Using InSAR Coherence for Investigating the Interplay of Fluvial and Aeolian Features in Arid Lands: Implications for Groundwater Potential in Egypt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. General Setting of the Study Area
3. Data and Methods
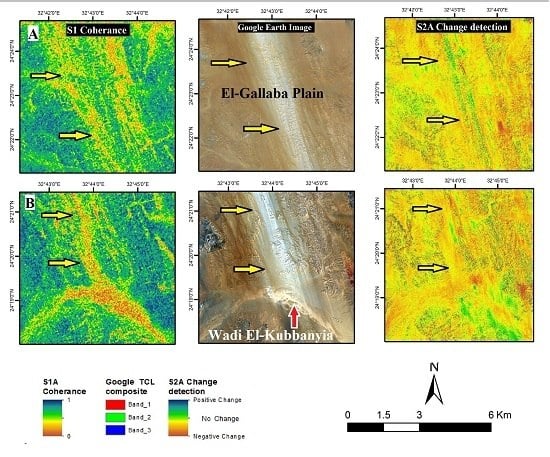
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayouty, M.K.; Ezzat, M.A. Hydrogeological observations in the search for underground water in the Western Desert of Egypt. IASH Symp. Athens I 1961, 56, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov, M.I. Groundwater of Egypt; Desert Institute, the Hydrology Division, the General Desert Development Organization: Cairo, Egypt, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- CEDARE. Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System (NSAS) M&E Rapid Assessment Report; Monitoring & Evaluation for Water In North Africa (MEWINA) Project, Water Resources Management Program; CEDARE: Cairo, Egypt, 2014; pp. 1–95. [Google Scholar]
- Voss, C.; Soliman, S.M. The transboundary non-renewable Nubian aquifer system of Chad, Egypt, Libya and Sudan: Classical groundwater questions and parsimonious hydrogeologic analysis and modelling. In Environmental Geochemistry and Health, with Special Reference to Developing Countries; Appleton, J.D., Fuge, R., McCall, G.J.H., Eds.; Geological Society Special Publication: London, UK, 2014; pp. 163–181. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnold, R.A. Journeys in the Libyan Desert. Geogr. J. 1931, 78, 13–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R.A. The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes; Methuen and Company: London, UK, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Sandford, K.S. Geology and Geomorphology of the Southern Libyan Desert. Geogr. J. 1933, 82, 213–219. [Google Scholar]
- Peel, R.F. The Gilf Kebir: Part 4. An Expedition to the Gilf Kebir and Uweinat, 1938. Geogr. J. 1939, 93, 297–307. [Google Scholar]
- Said, R. The Geology of Egypt; Elsevier Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Issawi, B. Geology of the Kurkur-Dungul area. Annals of the Geological Survey of Egypt; United States Congress Joint Committee on Printing: Washington, DC, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Issawi, B. New findings in the Gilf-Uweinat area. In Annals of the Geological Survey of Egypt; The Geological Survey of Egypt and Mining Authority: Cairo, Egypt, 1978; Volume 11, pp. 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- El-Baz, F. The meaning of desert color in Earth orbital photographs. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1978, 44, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- McCauley, J.F.; Schaber, G.G.; Breed, C.S.; Grolier, M.J.; Haynes, C.V.; Issawi, B. Subsurface valleys and geoarchaelology of Egypt and Sudan revealed by radar. Science 1982, 218, 1004–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elachi, C.; Roth, L.E.; Schaber, G.G. Spaceborne radar subsurface imaging in hyper-arid regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1984, 22, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaber, G.G.; McCauley, J.F.; Breed, C.S.; Olhoeft, G.R. Shuttle imaging radar: Physical controls on signal penetration and subsurface scattering in the eastern Sahara. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, 24, 603–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.G.; Elachi, C.; Hartl, P.; Chowdhury, K. Microwave penetration and attenuation in desert soil: A field experiment with the Shuttle Imaging Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, 24, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaber, G.G.; McCauley, J.F.; Breed, C.S. The use of multifrequency and polarimetric SIR-C/X-SAR data in geologic studies of Bir Safsat, Egypt. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 59, 337–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, M.G.; Robinson, C.; El-Baz, F.; Stern, R.J. Applications of orbital imaging radar for geologic studies in arid regions: The Saharan testimony. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 717–726. [Google Scholar]
- El-Baz, F. Sand accumulation and groundwater in the Eastern Sahara. Episodes 1998, 21, 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, C.A.; El-Baz, F.; Ozdogan, M.; Ledwith, M.; Blanco, D.; Oakley, S.; Inzana, J. Use of radar data to delineate palaeodrainage flow direction in the Selima sand sheet, Eastern Sahara. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 745–753. [Google Scholar]
- Paillou, P.; Grandjean, G.; Baghdadi, N.; Heggy, E.; August-Bernex, T.; Achache, J. Subsurface imaging in south-central Egypt using low-frequency radar: Bir Safsaf revisited. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1672–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillou, P.; Reynard, B.; Malézieux, J.-M.; Dejax, J.; Heggy, E.; Rochette, P.; Reimold, W.U.; Michel, P.; Baratoux, D.; Razin, P. An extended field of crater-shaped structures in the Gilf Kebir region—Egypt: Observations and hypotheses about their origin. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2006, 46, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baz, F.; Robinson, C.; Al-Saud, T. Radar images and geomorphology of the eastern Sahara. In Remote Sensing in Archaeology; Wiseman, J., El-Baz, F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ghoneim, E.; Robinson, C.; El-Baz, F. Radar topography data reveal drainage relics in the eastern Sahara. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1759–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillou, P.; Schuster, M.; Tooth, S.; Farr, T.; Rosenqvist, A.; Lopez, S.; Malézieux, J.M. Mapping of a major paleodrainage system in Eastern Libya using orbital imaging Radar: The Kufrah River. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 277, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillou, P.; Lopez, S.; Farr, T.; Rosenqvist, A. Mapping Subsurface Geology in Sahara using L-band SAR: First Results from the ALOS/PALSAR Imaging Radar. IEEE J. Select. Top. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, A.; Koch, M.; Helmi, M.; Motoyuki, S. SAR Remote Sensing of Buried Faults: Implications for Groundwater Exploration in the Western Desert of Egypt. Sens. Imaging 2011, 12, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillou, P. Mapping Palaeohydrography in Deserts: Contribution from Space-Borne Imaging Radar. Water 2017, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, G.; Gaber, A.; El-Baz, F. Mapping palaeolakes as potential areas for groundwater exploration in the Ténéré Desert of northeastern Niger using various space-borne data. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2017, 6, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, A.; Amarah, B.A.; Abdelfattah, M.; Ali, S. Investigating the use of the dual-polarized and large incident angle of SAR data for mapping the fluvial and aeolian deposits. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2017, 6, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, C.V. Great Sand Sea and Selima Sand Sheet: Geochronology of desertification. Science 1982, 217, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, B.J.; Haynes, C.V.; Maxwell, T.A. Ages of Quaternary pluvial episodes determined by uranium-series and radiocarbon dating of lacustrine deposits of Eastern Sahara. Paleogeogr. Paleoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1995, 113, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baz, F. Origin and evolution of the desert. Interdisciplin. Sci. Rev. 1988, 13, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, M.G.; Youssef, A.M.; Arafat, S.M.; Alfarhan, M. Rise and demise the New Lakes of the Sahara. Geosphere 2008, 4, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, A.; Soliman, F.; Koch, M.; El-Baz, F. Using full-polarimetric SAR data to characterize the surface sediments in desert areas: A case study in El-Gallaba Plain, Egypt. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Liu, J.G. Analysis of topographic decorrelation in SAR interferometry using ratio coherence imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.G.; Black, A.; Lee, H.; Hanaizumi, H.; Moore, J.M. Land surface change detection in a desert area in Algeria using multi-temporal ERS SAR coherence images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 2463–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodart, C.; Ozer, A. The use of SAR Interferometric Coherence images to study sandy desertification in southeast Niger: Preliminary results. In Proceedings of the 2007 ESA Symposium, Montreux, Switzerland, 23–27 April 2007; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bodart, C.; Gassani, J.; Salmon, M.; Ozer, A. Contribution of SAR interferometry (from ERS1/2) in the study of aeolian transport processes: The cases of Niger, Mauritania and Morocco. In Desertification and Risk Analysis Using High and Medium Resolution Satellite Data; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann, T.; Büdel, C.; Baumhauer, P.; Padashi, M. Sentinel-1 SAR Data Revealing Fluvial Morphodynamics in Damghan (Iran): Amplitude and Coherence Change Detection. Int. J. Earth Sci. Geophys. 2016, 2, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Havivi, S.; Amir, D.; Schvartzman, I.; August, Y.; Maman, S.; Rotman, S.; Blumberg, D. Mapping dune dynamics by InSAR coherence. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Rosen, P.A.; Goldstein, R.M.; Gabriel, A.; Werner, C.L. On the derivation of coseismic displacement fields using differential radar interferometry—The Landers earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 19617–19634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgmann, R.; Rosen, P.A.; Fielding, E.J. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry to measure Earth’s surface topography and its deformation. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colesanti, C.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. SAR monitoring of progressive and seasonal ground deformation using the permanent scatterers technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1685–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, D.G. Analysis of large aeolian (wind-blown) bedforms using the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) digital elevation data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Monti-Guarnieri, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Massonet, D. InSAR Principles-Guidelines for SAR Interferometry Processing and Interpretation; ESA Publications: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Embabi, N.S. The Geomorphology of Egypt: Landforms and Evolution. Vol. 1. The Nile Valley and Western Desert; The Egyptian Geographical Society: Cairo, Egypt, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- EGSM. Geological Map of Eastern Desert, Egypt. Scale 1:500,000; The Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation: Cairo, Egypt, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Conoco. Geological Map of Egypt, Scale 1:500,000, Sheet NG36NE Quseir, NG36NW Asyut, NG36SE Gebel Hamata, and NG36SW Luxor, Egypt; The Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation: Cairo, Egypt, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- El-Baz, F.; Mainguet, M.; Robinson, C. Fluvio-aeolian dynamics in the north-eastern Sahara: The relationship between fluvio/aeolian systems and groundwater concentration. J. Arid Environ. 2000, 44, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Gaber, A.; Gereish, M.; Zaghloul, S.; Arafat, S.; AbuBakr, M. Multisensor Characterization of Subsurface Structures in a Desert Plain Area in Egypt with Implications for Groundwater Exploration. Proc. SPIE 2013, 8887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, L.E.; Elachi, C. Coherent Electromagnetic Losses by Scattering from Volume in Homogeneities. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1975, 23, 674–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elachi, C.; Brown, W.E.; Cimino, J.B.; Dixon, T.; Evans, D.L.; Ford, J.P.; Saunders, R.S.; Breed, C.; Masursky, H.; McCauley, J.; et al. Shuttle imaging radar experiment. Science 1982, 218, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaber, A.; Koch, M.; Gereish, M.; Motoyuki, S.; El-Baz, F. Near-Surface Imaging of a Buried Foundation in the Western Desert, Egypt, Using Space-borne and Ground Penetrating Radar. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Lopez, A.; Bruniquel, J.; Vachon, P.W. Coherence Estimation for SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiss, M.; Stacy, N.J. Coherent Change Detection: Theoretical Description and Experimental Results (No. DSTO-TR-1851); Defence Science and Technology Organization: Edinburgh, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ESA. Copernicus Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Satellite Data. Available online: https://scihub.copernicus.eu/dhus/#/home (accessed on 24 May 2018).
- Jenson, S.; Dominique, J. Extracting topographic structure from digital elevation data for geographical information system analysis. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1988, 54, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar]
- El Bastawesy, M.; Faid, A.; El Gammal, S. The quaternary development of tributary channels to the Nile River at Kom Ombo area, Eastern Desert of Egypt, and their implication for groundwater resources. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 1856–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, F. Mapping of groundwater prospective zones using remote sensing and GIS techniques: A case study from the Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2012, 70, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandford, S.K. The Pliocene and Pleistocene deposits of Wadi Qena and of the Nile Valley between Luxor and Assiut (QAU). Q. J. Geol. Soc. 1929, 85, 493–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainguet, M.M. L’homme et la Secheresse; Collection Geographique: Mason, Paris, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- El-Baz, F.; Wolfe, R.W. Wind Patterns in the Western Desert; NASA Scientific and Technical Information Branch, CR-3611: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; pp. 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Hereher, M. Assessment of sand drift potential along the Nile Valley and Delta using climatic and satellite data. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 55, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainguet, M.M.; El-Baz, F. Effects of topography on dune orientation in the Farafra region, Western Desert of Egypt and implications to Mars. NASA Tech. Memo 1980, 82385, 298–300. [Google Scholar]
- Mo’men, A.; Darwish, M.; Abdelhady, A.; Essa, M.A. Structural and Lithostratigraphic evolution of Al Baraka Oil field, Komombo Basin, Upper Egypt as deduce from 2D seismic lines and well logging data. J. Basic Environ. Sci. 2017, 2, 149–169. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, T.; Koch, M.; Gumuzzio, J. Application of hyperspectral imagery to map soil salinity. In Remote Sensing of Soil Salinization: Impact and Land Management; Metternicht, G., Zinck, A., Eds.; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Publisher: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; Chapter 7; pp. 113–139. [Google Scholar]











© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaber, A.; Abdelkareem, M.; Abdelsadek, I.S.; Koch, M.; El-Baz, F. Using InSAR Coherence for Investigating the Interplay of Fluvial and Aeolian Features in Arid Lands: Implications for Groundwater Potential in Egypt. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060832
Gaber A, Abdelkareem M, Abdelsadek IS, Koch M, El-Baz F. Using InSAR Coherence for Investigating the Interplay of Fluvial and Aeolian Features in Arid Lands: Implications for Groundwater Potential in Egypt. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(6):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060832
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaber, Ahmed, Mohamed Abdelkareem, Ismail S. Abdelsadek, Magaly Koch, and Farouk El-Baz. 2018. "Using InSAR Coherence for Investigating the Interplay of Fluvial and Aeolian Features in Arid Lands: Implications for Groundwater Potential in Egypt" Remote Sensing 10, no. 6: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060832
APA StyleGaber, A., Abdelkareem, M., Abdelsadek, I. S., Koch, M., & El-Baz, F. (2018). Using InSAR Coherence for Investigating the Interplay of Fluvial and Aeolian Features in Arid Lands: Implications for Groundwater Potential in Egypt. Remote Sensing, 10(6), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060832