Remotely Sensing the Biophysical Drivers of Sardinella aurita Variability in Ivorian Waters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.1.1. Ocean Color Remote Sensing Data
2.1.2. Sardinella Fish Catch Dataset
2.1.3. Wind Data
2.1.4. Sea-Surface Temperature Data
2.1.5. In-Situ Data of Temperature and Nutrient Concentrations
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Estimation of Phenological Indices
2.2.2. Estimation of Upwelling Index (UI)
2.2.3. Estimation of Wind-Induced Turbulent Mixing
3. Results
3.1. Seasonal Variability of Biophysical Drivers in Ivorian Waters
3.2. Interannual Variability of Biophysical Drivers in Ivorian Waters
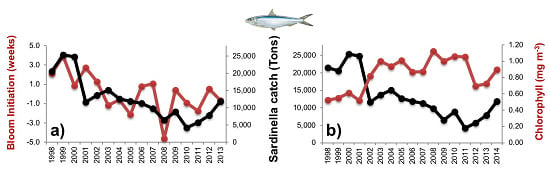
3.2.1. Phytoplankton Indices
3.2.2. Physical Indices
3.3. Diagnostic Model of Sardinella Catch
3.3.1. Empirical Relationships between Sardinella aurita and Biophysical Variables
3.3.2. Linear Regression Analysis and Model Equation
4. Discussion
4.1. Seasonal and Interannual Variability in Biophysical Conditions
4.2. Influence of Biophysical Conditions on the Recruitment of Sardinella Aurita
4.3. Relevance of Remote-Sensing Observations and Diagnostic Models for Sardinella Fisheries Management and Operational Applications
- (1)
- On a monthly basis, retrieval of data metrics, mapping of metric anomalies, and plotting of time-series metrics;
- (2)
- On a yearly basis, estimation of annual mean S. aurita catch, annual mean upwelling index, June to December mean wind-induced turbulent mixing, annual mean chlorophyll concentration, calculation of long-term chlorophyll threshold criterion and timing of initiation of the phytoplankton growing period;
- (3)
- Analysis of empirical relationships between S. aurita catch and the four biophysical variables, using data for all available years from 1998 to present;
- (4)
- If the empirical relationships are significant, estimate the new parameters of the multilinear diagnostic model and forecast, with confidence levels, the S. aurita catch in the following year; If the empirical relationships are not significant, further analyses and search of optimal diagnostic model need to be performed in consultation with experts from CURAT or other institutes, as relevant;
- (5)
- Produce an information bulletin providing an annual summary of biophysical metric status, including anomaly maps (such as presented for instance in Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 7, and Figure 8), time-series plots (for instance, as in Figure 6 and Figure 9), and the estimate, with a confidence level, of S. aurita catch forecast for the following year;
- (6)
- Review the information bulletin with the representatives in charge of the S. aurita stock assessment and issue advice on protection measures, as required;
- (7)
- Provide evidenced-based management advice to government agencies, enabling them to make informed decisions.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A




References
- Fréon, P. Les Grands Écosystèmes Mondiaux D’upwelling. Les Dossiers Thématiques de L’IRD. 2006. Available online: http://www.suds-en-ligne.ird.fr/ecosys/upwelling/upwelling.htm (accessed on 21 November 2017).
- Sherman, K. Sustainability of resources in large marine ecosystems. In Food Chains, Yields, Models, and Management of Large Marine Ecosystems; Sherman, K., Alexander, L.M., Gold, B.D., Eds.; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 1991; Volume 1, 320p. [Google Scholar]
- Bakun, A. Guinea Current Upwelling. Nature 1978, 271, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfi, R.; Pezennec, O.; Cissoko, S.; Mensah, M. Variation spatiale et temporelle de la résurgence ivoiro-ghanéene. In Pêcheries Ouest-Africaines. Variabilité, Instabilité et Changement; Cury, P., Roy, C., Eds.; Orstom: Paris, France, 1991; pp. 162–172. [Google Scholar]
- Arfi, R.; Pezennec, O.; Cissoko, S.; Mensah, M. Évolution temporelle d’un indice caractérisant l’intensité de la résurgence ivoiro-ghanéenne. In Environnement et Ressources Aquatiques de la Côte d’Ivoire; Le Loeuff, P., Koutia, A., Eds.; Orstom: Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 1993; pp. 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kassi, A.J.-B. Caractérisation et Suivi des Zones D’Upwelling Pour la Détermination des Zones de Rétention des Espèces Pélagiques Dans le Golfe de Guinée à L’Aide de la Télédétection et du Système D’Information Géographique: Cas de la Côte d’Ivoire. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Felix Houphouet-Boigny, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2012; 124p. [Google Scholar]
- Binet, D. Influences des variations climatiques sur la pêcherie des Sardinella aurita ivoiro-ghanéenne: Relation sécheresse-surpêche. Oceanol. Acta 1982, 5, 443–452. [Google Scholar]
- Chika, N.U.; Chidi, A.I.; Kenneth, S. A sixteen-country mobilization for sustainable fisheries in the Guinea Current Large Marine Ecosystem. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2006, 49, 385–412. [Google Scholar]
- Bakun, A.; Parrish, H.P. Turbulence, transport, and pelagic fish in the California and Peru current systems. CalCOFI Rep. 1982, XXIII, 99–112. [Google Scholar]
- Bakun, A.; Roy, C.; Cury, P. The comparative approach: Latitude dependence and effects of wind forcing on reproductive success. Sess. V SARP 1991, 45, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, T.; Fuentes-Yaco, C.; Frank, K. Spring algal bloom and larval fish survival. Nature 2003, 423, 398–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, T.; Sathyendranath, S. Ecological indicators for the pelagic zone of the ocean from remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3426–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, M.R. Field investigations on the early life stages of marine fish. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1992, 28, 1–174. [Google Scholar]
- Hjort, J. Fluctuations in the great fisheries of northern Europe, viewed in the light of biological research. In Rapports ET Proces-Verbaux. International Council for the Exploration of the Sea; Andr. Fred. Host & Fils: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1914; Volume 20, 228p. [Google Scholar]
- Lasker, R. Field criteria for survival of anchovy larvae: The relation between inshore chlorophyll maximum layers and successful first feeding. Fish. Bull. US 1975, 73, 453–678. [Google Scholar]
- Lasker, R.; Zweifel, J.R. Growth and survival of first-feeding northern anchovy (Engraulis mordax) in patches containing different proportions of large and small prey. In Spatial Pattern in Plankton Communities; Steele, J.H., Ed.; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 329–354. [Google Scholar]
- Lasker, R. The role of a stable ocean in larval fish survival and subsequent recruitment. In Marine Fish Larvae, Morphology, Ecology and Relation to Fisheries; University Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1981; pp. 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Cushing, D.H. Plankton production and year-class strength in fish populations: An update of the match/mis-match hypothesis. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1990, 26, 249–293. [Google Scholar]
- Koeller, P.; Fuentes-Yaco, C.; Platt, T.; Sathyendranath, S.; Richards, A.; Ouellet, P.; Orr, D.; Skúladóttir, U.; Wieland, K.; Savard, L.; et al. Basin-scale coherence in phenology of shrimps and phytoplankton in the North Atlantic. Science 2009, 324, 791–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iles, T.D.; Sinclair, M. Atlantic herring: Stock discreteness and abundance. Science 1982, 215, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, M. Marine Populations: An Essay on Population Regulation and Speciation; Washington Sea Grant Program, University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1988; 252p. [Google Scholar]
- Bakun, A. Comparative studies and the recruitment problem: Searching for generalizations. CalCOFI Rep. 1985, 26, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Binet, D. Phytoplancton et production primaire des régimes côtiers à upwelling saisonniers dans le golfe de Guinée. Océanogr. Trop. 1983, 18, 231–335. [Google Scholar]
- Binet, D. Zooplancton des régions côtières à upwellings saisonnières du Golfe de Guinée. Océanogr. Trop. 1983, 18, 357–380. [Google Scholar]
- Herbland, A.; Leloeuff, P. Les sels nutritifs au large de la Côte d’Ivoire. In Environnement et Ressources Aquatiques en Côte d’Ivoire; Orstom: Paris, France, 1993; pp. 123–148. [Google Scholar]
- John, A.W.G.; Reid, P.C.; Batten, S.D.; Anang, E.R. Monitoring Levels of “phytoplankton color” in the Gulf of Guinea Using Ships of Opportunity. In The Gulf of Guinea Large Marine Ecosystem; McGlade, J.M., Cury, P., Koranteng, K.A., Hardmann-Mountford, N.J., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Djagoua, E.M.V. Contribution de L’Imagerie Satellitaire Visible et Infrarouge Thermique à L’Étude de la Variabilité Spatio-Temporelle des Phénomènes Physiques de Surface du Littoral Marin Ivoirien et Implication dans la Variabilité du Phytoplancton et des Prises de Sardinella Aurita. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Cocody, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2003; 136p. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, K.; Mélin, F. Variability of chlorophyll-a concentration in the Gulf of Guinea and its relation to physical oceanographic variables. Prog. Oceanogr. 2017, 151, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandonneau, Y. Étude du phytoplancton sur le plateau continental de Côte-d’Ivoire: III Facteurs dynamiques et variations spatio-temporelles. Cah. Orstom Sér. Océanogr. 1973, 11, 431–454. [Google Scholar]
- Severin-Reyssac, J. Phytoplancton et production primaire dans les eaux marines Ivoiriennes. In Environnement et Ressources Aquatiques de la Côte d’Ivoire: I-Le Milieu Marin; Orstom: Paris, France, 1993; pp. 151–166. [Google Scholar]
- Arfi, R.; Bouvy, M.; Ménard, F. Environmental variability at a coastal station near Abidjan: Oceanic and continental influences. In The Gulf of Guinea Large Marine Ecosystem: Environmental Forcing and Sustainable Development of Marine Resources; Large Marine Ecosystems Series; McGlade, J.M., Cury, P., Koranteng, K.A., Hardman-Mountford, N.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 103–118. ISBN 0-444-51028-1. [Google Scholar]
- Djagoua, V.; Affian, K.; Larouche, P.; Saley, B. Variabilité saisonnière et interannuelle de la concentration de la chlorophylle dans le Golfe de Guinée à partir des images SeaWiFS. Télédétection 2006, 6, 143–151. [Google Scholar]
- Kassi, A.J.-B. Variabilité de L’Intensité de L’Upwelling Ivoiro-Ghanéen et son Impact sur la Biomasse Phytoplanctonique à L’Aide du Capteur MODIS du Satellite Aqua (2002–2005). Master’s Thesis, Université de Cocody, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kassi, J.-B.; Djagoua, E.V.; Mobio, A.B.; Gougnon, A.R.; Affian, K.; Tiemélé, J.A.; Kouadio, M.J.; Dro, C.Z.; Kouamé, A.D. Determination of the retention areas of pelagic species in Ivorian coastal water using remote sensing and geographic information system (GIS). Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 869–877. [Google Scholar]
- Pezennec, O.; Marchal, E.; Bard, F.X. Les espèces pélagiques côtières en Côte d’Ivoire: Ressources et exploitation. In Environnement et Ressources Aquatiques de la Côte d’Ivoire: I-Le Milieu Marin; Orstom: Paris, France, 1993; pp. 387–426. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, C.; Cury, P.; Kifani, S. Pelagic fish recruitment success and reproductive strategy in upwelling areas: Environmental compromises. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1992, 12, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koné, V.; Lett, C.; Penven, P.; Bourlès, B.; Djakouré, S. A biophysical model of S. aurita early life history in the northern Gulf of Guinea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2017, 151, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fréon, P. Réponses et Adaptations des Stocks de Clupéidés D’Afrique de L’Ouest à la Variabilité du Milieu et de L’Exploitation. Analyse et Réflexion à Partir de L’Exemple du Sénégal; Etudes et Thèses; Orstom: Paris, France, 1988; 287p. [Google Scholar]
- Massuti, O.M. La ponte de la sardine (Sardina pilchardus WALB.) dans le détroit de Gibraltar, la Mer d’Alboran, les eaux du Levant Espagnol et des Îles Baléares. Débats et Documents Techniques du Conseil Général des pêches pour la Méditerranée 1955, 3, 103–130. [Google Scholar]
- Komarovsky, B. A study of the food of Sardinella aurita off the Mediterranean coast of Israel during a peak season (May–June 1958). Débats et Documents Techniques du Conseil Général des pêches pour la Méditerranée 1959, 5, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Binet, D.; Marchal, E. The Large Marine Ecosystem of Shelf Areas in the Gulf of Guinea: Long-Term Variability Induced by Climatic Changes. In Large Marine Ecosystems: Stocks, Mitigation and Sustainability; Shermon, K., Alexander, L.M., Gold, B.D., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA; 1993; pp. 104–118. [Google Scholar]
- Marchal, E. Biologie et Ecologie des poissons péIagiques côtiers. In Environnement et Ressource Aquatiques de Côte d’Ivoire: I-Le Milieu Marin; Le Loeuff, P., Marchal, E., Amon Kothias, J.-B., Eds.; Orstom: Paris, France, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- DPH. Annuaire des Statistiques des Pêches et de L’Aquaculture Service des Études, des Statistiques et de la Documentation: Rapport D’Activité de Janvier 1997 à Décembre 2015; Direction de L’Aquaculture et des Pêches (DAP): Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Binet, D. Le zooplancton du plateau continental ivoirien: Essai de synthèse écologique. vOceanol. Acta 1979, 2, 397–410. [Google Scholar]
- Sathyendranath, S.; Krasemann, H. Climate Assessment Report: Ocean Color Climate Change Initiative (OC-CCI)—Phase One. 2014. Available online: http://www.esa-oceancolour-cci.org/?q=documents (accessed on 21 November 2017).
- Jackson, T.; Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T. An Exact Solution for Modeling Photoacclimation of the Carbon-to-Chlorophyll Ratio in Phytoplankton. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Baith, K.S.; McClain, C.R. The SeaWiFS Data Analysis System. In Proceedings of the 4th Pacific Ocean Remote Sensing Conference, Qingdao, China, 28–31 July 1998; pp. 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz, F.; Deschamps, P.; Ramon, D. Atmospheric correction in presence of sun glint: Application to MERIS. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racault, M.-F.; Platt, T.; Sathyendranath, S.; Ağirbaș, E.; Vicente-Martinez, V.; Brewin, R. Plankton indicators and ocean observing systems: Support to the marine ecosystem state assessment. J. Plankton Res. 2014, 36, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caddy, J.F.; Rodhouse, P.G. Cephalopod and groundfish landings: Evidence for ecological change in global fisheries. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1998, 8, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanatos, E.; Raitsos, D.E.; Triantafyllou, G.; Somarakis, S.; Tsonis, A.A. Indications of a climate effect on Mediterranean fisheries. Clim. Chang. 2014, 122, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakopoulos, P.; Raitsos, D.E.; Tzanatos, E.; Maravelias, C.D. Resilience dynamics and regime shifts in a marine biodiversity hotspot. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fréon, P.; Mullon, C.; Voisin, B. Investigating remote synchronous patterns in fisheries. Fish. Oceanogr. 2003, 12, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, R.; Pauly, D. Systematic distortions in world fisheries catch trends. Nature 2001, 414, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froese, R.; Kleiner, K.; Zeller, D.; Pauly, D. What catch data can tell us about the status of global fisheries. Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyer, T.P.; Antonov, J.I.; Baranova, O.K.; Coleman, C.; Garcia, A.; Grodsky, D.R. NOAA Atlas NESDIS 72. World Ocean Database 2013; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2013.
- Racault, M.-F.; Le Quéré, C.; Buitenhuis, E.; Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T. Phytoplankton phenology in the global ocean. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 14, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.A.; Doney, S.C.; Yoder, J.A. The North Atlantic spring phytoplankton bloom and Sverdrup’s critical depth hypothesis. Science 2002, 296, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakun, A. Coastal Upwelling Indices, West Coast of North America, 1946–1971; NOAA Technical Report; US Department of Commerce, NMFS SSAF: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1973; 103p.
- Ekman, V. On the influence of the earth’s rotation on ocean-currents. Ark. Mat. Astron. Fys. 1905, 2, 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Moliere, A. Les saisons marines devant Abidjan. Doc. Sci. Centre Rech. Océanogr. Abidjan 1970, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Moliere, A.; Rebert, J.P. Etude hydrologique du plateau continental Ivoirien. Doc. Sci. Centre Rech. Océanogr. Abidjan 1972, 3, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Varlet, F. Le régime de l’Atlantique près d’Abidjan (Côte d’Ivoire). Etudes Eburn. 1958, 7, 97–222. [Google Scholar]
- Colin, C.; Bakayoko, S. Variations saisonnières des structures hydrologiques et dynamiques observées sur le plateau continental ivoirien. In Archives Scientifiques; Centre de Recherche Océanographique: Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 1984; Volume 10, 64p. [Google Scholar]
- Colin, C.; Cissoko, S. Observations hydrologiques et dynamiques le long de deux radiales du plateau continental Ivoirien pendant l’année focal 1983. In Archives Scientifiques; Centre de Recherche Océanographique: Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 1984; Volume 10, 99p. [Google Scholar]
- Koranteng, K.A.; McGlade, J.M. Climatic trends in continental shelf waters off Ghana and in the Gulf of Guinea: 1963–1992. Oceanol. Acta 2002, 24, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbland, A.; Voituriez, B. Relation chlorophylle-a—Fluorescence in vivo dans l’atlantique tropical influence de la structure hydrologique. Cahiers O.R.S.T.O.M. Série Océanographie 1977, XV, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Micheli, F. Eutrophication, fisheries and consumer-resources dynamics in marine pelagic ecosystems. Science 1999, 285, 1396–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, G.; Treguer, P. Ecosystèmes pélagiques marins. In Collection d’Ecologie; Masson: Paris, France, 1986; 243p. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, J.P.; Davis, C.O.; Tufillaro, N.B.; Kudela, R.M.; Gao, B. Application of the Hyperspectral Imager for the Coastal Ocean to Phytoplankton Ecology Studies in Monterey Bay, CA, USA. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1007–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassi, A.J.-B.; Mobio, A.B.H.; Kouadio, M.J.; Tiemele, J.A. Seasonal Variation of Thermocline Depth: Consequence on Nutrient Availability in the Ivorian Coastal Zone. Eur. Sci. J. 2017, 13, 215–231. [Google Scholar]
- Ryther, J.H. The Sea; Hill, M.N., Ed.; Interscience: London, UK, 1963; pp. 347–380. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, C. An upwelling-induced retention area off Senegal: A mechanism to link upwelling and retention processes. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1998, 19, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, P.; Roy, C. Optimal environmental window and pelagic fish recruitment success in upwelling areas. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 46, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzelj, S. Etude de la Distribution et de L’Abondance des Larves de Clupéidés sur le Plateau Continental Ivoirien; Projet de Développement de la Pêche Pélagique Côtière Durant la Période 1971–72, FAO/PNUD IVC 6/288; Ministère de la Production Animale: Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 1972; 15p. [Google Scholar]
- Nieland, H. Die Nahrung von Sardinen, Sardinellen, und Maifischen vor der Westküste Afrikas; Institut Für Meereskunde an der Universitat Kiel: Kiel, Germany, 1980; 137p. [Google Scholar]
- Nieland, H. The food of Sardinella aurita (Val.) and S. eba (Val.) off the coast of Senegal. Rapp. P. V. Réun. Cons. Inl. Explor. Mer. 1982, 180, 369–373. [Google Scholar]
- Dia, A.E.K. Étude de la Nutrition de Certains Clupéidés (Poissons Téléostéens) de Côte d’Ivoire; CRO: Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 1972; Available online: http://www.documentation.ird.fr/hor/fdi:06674 (accessed on 21 November 2017).
- Van Thielen, R. The food of Sardinella aurita and of juvenile and adult Anchoa guineensis in near shore waters off Ghana, West Africa. Meeresforsch 1976, 25, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ghéno, Y.; Fontana, A. La Peche des Sardinelles à Pointe-Noire en 1970–1971–1972; Documents Centre ORSTOM: Pointe-Noire, Congo, 1973; Volume 33, 9p. [Google Scholar]
- PRU/ORSTOM. Rapport du Groupe de Travail sur la Sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) des cotes Ivoiro-Ghaneenes; ORSTOM: Paris, France, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Social and economic performance of tilapia farming in Africa. In Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular; Cai, J., Quagrainie, K.K., Hishamunda, N., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017; Volume 1130. [Google Scholar]
- Cury, P.; Roy, C. Upwelling et pêche des espèces pélagiques côtières des cotes de Côte d’Ivoire: Une approche globale. Oceanol. Acta 1987, 10, 347–357. [Google Scholar]
- Cury, P.; Roy, C. Environmental forcing and fisheries resources in Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana: Did something happen? In The Gulf of Guinea Large Marine Ecosystem: Environmental Forcing and Sustainable Development of Marine Resources (Large Marine Ecosystems Series); McGlade, J.M., Cury, P., Koranteng, K.A., Hardman-Mountford, N.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 241–260. ISBN 0-444-51028-1. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, V.; Cury, P. Pelagic fisheries and environmental constraints in upwelling areas: How much is possible? In Global Versus Local Changes in Upwelling Systems; Durand, M-H., Cury, P., Mendelssohn, R., Roy, C., Bakun, A., Pauly, D., Eds.; ORSTOM: Paris, France, 1998; pp. 391–407. ISBN 2-7099-1389-5. [Google Scholar]
- Cushing, D.H. Marine Ecology and Fisheries; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Sathyendranath, S.; Stuart, V.; Nair, A.; Oka, K.; Nakane, T.; Bouman, H.; Forget, M.-H.; Maass, H.; Platt, T. Carbon-to-chlorophyll ratio and growth rate of phytoplankton in the sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 383, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervigón, F.; Cipriani, R.; Fischer, W.; Garibaldi, L.; Hendrick, M.; Lemus, A.J.; Márquez, R.; Poutiers, J.M.; Robaina, G.; Rodriguez, B. Fichas FAO de identificación de especies para los fines de la pesca. In Guía de Campo de las Especies Comerciales Marinas y de Aquas Salobres de la Costa Septentrional de Sur América; Preparado con el financiamento de la Comisión de Comunidades Europeas y de NORAD; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1992; 513p. [Google Scholar]
- Aldebert, Y.; Tournier, H. Reproduction de la sardine dans le golfe du lion son importance pour l’avenir de la pêche. Sci. Pêche 1967, 159, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Caldeira, C.; Santos, A.M.P.; Ré, P.; Peck, M.A.; Saiz, E.; Garrido, S. Effects of prey concentration on ingestion rates of European sardine Sardina pilchardus larvae in the laboratory. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 517, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Yearbook of Fishery Statistics; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005; Volume 96. [Google Scholar]
- Belouahem, S. An Ecosystemic Approach to Fisheries. The Algerian Case. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Montpellier II, Montpellier, France, 2009; 96p. [Google Scholar]
- Gros, P. Production durable de ressources alimentaires marines: Des pêcheries viables dans un monde changeant. Inst. Fr. Nutr. 2008, 130, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Gascuel, D. Halieutique: Peut-on exploiter les ressources vivantes marines de manière durable? In Module E-Learning UVED Dynamique des Ressources Naturelles; Pôle Halieutique Agrocampus Rennes, UMR INRA/Agrocampus “Ecologie et santé des écosystèmes”; 2015; Chapter 9.2; Available online: https://ressources.uved.fr/modules/moduleDynRessNat/html/m2c3_m2c3p2_1.html (accessed on 21 November 2017).
- Polidoro, B.; Ralph, G.M.; Strongin, K.; Harvey, M.; Carpenter, K.E.; Adeofe, A.T.; Arnold, R.; Bannerman, P.; Nguema, J.-N.B.B.; Buchanan, J.R.; et al. Red List of Marine Bony Fishes of the Eastern Central Atlantic; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2016; 80p, ISBN 978-2-83-171795-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failler, P.; Hachim El, A.; Konan, A. Industrie des Pêches et de L’Aquaculture en Côte d’Ivoire; Rapport n°7 de la Revue de L’industrie des Pêches et de L’aquaculture dans la zone de la COMHAFAT; ATLAFCO: Rabat, Marocco, 2014; 99p. [Google Scholar]
- Ekouala, L. Le Développement Durable et le Secteur des Pêches et de L’Aquaculture au Gabon: Une Étude de la Gestion Durable des Ressources Halieutiques et de Leur Écosystème Dans les Provinces de L’Estuaire et de L’Ogooué Maritime. Ph.D. Thesis, Université du Littoral Côte d’Opale, Dunkirk, France, 2013; 408p. [Google Scholar]
- Bakun, A. Global Climate Change and Intensification of Coastal Ocean Upwelling. Science 1990, 247, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niang, I.; Ruppel, O.C.; Abdrabo, M.A.; Essel, A.; Lennard, C.; Padgham, J.; Urquhart, P. Africa. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part B: Regional Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Barros, V.R., Field, C.B., Dokken, D.J., Mastrandrea, M.D., Mach, K.J., Bilir, T.E., Chatterjee, M., Ebi, K.L., Estrada, Y.O., Genova, R.C., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1199–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Bamba, A.; Dieppois, B.; Konaré, A.; Pellarin, T.; Balogun, A.; Dessay, N.; Kamagaté, B.; Savané, I.; Diédhiou, A. Changes in Vegetation and Rainfall over West Africa during the Last Three Decades (1981–2010). Atmos. Clim. Sci. 2015, 5, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checkley, D.M., Jr.; Asch, R.G.; Rykaczewski, R.R. Climate, Anchovy, and Sardine. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2017, 9, 469–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kassi, J.-B.; Racault, M.-F.; Mobio, B.A.; Platt, T.; Sathyendranath, S.; Raitsos, D.E.; Affian, K. Remotely Sensing the Biophysical Drivers of Sardinella aurita Variability in Ivorian Waters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050785
Kassi J-B, Racault M-F, Mobio BA, Platt T, Sathyendranath S, Raitsos DE, Affian K. Remotely Sensing the Biophysical Drivers of Sardinella aurita Variability in Ivorian Waters. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(5):785. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050785
Chicago/Turabian StyleKassi, Jean-Baptiste, Marie-Fanny Racault, Brice A. Mobio, Trevor Platt, Shubha Sathyendranath, Dionysios E. Raitsos, and Kouadio Affian. 2018. "Remotely Sensing the Biophysical Drivers of Sardinella aurita Variability in Ivorian Waters" Remote Sensing 10, no. 5: 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050785
APA StyleKassi, J. -B., Racault, M. -F., Mobio, B. A., Platt, T., Sathyendranath, S., Raitsos, D. E., & Affian, K. (2018). Remotely Sensing the Biophysical Drivers of Sardinella aurita Variability in Ivorian Waters. Remote Sensing, 10(5), 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050785