Automated Extraction of Built-Up Areas by Fusing VIIRS Nighttime Lights and Landsat-8 Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
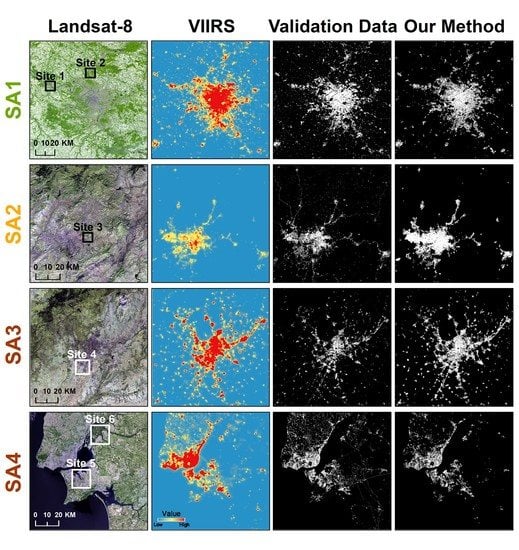
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Data
2.3. Automatic Selection of Built-Up Training Samples
2.4. Built-Up Area Preliminary Classification
2.5. Fine Classification of Built-Up Areas
2.6. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A.; Potere, D. Mapping global urban areas using MODIS 500-m data: New methods and datasets based on ‘urban ecoregions’. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. Use of impervious surface in urban land-use classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Remote sensing of impervious surfaces in the urban areas: Requirements, methods, and trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global Consequences of Land Use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global Change and the Ecology of Cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Tian, J.; Ma, Q. Urban expansion dynamics and natural habitat loss in China: A multiscale landscape perspective. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2886–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.I.; Kareiva, P.; Forman, R.T.T. The implications of current and future urbanization for global protected areas and biodiversity conservation. Biol. Cons. 2008, 141, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.X.; Pla, F.; Latorre-Carmona, P.; Myint, S.W.; Caetano, M.; Kieu, H.V. Characterizing the relationship between land use land cover change and land surface temperature. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 124, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sofia, G.; Roder, G.; Dalla Fontana, G.; Tarolli, P. Flood dynamics in urbanised landscapes: 100 years of climate and humans’ interaction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Organ. Environ. 2014, 24, 535–613. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Chen, W.; Zheng, G.; Shum, C.K.; Yang, K.; Piao, S.; Sheng, Y.; Yi, S.; Li, J.; et al. Regional differences of lake evolution across China during 1960s–2015 and its natural and anthropogenic causes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 386–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ougaard, M. The Transnational State and the Infrastructure Push. New Political Econ. 2018, 23, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Heldens, W.; Hirner, A.; Keil, M.; Marconcini, M.; Roth, A.; Zeidler, J.; Dech, S.; Strano, E. Breaking new ground in mapping human settlements from space—The Global Urban Footprint. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 134, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potere, D.; Schneider, A.; Angel, S.; Civco, D.L. Mapping urban areas on a global scale: Which of the eight maps now available is more accurate? Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 6531–6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Pei, F.; Wang, S. High-resolution multi-temporal mapping of global urban land using Landsat images based on the Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L.; Niu, Z.; Huang, X.; Fu, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Finer resolution observation and monitoring of global land cover: First mapping results with Landsat TM and ETM+ data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 34, 2607–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, G.; Peng, S.; Lu, M.; et al. Global land cover mapping at 30m resolution: A POK-based operational approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dell’Acqua, F.; Gamba, P. Discriminating urban environments using multiscale texture and multiple SAR images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3797–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Y.; Jacob, A.; Gamba, P. Spaceborne SAR data for global urban mapping at 30 m resolution using a robust urban extractor. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Deng, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, N.; Si, Q. Effective Mapping of Urban Areas Using ENVISAT ASAR, Sentinel-1A, and HJ-1-C Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Shi, P.; Xie, D.; Zhao, Y. Improving the normalized difference built-up index to map urban built-up areas using a semiautomatic segmentation approach. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 1, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabo, F.; Corbane, C.; Florczyk, A.J.; Ferri, S.; Pesaresi, M.; Kemper, T. Comparison of built-up area maps produced within the global human settlement framework. Trans. GIS 2018, 22, 1406–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, R.; Stuhlmacher, M.F.; Tellman, B.; Clinton, N.; Hanson, G.; Georgescu, M.; Wang, C.; Serrano-Candela, F.; Khandelwal, A.K.; Cheng, W.-H.; et al. Using Landsat and nighttime lights for supervised pixel-based image classification of urban land cover. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, L. Using VIIRS-DNB and landsat data for impervious surface area mapping in an arid/semiarid region. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wan, B.; Guo, Q.; Hu, M.; Zhou, S. Mapping Regional Urban Extent Using NPP-VIIRS DNB and MODIS NDVI Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.; Sun, S. A novel method for urban area extraction from VIIRS DNB and MODIS NDVI data: A case study of Chinese cities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 6094–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, A.; Balzter, H.; Ibrahim, R.G.; Hameed, M.H.; Wheeler, J.; Adamu, B.; Ibrahim, S.; Najmaddin, M.P. Applying Built-Up and Bare-Soil Indices from Landsat 8 to Cities in Dry Climates. Land 2018, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, Y. A Genetic Algorithm-Based Urban Cluster Automatic Threshold Method by Combining VIIRS DNB, NDVI, and NDBI to Monitor Urbanization. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y. Urban mapping using DMSP/OLS stable night-time light: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 6030–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Huang, C.; Yu, B.; Yin, B.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS night-time light composite data for extracting built-up urban areas. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Imura, H.; Higashi, O. A SVM-based method to extract urban areas from DMSP-OLS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2205–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Spatiotemporally enhancing time-series DMSP/OLS nighttime light imagery for assessing large-scale urban dynamics. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Lu, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Mapping Impervious Surface Distribution with Integration of SNNP VIIRS-DNB and MODIS NDVI Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12459–12477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latifovic, R.; Pouliot, D.; Olthof, I. Circa 2010 Land Cover of Canada: Local Optimization Methodology and Product Development. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Hu, T.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Benediktsson, J.A. Mapping Urban Areas in China Using Multisource Data With a Novel Ensemble SVM Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4258–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhao, K.; Thomson, A.; Imhoff, M. A cluster-based method to map urban area from DMSP/OLS nightlights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Ehrlich, D.; Ferri, S.; Florczyk, A.; Manuel, C.F.S.; Halkia, S.; Maria, J.A.; Thomas, K.; Pierre, S.; Vasileios, S. Operating Procedure for the Production of the Global Human Settlement Layer from Landsat Data of the Epochs 1975, 1990, 20001975, 1990, 2000, and 2014; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Corbane, C.; Pesaresi, M.; Politis, P.; Syrris, V.; Florczyk, A.J.; Soille, P.; Maffenini, L.; Burger, A.; Vasilev, V.; Rodriguez, D.; et al. Big earth data analytics on Sentinel 1 and Landsat imagery in support to global human settlements mapping. Big Earth Data 2017, 1, 118–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Huang, C.; Brown de Colstoun, E.C.; Tilton, J.C.; Tan, B. Global Human Built-Up And Settlement Extent (HBASE) Dataset From Landsat; NASA Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC): Palisades, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- The National Land Cover Database. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/centers/eros/science/national-land-cover-database (accessed on 15 December 2018).
- Copernicus Land Monitoring Service—High Resolution Layer Imperviousness: Product Specifications Document. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/user-corner/technical-library/hrl-imperviousness-technical-document-prod-2015 (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Florczyk, A.J.; Ferri, S.; Syrris, V.; Kemper, T.; Halkia, M.; Soille, P.; Pesaresi, M. A New European Settlement Map From Optical Remotely Sensed Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 1978–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveland, T.R.; Irons, J.R. Landsat 8: The plans, the reality, and the legacy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Claverie, M.; Franch, B. Preliminary analysis of the performance of the Landsat 8/OLI land surface reflectance product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Helder, D.; Irons, J.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Kennedy, R.; et al. Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, M.M.; Smith, L.C. Advances in using multitemporal night-time lights satellite imagery to detect, estimate, and monitor socioeconomic dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 176–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.-C. Why VIIRS data are superior to DMSP for mapping nighttime lights. Proc. Asia Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Straka, W.; Mills, S.; Elvidge, C.; Lee, T.; Solbrig, J.; Walther, A.; Heidinger, A.; Weiss, S. Illuminating the Capabilities of the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (NPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) Day/Night Band. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6717–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elvidge, C.; Hsu, F.-C.; Baugh, K.; Ghosh, T. National Trends in Satellite-Observed Lighting: 1992–2012. In Global Urban Monitoring and Assessment through Earth Observation; CRC Press: London, UK, 2014; Volume 23, pp. 97–120. [Google Scholar]
- HRL Imperviousness Degree 2015 Validation Report. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/user-corner/technical-library/hrl-2015-imperviousness-validation-report (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- North, M.A. A Method for Implementing a Statistically Significant Number of Data Classes in the Jenks Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2009 Sixth International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, Tianjin, China, 14–16 August 2009; pp. 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tu, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, W. A Novel Approach for Identifying Urban Built-Up Area Boundaries Using High-Resolution Remote-Sensing Data Based on the Scale Effect. ISPRS Int. J. Geo. Inf. 2018, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, G.F. The Data Model Concept in Statistical Mapping. Int. Yearb. Cartogr. 1967, 7, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myneni, R.B.; Hall, F.G.; Sellers, P.J.; Marshak, A.L. The interpretation of spectral vegetation indexes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 1995, 33, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Song, K.; Kim, S.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Davis, P.; Masek, J.G.; Goward, S.N. Use of a dark object concept and support vector machines to automate forest cover change analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 970–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Davis, L.S.; Townshend, J.R.G. An assessment of support vector machines for land cover classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 725–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Gong, P. Comparison of Classification Algorithms and Training Sample Sizes in Urban Land Classification with Landsat Thematic Mapper Imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 964–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herold, M.; Gardner, M.E.; Roberts, D.A. Spectral resolution requirements for mapping urban areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1907–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okujeni, A.; van der Linden, S.; Hostert, P. Extending the vegetation–impervious–soil model using simulated EnMAP data and machine learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popular Repositories. Available online: https://github.com/njuRS (accessed on 9 March 2019).
- Tian, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X. Perpendicular Impervious Index for Remote Sensing of Multiple Impervious Surface Extraction in Cities. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, K.; Cheng, L.; Li, M.; Guo, Z. A comparison of Landsat8 impervious surface extraction methods. Remote Sens. Land Resour. (accepted).
- Jiang, W.; He, G.; Long, T.; Guo, H.; Yin, R.; Leng, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, G. Potentiality of Using Luojia 1-01 Nighttime Light Imagery to Investigate Artificial Light Pollution. Sensors 2018, 18, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Abbreviation | Map | Producer | Reference Year(s) | Resolution | Extent | Data | Method | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLC30 | GlobeLand30 | NGCC | 2010 | 30 m | Global | Landsat | Supervised classification based on POK | UA: 86.7% | [17] |
| FROM-GLC | Finer Resolution Observation and Monitoring of Global Land Cover | THU | 2010, 2015, 2017 | 30 m | Global | Landsat | Supervised classification | UA: 30.8% (2010) | [16] |
| GUL | Global Urban Land | SYSU | 1990–2015, every five years | 30 m | Global | Landsat, DMSP-OLS | NUACI | TA: 81%-84% | [15] |
| GHS | Global Human Settlement | JRC | 1975, 1990, 2000, 2014 | 38 m | Global | Landsat | Supervised classification based on SML | TA: 89% | [37] |
| 2016 | 20 m | Global | Sentinel-1 | Supervised classification based on SML | ** | [38] | |||
| HBASE | Global Human Built-up And Settlement Extent | NASA | 2010 | 30 m | Global | Landsat | Supervised classification based on texture features | ** | [39] |
| GUF | Global Urban Footprint | DLR | 2011 | 12 m | Global | TerraSAR X, TanDEM X | Unsupervised classification based on texture features | TA: 85% | [13] |
| NLCD | National Land Cover Database | MRLC | 2001, 2006, 2011 | 30 m | USA | Landsat | Supervised classification based on decision-tree classification | RMSE: 6.86-13.12% (2006) | [40] |
| HRL IMD | High Resolution Layer Imperviousness Degree | EEA | 2006, 2009, 2012, 2015 | 20 m | Europe | Landsat, SPOT-5 | Supervised classification | UA>90% PA>90% | [41] |
| ESM | European Settlement Map | JRC | 2012 | 2.5 m, 10 m | Europe | SPOT-5, SPOT-6 | Supervised classification based on SML | TA>95% | [42] |
| Study Area | Path-Row | Imaging Date |
|---|---|---|
| 1 (Paris) | 199-26 | 2015-09-27 |
| 2 (Ankara) | 177-32 | 2015-11-04 |
| 3 (Madrid) | 201-32 | 2015-09-25 |
| 4 (Lisbon) | 204-33 | 2015-06-26 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Yang, K.; Bennett, M.M.; Guo, Z.; Cheng, L.; Li, M. Automated Extraction of Built-Up Areas by Fusing VIIRS Nighttime Lights and Landsat-8 Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131571
Liu C, Yang K, Bennett MM, Guo Z, Cheng L, Li M. Automated Extraction of Built-Up Areas by Fusing VIIRS Nighttime Lights and Landsat-8 Data. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(13):1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131571
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chang, Kang Yang, Mia M. Bennett, Ziyan Guo, Liang Cheng, and Manchun Li. 2019. "Automated Extraction of Built-Up Areas by Fusing VIIRS Nighttime Lights and Landsat-8 Data" Remote Sensing 11, no. 13: 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131571
APA StyleLiu, C., Yang, K., Bennett, M. M., Guo, Z., Cheng, L., & Li, M. (2019). Automated Extraction of Built-Up Areas by Fusing VIIRS Nighttime Lights and Landsat-8 Data. Remote Sensing, 11(13), 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131571