Analysis of Factors Affecting Asynchronous RTK Positioning with GNSS Signals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Observation Model and Error Analysis for Asynchronous RTK
2.2. Method for Evaluating Errors in the ARTK Model
2.2.1. Broadcast Ephemeris Error
2.2.2. Atmosphere Error
3. Results Analysis
3.1. Data Collection and Processing Strategy
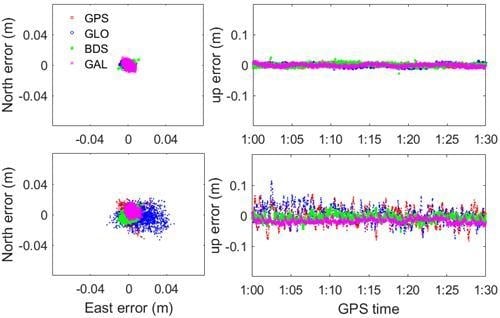
3.2. Impact of Time Delays on RTK Results over Short-Baselines
3.3. Broadcast Orbit and Clock Offset Error Analysis
3.4. Ionosphere Error Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teunissen, P.J. The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: a method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J. Geod. 1995, 70, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhodzishsky, M.; Vorobiev, M.; Khvalkov, A.; Ashjaee, J. Real-time kinematic (RTK) processing for dual-frequency GPS/GLONASS. In Proceedings of the ION GPS 1998, Nashville, TN, USA, 15–18 September 1998; pp. 1325–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, S.; Cross, P.; Barnes, J.; Betaille, D. A methodology for benchmarking real time kinematic GPS. Surv Rev. 1999, 35, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Tang, W.; Liu, J.; Shi, C. Reliable single-epoch ambiguity resolution for short baselines using combined GPS/BeiDou system. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J.; Guo, H.; Wang, A. Performance assessment of single-and dual-frequency BeiDou/GPS single-epoch kinematic positioning. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J.; Odijk, D. Combined BDS, Galileo, QZSS and GPS single-frequency RTK. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J.; Wielgosz, P. Assessment of GPS+ Galileo and multi-frequency Galileo single-epoch precise positioning with network corrections. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Wanninger, L. Differential Positioning. In Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Teunissen, P.G., Montenbruck, O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-42926-7. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, D.G. Reference Carrier Phase Prediction for Kinematic GPS. US Patent 5,903,236, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hatch, R.R.; Richard, T.S.; Yang, Y. GPS Navigation Using Successive Differences of Carrier-Phase Measurements. U.S. Patent 7,212,155, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Ou, J.; Yuan, Y. Strategy of data processing for GPS rover and reference receivers using different sampling rates. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Lv, H.; Wang, D.; Hou, Y.; Wu, J. Asynchronous RTK precise DGNSS positioning method for deriving a low-latency high-rate output. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 641–653. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.D.; Zhang, W.X.; Wang, C.; Yao, X.G.; Shi, C.; Liu, J.N. The impact of orbital errors on the estimation of satellite clock errors and PPP. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Gill, E.; Kroes, E. Rapid orbit determination of LEO satellites using IGS clock and ephemeris products. GPS Solut. 2005, 9, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Cai, S. Impact of sampling rate of IGS satellite clock on precise point positioning. Geo-spat Inf.Sci. 2010, 13, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, L.; Gao, G.X.; Walter, T.; Enge, P. Statistical characterization of GPS signal-in-space errors. In Proceedings of the ION ITM 2011, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–26 January 2011; pp. 312–319. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Jiao, W.; Huang, X.; Geng, C.; Ai, L.; Lu, L.; Hu, Z. Study on signal-in-space errors calculation method and statistical characterization of BeiDou navigation satellite system. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC), Wuhan, China, 15–17 May 2013; pp. 423–434. [Google Scholar]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Hauschild, A. Broadcast versus precise ephemerides: a multi-GNSS perspective. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RTCM Standard 10403.2—Differential GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite Systems) Services Version 3; Radio Technical Commision for Maritime Services: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013.
- Wang, J. An approach to GLONASS ambiguity resolution. J. Geod. 2000, 74, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanninger, L. Carrier-phase inter-frequency biases of GLONASS receivers. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euler, H.J.; Goad, C.C. On optimal filtering of GPS dual frequency observations without using orbit information. Bull. Geod. 1991, 65, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malys, S.; Larezos, M.; Gottschalk, S.; Mobbs, S.; Winn, B.; Feess, W.; Mathon, W. The GPS accuracy improvement initiative. In Proceedings of the ION GPS, Kansas, MO, USA, 16–19 September 1997; pp. 375–384. [Google Scholar]
- Robustelli, U.; Benassai, G.; Pugliano, G. Signal in Space Error and Ephemeris Validity Time Evaluation of Milena and Doresa Galileo Satellites. Sensors. 2019, 19, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Li, X.; Nilsson, T.; Ning, T.; Heinkelmann, R.; Ge, M. Real-time retrieval of precipitable water vapor from gps and beidou observations. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadas, T.; Teferle, F.N.; Kazmierski, K.; Hordyniec, P.; Bosy, J. Optimum stochastic modeling for GNSS tropospheric delay estimation in real-time. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Z. Investigating the inconsistency of ionospheric ROTI indices derived from GPS modernized L2C and legacy L2 P (Y) signals at low-latitude regions. GPS Solut 2017, 21, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://saegnss2.curtin.edu.au/ldc/rawdata (accessed on 26 May 2019).
- Alber, C.; Ware, R.; Rocken, C.; Braun, J. Obtaining single path phase delays from GPS double differences. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 2661–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www2.unb.ca/gge/Resources/GPSConstellationStatus.txt (accessed on 26 May 2019).
- Li, H.; Liao, X.; Li, B.; Yang, L. Modeling of the GPS satellite clock error and its performance evaluation in precise point positioning. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bree, R.J.P.; Tiberius, C.C.J.M.; Hauschild, A. Real time satellite clocks in single frequency precise point positioning. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS, Savannah, GA, USA, 22–25 September 2009. [Google Scholar]













| System | Satellite Types | Satellite Number | PRN |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS | IIR-A/B/M, IIF | 32 | G01-32 |
| GLONASS | — | 24 | R01-24 |
| GALILEO | IOV | 4 | E11,E12,E19,E20 |
| FOC | 12 | E01-05, E07-09, E22,E24,E26,E30 | |
| ECC | 2 | E14, E18 | |
| BDS-II | GEO | 5 | C01-05 |
| IGSO | 6 | C06-C10, C13 | |
| MEO | 3 | C11, C12, C14 |
| System | ||
|---|---|---|
| GPS | 0.98 | 1/49 |
| GLONASS | 0.98 | 1/45 |
| Galileo | 0.98 | 1/61 |
| BDS(MEO) | 0.98 | 1/54 |
| BDS(GEO, IGSO) | 0.99 | 1/127 |
| Baseline | Stations | Receiver Type | Antenna | Length | Constellation | Lat. and Lon.(o) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bs.1 | WHU1-WHU2 | Novatel OEM6 | TRM 59800.00 SCIS | 5.21 m | GPS/GLO/BDS | 30.49 and 114.53 |
| Bs.2 | CUT0-CUTA | Trimble NetR9 | TRM 59800.00 SCIS | 8.42 m | GPS/GLO/BDS/GAL | −32.00 and 115.89 |
| Baseline | Session | GPS Time/Date | GPS | GLONASS | BDS | Galileo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bs.1 | A1 | 1:00–1:30 10 Jan. 2018 | 02,05,13,15,18,20,21,24,29,30 | 06,07,08,09,16,20,21,22 | 01,02,03,04,05,06,08,09,13,14 | – |
| Bs.2 | A1 | 1:00–1:30 10 Jan. 2018 | 02,06,12,15,19,24,25,29,32 | 09,10,11,19,20,21 | 01,02,03,04,05,07,08,09,10,11,13 | 02,03,08,11,12,14,24 |
| Bs.2 | A2 | 6:30–7:00 10 Jan. 2018 | 10,15,16,18,20,21,25,26,27,29,31 | 01,07,08,12,13,14,22,23,24 | 01,02,03,04,05,06,07,08,10,13 | 02,03,05,09,14 |
| Bs.2 | A3 | 14:30–15:00 10 Jan. 2018 | 01,03,06,07,09,11,17,19,22,23,31 | 03,04,05,13,14,15,18,19,20 | 01,02,03,04,05,06,07,08,09,12,13 | 02,07,08,18,26 |
| Bs.2 | B1 | 1:00–1:30 9 Oct. 2013 | 01,04,07,11,13,17,20,23,31,32 | 04,05,06,14,15,16,19,20,21 | 01,02,03,04,05,06,07,09,10 | – |
| Bs.2 | B2 | 6:30–7:00 9 Oct. 2013 | 05,07,08,09,10,13,15,17,26,28 | 01,07,08,09,10,11,19,20 | 01,02,03,04,05,06,07,08,09,10 | – |
| Bs.2 | B3 | 14:30–15:00 9. Oct. 2013 | 05,12,21,25,29,31 | 01,08,13,14,15,17,23,24 | 01,02,03,04,05,06,07,08,10,11,12 | – |
| GPS | GLONASS | BDS | Galileo | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | N | U | E | N | U | E | N | U | E | N | U | ||
| Bs.1 | SRTK | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 3 | - | - | - |
| ARTK | 19 | 15 | 35 | 16 | 17 | 30 | 6 | 10 | 12 | - | - | - | |
| Bs. 2 | SRTK | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
| ARTK | 6 | 7 | 27 | 17 | 9 | 26 | 4 | 5 | 12 | 5 | 6 | 18 | |
| Latency Time | GPS (Ten Block IIF) | GPS (Other Satellites) | GLONASS | BDS | Galileo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1s | 0.5 | 1.2 | 1.9 | 0.4 | 0.9 |
| 5s | 2.6 | 5.8 | 9.5 | 2.2 | 1.4 |
| 10s | 3.4 | 10.0 | 13.3 | 5.9 | 2.6 |
| 15s | 4.3 | 14.4 | 16.9 | 7.3 | 3.0 |
| Session | GPS | GLONASS | BDS | Galileo | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | N | U | E | N | U | E | N | U | E | N | U | ||
| A1 | brdc | 6 | 7 | 27 | 17 | 9 | 26 | 4 | 5 | 12 | 5 | 6 | 18 |
| c2t | 4 | 3 | 8 | 13 | 6 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 13 | 5 | 6 | 21 | |
| A2 | brdc | 11 | 10 | 34 | 11 | 13 | 42 | 4 | 7 | 19 | 18 | 6 | 39 |
| c2t | 7 | 7 | 29 | 5 | 16 | 36 | 12 | 11 | 34 | 28 | 8 | 46 | |
| A3 | brdc | 7 | 7 | 15 | 12 | 14 | 35 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 12 |
| c2t | 3 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 15 | 6 | 4 | 9 | 6 | 5 | 13 | |
| B1 | brdc | 12 | 18 | 20 | 10 | 8 | 51 | 4 | 5 | 16 | — | — | — |
| c2t | 11 | 16 | 18 | 6 | 6 | 41 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| B2 | brdc | 12 | 12 | 24 | 20 | 16 | 47 | 6 | 12 | 16 | — | — | — |
| c2t | 6 | 11 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 46 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| B3 | brdc | 11 | 16 | 32 | 13 | 13 | 30 | 3 | 6 | 14 | — | — | — |
| c2t | 5 | 6 | 12 | 7 | 4 | 16 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, B.; Liu, H.; Feng, Y.; Xu, L.; Qian, C.; Yang, Z. Analysis of Factors Affecting Asynchronous RTK Positioning with GNSS Signals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101256
Shu B, Liu H, Feng Y, Xu L, Qian C, Yang Z. Analysis of Factors Affecting Asynchronous RTK Positioning with GNSS Signals. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(10):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101256
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Bao, Hui Liu, Yanming Feng, Longwei Xu, Chuang Qian, and Zhixin Yang. 2019. "Analysis of Factors Affecting Asynchronous RTK Positioning with GNSS Signals" Remote Sensing 11, no. 10: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101256
APA StyleShu, B., Liu, H., Feng, Y., Xu, L., Qian, C., & Yang, Z. (2019). Analysis of Factors Affecting Asynchronous RTK Positioning with GNSS Signals. Remote Sensing, 11(10), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101256