Mitigation of Unmodeled Error to Improve the Accuracy of Multi-GNSS PPP for Crustal Deformation Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. PPP Model and Data Processing Strategy
2.2. Mathematic Relationship of Residuals on Different Frequencies
3. Data Collection
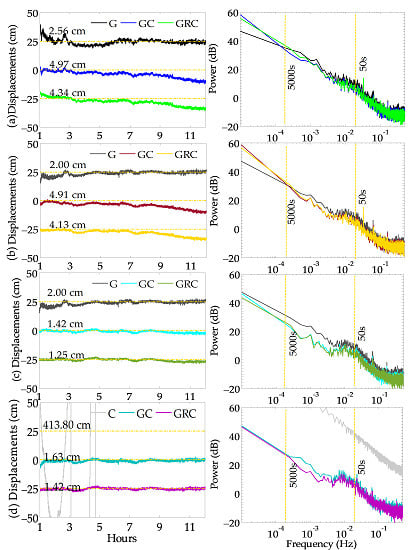
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Equation Validation
4.2. GEO Residual Analysis
4.3. Assessment of BDS-Only PPP with Multipath Correction
4.4. Assessment of Multi-GNSS PPP with Multipath Correction
4.5. A Case Study for the Mw6.3 Jiuzhaigou Earthquake
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larson, K. GPS seismology. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, Y.; Melgar, D.; Crowell, B.W. Real-time strong-motion broadband displacements from collocated GPS and accelerometers. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2011, 101, 2904–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowell, B.W.; Bock, Y.; Melgar, D. Real-time inversion of GPS data for finite fault modeling and rapid hazard assessment. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L09305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Guo, B.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Temporal point positioning approach for real-time GNSS seismology using a single receiver. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5677–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larson, K.; Bodin, P.; Gomberg, J. Using 1-Hz GPS data to measure deformations caused by the Denali fault earthquake. Science 2003, 300, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhl, C.J.; Melgar, D.; Chung, A.I.; Grapenthin, R.; Allen, R.M. Quantifying the Value of Real-Time Geodetic Constraints for Earthquake Early Warning Using a Global Seismic and Geodetic Data Set. J. Geophys. Res. 2019, 124, 3819–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genrich, J.F.; Bock, Y. Instantaneous geodetic positioning with 10–50 Hz GPS measurements: Noise characteristics and implications for monitoring networks. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, B03403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, P.; Henton, J.; Mireault, Y.; Heroux, P.; Schmidt, M.; Dragert, H.; Bisnath, S. Precise point positioning for real-time determination of co-seismic crustal motion. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS 2009, Savannah, GA, USA, 22–25 September 2009; pp. 2479–2488. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, B.; Wang, R.; Klotz, J.; Wickert, J. Real-time high-rate co-seismic displacement from ambiguity-fixed precise point positioning: Application to earthquake early warning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Zhang, H.; Wickert, J. A method for improving uncalibrated phase delay estimation and ambiguity-fixing in real-time PPP. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Dai, X.; Ren, X.; Fritsche, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Accuracy and reliability of multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 607–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Shi, C.; Fang, R.; Liu, J.; Niu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yanagidani, T. High-rate precise point positioning (PPP) to measure seismic wave motions: An experimental comparison of GPS PPP with inertial measurement units. J Geod. 2013, 87, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Li, P.; Sang, J.; Ma, T.; Schuh, H. Capturing coseismic displacement in real time with mixed single- and dual-frequency receivers: Application to the 2018 Mw7.9 Alaska earthquake. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgar, D.; Fan, W.; Riquelme, S.; Geng, J.; Liang, C.; Fuentes, M.; Vargas, G.; Allen, R.M.; Shearer, P.M.; Fielding, E.J. Slip segmentation and slow rupture to the trench during the 2015, Mw8.3 Illapel, Chile earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Jiang, P.; Liu, J. Integrating GPS with GLONASS for high-rate seismogeodesy. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 3139–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C.; Parkinson, B. Mitigating multipath error in GPS-based attitude determination. In Proceedings of the Advances in the Astronautical Sciences, AAS Guidance and Control Conference, Keystone, CO, USA, 2–6 February 1991; pp. 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, D.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Zeng, Z.; Song, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, M.; Cheng, Y.; Lv, J. Mitigation of multipath effect in GNSS short baseline positioning by the multipath hemispherical map. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Bilich, A.; Larson, K.; Axelrad, P. Modifed sidereal fltering: Implications for high-rate GPS positioning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, B.; Gao, Y.; Shen, Y. Real-time carrier phase multipath detection based on dual-frequency C/N0 data. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, T.; Luo, X.; Knöpfler, A.; Mayer, M. Generating statistically robust multipath stacking maps using congruent cells. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. Noise characteristics of high-rate multi-GNSS for subdaily crustal deformation monitoring. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 1987–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, A.; Xu, J.; He, H.; Guo, H.; Shen, J.; Dai, X. Preliminary assessment of the navigation and positioning performance of BeiDou regional navigation satellite system. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, Z.; Liu, J. Precise relative positioning using real tracking data from COMPASS GEO and IGSO satellites. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Timing group delay and differential code bias corrections for BeiDou positioning. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Feng, G.; Guo, F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K. Spatial–temporal characteristic of BDS phase delays and PPP ambiguity resolution with GEO/IGSO/MEO satellites. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J. A Guide to Using International GNSS Service (IGS) Products. Available online: http://kb.igs.org/hc/en-us/articles/201271873-A-Guide-to-Using-the-IGS-Products (accessed on 15 September 2019).
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. Three-frequency BDS precise point positioning ambiguity resolution based on raw observables. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Springer, T.; Prange, L.; Uhlemann, M. Orbit and clock determination-BeiDou. In Proceedings of the IGS workshop 2014, Pasadena, CA, USA, 23–27 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction—Part II. Refraction corrections in satellite geodesy. Bull. Géod. 1973, 47, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrad, P.; Larson, K.; Jones, B. Use of the correct satellite repeat period to characterize and reduce site-specific multipath errors. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS 18th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division, Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–16 September 2005; pp. 2638–2648. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, K.; Bilich, A.; Axelrad, P. Improving the precision of high-rate GPS. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, B05422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, D.C.; Larson, K.M. Finding the repeat times of the GPS constellation. GPS Solut. 2007, 11, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Tao, T.; Wu, D.; Chen, R. A Review of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)-based Dynamic Monitoring Technologies for Structural Health Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, K.E. An Introduction to Numerical Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, P.; Tang, W.; Xia, P. Carrier phase multipath mitigation for BeiDou navigation satellite system. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Gan, W.J.; Chen, W.T.; You, X.Z.; Lian, W.P. Coseismic displacements of the 2017 Jiuzhaigou M7.0 earthquake observed by GNSS: Preliminary results. Chin. J. Geophys. 2018, 61, 161–170. [Google Scholar]













| Item | Processing Information |
|---|---|
| Estimator | Least-squares estimator for generating phase residuals |
| Observations | Raw pseudo-range and carrier-phase observations from GPS, GLONASS, and BDS |
| Sampling rate | 1 s |
| Elevation cutoff | 7° |
| Weighting scheme | Elevation-dependent weight; 3 dm and 3 mm for GPS pseudo-range and carrier-phase; 4.5 dm and 3 mm for GLONASS pseudo-range and carrier-phase; 9.0 dm for BDS pseudo-range; and 5 mm and 15 mm for IGSO/MEO and GEO carrier-phase, respectively |
| Satellite orbit/clock | GBM final precise orbit/clock products generated by GFZ (Deng et al. [29]) |
| Tropospheric delay | The zenith hydrostatic delay corrected by Saastamoinen’s model [30]; the zenith wet delay and the horizontal gradients estimated as piecewise constants every hour and six hours, respectively; Global Mapping Function (GMF) applied |
| Ionospheric delay | Estimated epoch by epoch |
| Satellite/Receiver antenna phase center | GPS/GLONASS: Corrected both at satellite and receiver BDS: PCO and PCV corrected at satellite, while replaced by GPS at receiver |
| Phase-windup effect | Corrected |
| ISB and IFB | ISB estimated as white noise, GPS as reference, whereas IFB estimated as constant for a whole day |
| Station displacement | Solid Earth tide, pole tide, ocean tide loading, IERS Convention 2010 |
| Receiver coordinate | Estimated as constants for daily solution |
| Receiver clock | Estimated as white noise |
| Ambiguity | Estimated as constant for each arc: float value |
| Station | Location (Lat/Long.) | Receiver Type | Antenna Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| GMSD | 30.56°/ 131.02° | TRIMBLE NETR9 | TRM59800.00 SCIS |
| CIBG | –6.49°/ 106.85° | LEICA GR10 | LEIAR25.R3 NONE |
| JFNG | 30.52°/ 114.49° | TRIMBLE NETR9 | TRM59800.00 NONE |
| DAE2 | 36.40°/ 127.37° | TRIMBLE NETR9 | TRM59800.00 SCIS |
| DAEJ | 37.00°/ 127.37° | TRIMBLE NETR9 | TRM59800.00 SCIS |
| Experiment | GRC with SF | GEO with SF | GEO Excluded |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | No | No | / |
| (2) | Yes | No | / |
| (3) | Yes | Yes | / |
| (4) | Yes | / | Yes |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Li, P.; Chang, X.; Sang, J.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. Mitigation of Unmodeled Error to Improve the Accuracy of Multi-GNSS PPP for Crustal Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192232
Zheng K, Zhang X, Li X, Li P, Chang X, Sang J, Ge M, Schuh H. Mitigation of Unmodeled Error to Improve the Accuracy of Multi-GNSS PPP for Crustal Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(19):2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192232
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Kai, Xiaohong Zhang, Xingxing Li, Pan Li, Xiao Chang, Jizhang Sang, Maorong Ge, and Harald Schuh. 2019. "Mitigation of Unmodeled Error to Improve the Accuracy of Multi-GNSS PPP for Crustal Deformation Monitoring" Remote Sensing 11, no. 19: 2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192232
APA StyleZheng, K., Zhang, X., Li, X., Li, P., Chang, X., Sang, J., Ge, M., & Schuh, H. (2019). Mitigation of Unmodeled Error to Improve the Accuracy of Multi-GNSS PPP for Crustal Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sensing, 11(19), 2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192232