Radar Measurements of Morphological Parameters and Species Identification Analysis of Migratory Insects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Estimation of Morphological Parameters
2.1. Multi-Frequency Insect RCS Measurements
2.2. Multi-Frequency Scattering Characteristic Analysis
2.3. Multi-Frequency Scattering Feature Extraction
2.4. Estimation of Morphological Parameters
3. Species Identification of Migratory Insects
3.1. Data Description
3.2. Classification Method
3.3. Separability Analysis of the Thorax Width
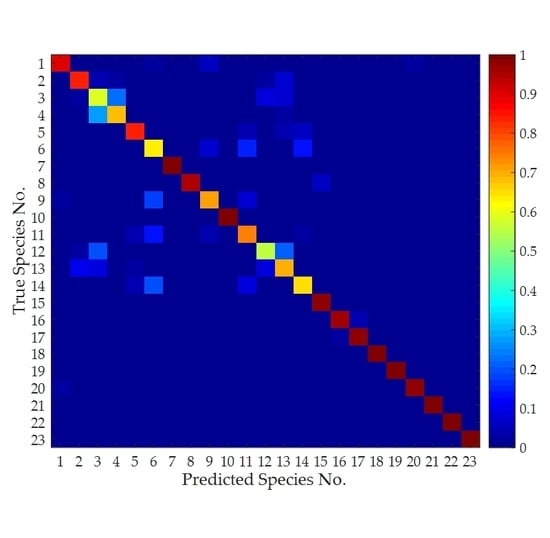
3.4. Classification Performance Achieved Using All Features
3.5. Classification Performance Achieved Using Single Features
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Chapman, J.W.; Reynolds, D.R.; Smith, A.D. Vertical-Looking Radar: A new tool for monitoring high-altitude insect migration. BioScience 2003, 53, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Lim, K.S.; Horvitz, N.; Clark, S.J.; Reynolds, D.R.; Sapir, N.; Chapman, J.W. Mass seasonal bioflows of high-flying insect migrants. Science 2016, 354, 1584–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nebuloni, R.; Capsoni, C.; Vigorita, V. Quantifying bird migration by a high-resolution weather radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1867–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.; Hoye, B.J. Migratory animals couple biodiversity and ecosystem functioning worldwide. Science 2014, 344, 1242552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, R.A.; Wikelski, M.; Wilcove, D.S. How and why do insects migrate. Science 2006, 313, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, D.; Deveson, T. Forecasting and management of migratory pests in Australia. Insect Sci. 2010, 9, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D.R.; Chapman, J.W.; Harrington, R. The migration of insect vectors of plant and animal viruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2006, 67, 453–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chapman, J.W.; Reynolds, D.R.; Wilson, K. Long-range seasonal migration in insects: Mechanisms, evolutionary drivers and ecological consequences. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, V.A.; Farrow, R.A. A radar and aerial-trapping study of an early spring migration of moths (Lepidoptera) in inland New South Wales. Austral. J. Ecol. 1985, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.W.; Reynolds, D.R.; Smith, A.D.; Riley, J.R.; Pedgley, D.E.; Woiwod, I.P. High-altitude migration of the diamondback moth Plutella xylostella to the UK: A study using radar, aerial netting, and ground trapping. Ecol. Entomol. 2002, 27, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolyn, M.; Brzustowski, J.M.; Taylor, P.D.; Peckford, M.L.; Dave, W. RadR: An open-source platform for acquiring and analysing data on biological targets observed by surveillance radar. BMC Ecol. 2010, 10, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, G.W. An Airborne Radar Technique for the Investigation and Control of Migrating Pest Insects. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1979, 287, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, S.E.; Wolf, W.W. An airborne radar technique for studying insect migration. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1989, 79, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.R.; Reynolds, D.R.; Smith, A.D.; Edwards, A.S.; Zhai, B.P. Observations of the autumn migration of the rice leaf roller cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) and other moths in eastern china. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1995, 85, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbrook, J.K.; Eystera, R.S.; Wolf, W.W.; Lingrena, P.D.; Raulstonb, J.R. Migration pathways of corn earworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) indicated by tetroon trajectories. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 73, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Deng, Y.K.; Wang, R.; Liu, C.J.; Long, T. High accuracy acquisition of 3-d flight trajectory of individual insect based on phase measurement. Sensors 2016, 16, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, V.A. Automatically operating radars for monitoring insect pest migrations. Insect Sci. 2002, 9, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.R. Riding on the Wind: A Radar Perspective of Insect Flight; Inaugural Lecture Series; University of Greenwich: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, J.H.; Jensen, D.R.; Noonkester, V.R.; Kreasky, J.B.; Stimmann, M.W.; Wolf, W.W. Remote Radar Sensing: Atmospheric Structure and Insects. Science 1973, 180, 1176–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, J.R. Collective orientation in night-flying insects. Nature 1975, 253, 113–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.M.; Reynolds, D.R.; Sane, S.P.; Hu, G.; Chapman, J.W. Orientation in high-flying migrant insects in relation to flows: Mechanisms and strategies. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.R.; Reynolds, D.R. Radar-based studies of the migratory flight of grasshoppers in the middle Niger area of Mali. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1979, 204, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, V.A.; Wang, H.K.; Harman, I.T. Insect monitoring radar: Remote and network operation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2002, 35, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.W.; Smith, A.D.; Woiwood, I.P.; Reynolds, D.R.; Riley, J.R. Development of vertical-looking radar technology for monitoring insect migration. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2002, 35, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.W.; Drake, V.A.; Reynolds, D.R. Recent insights from radar studies of insect flight. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, V.A.; Chapman, J.W.; Lim, K.S.; Reynolds, D.R.; Riley, J.R.; Smith, A.D. Ventral-aspect radar cross sections and polarization patterns of insects at X band and their relation to size and form. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5022–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.R. Radar cross section of insects. Proc. IEEE 1985, 73, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hu, C.; Fu, X.; Long, T.; Zeng, T. Micro-doppler measurement of insect wing-beat frequencies with W-band coherent radar. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hu, C.; Liu, C.J.; Kong, S.Y.; Lang, T.J. Migratory Insect Multifrequency Radar Cross Sections for Morphological Parameter Estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 3450–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, W.W.; Vaughn, C.R.; Harris, R.; Loper, G.M. Insect radar cross-sections for aerial density measurements and target classification. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1993, 36, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhous, A.C. An Investigation of the Polarisation Dependence of Insect Radar Cross Sections at Constant Aspect. Ph.D. Thesis, Cranfield Institute of Technology, Cranfield, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Li, W.D.; Wang, R.; Liu, C.J.; Zhang, T.R.; Li, W.Q. Accurate Insect Orientation Extraction Based on Polarization Scattering Matrix Estimation. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1755–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, S.E.; Aldhous, A.C. Insect ventral radar cross-section polarisation dependence measurements for radar entomology. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2006, 153, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean, T.J.; Drake, V.A. Monitoring insect migration with radar: The ventral-aspect polarization pattern and its potential for target identification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 3957–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.D.; Riley, J.R.; Gregory, R.D. A method for routine monitoring of the aerial migration of insects by using a vertical-looking radar. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1993, 340, 393–404. [Google Scholar]
- Melnikov, V.M.; Istok, M.J.; Westbrook, J.K. Asymmetric radar echo patterns from insects. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 659–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.O.; Bartley, P.G.; Lawrence, K.C. RF and microwave dielectric properties of stored-grain insects and their implications for potential insect control. T. ASABE 1998, 41, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doviak, R.J.; Dusan, S. Doppler Radar and Weather Observations, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Kong, S.Y.; Wang, R.; Long, T.; Fu, X.W. Identification of Migratory Insects from their Morphological Features using a Decision-Tree Support Vector Machine and its Application to Radar Entomology. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.-Q.; Wu, K.-M.; Ni, Y.-X.; Cheng, D.-F.; Guo, Y.-Y. Nocturnal migration of dragonflies over the Bohai Sea in northern China. Ecol. Entomol. 2006, 31, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V.N. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. Libsvm: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, R.G.; Lloyd, G.R. Support vector machines for classification and regression. Analyst 2010, 135, 230–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Qing, Z.; Zhen, Z. Automatic insect classification based on local mean colour feature and Supported Vector Machines. Orient. Insects 2012, 46, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, M.; Watson, A.T. Automatic species identification of live moths. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovative Techniques and Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Cambridge, UK, 11–13 December 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Davis, L.S.; Townshend, J.R.G. An assessment of support vector machines for land cover classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 725–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, F.; Abe, S. Decision-tree-based multiclass support vector machines. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Singapore, 18–22 November 2002; Volume 3, pp. 1418–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Drake, V.A. Distinguishing target classes in observations from vertically pointing entomological radars. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2016, 37, 3811–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, W.J.; Shapiro, A. Discrimination of bird and insect radar echoes in clear air using high-resolution radars. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 1215–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.L.; Well, A.D. Research Design and Statistical Analysis. In Research Design and Statistical Analysis, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2003; p. 508. [Google Scholar]
- Yannis, G.; Antoniou, C.; Papadimitriou, E. Autoregressive nonlinear time-series modeling of traffic fatalities in Europe. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2011, 3, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davier, A.A.; Holland, P.W.; Thayer, D.T. Kernel equating: Continuization and equating. In The Kernel Method of Test Equating; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; p. 66. [Google Scholar]













| Method | Mass | Body Length | Thorax Width | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSPE 3 | RMSPE | RMSPE | ||||
| 0.9526 (<0.001) | 16.31% | 0.8836 (<0.001) | 11.25% | 0.916 (<0.001) | 13.37% | |
| 0.9464 (<0.001) | 23.53% | 0.8927 (<0.001) | 10.74% | 0.8575 (<0.001) | 20.86% | |
| Label | Species | Family | Order | Quantity | Thorax Width (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean | Std. Dev. | |||||
| 1 | Eriopyga grandis | Noctuidae | Lepidoptera | 473 | 2–5 | 3.35 | 0.68 |
| 2 | Agrotis tokionis | Noctuidae | Lepidoptera | 382 | 5–9 | 7.11 | 0.84 |
| 3 | Xestia c-nigrum | Noctuidae | Lepidoptera | 43 | 5–7 | 5.47 | 0.55 |
| 4 | Agrotis praecox | Noctuidae | Lepidoptera | 78 | 5–6 | 5.70 | 0.46 |
| 5 | Spodoptera litura | Noctuidae | Lepidoptera | 129 | 3–5 | 3.86 | 0.54 |
| 6 | Heliothis dipsacea | Noctuidae | Lepidoptera | 84 | 2–5 | 3.58 | 0.54 |
| 7 | Speiredonia retorta | Noctuidae | Lepidoptera | 32 | 3–5 | 3.91 | 0.69 |
| 8 | Dermaleipa juno | Noctuidae | Lepidoptera | 61 | 10–14 | 11.52 | 0.89 |
| 9 | Acronicta rumicis | Noctuidae | Lepidoptera | 58 | 2–3 | 2.97 | 0.18 |
| 10 | Calospilos suspecta | Geometridae | Lepidoptera | 147 | 2–3 | 2.03 | 0.16 |
| 11 | Spilarctia subcarnea | Arctiidae | Lepidoptera | 296 | 2–6 | 4.33 | 0.70 |
| 12 | Spilosoma niveus | Arctiidae | Lepidoptera | 48 | 4–6 | 5.46 | 0.54 |
| 13 | Amsacta lactinea | Arctiidae | Lepidoptera | 27 | 4–6 | 5.26 | 0.53 |
| 14 | Rhyparioides amurensis | Arctiidae | Lepidoptera | 144 | 3–5 | 3.78 | 0.43 |
| 15 | Clanis bilineata | Sphingidae | Lepidoptera | 53 | 8–16 | 12.34 | 1.75 |
| 16 | Psilogramma menephron | Sphingidae | Lepidoptera | 29 | 7–10 | 8.52 | 0.63 |
| 17 | Ampelophaga rubiginosa | Sphingidae | Lepidoptera | 41 | 7–11 | 9.24 | 0.77 |
| 18 | Callambulyx tartarunovii | Sphingidae | Lepidoptera | 35 | 12–15 | 13.91 | 0.95 |
| 19 | Macroglossum stellatarum | Sphingidae | Lepidoptera | 84 | 10–14 | 12.37 | 0.77 |
| 20 | Loxostege sticticalis | Pyralididae | Lepidoptera | 892 | 1–2 | 1.37 | 0.48 |
| 21 | Spoladea recurvalis | Pyralididae | Lepidoptera | 1574 | 1–2 | 1.02 | 0.13 |
| 22 | Pantala flavescens | Libellulidae | Odonata | 768 | 11–14 | 12.39 | 0.72 |
| 23 | Enallagma cyathigerum | Coenagriidae | Odonata | 54 | 4–6 | 5.28 | 0.56 |
| Label | Identification Accuracy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wingbeat Frequency | Mass | Body Length | Thorax Width | Aspect Ratio | |
| 1 | 0 | 0.804 | 0.8576 | 0.0052 | 0.1184 |
| 2 | 0.3228 | 0.9928 | 0.0332 | 0.0144 | 0.6388 |
| 3 | 0 | 0.8628 | 0.0616 | 0.0256 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0.6608 | 0.5372 | 0.2388 | 0.6532 |
| 5 | 0 | 0.9648 | 0.0396 | 0 | 0.0228 |
| 6 | 0.118 | 0.9436 | 0.2248 | 0 | 0.1464 |
| 7 | 0.5804 | 0.1428 | 0 | 0.1848 | 0 |
| 8 | 0.6884 | 0.8952 | 0.8832 | 0.8132 | 0.5088 |
| 9 | 0.012 | 0.8564 | 0.7596 | 0.7692 | 1 |
| 10 | 0.226 | 0.8852 | 0.3772 | 0.776 | 1 |
| 11 | 0 | 0.8632 | 0.46 | 0 | 0.2188 |
| 12 | 0.4056 | 0.9724 | 0.608 | 0 | 0.078 |
| 13 | 0.6932 | 0 | 0.68 | 0.0556 | 0.1952 |
| 14 | 0.0432 | 0.8492 | 0.4248 | 0 | 0.7172 |
| 15 | 0.9272 | 0.4732 | 0.0304 | 0.2644 | 0.0052 |
| 16 | 0.7876 | 0.9304 | 0.1628 | 0.0224 | 0.6488 |
| 17 | 0.6764 | 0.9992 | 0.7688 | 0.028 | 0.5936 |
| 18 | 0.474 | 0.7544 | 0.9104 | 0.5156 | 0.75 |
| 19 | 0.9996 | 0.4964 | 0.2896 | 0.5052 | 0.6272 |
| 20 | 0 | 0.8332 | 0.9276 | 0.03 | 0.468 |
| 21 | 0 | 1 | 0.986 | 0.618 | 1 |
| 22 | 1 | 0.3928 | 1 | 0.566 | 0.0636 |
| 23 | 0.996 | 0.9376 | 0.1632 | 0.3812 | 0.1632 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, C.; Kong, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F. Radar Measurements of Morphological Parameters and Species Identification Analysis of Migratory Insects. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11171977
Hu C, Kong S, Wang R, Zhang F. Radar Measurements of Morphological Parameters and Species Identification Analysis of Migratory Insects. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(17):1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11171977
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Cheng, Shaoyang Kong, Rui Wang, and Fan Zhang. 2019. "Radar Measurements of Morphological Parameters and Species Identification Analysis of Migratory Insects" Remote Sensing 11, no. 17: 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11171977
APA StyleHu, C., Kong, S., Wang, R., & Zhang, F. (2019). Radar Measurements of Morphological Parameters and Species Identification Analysis of Migratory Insects. Remote Sensing, 11(17), 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11171977