Satellite-Observed Urbanization Characters in Shanghai, China: Aerosols, Urban Heat Island Effect, and Land–Atmosphere Interactions. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Qin, F.; Jiang, H.; Cai, Y. Influences of land cover types, meteorological conditions, anthropogenic heat and urban area on surface urban heat island in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Sheng, Y. The Impact of Energy Consumption on the Surface Urban Heat Island in China’s 32 Major Cities. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmohamadi, P.; Che-Ani, A.I.; Etessam, I.; Maulud, K.N.A.; Tawil, N.M. Healthy Environment: The Need to Mitigate Urban Heat Island Effects on Human Health. Procedia Eng. 2011, 20, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnds, D.; Böhner, J.; Bechtel, B. Spatio-temporal variance and meteorological drivers of the urban heat island in a European city. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 128, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Ottle, C.; Bréon, F.M.; Nan, H.; Zhou, L.; Myneni, R.B. Surface urban heat island across 419 global big cities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, C. Surface urban heat island in China’s 32 major cities: Spatial patterns and drivers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Li, D.; Sun, G.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Hao, L. Contrasting effects of urbanization and agriculture on surface temperature in eastern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 9597–9606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLachlan, A.; Biggs, E.; Roberts, G.; Boruff, B. Urbanisation-Induced Land Cover Temperature Dynamics for Sustainable Future Urban Heat Island Mitigation. Urban Sci. 2017, 1, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Myint, S.W.; Wentz, E.A.; Fan, C. Rooftop Surface Temperature Analysis in an Urban Residential Environment. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12135–12159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafoni, S.; Baldinelli, G.; Verducci, P. Sustainable strategies for smart cities: Analysis of the town development effect on surface urban heat island through remote sensing methodologies. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 29, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jing, X.-M.; Chen, J.-Y.; Li, J.-J.; Schwegler, B. Characterizing Urban Fabric Properties and Their Thermal Effect Using QuickBird Image and Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared (TIR) Data: The Case of Downtown Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafoni, S.; Baldinelli, G.; Verducci, P.; Presciutti, A. Remote Sensing Techniques for Urban Heating Analysis: A Case Study of Sustainable Construction at District Level. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Bou-Zeid, E. Synergistic interactions between urban heat islands and heat waves: The impact in cities is larger than the sum of its parts. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| City | Season | 10:00 | 14:00 | 22:00 | 02:00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bangkok | Summer | x (0.70) | x (0.70) | x (0.75) | x (0.75) |
| Winter | x (0.74) | x (0.73) | x (0.66) | x (0.64) | |
| Chiang May | Summer | x (0.73) | x (0.73) | x (0.90) | x (0.87) |
| Winter | x (0.71) | x (0.69) | x (0.86) | x (0.82) | |
| Nakhon | Summer | - | - | x (0.72) | x (0.82) |
| Ratchasima | Winter | - | - | x (0.73) | x (0.79) |
| Ubon | Summer | x (0.60) | x (0.63) | x (0.87) | x (0.83) |
| Ratchathani | Winter | x (0.73) | x (0.69) | - | - |
| Khon Kaen | Summer | - | - | x (0.81) | x (0.77) |
| Winter | x (0.73) | x (0.68) | x (0.82) | x (0.82) | |
| Udon Thani | Summer | x (0.71) | x (0.70) | x (0.81) | x (0.84) |
| Winter | x (0.88) | x (0.88) | x (0.67) | x (0.70) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keeratikasikorn, C.; Bonafoni, S. Satellite Images and Gaussian Parameterization for an Extensive Analysis of Urban Heat Islands in Thailand. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050665
Keeratikasikorn C, Bonafoni S. Satellite Images and Gaussian Parameterization for an Extensive Analysis of Urban Heat Islands in Thailand. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(5):665. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050665
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeeratikasikorn, Chaiyapon, and Stefania Bonafoni. 2018. "Satellite Images and Gaussian Parameterization for an Extensive Analysis of Urban Heat Islands in Thailand" Remote Sensing 10, no. 5: 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050665
APA StyleKeeratikasikorn, C., & Bonafoni, S. (2018). Satellite Images and Gaussian Parameterization for an Extensive Analysis of Urban Heat Islands in Thailand. Remote Sensing, 10(5), 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050665