An Inverse Model for Raindrop Size Distribution Retrieval with Polarimetric Variables
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Representation of Raindrop Size Distribution
2.1. Gamma Model
2.2. Bulk Properties of DSD
2.3. Dataset
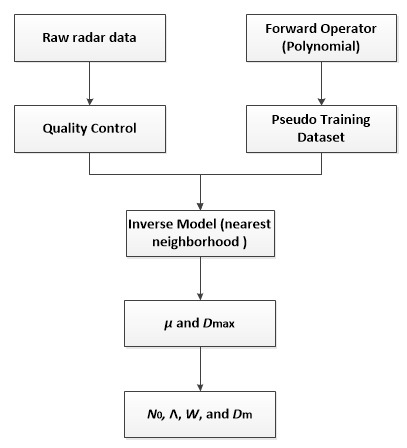
3. Forward Operator for Polarimetric Variables
3.1. Polarimetric Variables
3.2. Forward Operator
3.3. Pseudo Training Dataset
4. Inverse Model for Gamma Parameter Retrieval
4.1. Non-Parametric Estimator for the Inverse Model
- Subtract the averaged values from the data matrix.
- Calculate the covariance of the residual matrix.
- Calculate an upper-triangular matrix of the covariance using Cholesky factorization.
- Divisde the residual matrix by the upper-triangular matrix.
4.2. Model Selection
4.3. Error Characteristics
5. Results
5.1. DSD Retrieval with Disdrometer-Simulated Data
5.2. DSD Retrieval with Real Radar Data
5.3. Rainfall Rate Estimation
6. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seliga, T.A.; Bringi, V.N. Potential use of radar differential reflectivity measurements at orthogonal polarizations for measuring precipitation. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1976, 15, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliga, T.A.; Bringi, V.N. Differential reflectivity and differential phase shift: Applications in radar meteorology. Radio Sci. 1978, 13, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, T.; Glasson, K.; Cummings, F.; Bird, T.S.; Keeler, J.; Lutz, J. The BMRC/NCAR C-band polarimetric (C-POL) radar system. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 871–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostou, E.N.; Anagnostou, M.N.; Krajewski, W.F.; Kruger, A.; Miriovsky, B.J. High-resolution rainfall estimation from X-band polarimetric radar measurements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar: Principles and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; p. 636. [Google Scholar]
- Doviak, R.J.; Zrnić, D.S. Doppler Radar and Weather Observations, 2nd ed.; Dover Publications, Inc.: Mineola, NY, USA, 2006; p. 562. [Google Scholar]
- Ulbrich, C.W. Natural variations in the analytical form of the raindrop size distribution. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1983, 22, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekanandan, J.; Zhang, G.; Brandes, E. Polarimetric Radar Estimators Based on a Constrained Gamma Drop Size Distribution Model. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. Drop Size Distribution Retrieval with Polarimetric Radar: Model and Application. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. An Evaluation of a Drop Distribution–Based Polarimetric Radar Rainfall Estimator. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J.; Brandes, E. A method for estimating rain rate and drop size distribution from polarimetric radar measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgucci, E.; Chandrasekar, V.; Bringi, V.N.; Scarchilli, G. Estimation of Raindrop Size Distribution Parameters from Polarimetric Radar Measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 2373–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willis, P.T. Functional fits to some observed drop size distributions and parameterization of rain. J. Atmos. Sci. 1984, 41, 1648–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illingworth, A.J.; Blackman, T.M. The Need to Represent Raindrop Size Spectra as Normalized Gamma Distributions for the Interpretation of Polarization Radar Observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. Comparison of Polarimetric Radar Drop Size Distribution Retrieval Algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostou, M.N.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Vulpiani, G.; Montopoli, M.; Marzano, F.S.; Vivekanandan, J. Evaluation of X-Band Polarimetric-Radar Estimates of Drop-Size Distributions From Coincident S-Band Polarimetric Estimates and Measured Raindrop Spectra. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3067–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Huang, G.-J.; Chandrasekar, V.; Gorgucci, E. A Methodology for Estimating the Parameters of a Gamma Raindrop Size Distribution Model from Polarimetric Radar Data: Application to a Squall-Line Event from the TRMM/Brazil Campaign. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V.; Hubbert, J.; Gorgucci, E.; Randeu, W.L.; Schoenhuber, M. Raindrop Size Distribution in Different Climatic Regimes from Disdrometer and Dual-Polarized Radar Analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostou, M.N.; Kalogiros, J.; Marzano, F.S.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Montopoli, M.; Piccioti, E. Performance Evaluation of a New Dual-Polarization Microphysical Algorithm Based on Long-Term X-Band Radar and Disdrometer Observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 560–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogiros, J.; Anagnostou, M.N.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Montopoli, M.; Picciotti, E.; Marzano, F.S. Optimum Estimation of Rain Microphysical Parameters From X-Band Dual-Polarization Radar Observables. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3063–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, T.H.; Berne, A. Retrieval of the raindrop size distribution from polarimetric radar data using double-moment normalisation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 2573–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vulpiani, G.; Marzano, F.S.; Chandrasekar, V.; Berne, A.; Uijlenhoet, R. Polarimetric Weather Radar Retrieval of Raindrop Size Distribution by Means of a Regularized Artificial Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3262–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Brandes, E.A.; Schuur, T.J. Polarimetric Radar Rain Estimation through Retrieval of Drop Size Distribution Using a Bayesian Approach. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 973–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, E.; Chandrasekar, V.; Ushio, T.; Matsuda, T. A Bayesian Approach for Integrated Raindrop Size Distribution (DSD) Retrieval on an X-Band Dual-Polarization Radar Network. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2016, 33, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Xue, M. A Variational Approach for Retrieving Raindrop Size Distribution from Polarimetric Radar Measurements in the Presence of Attenuation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, G.; Xiao, H.; Yang, H.; Bi, Y.; Xu, W. Characteristics of summer and winter precipitation over northern China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 197, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, A.; Krajewski, W.F. Two-Dimensional Video Disdrometer: A Description. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 602–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler-Mang, M.; Joss, J. An Optical Disdrometer for Measuring Size and Velocity of Hydrometeors. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, G.; Levin, Z. The Lognormal Fit to Raindrop Spectra from Frontal Convective Clouds in Israel. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1986, 25, 1346–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marshall, J.S.; Palmer, W.M.K. The distribution of raindrops with size. J. Meteorol. 1948, 5, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, W.B., II; Avery, S.K. Retrieval of Raindrop Size Distributions Using Two Doppler Wind Profilers: Model Sensitivity Testing. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 1623–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schönhuber, M.; Lammer, G.; Randeu, W. One decade of imaging precipitation measurement by 2D-video-distrometer. Adv. Geosci. 2007, 10, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumjian, M.R.; Ryzhkov, A.V. The Impact of Size Sorting on the Polarimetric Radar Variables. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 2042–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testud, J.; Oury, S.; Black, R.A.; Amayenc, P.; Dou, X. The Concept of “Normalized” Distribution to Describe Raindrop Spectra: A Tool for Cloud Physics and Cloud Remote Sensing. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 1118–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhon, R.S.; Srivastava, R.C. Snow Size Spectra and Radar Reflectivity. J. Atmos. Sci. 1970, 27, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thurai, M.; Bringi, V.N. Application of the Generalized Gamma Model to Represent the Full Rain Drop Size Distribution Spectra. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.W.; Zawadzki, I.; Szyrmer, W.; Sempere-Torres, D.; Uijlenhoet, R. A General Approach to Double-Moment Normalization of Drop Size Distributions. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 264–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J. Experiments in Rainfall Estimation with a Polarimetric Radar in a Subtropical Environment. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, D.; Srivastava, R.; Sekhon, R.S. Doppler radar characteristics of precipitation at vertical incidence. Rev. Geophys. 1973, 11, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruppacher, H.R.; Beard, K.V. A wind tunnel investigation of the internal circulation and shape of water drops falling at terminal velocity in air. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1970, 96, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmus, J.; Collis, S. The Python ARM Radar Toolkit (Py-ART), a library for working with weather radar data in the Python programming language. J. Open Res. Softw. 2016, 4, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heistermann, M.; Collis, S.; Dixon, M.J.; Giangrande, S.; Helmus, J.J.; Kelley, B.; Koistinen, J.; Michelson, D.B.; Peura, M.; Pfaff, T.; et al. The Emergence of Open-Source Software for the Weather Radar Community. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, V.; Karstens, C.; Krause, J.; Tang, L. Quality Control of Weather Radar Data Using Polarimetric Variables. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 1234–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, V.; Jian, Z. Censoring Biological Echoes in Weather Radar Images. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on FSKD ‘09 Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, Tianjin, China, 14–16 August 2009; pp. 491–495. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmanan, V.; Smith, T.; Stumpf, G.; Hondl, K. The Warning Decision Support System–Integrated Information. Weather Forecast. 2007, 22, 596–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulpiani, G.; Montopoli, M.; Passeri, L.D.; Gioia, A.G.; Giordano, P.; Marzano, F.S. On the Use of Dual-Polarized C-Band Radar for Operational Rainfall Retrieval in Mountainous Areas. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klazura, G.E.; Imy, D.A. A Description of the Initial Set of Analysis Products Available from the NEXRAD WSR-88D System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 74, 1293–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crum, T.; Smith, S.; Chrisman, J.; Vogt, R.; Istok, M.; Hall, R.; Saffle, B. WSR-88D Radar Projects: 2013 Update. In Proceedings of the 29th Conference on Environmental Information Processing Technologies, Austin, TX, USA, 9 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nešpor, V.; Krajewski, W.F.; Kruger, A. Wind-Induced Error of Raindrop Size Distribution Measurement Using a Two-Dimensional Video Disdrometer. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Protat, A.; May, P.T.; Wang, X.; Moran, W. A Cluster-Based Method for Hydrometeor Classification Using Polarimetric Variables. Part I: Interpretation and Analysis. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 1320–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, J.M.; Zrnić, D.S.; Ryzhkov, A.V. Bulk hydrometeor classification and quantification using polarimetric radar data: Synthesis of relations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1341–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchenko, M.I. Calculation of the amplitude matrix for a nonspherical particle in a fixed orientation. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterman, P.C. Symmetry, unitarity, and geometry in electromagnetic scattering. Phys. Rev. D 1971, 3, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.S. Broadband complex refractive indices of ice and water. Appl. Opt. 1972, 11, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurai, M.; Bringi, V.; May, P. Drop shape studies in rain using 2-D video disdrometer and dual-wavelength, polarimetric CP-2 radar measurements in south-east Queensland, Australia. In Proceedings of the 34th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Williamsburg, VA, USA, 5–9 October 2009; American Meteor Society Press: Geneseo, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.-J.; Bringi, V.N.; Thurai, M. Orientation Angle Distributions of Drops after an 80-m Fall Using a 2D Video Disdrometer. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarchilli, G.; Gorgucci, V.; Chandrasekar, V.; Dobaie, A. Self-consistency of polarization diversity measurement of rainfall. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atlas, D.; Ulbrich, C. Drop size spectra and integral remote sensing parameters in the transition from convective to stratiform rain. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moisseev, D.N.; Chandrasekar, V. Examination of the μ–Λ Relation Suggested for Drop Size Distribution Parameters. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, G. Errors in Estimating Raindrop Size Distribution Parameters Employing Disdrometer and Simulated Raindrop Spectra. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J.; Brandes, E.A.; Meneghini, R.; Kozu, T. The Shape–Slope Relation in Observed Gamma Raindrop Size Distributions: Statistical Error or Useful Information? J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.R.; Bringi, V.N.; Carey, L.D.; Chandrasekar, V.; Gatlin, P.N.; Haddad, Z.S.; Meneghini, R.; Munchak, S.J.; Nesbitt, S.W.; Petersen, W.A.; et al. Describing the Shape of Raindrop Size Distributions Using Uncorrelated Raindrop Mass Spectrum Parameters. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 53, 1282–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Brandes, E.; Schuur, T.; Ryzhkov, A.; Ikeda, K. Analysis of video disdrometer and polarimetric radar data to characterize rain microphysics in Oklahoma. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 2238–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härter, F.P.; de Campos Velho, H.F. New approach to applying neural network in nonlinear dynamic model. Appl. Math. Model. 2008, 32, 2621–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemm, J.C. Bayesian Field Theory; JHU Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Teboul, S.; Blanc-Feraud, L.; Aubert, G.; Barlaud, M. Variational approach for edge-preserving regularization using coupled PDEs. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1998, 7, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, G.; Protat, A.; May, P.T.; Moran, W.; Dixon, M. A Cluster-Based Method for Hydrometeor Classification Using Polarimetric Variables. Part II: Classification. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2016, 33, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, O.P.; Barros, A.P.; Testik, F.Y. On the Influence of Raindrop Collision Outcomes on Equilibrium Drop Size Distributions. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 1534–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adderio, L.P.; Porcù, F.; Tokay, A. Identification and Analysis of Collisional Breakup in Natural Rain. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 3404–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adderio, L.P.; Porcù, F.; Tokay, A. Evolution of drop size distribution in natural rain. Atmos. Res. 2018, 200, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.L.; Kliche, D.V.; Johnson, R.W. The Bias and Error in Moment Estimators for Parameters of Drop Size Distribution Functions: Sampling from Gamma Distributions. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 2118–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Williams, C.R.; Thurai, M.; May, P.T. Using dual-polarized radar and dual-frequency profiler for DSD characterization: A case study from Darwin, Australia. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2107–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnott, R.W. Virtues of the Haversine. Sky Telesc. 1984, 68, 159. [Google Scholar]
- Kozu, T.; Nakamura, K. Rainfall Parameter Estimation from Dual-Radar Measurements Combining Reflectivity Profile and Path-integrated Attenuation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1991, 8, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Chandrasekar, V.; Bechini, R. An improved dual-polarization radar rainfall algorithm (DROPS2. 0): Application in NASA IFloodS field campaign. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 917–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Giangrande, S.E.; Schuur, T.J. Rainfall Estimation with a Polarimetric Prototype of WSR-88D. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2005, 44, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-G.; Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V.; Maki, M.; Iwanami, K. Correction of Radar Reflectivity and Differential Reflectivity for Rain Attenuation at X Band. Part I: Theoretical and Empirical Basis. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Chandrasekar, V.; Yoshikawa, E. A rain drop size distribution (DSD) retrieval algorithm for CASA DFW urban radar network. In Proceedings of the 36th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Denver, CO, USA, 16–20 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cifelli, R.; Chandrasekar, V.; Chen, H.; Johnson, L.E. High resolution radar quantitative precipitation estimation in the San Francisco Bay area: Rainfall monitoring for the urban environment. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 96, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Zh (dBZ) | Zdr (dB) | Kdp (deg/km) | Dm (mm) | W (g/m3) | R (mm/h) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 36.8 | 0.67 | 0.076 | 1.30 | 0.314 | 5.4 |
| STD | 7.0 | 0.60 | 0.251 | 0.40 | 0.986 | 16.1 |
| Min | 3.6 | 0 | 0 | 0.36 | 0.0004 | 0.1 |
| Max | 58.2 | 5.87 | 7.031 | 5.74 | 35.031 | 479.5 |
| b | p | a0 | a1 | a2 | a3 | a4 | Bias | MSE | RE | CC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zh | 6 | 3 | 1.004 | −0.020 | 0.021 | −0.417 | 28.965 | 1 | |||
| Zv | 6 | 4 | 0.998 | 0.028 | −0.055 | −0.265 | 13.420 | 1 | |||
| Kdp | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| MSE | MAE | RSE | RAE | CC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dm (IM) | 0.030 | 0.124 | 0.183 | 0.405 | 0.917 |
| Dm (BA) | 0.091 | 0.239 | 0.552 | 0.782 | 0.821 |
| W (IM) | 0.113 | 0.062 | 0.128 | 0.178 | 0.963 |
| W (BA) | 0.218 | 0.090 | 0.246 | 0.257 | 0.934 |
| MSE | MAE | RSE | RAE | CC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dm (IM) | 0.062 | 0.181 | 0.747 | 0.882 | 0.504 |
| Dm (BA) | 0.123 | 0.270 | 1.470 | 1.315 | 0.463 |
| W (IM) | 1.081 | 0.300 | 0.515 | 0.492 | 0.705 |
| W (BA) | 1.167 | 0.317 | 0.557 | 0.522 | 0.679 |
| RMSE | MAE | RRSE | RAE | CC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeroth | 14,373.8 | 4602.5 | 1.233 | 0.986 | 0.651 |
| Second | 2453.2 | 660.7 | 0.746 | 0.497 | 0.696 |
| Fourth | 2469.1 | 734.6 | 0.721 | 0.480 | 0.714 |
| Sixth | 16,391.1 | 3800.8 | 0.855 | 0.455 | 0.659 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, G.; Chen, H.; Zhang, G.; Sun, J. An Inverse Model for Raindrop Size Distribution Retrieval with Polarimetric Variables. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10081179
Wen G, Chen H, Zhang G, Sun J. An Inverse Model for Raindrop Size Distribution Retrieval with Polarimetric Variables. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(8):1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10081179
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Guang, Haonan Chen, Guifu Zhang, and Jiming Sun. 2018. "An Inverse Model for Raindrop Size Distribution Retrieval with Polarimetric Variables" Remote Sensing 10, no. 8: 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10081179
APA StyleWen, G., Chen, H., Zhang, G., & Sun, J. (2018). An Inverse Model for Raindrop Size Distribution Retrieval with Polarimetric Variables. Remote Sensing, 10(8), 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10081179