Characteristics of Absorption Spectra of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter in the Pearl River Estuary in Spring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Absorption Spectra Collection
2.2. Spectral Slopes and Absorption Ratios
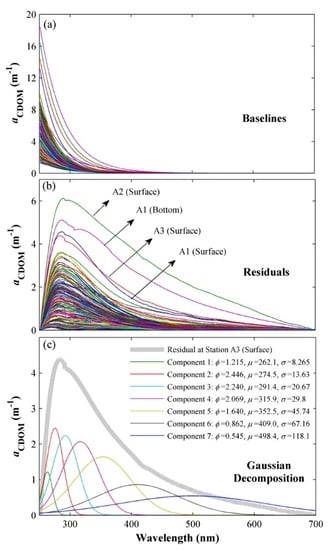
2.3. Gaussian Decomposition Approach
3. Results
3.1. Spectral Slopes and Absorption Ratios
3.2. Gaussian Decomposition
4. Discussion
4.1. Spectral Signatures
4.2. Gaussian Decomposition
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carlson, C.; Hansell, D. DOM sources, sinks, reactivity, and budgets. In Biogeochemistry of Marine Dissolved Organic Matter, 2nd ed.; Hansell, D., Carlson, C., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 65–125. [Google Scholar]
- Ducklow, H.W. Forword. In Biogeochemistry of Marine Dissolved Organic Matter; Hansell, D., Carlson, C., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. xv–xix. [Google Scholar]
- Azam, F. Forword. In Biogeochemistry of Marine Dissolved Organic Matter, 2nd ed.; Hansell, D., Carlson, C., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. xiii–xv. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Hur, J. Utilization of UV-Vis spectroscopy and related data analyses for dissolved organic matter (DOM) studies: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stedmon, C.A.; Nelson, N.B. The optical properties of DOM in the ocean. In Biogeochemistry of Marine Dissolved Organic Matter, 2nd ed.; Hansell, D., Carlson, C., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 481–508. [Google Scholar]
- Massicotte, P.; Markager, S. Using a Gaussian decomposition approach to model absorption spectra of chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Mar. Chem. 2016, 180, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, M.; Burden, A.; Cooper, M.; Dunn, C.; Evans, C.D.; Fenner, N.; Freeman, C.; Gough, R.; Hughes, D.; Hughes, S.; et al. Quantifying dissolved organic carbon concentrations in upland catchments using phenolic proxy measurements. J. Hydrol. 2013, 477, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osburn, C.L.; Boyd, T.J.; Montgomery, M.T.; Coffin, R.B.; Bianchi, T.S.; Paerl, H.W. Optical proxies for terrestrial dissolved organic matter in estuaries and coastal waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 2, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichot, C.G.; Benner, R.; Kaiser, K.; Shen, Y.; Amon, R.M.W.; Ogawa, H.; Lu, C.J. Predicting dissolved lignin phenol concentrations in the coastal ocean from chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) absorption coefficients. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Senesi, N.; Schnitzer, M. Information provided on humic substances by E4:E6 ratios. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977, 41, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haan, D.H.; Boer, T.D. Applicability of light absorbance and fluorescence as measures of concentration and molecular size of dissolved organic carbon in humic Lake Tjeukemeer. Water Res. 1987, 21, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J. Dissolved organic matter and its optical properties in a black water tributary of the upper Orinoco river, Venezuela. Org. Geochem. 1998, 28, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslewicz, J.; Gonet, S.S. Properties of humic acids as biomarkers of lake catchment management. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 66, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peuravuori, J.; Pihlaja, K. Molecular size distribution and spectroscopic properties of aquatic humic substances. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1997, 337, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlandsson, M.; Futter, M.N.; Kothawala, D.N.; Kohler, S.J. Variability in spectral absorbance metrics across boreal lake waters. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 2643–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.; Pinto, A.; Filipe, O.; Cunha, A.; Santos, E.B.H.; Almeida, A. Insights on the optical properties of estuarine DOM? Hydrological and biological influences. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helms, J.R.; Stubbins, A.; Ritchie, J.D.; Minor, E.C.; Kieber, D.J.; Mopper, K. Absorption spectral slopes and slope ratios as indicators of molecular weight, source, and photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaffe, R.; Boyer, J.N.; Lu, X.; Marie, N.; Yang, C.; Scully, N.M.; Mock, S. Source characterization of dissolved organic matter in a subtropical mangrove-dominated estuary by fluorescence analysis. Mar. Chem. 2004, 84, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerlov, N.G. Optical Oceanography; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Bricaud, A.; Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Absorption by dissolved organic matter of the sea (yellow substance) in the UV and visible domains. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1981, 26, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stedmon, C.A.; Markager, S.; Kaas, H. Optical properties and signatures of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in Danish coastal waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 51, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichot, C.G.; Benner, R. The spectral slope coefficient of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (S275–295) as a tracer of terrigenous dissolved organic carbon in river-influenced ocean margins. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1453–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiselle, S.A.; Bracchini, L.; Dattilo, A.M.; Ricci, M.; Tognazzi, A. Optical characterization of chromophoric dissolved organic matter using wavelength distribution of absorption spectral slopes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiselle, S.A.; Vione, D.; Minero, C.; Maurino, V.; Tognazzi, A.; Dattilo, A.M.; Rossi, C.; Bracchini, L. Chemical and optical phototransformation of dissolved organic matter. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3197–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twardowski, M.S.; Boss, E.; Sullivan, J.M.; Donaghay, P.L. Modeling the spectralshape of absorption by chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Mar. Chem. 2004, 89, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.N.; Kowalczuk, P.; Kaczmarek, S.A.; Cota, G.F. Two models for absorptionby coloured dissolved organic matter (CDOM). Oceanologia 2002, 44, 209–241. [Google Scholar]
- Catala, T.S.; Reche, I.; Ramon, C.L.; Lopez-Sanz, A.; Alvarez, M.; Calvo, E.; Alvarez-Salgado, X.A. Chromophoric signatures of microbial by-products in the dark ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 7639–7648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, M.G.; Lutz, V.; Frouin, R. Spectral absorption by marine chromophoric dissolved organic matter: Laboratory determination and piecewise regression modeling. Mar. Chem. 2017, 194, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Pan, J.; Devlin, A.T. Mixing behavior of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the Pearl River Estuary in spring. Cont. Shelf Res. 2018, 154, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blough, N.V.; Del Vecchio, R. Chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in the coastal environment. In Biogeochemistry of Marine Dissolved Organic Matter; Hansell, D., Carlson, C., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 509–546. [Google Scholar]
- Boyle, E.S.; Guerriero, N.; Thiallet, A.; Del Vecchio, R.; Blough, N.V. Optical properties of humic substances and CDOM: Relation to structure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2262–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpless, C.M.; Blough, N.V. The importance of charge-transfer interactions in determining chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) optical and photochemical properties. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 654–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalzell, B.J.; Minor, E.C.; Mopper, K.M. Photodegradation of estuarine dissolved organic matter: A multi-method assessment of DOM transformation. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repeta, D.J. Chemical characterization and cycling of dissolved organic matter. In Biogeochemistry of Marine Dissolved Organic Matter, 2nd ed.; Hansell, D., Carlson, C., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 21–63. [Google Scholar]
- Mopper, K.; Kieber, D.J.; Stubbins, A. Marine photochemistry of organic matter: Processes and impacts. In Biogeochemistry of Marine Dissolved Organic Matter, 2nd ed.; Hansell, D., Carlson, C., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 389–450. [Google Scholar]
- Yentsch, C.S.; Eichert, C.A. The interrelationship between water-soluble yellow substances and chloroplastic pigments in marine algae. Bot. Mar. 1962, 3, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Seritti, A.; Morelli, E.; Nannicini, L.; Del Vecchio, R. Production of hydrophobic fluorescent organic matter by the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Chemosphere 1994, 28, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Surface | Bottom | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean ± SD | Range | Mean ± SD | |
| a(300) (m−1) | 0.59–9.75 | 2.69 ± 1.52 | 0.43–9.72 | 1.78 ± 1.41 |
| SUVC (nm−1) | 0.0076–0.0183 | 0.0121 ± 0.002 | 0.0076–0.0183 | 0.0132 ± 0.0019 |
| SUVB (nm−1) | 0.0127–0.0303 | 0.0184 ± 0.003 | 0.0127–0.0303 | 0.0208 ± 0.003 |
| SUVA (nm−1) | 0.0085–0.0219 | 0.0173 ± 0.0026 | 0.0085–0.0219 | 0.0166 ± 0.0022 |
| SVIS (nm−1) | 0.0029–0.0199 | 0.0131 ± 0.0035 | 0.0029–0.0199 | 0.0132 ± 0.01 |
| S275–295 (nm−1) | 0.0122–0.0298 | 0.0184 ± 0.0037 | 0.0122–0.0298 | 0.0205 ± 0.0034 |
| S350–400 (nm−1) | 0.0068–0.0335 | 0.016 ± 0.0031 | 0.0068–0.0335 | 0.0177 ± 0.0041 |
| SR | 0.72–2.93 | 1.20 ± 0.38 | 0.72–2.93 | 1.20 ± 0.38 |
| E2/E3 | 3.11–13.27 | 6.94 ± 1.36 | 3.11–13.27 | 7.22 ± 1.5 |
| E2/E4 | 4.71–37.73 | 19.26 ± 5 | 4.71–37.73 | 18.96 ± 6.8 |
| φ (m−1) | 0.12–6.13 | 1.87 ± 1.1 | 0.12–6.13 | 1.12 ± 0.89 |
| %Residual | 6–59 | 47 | 6–59 | 39 |
| N | 2–8 | 5.44 ± 1.6 | 2–8 | 4.8 ± 1.7 |
| ϕ (m−1) | 0.015–2.934 | 0.6889 ± 0.5080 | 0.007–2.612 | 0.4614 ± 0.4062 |
| µ (nm) | 250–650 | 318 ± 56.4 | 250–650 | 330.5 ± 73.9 |
| σ (nm) | 0–100 | 39.2 ± 38.9 | 0–100 | 43.6 ± 43.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, X.; Pan, J.; Devlin, A.T. Characteristics of Absorption Spectra of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter in the Pearl River Estuary in Spring. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131533
Lei X, Pan J, Devlin AT. Characteristics of Absorption Spectra of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter in the Pearl River Estuary in Spring. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(13):1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131533
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Xia, Jiayi Pan, and Adam T. Devlin. 2019. "Characteristics of Absorption Spectra of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter in the Pearl River Estuary in Spring" Remote Sensing 11, no. 13: 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131533
APA StyleLei, X., Pan, J., & Devlin, A. T. (2019). Characteristics of Absorption Spectra of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter in the Pearl River Estuary in Spring. Remote Sensing, 11(13), 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131533