Coupling Ocean Currents and Waves with Wind Stress over the Gulf Stream
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modeling Methods
2.1. Coupling between Each Model Component
2.2. Flux Parameterization and Experimental Design
2.3. Experiment Details
3. Modeling Results
3.1. Impact on the Wind Stress, Its Curl, and Waves
3.2. Impact on SST and Heat Fluxes
3.3. Impact on Surface Wind and Wind work
4. Discussion
4.1. Ocean and Atmopsheric Responses to the Three-Way Coupling
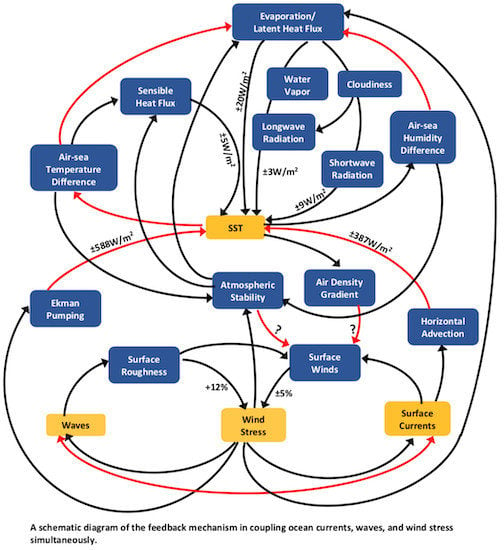
4.2. Feedback Processes
4.3. Importance of Horizontal Resolution
5. Comparison of Model and Observations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J. Wind-induced drift currents. J. Fluid Mech. 1975, 68, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonekamp, H.; Komen, G.J.; Sterl, A.; Janssen, P.A.E.M.; Taylor, P.K.; Yelland, M.J. Statistical Comparisons of Observed and ECMWF Modeled Open Ocean Surface Drag. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 1010–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kara, A.B.; Metzger, E.J.; Bourassa, M.A. Ocean current and wave effects on wind stress drag coefficient over the global ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L01604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ginis, I.; Hara, T.; Fan, Y.; Ginis, I.; Hara, T. The Effect of Wind–Wave–Current Interaction on Air–Sea Momentum Fluxes and Ocean Response in Tropical Cyclones. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 39, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourassa, M.A.; Gille, S.T.; Bitz, C.; Carlson, D.; Cerovecki, I.; Clayson, C.A.; Cronin, M.F.; Drennan, W.M.; Fairall, C.W.; Hoffman, R.N.; et al. High-Latitude Ocean and Sea Ice Surface Fluxes: Challenges for Climate Research. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Miller, A.J.; Norris, J. Eddy – Wind Interaction in the California Current System: Dynamics and Impacts. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2016, 46, 439–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.W.K.; Renfrew, I.A. An Assessment of the Surface Turbulent Heat Fluxes from the NCEP—NCAR Reanalysis over the Western Boundary Currents. J. Clim. 2002, 2020–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.B.; Robertson, F.R.; Clayson, C.A.; Bosilovich, M.G. Characterization of turbulent latent and sensible heat flux exchange between the atmosphere and ocean in MERRA. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cronin, M.F.; Wen, C.; Xue, Y.; Kumar, A.; McClurg, D. Assessing surface heat fluxes in atmospheric reanalyses with a decade of data from the NOAA Kuroshio Extension Observatory. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 6874–6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.P. Air sea interaction: Connecting the ocean and atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourassa, M.A. Satellite-based observations of surface turbulent stress during severe weather. Atmos. Interact. 2006, 2, 35–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Lee, S.-K.; Wu, L.; Mechoso, C.R. A global perspective on CMIP5 climate model biases. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, C. Processes and mechanisms for the model SST biases in the North Atlantic and North Pacific: A link with the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2015, 7, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuidema, P.; Chang, P.; Medeiros, B.; Kirtman, B.P.; Mechoso, R.; Schneider, E.K.; Toniazzo, T.; Richter, I.; Small, R.J.; Bellomo, K.; et al. Challenges and Prospects for Reducing Coupled Climate Model SST Biases in the Eastern Tropical Atlantic and Pacific Oceans: The U.S. CLIVAR Eastern Tropical Oceans Synthesis Working Group. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 2305–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kara, A.B.; Wallcraft, A.J.; Metzger, E.J.; Hurlburt, H.E.; Fairall, C.W.; Kara, A.B.; Wallcraft, A.J.; Metzger, E.J.; Hurlburt, H.E.; Fairall, C.W. Wind Stress Drag Coefficient over the Global Ocean. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5856–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornillon, P.; Park, K.-A. Warm core ring velocities inferred from NSCAT. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.A.; Dickinson, S.; McPhaden, M.J.; Johnson, G.C. Ocean currents evident in satellite wind data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 2469–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelton, D.B.; Schlax, M.G.; Freilich, M.H.; Milliff, R.F. Satellite Measurements Reveal Persistent Small-Scale Features in Ocean Winds. Science 2004, 303, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, K.A.; Cornillon, P.; Codiga, D.L. Modification of surface winds near ocean fronts: Effects of Gulf Stream rings on scatterometer (QuikSCAT, NSCAT) wind observations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2006, 111, C03032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaube, P.; Chelton, D.B.; Samelson, R.M.; Schlax, M.G.; O’Neill, L.W. Satellite Observations of Mesoscale Eddy-Induced Ekman Pumping. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2015, 45, 104–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawe, J.T.; Thompson, L.A. Effect of ocean surface currents on wind stress, heat flux, and wind power input to the ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L09604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.A.E.M. Wave-Induced Stress and the Drag of Air Flow over Sea Waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1989, 19, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, R.A. Surface Fluxes and Remote Sensing of Air–Sea Interactions. In Surface Waves and Fluxes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 7–27. [Google Scholar]
- Komen, G.; Janssen, P.A.E.M.; Makin, V.; Oost, W. On the sea state dependence of the Charnock parameter. Glob. Atmos. Ocean Syst. 1998, 5, 367–388. [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins, S.; Mailhot, J.; Lalbeharry, R.; Desjardins, S.; Mailhot, J.; Lalbeharry, R. Examination of the Impact of a Coupled Atmospheric and Ocean Wave System. Part I: Atmospheric Aspects. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2000, 30, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalbeharry, R.; Mailhot, J.; Desjardins, S.; Wilson, L.; Lalbeharry, R.; Mailhot, J.; Desjardins, S.; Wilson, L. Examination of the Impact of a Coupled Atmospheric and Ocean Wave System. Part II: Ocean Wave Aspects. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2000, 30, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drennan, W.M.; Taylor, P.K.; Yelland, M.J.; Drennan, W.M.; Taylor, P.K.; Yelland, M.J. Parameterizing the Sea Surface Roughness. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2005, 35, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.D.; Anderson, R.J.; Oost, W.A.; Kraan, C.; Maat, N.; De Cosmo, J.; Katsaros, K.B.; Davidson, K.L.; Bumke, K.; Hasse, L.; et al. Sea surface wind stress and drag coefficients: The hexos results. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 1992, 60, 109–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Powell, M.D.; Vickery, P.J.; Reinhold, T.A. Reduced drag coefficient for high wind speeds in tropical cyclones. Nature 2003, 422, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, I.-J.; Hara, T.; Ginis, I.; Belcher, S.E.; Tolman, H.L.; Moon, I.-J.; Hara, T.; Ginis, I.; Belcher, S.E.; Tolman, H.L. Effect of Surface Waves on Air–Sea Momentum Exchange. Part I: Effect of Mature and Growing Seas. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 2321–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelzang, J.; Stoffelen, A. ASCAT Ultrahigh-Resolution Wind Products on Optimized Grids. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2332–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourassa, M.A.; Stoffelen, A.; Bonekamp, H.; Chang, P.; Chelton, D.B.; Courtney, J.; Edson, R.; Figa, J.; He, Y.; Hersbach, H.; et al. Remotely Sensed Winds and Wind Stresses for Marine Forecasting and Ocean Modeling. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, Submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Bourassa, M.; Gille, S.; Jackson, D.; Roberts, J.B.; Wick, G. Ocean Winds and Turbulent Air–Sea Fluxes Inferred From Remote Sensing. Oceanography 2010, 23, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.C.; Armstrong, B.; He, R.; Zambon, J.B. Development of a Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere-Wave-Sediment Transport (COAWST) Modeling System. Ocean Model. 2010, 35, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabarrieta, M.; Warner, J.C.; Kumar, N. Wave-current interaction in Willapa Bay. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, C12014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabarrieta, M.; Warner, J.C.; Armstrong, B.; Zambon, J.B.; He, R. Ocean–atmosphere dynamics during Hurricane Ida and Nor’Ida: An application of the coupled ocean–atmosphere–wave–sediment transport (COAWST) modeling system. Ocean Model. 2012, 43, 112–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.; He, R. Effect of the Gulf Stream on winter extratropical cyclone outbreaks. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2012, 13, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phibbs, S.; Toumi, R. Modeled dependence of wind and waves on ocean temperature in tropical cyclones. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 7383–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, S.D.; Decker, S.G. Impact of Coupling an Ocean Model to WRF Nor’easter Simulations. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 4997–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coniglio, M.C.; Correia, J.; Marsh, P.T.; Kong, F. Verification of Convection-Allowing WRF Model Forecasts of the Planetary Boundary Layer Using Sounding Observations. Weather Forecast. 2013, 28, 842–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.E.; Cavallo, S.M.; Coniglio, M.C.; Brooks, H.E. A Review of Planetary Boundary Layer Parameterization Schemes and Their Sensitivity in Simulating Southeastern U.S. Cold Season Severe Weather Environments. Weather Forecast. 2015, 30, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Hall, A.; Teixeira, J. Evaluation of the WRF PBL Parameterizations for Marine Boundary Layer Clouds: Cumulus and Stratocumulus. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 2265–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komen, G.J.; Hasselmann, K.; Hasselmann, K.; Komen, G.J.; Hasselmann, K.; Hasselmann, K. On the Existence of a Fully Developed Wind-Sea Spectrum. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1984, 14, 1271–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourassa, M.A.; Vincent, D.G.; Wood, W.L. A Flux Parameterization Including the Effects of Capillary Waves and Sea State. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, C.W.; Bradley, E.F.; Hare, J.E.; Grachev, A.A.; Edson, J.B.; Fairall, C.W.; Bradley, E.F.; Hare, J.E.; Grachev, A.A.; Edson, J.B. Bulk Parameterization of Air–Sea Fluxes: Updates and Verification for the COARE Algorithm. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 571–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edson, J.B.; Jampana, V.; Weller, R.A.; Bigorre, S.P.; Plueddemann, A.J.; Fairall, C.W.; Miller, S.D.; Mahrt, L.; Vickers, D.; Hersbach, H. On the Exchange of Momentum over the Open Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 1589–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grachev, A.A.; Fairall, C.W. Dependence of the Monin–Obukhov Stability Parameter on the Bulk Richardson Number over the Ocean. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.K.; Yelland, M.J. The Dependence of Sea Surface Roughness on the Height and Steepness of the Waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 572–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oost, W.A.; Komen, G.J.; Jacobs, C.M.J.; Van Oort, C. New evidence for a relation between wind stress and wave age from measurements during ASGAMAGE. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2002, 103, 409–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.A. A Dynamic Roughness Equation and Its Application to Wind Stress Determination at the Air–Sea Interface. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1974, 4, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S. The Kain–Fritsch Convective Parameterization: An Update. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, M.J.; Delamere, J.S.; Mlawer, E.J.; Shephard, M.W.; Clough, S.A.; Collins, W.D. Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidvogel, D.B.; Beckmann, A. Numerical Ocean Circulation Modeling; Series on Environmental Science and Management; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Booij, N.; Ris, R.C.; Holthuijsen, L.H. A third-generation wave model for coastal regions: 1. Model description and validation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1999, 104, 7649–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Settelmaier, J. Gibbs, a Simulating Waves Nearshore (SWAN) modeling efforts at the National Weather Service (NWS) Southern Region (SR) coastal Weather Forecast Offices (WFOs). In Proceedings of the 91st AMS Annual Meeting, Seattle, WA, USA, 22–28 January 2011; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chelton, D.B.; Schlax, M.G.; Samelson, R.M. Summertime Coupling between Sea Surface Temperature and Wind Stress in the California Current System. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2007, 37, 495–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.W.; Esbensen, S.K.; Thum, N.; Samelson, R.M.; Chelton, D.B. Dynamical analysis of the boundary layer and surface wind responses to mesoscale SST perturbations. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 559–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, N.; Qiu, B. The Atmospheric Response to Weak Sea Surface Temperature Fronts*. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 3356–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, L.W. Wind speed and stability effects on coupling between surface wind stress and SST observed from buoys and satellite. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 1544–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Chelton, D.B.; Esbensen, S.K.; Thum, N.; O’Neill, L.W. Coupling between sea surface temperature and low-level winds in mesoscale numerical models. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 146–164. [Google Scholar]
- Chelton, D.B.; Xie, S.-P. Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction at Oceanic Mesoscales. Oceanography 2010, 23, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthuijsen, L.H.; Tolman, H.L. Effects of the Gulf Stream on ocean waves. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1991, 96, 12755–12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, K.E.; Sheres, D.; Kenyon, K.E.; Sheres, D. Wave Force on an Ocean Current. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2006, 36, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caniaux, G.; Planton, S. A three-dimensional ocean mesoscale simulation using data from the SEMAPHORE eperiment: Mixed layer heat Budget. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 25081–25099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, J.W.; Niiler, P.P. Upper Ocean Heat Budget During the Hawaii−to−Tahiti Shuttle Experiment. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1983, 13, 1894–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, A.B.; Rochford, P.A.; Hurlburt, H.E. Mixed layer depth variability and barrier layer formation over the North Pacific Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2000, 105, 16783–16801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kara, A.B.; Rochford, P.A.; Hurlburt, H.E. An optimal definition for ocean mixed layer depth. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 16803–16821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchepetkin, A.F.; Mcwilliams, J.C. Quasi-Monotone Advection Schemes Based on Explicit Locally Adaptive Dissipation. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1998, 126, 1541–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, M.M.-K.; Stage, S.A. Dynamical analyses of marine atmospheric boundary layer structure near the Gulf Stream oceanic front. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1989, 115, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.M.; Mitchell, T.P.; Deser, C. The Influence of Sea-Surface Temperature on Surface Wind in the Eastern Equatorial Pacific: Seasonal and Interannual Variability. J. Clim. 1989, 2, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, R.J.; Xie, S.-P.; Wang, Y.; Esbensen, S.K.; Vickers, D. Numerical Simulation of Boundary Layer Structure and Cross-Equatorial Flow in the Eastern Pacific. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 1812–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.H.; Hong, S.-Y.; Dudhia, J. Impacts of the Lowest Model Level Height on the Performance of Planetary Boundary Layer Parameterizations. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 664–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez-Belchí, P.; Tintoré, J. Vertical velocities at an ocean front. Sci. Mar. 2001, 65, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourassa, M.A.; Ford, K.M. Uncertainty in scatterometer-derived vorticity. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.B.; Overland, J.; Plerson, W.J.; Cardone, V.J.; McPherson, R.D.; Yu, T.-W. Chapter 4 Oceanic Surface Winds. Adv. Geophys. 1985, 27, 101–140. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.T.; Tang, W. Equivalent Neutral Winds; JPL Publication 96-17, Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kara, A.B.; Wallcraft, A.J.; Bourassa, M.A. Air–sea stability effects on the 10 m winds over the global ocean: Evaluations of air–sea flux algorithms. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, F.J.; Ricciardulli, L.; Rodriguez, E.; Stiles, B.W.; Bourassa, M.A.; Long, D.G.; Hoffman, R.N.; Stoffelen, A.; Verhoef, A.; O’Neill, L.W.; et al. Evaluating and Extending the Ocean Wind Climate Data Record. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2165–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, E.; Wineteer, A.; Perkovic-Martin, D.; Gál, T.; Stiles, B.W.; Niamsuwan, N.; Monje, R.R. Estimating Ocean VectorWinds and currents using a Ka-band pencil-beam Doppler Scatterometer. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


















| Experiments | Roughness Length Algorithm | Wind Input for Surface Stress Formulation |
|---|---|---|
| CTL | COARE 3.0 | |
| CUR | COARE 3.0 | |
| WAV | Taylor and Yelland | |
| CUR_WAV | Taylor and Yelland |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Q.; Bourassa, M.A. Coupling Ocean Currents and Waves with Wind Stress over the Gulf Stream. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121476
Shi Q, Bourassa MA. Coupling Ocean Currents and Waves with Wind Stress over the Gulf Stream. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(12):1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121476
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Qi, and Mark A. Bourassa. 2019. "Coupling Ocean Currents and Waves with Wind Stress over the Gulf Stream" Remote Sensing 11, no. 12: 1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121476
APA StyleShi, Q., & Bourassa, M. A. (2019). Coupling Ocean Currents and Waves with Wind Stress over the Gulf Stream. Remote Sensing, 11(12), 1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121476