InSAR Deformation Analysis with Distributed Scatterers: A Review Complemented by New Advances
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Statistics for Distributed Scatterers
- the backscatter from a resolution cell is the superposition of the backscatter of stochastically independent elementary scatterers;
- their number is large;
- amplitude and phase are independent random variables;
- the phase is uniformly distributed;
- no individual scatterer dominates the resolution cell;
- the resolution cell is large compared to the single scatterer.
- presence of thermal noise (thermal decorrelation);
- effect of different viewing geometry (spatial baseline and rotation decorrelation);
- small random movements of the scatterers (temporal decorrelation).
- removal of residual fringes;
- grouping of a statistically homogeneous neighborhood ;
- bias reduction.
3. Estimation of Distributed Scatterer Signals for Preprocessing of Multitemporal InSAR Data
- Grouping of a neighborhood ;
- Estimation of the covariance matrix;
- Phase triangulation or more generally estimation of the DS signal;
- Calculation of a quality number for the DS.
3.1. Estimators of Distributed Scatterer Signal
3.2. Filtering of Interferograms and Coherence Estimation
3.2.1. Nonstationary Phases
- denoising of the phases and correction of interferograms;
- estimation of covariance or coherence from the corrected interferograms;
- adding back denoised phases to covariances;
- DS signal estimation.
3.2.2. Grouping of Statistically Homogeneous Neighborhoods
3.2.3. Nonlocal (NL) Methods
- for each pixel to be estimated, a patch is shifted around and a similarity measure (based on the statistical characteristics of the data) is calculated for every position; for multichannel data, it can be a 3D block instead of a patch;
- weights are computed from the calculated similarity measure;
- a weighted mean or a weighted MLE provides the result.
3.2.4. Bias Correction and Regularization
3.3. Quality Numbers for Distributed Scatterers for Preprocessing
3.4. Algorithmic Approaches to Reduce Run Time
4. Phase Model Parameter Estimation for Distributed Scatterers
4.1. Estimators of Model Parameters
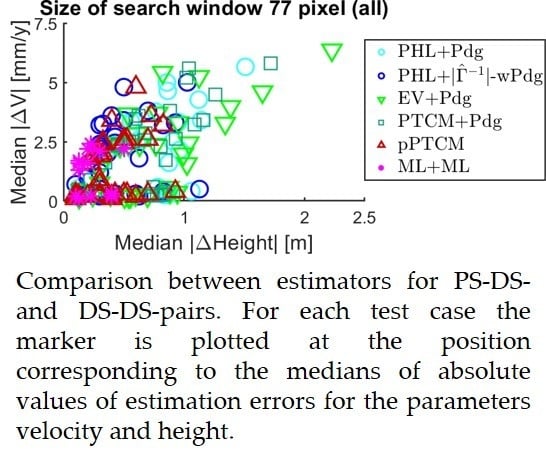
4.2. Results of Investigations on Simulated Data for Parameter Estimation from Pixel Pairs
5. Discussion
- large , entropy close to 0: PhL;
- small , entropy close to 0: PTCM;
- entropy not close to 0: EVG.
- use of a proper 3D neighborhood in the sense that, although a pixel is included in the neighborhood, some of its values corresponding to certain points in time may be excluded; alternatively, a NL analog of this might be taken;
- robust and effective treatment of fringes;
- some bias correction or regularization.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bamler, R.; Hartl, P. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. Inverse Probl. 1998, 14, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S.; Joughin, I.R.; Li, F.; Madsen, S.; Rodrìguez, E.; Goldstein, R.M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. Proc. IEEE 2000, 83, 333–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis, 1st ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; ISBN 978-0-7923-6945-5. [Google Scholar]
- Perissin, D.; Ferretti, A. Urban-Target Recognition by Means of Repeated Spaceborne SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 4043–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, G.; Lombardini, F.; Pauciullo, A.; Reale, D.; Viviani, F. Tomographic Processing of Interferometric SAR data: Developments, applications and future research perspectives. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2014, 31, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Montazeri, S.; Gisinger, C.; Hanssen, R.F.; Bamler, R. Geodetic SAR Tomography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping Small Elevation Changes over Large Areas: Differential Radar Interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A.; Werner, C.L. Satellite Radar Interferometry: Two-dimensional phase unwrapping. Radio Sci. 1988, 23, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Goldstein, R.M. Studies of multi-baseline spaceborne interferometric synthetic aperture radars. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1990, 28, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrìguez, E.; Martin, J.M. Theory and design of interferometric synthetic aperture radars. IEE Proc. F 1992, 139, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Improving slant-range resolution with multiple SAR surveys. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electr. Syst. 1993, 29, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, M.S.; Cumming, I.G. Maximum likelihood estimator for SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the IGARSS, Pasadena, CA, USA, 8–12 August 1994; pp. 2272–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, D.; Bamler, R. Phase Statistics of Interferograms with Applications to Synthetic Aperture Radar. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 4361–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouvé, E.; Caramma, M.; Maître, H. Fringe detection in noisy complex interferograms. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 3799–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Radio Sci. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S. Atmospheric effects in interferometric synthetic aperture radar surface deformation and topographic maps. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 7547–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandwell, D.T.; Price, E.J. Phase gradient approach to stacking interferograms. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 30183–30204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.; Parsons, B.; Fielding, E. Measurement of interseismic strain accumulation across the North Anatolian Fault by satellite radar interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 2117–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Monti Guarnieri, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Multi-image DEM reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IGARSS, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–10 July 1998; pp. 1367–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A small baseline approach for investigating deformations on full-resolution differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.J. Persistent Scatterer Radar Interferometry for Crustal Deformation Studies and Modeling of Volcanic Deformation. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H. Persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar for crustal deformation analysis, with application to Volcán Alcedo, Galápagos. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A. A multi-temporal InSAR method incorporating both persistent scatterer and small baseline approaches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zan, F.; Rocca, F. Coherent Processing of Long Series of SAR Images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS, Seoul, Korea, 25–29 July 2005; pp. 1987–1990. [Google Scholar]
- De Zan, F. Optimizing SAR Interferometry for Decorrelating Scatterers. Ph.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Milano, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Monti Guarnieri, A.; Tebaldini, S. Hybrid Cramér-Rao Bounds for Crustal Displacement Field Estimators in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Signal Proc. Lett. 2007, 14, 1012–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti Guarnieri, A.; Tebaldini, S. On the Exploitation of Target Statistics for SAR Interferometry Applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3436–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. The second generation PSInSAR approach: SqueeSAR. In Proceedings of the International Fringe Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 30 November–4 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A New Algorithm for Processing Interferometric Data-Stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, G.; Reale, D.; Verde, S. Adaptive spatial multilooking and temporal multilinking in SBAS interferometry. In Proceedings of the IGARSS, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; p. 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyush Shanker, A.; Zebker, H. Edgelist phase unwrapping algorithm for time series InSAR analysis. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2010, 27, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornaro, G.; Pauciullo, A.; Reale, D. A Null-Space Method for the Phase Unwrapping of Multitemporal SAR Interferometric Stacks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2323–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Malvarosa, F.; Minati, F. A General Formulation for Redundant Integration of Finite Differences and Phase Unwrapping on a Sparse Multidimensional Domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Yang, Y.; Manzo, M.; Lanari, R. Improved EMCF-SBAS processing chain based on advanced techniques for the noise-filtering and selection of small baseline multilook DInSAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4394–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Lanari, R. On the Extension of the Minimum Cost Flow Algorithm for Phase Unwrapping of Multitemporal Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, K. Advanced Stacking Techniques and Applications in High Resolution SAR Interferometry. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, München, Germany, 27 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, M. Reconstruction of Urban Surface Models from Multi-Aspect and Multi-Baseline Interferometric SAR. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, München, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M. InSAR Coherence Estimation and Applications to Earth Observation. Ph.D. Thesis, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Advances in Meter-resolution Multipass Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, München, Germany, 19 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Samiei-Esfahany, S. Exploitation of Distributed Scatterers in Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universiteit Delft, Delft, The Netherlands, 31 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kuruoğlu, E.E.; Zerubia, J. Modeling SAR Images with a Generalization of the Rayleigh Distribution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Dobson, M.C. Handbook of Radar Statistics for Terrain; Artech House: Dedham, MA, USA, 1989; ISBN 978-0890063361. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, J.W. Some fundamental properties of speckle. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1976, 66, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikias, C.L.; Shao, M. Signal Processing with Alpha-Stable Distributions and Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1995; ISBN 978-0471106470. [Google Scholar]
- Ollila, E.; Eriksson, J.; Koivunen, V.; Poor, H.V. Complex Elliptically Symmetric Random Variables—Generation, Characterization, and Circularity Tests. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollila, E.; Tyler, D.E.; Koivunen, V. Complex Elliptically Symmetric Distributions: Survey, New Results and Applications. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 5597–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollila, E.; Tyler, D.E. Regularized M-Estimators of Scatter Matrix. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 6059–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G. Statistical Modeling of SAR Imagery: A Survey. Sensors 2000, 10, 775–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picinbono, B. Second-Order Complex Random Vectors and Normal Distributions. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1996, 44, 2637–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Colesanti, C.; Perrisin, D.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Evaluating the Effect of the Observation Time on the Distribution of SAR Permanent Scatterers. In Proceedings of the Fringe Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 1–5 December 2003; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Morishita, Y.; Hanssen, R.F. Temporal Decorrelation in L-, C-, and X-band Satellite Radar Interferometry for Pasture on Drained Peat Soils. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, Y.; Hanssen, R.F. Deformation Parameter Estimation in Low Coherence Areas Using a Multisatellite InSAR Approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4275–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, F. Modeling interferogram stacks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3289–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zan, F.; Zonno, M.; López-Dekker, P. Phase Inconsistencies and Multiple Scattering in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 6608–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zan, F.; Parizzi, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; López-Dekker, P. A SAR interferometric Model for Soil Moisture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zwieback, S.; Liu, X.; Antonova, S.; Heim, B.; Bartsch, A.; Boike, J.; Hajnsek, I. A Statistical Test of Phase Closure to Detect Influences on DInSAR Deformation Estimates besides Displacements and Decorrelation Noise: Two Case Studies in High-Latitude Regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5588–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, N.R. Statistical analysis based on a certain multivariate complex Gaussian distribution (an introduction). Ann. Math. Stat. 1963, 34, 152–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tough, R.J.A.; Blacknell, D.; Quegan, S. A statistical Description of Polarimetric and Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar. Proc. R. Soc. 1995, 449, 567–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joughin, I.R.; Winebrenner, D.P.; Percival, D.B. Probability density functions for multilook polarimetric signatures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Lopes, A. Statistics of the Stokes parameters and of the complex coherence parameters in one-look and multilook speckle fields. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Lopes, A.; Bruniquel, J.; Vachon, P.W. Coherence estimation for SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, C.; Pottier, E. Coherence estimation in synthetic aperture radar data based on speckle noise modeling. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zebker, H.A.; Chen, K. Accurate estimation of correlation in InSAR observations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2005, 2, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hoppel, K.W.; Mango, S.A.; Miller, A.R. Intensity and phase statistics of multilook polarimetric and interferometric SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabandi, K. Derivation of phase statistics from the Mueller matrix. Radio Sci. 1992, 27, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Mercer, B. Interferometric SAR Extended Coherence Calculation Based on Fractional Lower Order Statistics. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maronna, M.A.; Martin, R.D.; Yohai, V.J. Robust Statistics—Theory and Methods, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-470-01092-1. [Google Scholar]
- Even, M. Advanced InSAR Processing in the Footsteps of SqueeSAR. In Proceedings of the Fringe Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 23–27 March 2015; p. 6, ISBN 978-92-9221-295-7. [Google Scholar]
- Shevlyakov, G.L.; Oja, H. Robust Correlation—Theory and Applications, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-11849345-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sica, F.; Reale, D.; Poggi, G.; Verdoliva, L.; Fornaro, G. Nonlocal Adaptive Multilooking in SAR Multipass Differential Interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1727–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardini, F. Optimum absolute phase retrieval in three-element SAR interferometer. IET Electr. Lett. 1998, 34, 1522–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992; pp. 394–455. ISBN 0-521-43108-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bapat, R.B.; Kwong, M.K. A generalization of A−1 ∘ A ≥ I. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 1987, 93, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, F.; Rucci, A.; Ferretti, A.; Bohane, A. Advanced InSAR interferometry for reservoir monitoring. First Break 2013, 31, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Fornaro, G.; Verde, S.; Reale, D.; Pauciullo, A. CAESAR: An Approach Based on Covariance Matrix Decomposition to Improve Multibaseline–Multitemporal Interferometric SAR Processing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2050–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; De Zan, F.; Rucci, A.; Tebaldini, S. Process for Filtering Interferograms Obtained from SAR Images Acquired on the Same Area. CA Patent 2,767,144, 13 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Peressin, D.; Wang, T. Repeat-Pass SAR Interferometry with Partially Coherent Targets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiei-Esfahany, S.; Esteves Martins, J.; van Leijen, F.; Hanssen, R.F. Phase Estimation for Distributed Scatterers in InSAR Stacks Using Integer Least Squares Estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5671–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Birsen, Y.; Zeghal, M.; Bennett, V.; Abdoun, T. Joint-Scatterer Processing for Time-Series InSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 7205–7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinel-Puysségur, B.; Rémi, M.; Avouac, J.-P. Multi-Link InSAR Time Series: Enhancement of a Wrapped Interferometric Database. IEEE JSTARS 2012, 5, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinel-Puysségur, B.; Karnoukian, M.; Granin, R.; Lasserre, C.; Doin, M.-P. Wrapped Interferograms Enhanced By MuLSAR Method: Applications And Comparison To Other Methods. In Proceedings of the ESA Living Planet Symposium, Edinburgh, UK, 9–13 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Trouvé, E.; Nicolas, J.-M.; Maître, H. Improving Phase Unwrapping Techniques by the Use of Local Frequency Estimates. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, G.W.; Bamler, R. Multiresolution Phase Unwrapping for SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Bamler, R. Retrieval of phase history parameters from distributed scatterers in urban areas using very high resolution SAR data. ISPRS J. Photogr. Remote Sens. 2012, 73, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, I.; Stewart, M.P.; Kampes, B.M.; Perski, Z.; Lilly, P. A Modification to the Goldstein Radar Interferogram Filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2114–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, G.; Trouvé, E.; Petillot, I.; Bolon, P.; Nicolas, J.-M.; Gay, M.; Chanussot, J.; Landes, T.; Grussenmeyer, P.; Buzuloiu, V.; et al. High-Resolution SAR Interferometry: Estimation of Local Frequencies in the Context of Alpine Glaciers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goel, K.; Adam, N. An advanced algorithm for deformation estimation in non-urban areas. ISPRS J. Photogr. Remote Sens. 2012, 73, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, K.; Adam, N.A. Distributed Scatterer Interferometry Approach for Precision Monitoring of Known Surface Deformation Phenomena. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 5454–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuc, M.; Bolon, P.; Trouvé, E.; Buzuloiu, V.; Rudant, J.-P. Adaptive-neighborhood speckle removal in multitemporal synthetic aperture radar images. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 5954–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, R.; Rangayyan, R.M. Feature enhancement of film mammograms using fixed and adaptive neighborhoods. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-S. Digital image smoothing and the sigma filter. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1983, 24, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, G.; Trouvé, E.; Lee, J.-S.; Buzuloiu, V. Intensity-Driven Adaptive-Neighborhood Technique for Polarimetric and Interferometric SAR Parameters Estimation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 44, 1609–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizzi, A.; Brcic, R. Adaptive InSAR Stack Multilooking Exploiting Amplitude Statistics: A Comparison Between Different Techniques and Practical Results. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 8, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even, M. Advanced InSAR Processing for Distributed Scatterers. In Proceedings of the Fringe Workshop, Helsinki, Finland, 5–9 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons, J.; Chakraborti, S. Nonparametric Statistical Inference, 4th ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA; Basel, Switzerland, 2003; ISBN 0-8247-4052-1. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, F.W.; Stephens, M.A. K-Sample Anderson-Darling Tests. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1987, 82, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.; Stilla, U. Adaptive multilooking of airborne Ka-band multi-baseline InSAR data of urban areas. In Proceedings of the IGARSS, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; p. 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.; Stilla, U. Adaptive Multilooking of Airborne Single-Pass Multi-Baseline InSAR Stacks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.; Schönberger; Stilla, U. Adaptive Covariance Matrix Estimation for Multi-Baseline InSAR Data Stacks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6807–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deledalle, C.-A.; Loic, D.; Tupin, F. NL-InSAR: Nonlocal Interferogram Estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ding, X.; Hanssen, R.F.; Malhotra, R.; Chang, L. Fast Statistically Homogeneous Pixel Selection for Covariance Matrix Estimation for Multitemporal InSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Grunes, M.R.; de Grandi, G. Polarimetric SAR speckle filtering and its implication for classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Cloude, S.; Papathanassiou, C.; Grunes, M.; Woodhouse, I. Speckle filtering and coherence estimation of polarimetric SAR interferometry data for forest applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, M.; Vandervieren, E. An adjusted boxplot for skewed distributions. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2008, 52, 5186–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buades, A.; Coll, B.; Morel, J.-M. A non-local algorithm for image denoising. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Deledalle, C.-A.; Loic, D.; Tupin, F. Iterative Weighted Maximum Likelihood Denoising With Probabilistic Patch-Based Weights. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deledalle, C.-A.; Loic, D.; Tupin, F. How to compare noisy patches? Patch similarity beyond Gaussian noise. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 99, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deledalle, C.-A.; Loic, D.; Poggi, G.; Tupin, F.; Verdoliva, L. Exploiting patch similarity for SAR image processing: The nonlocal paradigm. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2014, 31, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deledalle, C.-A.; Loic, D.; Tupin, F.; Reigber, A.; Jäger, M. NL-SAR: A Unified Nonlocal Framework for Resolution-Preserving (Pol)(In)SAR Denoising. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2021–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilli, S.; Poderico, M.; Angelino, C.V.; Verdoliva, L. A Nonlocal SAR Image Denoising Algorithm Base don LLMMSE Wavelet Shrinkage. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, F.; Cozzolino, D.; Zhu, X.; Verdoliva, L.; Poggi, G. InSAR-BM3D: A Nonlocal Filter for SAR Interferometric Phase Restoration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deledalle, C.-A.; Loic, D.; Tabti, S.; Tupin, F. MuLoG, or How to apply Gaussian denoisers to multi-channel SAR speckle reduction? IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 4389–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Ding, X.; Li, Z. Hybrid Approach for Unbiased Coherence Estimation for Multitemporal InSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2459–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, R.; Nicolas, J.-M. Interferometric SAR coherence magnitude estimation using second kind statistics. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1942–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ding, X.; Li, Z.; Tian, X.; Wang, C.; Zhu, W. InSAR Coherence Estimation for Small Data Sets and Its Impact on Temporal Decorrelation Extraction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6584–6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoit, O.; Wolf, M. A well-conditioned estimator for large-dimensional covariance matrices. J. Multivar. Anal. 2004, 88, 365–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, P.J.; Fernández, J. Error estimation in multitemporal InSAR deformation time series, with application to Lanzarote, Canary Islands. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauknes, T.R.; Zebker, H.A.; Larsen, Y. InSAR Deformation Time Series Using an L1-Norm Small Baseline Approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goel, K.; Adam, N. High Resolution Deformation Time Series Estimation for Distributed Scatterers Using TerraSAR-X Data. ISPRS Ann. Photogr. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, I-7, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Sanchez, V.D.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M. Spatial Adaptive Speckle Filtering Driven by Temporal Polarimetric Statistics and Its Application to PSI. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4548–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansari, H.; De Zan, F.; Bamler, R. Sequential Estimator: Toward Efficient InSAR Time Series Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5637–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, X. Robust Estimators for Multipass SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| (Days) | Modifications | |
|---|---|---|
| 0.9 | 30, 45, 60, 90, 720, 1440 | - |
| 0.9 | 90 | One snow date |
| 0.9 | 60 | Two snow dates |
| 0.95 | 720 | Seasonal model = 0.05 |
| 0.9 | 60, 720 | Contaminated with 10% or 20% outliers |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Even, M.; Schulz, K. InSAR Deformation Analysis with Distributed Scatterers: A Review Complemented by New Advances. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050744
Even M, Schulz K. InSAR Deformation Analysis with Distributed Scatterers: A Review Complemented by New Advances. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(5):744. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050744
Chicago/Turabian StyleEven, Markus, and Karsten Schulz. 2018. "InSAR Deformation Analysis with Distributed Scatterers: A Review Complemented by New Advances" Remote Sensing 10, no. 5: 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050744
APA StyleEven, M., & Schulz, K. (2018). InSAR Deformation Analysis with Distributed Scatterers: A Review Complemented by New Advances. Remote Sensing, 10(5), 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050744