The Development of a GIS Methodology to Identify Oxbows and Former Stream Meanders from LiDAR-Derived Digital Elevation Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Preprocessing
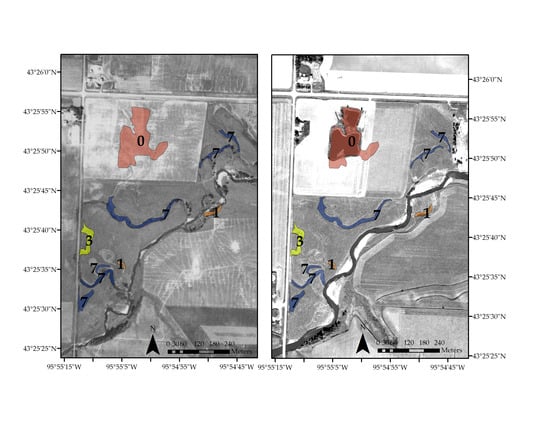
2.4. Riparian Depression Identification
2.5. Model Creation and Evaluation
- Intersection with either a stream channel, oxbow, or oxbow scar within one aerial image
- Maintenance of the original shape of the historical channel, oxbow, or oxbow scar
3. Results
3.1. Model Accuracies
3.2. Model Accuracy at Identifying Chosen Restoration Sites
3.3. Ranking Sites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Disclaimer
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cramer, M.L. Stream Habitat Restoration Guidelines; Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife: Olympia, WA, USA; Washing Department of Natural Resources: Olympia, WA, USA; Washington Department of Transportation: Olympia, WA, USA; Washington Department of Ecology: Olympia, WA, USA; Washington State Recreation and Conservation Office: Olympia, WA, USA; Puget Sound Partnership: Olympia, WA, USA; U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service: Olympia, WA, USA, 2012.
- Gallardo, B.; Cabezas, Á.; Gonzalez, E.; Comín, F.A. Effectiveness of a newly created oxbow lake to mitigate habitat loss and increase biodiversity in a regulated floodplain. Restor. Ecol. 2012, 20, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landress, C.M. Fish assemblage associations with floodplain connectivity following restoration to benefit an endangered catostomid. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2016, 145, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, C.; Cernera, P.J.; Ramey, M.P.; Reiser, D.W. Development of off-channel habitats for use by juvenile chinook salmon. N. Am. J. Fish Manag. 1992, 12, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheerer, P.D. Implications of floodplain isolation and connectivity on the conservation of an endangered minnow, Oregon Chub, in the Willamette River, Oregon. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2002, 131, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junk, W.J.; Bayley, P.B.; Sparks, R.E. The flood pulse concept in river-floodplain systems. Proc. Int. Large River Symp. Can. Spec. Publ. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 106, 11–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zeug, S.C.; Winemiller, K.O. Relationships between hydrology, spatial heterogeneity, and fish recruitment dynamics in a temperate floodplain river. River Res. Applic. 2008, 24, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, D.W.; Bachmann, R.W. Effects of Stream Channelization and Bank Stabilization on Warmwater Sport Fish in Iowa: Subproject No. 4. The Effects of Long-Reach Channelization on Habitat and Invertebrate Drift in Some Iowa Streams; U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1976.
- Lau, J.K.; Lauer, T.E.; Weinman, M.L. Impacts of channelization on stream habitats and associated fish assemblages in East Central Indiana. Am. Midl. Nat. 2006, 156, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, M.A.; Rhoads, B.L. Catastrophic human-induced change in stream-channel planform and geometry in an agricultural watershed, Illinois, USA. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2003, 93, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantine, J.A.; Dunne, T. Meander cutoff and the controls on the production of oxbow lakes. Geology 2008, 36, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, Y.; Hori, K. Formation and infilling of oxbow lakes in the Ishikari lowland, northern Japan. Quat. Int. 2016, 397, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, G.R.; Gay, H.H.; Gay, H.H.; Martinson, H.A.; Meade, R.H. Evolution of cutoffs across meander necks in Powder River, Montana, USA. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1998, 23, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.R.; Bakevich, B.D.; Shea, C.P.; Pierce, C.L.; Quist, M.C. Floods, drying, habitat connectivity and fish occupancy dynamics in restored and unrestored oxbows of West-Central Iowa, USA. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, J.; Stuart, I.; Ramsey, D.; O’Mahony, J. The effect of water level on lateral movements of fish between river and off-channel habitats and implications for management. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2010, 61, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miranda, L.E. Fish assemblages in oxbow lakes relative to connectivity with the Mississippi River. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2005, 134, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, P.F.; Heitmuller, F.T.; Leitch, M.B. Hydrologic connectivity of oxbow lakes along the lower Guadalupe River, Texas: The influence of geomorphic and climatic controls on the “flood pulse concept”. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414–415, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, S.J.; Howell, J.A.; Enge, H.D.; Kurz, T.H. Terrestrial laser scanning in geology: Data acquisition, processing, and accuracy. J. Geol. Soc. 2008, 165, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS 3D Elevation Program. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/ngp/3dep (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Iowa LiDAR Mapping Project. Available online: http://www.geotree.uni.edu/lidar/ (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. MnTOPO. Available online: https://www.dnr.state.mn.us/maps/mntopo/index.html (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Li, S.; MacMillian, R.A.; Lobb, D.A.; McConkey, B.G.; Moulin, A.; Fraser, W.R. Lidar DEM error analysis and topographic depression identification in a hummocky landscape in the prairie region of Canada. Geomorphology 2011, 129, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, K.; Redden, A.M.; Webster, T.; Stewart, H. Use of GIS and high resolution LiDAR in salt marsh restoration site suitability assessment in the upper Bay of Fundy, Canada. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 21, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Lane, C.; Liu, H. An effective method for detecting potential woodland vernal pools using high-resolution LiDAR data and aerial imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11444–11467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Lane, C.R. Delineation and quantification of wetland depressions in the prairie pothole region of North Dakota. Wetlands 2016, 36, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terefenko, P.; Wziatek, D.Z.; Dalyot, S.; Boski, T.; Lima-Filho, F.P. A High-Precision LiDAR-Based Methodology for Surveying and Classifying Coastal Notches. J. Geol. Soc. 2018, 7, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, G.G. From Coastal Wilderness to Fruited Plain: A History of Environmental Change in Temperate North America from 1500 to the Present; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996; ISBN 0 521 57658 X. [Google Scholar]
- Gelder, B.K. Automation of DEM Cutting for Hydrologic/Hydraulic Modeling; Technical Report; Iowa State University Institution for Transportation: Ames, IA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tabor, V.M. Final Rule to List the Topeka Shiner as Endangered; Federal Register 63:240; U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service: Manhattan, KS, USA, 1998; pp. 69008–69021. 26p. Available online: https://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-1998-12-15/pdf/98-33100.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2017).
- Bakevich, B.D.; Pierce, C.L.; Quist, M.C. Status of the Topeka Shiner in West-Central Iowa. Am. Midl. Nat. 2015, 174, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zambory, C.L.; Bybel, A.P.; Pierce, C.L.; Roe, K.J.; Weber, M.J. Habitat Improvement Projects for Stream and Oxbow Fish of Greatest Conservation Need; Annual Progress Report; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 2017; Available online: https://www.cfwru.iastate.edu/files/project/files/2016_swgc_annualreport_final.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2017).
- Simpson, N.T.; Pierce, C.L.; Roe, K.J.; Weber, M.J. Boone River Watershed Stream Fish and Habitat Monitoring, IA; Annual Progress Report; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 2016; Available online: https://www.cfwru.iastate.edu/files/project/files/2016_brw_annualreport_final.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2017).
- Clark, S.J. Relationship of Topeka Shiner Distribution to Geographical Features of the Des Moines Lobe in Iowa. Master’s Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, J.A.; Petersen, T.A.; Anderson, Y.; Baker, R. Hydrogeology of the Rock River Watershed, Minnesota and Associated Off-Channel Habitats of the Topeka Shiner. Final Report Submitted by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources 2004. Available online: http://files.dnr.state.mn.us/eco/nongame/projects/consgrant_reports/2004/2004_berg_etal.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2017).
- Bakevich, B.D.; Pierce, C.L.; Quist, M.C. Habitat, fish species, and fish assemblage associations of the Topeka Shiner in West-Central Iowa. N. Am. J. Fish Manag. 2013, 33, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, J.T. What we know about Minnesota’s first endangered fish species: The Topeka shiner. J. Minn. Acad. Sci. 2001, 65, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, S. Dugouts and stream fishes, especially the endangered Topeka Shiner; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. Available online: https://directives.sc.egov.usda.gov/OpenNonWebContent.aspx?content=29145.wba (accessed on 1 November 2018).
- Thomson, S.K.; Berry, C.R., Jr.; Niehs, C.A.; Wall, S.S. Constructed impoundments in the floodplain: A source or sink for native prairie fishes, in particular the endangered Topeka shiner (Notropis topeka)? In Proceedings of the 2005 Watershed Management Conference, Williamsburg, VA, USA, 19–22 July 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehle, J.J.; Adelman, I.R. The effects of temperature, dissolved oxygen, and Asian tapeworm infection on growth and survival of the Topeka shiner. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2007, 136, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, A. The Topeka Shiner: Shining a Spotlight on an Iowa Success Story. Endangered Species Program News Bulletin. 2013. Available online: https://www.fws.gov/endangered/news/episodes/bu-01-2013/story3/. (accessed on 13 November 2017).
- Kenny, A.; United States Fish and Wildlife Service, Rock Island, IL, USA. Personal communication, 2017.
- Ralston, S.; United States Fish and Wildlife Service, Windom, MN, USA. Personal communication, 2016.
- Heit, M.; Parker, H.; Shortreid, A. GIS Applications in Natural Resources; GIS World Books: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1991; ISBN 1882610172. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.P.; Gallant, J.C. Terrain Analysis: Principles and Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0471321885. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, G.E.; Omernik, J.M.; Wilton, T.F.; Pierson, S.M. Ecoregions and subregions of Iowa: A framework for water quality assessment and management. J. Iowa Acad. Sci. 1994, 101, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Iowa State University Geographic Information Systems Facility ACPF DEM Download. Available online: https://www.gis.iastate.edu/gisf/projects/acpf. (accessed on 4 August 2016).
- ACPF Watershed Database Land Use Viewing and Data Downloading. Available online: https://www.nrrig.mwa.ars.usda.gov/st40_huc/dwnldACPF.html (accessed on 25 July 2017).
- Tomer, M.D.; James, D.E.; Sandoval-Green, M.J. Agricultural Conservation Planning Framework: 3. Land Use and Field Boundary Database Development and Structure. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watershed Planning Tool: Agricultural Conservation Planning Framework (ACPF). Available online: http://northcentralwater.org/acpf/ (accessed on 4 August 2016).
- Tarboton, D.G. Terrain Analysis Using Digital Elevation Models (Taudem). Utah Water Research Laboratory, Utah State University. 2016. Available online: http://hydrology. usu.edu/taudem/taudem5/support.html (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Grohmann, C.H.; Smith, M.J.; Riccomini, C. Multiscale Analysis of Topographic Surface Roughness in the Midland Valley, Scotland. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1200–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iowa Geographic Map Server. Available online: https://ortho.gis.iastate.edu/ (accessed on 13 November 2017).
- Japkowicz, N.; Stephen, S. The class imbalance problem: A systematic study. Intelligent Data Analysis. Intell. Data Anal. 2002, 6, 429–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E.; Stork, D.G. Pattern Classification, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 0471056693. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, A.P. The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms. Pattern Recognit. 1997, 30, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Górski, K.; De Leeuw, J.J.; Winter, H.V.; Vekhov, D.A.; Minin, A.E.; Buijse, A.D.; Nagelkerke, A.J. Fish recruitment in a large, temperate floodplain: The importance of annual flooding, temperature and habitat complexity. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 2210–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.E.; Ploskey, G.R.; Sather, N.K.; Teel, D.K. Residence times of juvenile salmon and steelhead in off-channel tidal freshwater habitats, Columbia River, USA. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, R.A. Iowa’s wetlands. Proc. Iowa Acad. Sci. 1981, 88, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.D. Iowa prairie—An endangered ecosystem. Proc. Iowa Acad. Sci. 1981, 88, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zucker, L.A.; Brown, L.C. Agricultural Drainage: Water Quality Impacts and Subsurface Drainage Studies in the Midwest; Ohio State University Extension: Columbus, OH, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chirol, C.; Haigh, I.D.; Pontee, N.; Thompson, C.E.; Gallop, S.L. Parametrizing tidal creek morphology in mature saltmarshes using semi-automated extraction from lidar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waz, A.; Creed, I.F. Automated Techniques to Identify Lost and Restorable Wetlands in the Prairie Pothole Regions. Wetlands 2017, 37, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDeid, S.M.; Green, D.L.; Crumpton, W.G. Morphology of Drained Upland Depressions on the Des Moines Lobe of Iowa. Wetlands 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conger, C.L.; Fletcher, C.H.; Hochberg, E.H.; Frazer, N.; Rooney, J.J.B. Remote sensing of sand distribution patterns across an insular shelf: Oahu, Hawaii. Mar. Geol. 2009, 267, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doctor, D.H.; Young, J.A. An Evaluation of Automated GIS Tools for Delineating Karst Sinkholes and Closed Depressions from 1-Meter LiDAR-Derived Digital Elevation Data. In Proceedings of the NCKRI Symposium 13th Sinkhole Conference, Carlsbad, NM, USA, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 449–458. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Pierskalla, W.P., Jr. Applying a weighted random forests method to extract karst sinkholes from LiDAR data. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Oguchi, T.; Wu, P. Morphometric analysis of sinkholes using a semi-automatic approach in Zhijin County, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, J.C.; Belmont, P. TerEx Toolbox for semi-automated selection of fluvial terrace and floodplain features from lidar. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 39, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, D.F.; Mitsch, W.J. Hydrology and nutrient biogeochemistry in a created river diversion oxbow wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 30, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Lane, C.R.; Wang, L.; Vanderhoof, M.K.; Christensen, J.R.; Liu, H. Efficient delineation of nested depression hierarchy in digital elevation models for hydrological analysis using level-set method. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the normalize difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.E.; Kult, K.; Wilke, K.; Streeter, M.; Vogelgesang, J. Nitrate reduction in a reconstructed floodplain oxbow fed by tile drainage. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Morphometric Characteristic | Formula | Shapes Representing the Extremes of Each Metric | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circularity (CIR) |  |  | |
| Solidity (SLD) |  |  | |
| Rectangularity (REC) |  |  | |
| Convexity (CVX) |  |  | |
| Concavity (CON) |  |  | |
| Watershed/Watershed Combination | Total Depressions | Non-target Features | Target Features | % Target Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boone River Watershed | 9278 | 9047 | 231 | 2.49 |
| North Raccoon River Watershed | 33,485 | 32,719 | 766 | 2.29 |
| Des Moines Lobe Watersheds | 42,763 | 41,766 | 997 | 2.33 |
| Rock River Watershed | 22,411 | 21,491 | 920 | 4.11 |
| All-watersheds combined | 65,174 | 63,257 | 1917 | 2.94 |
| Watershed | Specificity | Sensitivity | Precision | Correct Classification Rate | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boone | 0.89 | 0.75 | 0.16 | 0.88 | 0.82 |
| North Raccoon | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.19 | 0.91 | 0.87 |
| Des Moines Lobe | 0.92 | 0.80 | 0.20 | 0.91 | 0.86 |
| Rock River | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.39 | 0.94 | 0.91 |
| All-watershed | 0.93 | 0.82 | 0.26 | 0.92 | 0.87 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
L. Zambory, C.; Ellis, H.; L. Pierce, C.; J. Roe, K.; J. Weber, M.; E. Schilling, K.; C. Young, N. The Development of a GIS Methodology to Identify Oxbows and Former Stream Meanders from LiDAR-Derived Digital Elevation Models. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010012
L. Zambory C, Ellis H, L. Pierce C, J. Roe K, J. Weber M, E. Schilling K, C. Young N. The Development of a GIS Methodology to Identify Oxbows and Former Stream Meanders from LiDAR-Derived Digital Elevation Models. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleL. Zambory, Courtney, Harvest Ellis, Clay L. Pierce, Kevin J. Roe, Michael J. Weber, Keith E. Schilling, and Nathan C. Young. 2019. "The Development of a GIS Methodology to Identify Oxbows and Former Stream Meanders from LiDAR-Derived Digital Elevation Models" Remote Sensing 11, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010012
APA StyleL. Zambory, C., Ellis, H., L. Pierce, C., J. Roe, K., J. Weber, M., E. Schilling, K., & C. Young, N. (2019). The Development of a GIS Methodology to Identify Oxbows and Former Stream Meanders from LiDAR-Derived Digital Elevation Models. Remote Sensing, 11(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010012