InSAR Reveals Land Deformation at Guangzhou and Foshan, China between 2011 and 2017 with COSMO-SkyMed Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Dataset and Methodology
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Methodology
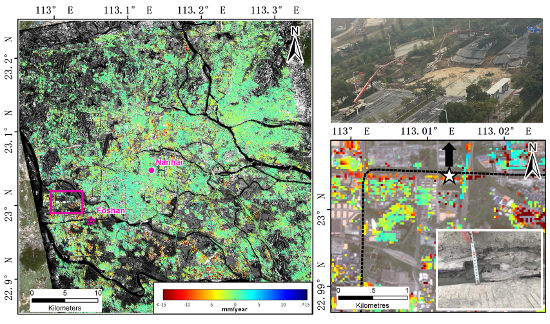
4. InSAR Results
5. Discussion
5.1. General Land Displacement Pattern and Evolution
5.2. Groundwater Subsidence
5.3. Subsidence Observed along the Subway/Railway Lines
5.4. Identification of Potential Areas of Risk
5.5. TS-InSAR Results in Different Land Use Types
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Kettner, A.J.; Overeem, I.; Hutton, E.W.H.; Hannon, M.T.; Brakenridge, G.R.; Day, J.; Vörösmarty, C.; Saito, Y.; Giosan, L.; et al. Sinking deltas due to human activities. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakr, M. Influence of groundwater management on land subsidence in Deltas. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1541–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wright, T.J.; Yu, Y.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L.; Li, C.; Qiu, G. InSAR reveals coastal subsidence in the Pearl River Delta, China. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L.; Chen, F.; Cheng, S. A study of ground deformation in the Guangzhou urban area with Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Sensors 2009, 9, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Xu, B.; Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhu, J. Deriving spatio-temporal development of ground subsidence due to subway construction and operation in delta regions with PS-InSAR data: A case study in Guangzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z. Ground subsidence geo-hazards induced by rapid urbanization: Implications from InSAR observation and geological analysis. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, K. The changing pattern of urban flooding in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, H.-M.; Wang, G.-F.; Shen, J.; Lu, L.-H.; Wang, G.-Q. Analysis and GIS mapping of flooding hazards on 10 May 2016, Guangzhou, China. Water 2016, 8, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strozzi, T.; Delaloye, R.; Poffet, D.; Hansmann, J.; Loew, S. Surface subsidence and uplift above a headrace tunnel in metamorphic basement rocks of the Swiss Alps as detected by satellite SAR interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milillo, P.; Giardina, G.; DeJong, M.; Perissin, D.; Milillo, G. Multi-Temporal InSAR Structural Damage Assessment: The London Crossrail Case Study. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, J.G.; Black, M.; Gomar, B.S. Correlation Study between In-Situ Auscultation and Satellite Interferometry for the Assessment of Nonlinear Ground Motion on Crosrail London; Crossrail Learning Legacy Report: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chaussard, E.; Milillo, P.; Burgmann, R.; Perissin, D.; Fielding, J.F.; Baker, B. Remote Sensing of Ground Deformation for Monitoring Groundwater Management Practices: Application to the Santa Clara Valley During the 2012–2015 California Drought. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 8566–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonì, R.; Cigna, F.; Bricker, S.; Meisina, C.; McCormack, H. Characterisation of hydraulic head changes and aquifer properties in the London Basin using Persistent Scatterer Interferometry ground motion data. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A new algorithm for processing Interferometric Data-Stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent Scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using Permanent Scatterers in Differential SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beradino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampes, B.M. Radar Interferometry: Persistent Scatterer Technique, 1st ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2006; p. 211. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Ge, L.; Ng, A.H.-M.; Xiaojing, L.; Li, L. Mapping land subsidence over the eastern Beijing city using Satellite Radar Interferometry. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2017, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.-M.; Ge, L.; Li, X. Assessments of land subsidence in the Gippsland Basin of Australia using ALOS PALSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Ng, A.H.-M.; Li, X.; Abidin, H.Z.; Gumilar, I. Land subsidence characteristics of Bandung Basin as revealed by ENVISAT ASAR and ALOS PALSAR Interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H. Shanghai subway tunnels and highways monitoring through Cosmo-SkyMed Persistent Scatterers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 73, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.-M.; Ge, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, X. Estimating horizontal and vertical movement due to underground mining using ALOS PALSAR. Eng. Geol. 2012, 143–144, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lin, H.; Zhou, W.; Hong, T.; Wang, G. Surface deformation detected by ALOS PALSAR Small Baseline SAR Interferometry over permafrost environment of Beiluhe section, Tibet Plateau, China. Remote Sens Environ. 2013, 138, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L. Ground deformation monitoring in Pearl River Delta region with Stacking D-InSAR technique. In Geoinformatics 2008 and Joint Conference on GIS and Built Environment: Monitoring and Assessment of Natural Resources and Environments; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2008; Volume 7145. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yu, Y.-P.; Jiang, L.L. Monitoring land subsidence in Guangzhou and Foshan using InSAR. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2014, 39, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Nof, R.N.; Baer, G.; Ziv, A.; Raz, E.; Atzori, S.; Salvi, S. Sinkhole precursors along the Dead Sea, Israel, revealed by SAR interferometry. Geology 2013, 41, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Hanssen, R.F. Detection of cavity migration and sinkhole risk using Radar Interferometric time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.-J.; Shen, S.-L.; Cheng, W.-C.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Z.-F. Geological formation and geo-hazards during subway construction in Guangzhou. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shen, S.L.; Wu, H.N.; Wang, Z.F.; Horpibulsuk, S. Geotechnical characteristics of weathered granitic gneiss with geo-hazards investigation of pit excavation in Guangzhou, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2017, 76, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.-M.; Ge, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, K. Monitoring ground deformation in Beijing, China with Persistent Scatterer SAR Interferometry. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Rossi, M.; Carmona, C.; Adragna, F.; Peltzer, G.; Feigl, K.; Rabaute, T. The displacement field of the Landers Earthquake mapped by Radar Interferometry. Nature 1993, 364, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Ng, A.H.-M.; Wang, H.; Rizos, C. Crustal deformation in Australia measured by Satellite Radar Interferometry using ALOS/PALSAR imagery. J. Appl. Geod. 2009, 3, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Morris, C.S.; Belz, J.E.; Chapin, E.C.; Martin, J.M.; Daffer, W.; Hensley, S. An Assessment of the SRTM Topographic Products; Report No. JPL D-31639; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2005.
- Guarnieri, A.M.; Tebaldini, S. On the exploitation of target statistics for SAR Interferometry applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3436–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colesanti, C.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. SAR monitoring of progressive and seasonal ground deformation using the Permanent Scatterers technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1685–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.-M.; Ge, L.; Li, X.; Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Zhang, K. Mapping land subsidence in the Jakarta city, Indonesia using Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) technique with ALOS PALSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 18, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialko, Y.; Simons, M.; Agnew, D. The complete (3-D) surface displacement field in the epicentral area of the 1999 Mw 7.1 Hector Mine Earthquake, California, from space geodetic observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 3063–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M. Foshan Groundwater Resources to be Thoroughly. Guangzhou Daily, 11 January 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, H.; Gu, Z.; Wang, R.; Li, X.; Zhao, W. Characterization of land subsidence induced by groundwater withdrawals in the plain of Beijing city, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, B.; Dai, Z.; Teatini, P. Land subsidence due to groundwater withdrawal in the Northern Beijing Plain, China. Eng. Geol. 2015, 193, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangsaatmaja, S.; Sutadian, A.D.; Prasetiati, M.N. A review of groundwater issues in the Bandung Basin, Indonesia: Management and recommendations. Int. Rev. Environ. Strateg. 2006, 6, 425–441. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Li, Y. Residents are Worried about Frequent Cracks Found in Half of the Residential Buidlings in an Area of Haizhu. Guangzhou News Express, 30 March 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C. Engineering geologic problems of Guangzhou Metro Line 5 and the countermeasures. Urban Mass Transit 2006, 7, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- AFP. Massive Sinkhole the Size of Two Basketball Courts Swallows Eight-Lane Road in a Chinese City, Leaving at Least Eight Dead. Daily Mail, 8 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.-N.; Sun, Z.-J.; Yu, J.-L. Analysis of displacement of adjacent buried pipeline caused by ground surcharge. Rock Soil Mech. 2015, 36, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Prassetyo, S.H.; Gutierrez, M. Effect of surface loading on the hydro-mechanical response of a tunnel in saturated ground. Undergr. Sp. 2016, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




















| Land Use Type | Land Use Sub-Type | PS + DS | PS * | DS ** | Area (km2) | PS Density (point/km2) | DS Density (point/km2) | Mean Subsidence Rate (mm/year) | Subsidence Rate Standard Deviations (mm/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building | 1,052,854 | 48,358 | 1,004,496 | 253.6 | 190.7 | 3961.7 | −0.2 | 1.8 | |
| Low-rise building | 402,511 | 18,611 | 383,900 | 115.7 | 160.8 | 3317.4 | −0.5 | 2.1 | |
| High-rise building | 650,343 | 29,747 | 620,596 | 137.8 | 215.8 | 4502.7 | −0 | 1.5 | |
| Woodland | 24,378 | 866 | 23,512 | 28.4 | 30.5 | 827.9 | −0.8 | 2.7 | |
| Orchard | 2088 | 86 | 2002 | 5.4 | 15.9 | 370.7 | −1.6 | 2.8 | |
| Nursery land | 21,400 | 752 | 20,648 | 21.7 | 34.7 | 952.3 | −0.7 | 2.7 | |
| Mulberry farm | 890 | 28 | 862 | 1.3 | 21.2 | 653.8 | −1.5 | 3.9 | |
| Forest | 78,847 | 3992 | 74,855 | 71.7 | 55.7 | 1043.5 | −0.4 | 1.9 | |
| Bamboo | 39,271 | 1928 | 37,343 | 14.5 | 132.7 | 2569.6 | −0.7 | 2.1 | |
| Shrub | 1026 | 44 | 982 | 1.4 | 31.2 | 697.3 | −0.7 | 2.4 | |
| Tree Forest | 38,550 | 2020 | 36,530 | 55.8 | 36.2 | 654.8 | −0.1 | 1.7 | |
| Crop land | 8949 | 518 | 8431 | 14.3 | 36.2 | 590.0 | −1 | 2.9 | |
| Paddy field | 560 | 8 | 552 | 1.8 | 4.5 | 307.7 | −2 | 3.6 | |
| Dry land | 8389 | 510 | 7879 | 12.5 | 40.8 | 630.5 | −1 | 2.8 | |
| Grassland | 23,992 | 661 | 23,331 | 12.4 | 53.2 | 1877.5 | −1.4 | 3.6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ng, A.H.-M.; Wang, H.; Dai, Y.; Pagli, C.; Chen, W.; Ge, L.; Du, Z.; Zhang, K. InSAR Reveals Land Deformation at Guangzhou and Foshan, China between 2011 and 2017 with COSMO-SkyMed Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060813
Ng AH-M, Wang H, Dai Y, Pagli C, Chen W, Ge L, Du Z, Zhang K. InSAR Reveals Land Deformation at Guangzhou and Foshan, China between 2011 and 2017 with COSMO-SkyMed Data. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(6):813. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060813
Chicago/Turabian StyleNg, Alex Hay-Man, Hua Wang, Yiwei Dai, Carolina Pagli, Wenbin Chen, Linlin Ge, Zheyuan Du, and Kui Zhang. 2018. "InSAR Reveals Land Deformation at Guangzhou and Foshan, China between 2011 and 2017 with COSMO-SkyMed Data" Remote Sensing 10, no. 6: 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060813
APA StyleNg, A. H. -M., Wang, H., Dai, Y., Pagli, C., Chen, W., Ge, L., Du, Z., & Zhang, K. (2018). InSAR Reveals Land Deformation at Guangzhou and Foshan, China between 2011 and 2017 with COSMO-SkyMed Data. Remote Sensing, 10(6), 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060813